BLITZ! An individual entrepreneur can receive a tax deduction after purchasing real estate! But this requires the use of OSNO, or the payment of personal income tax on income from work combined with entrepreneurial activity. If the individual entrepreneur is on a simplified basis, unified agricultural tax, patent or UTII, filing a tax refund is trivial out of nowhere.
Now more details.
From the moment of registration with the state, individual entrepreneurs automatically become subjects of taxation, that is, they have an obligation to pay taxes. The amount and types of taxes vary between different tax schemes, although the total tax collections are in any case quite large. It is in order to reduce the tax burden that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has developed such a concept as “tax deduction”. In essence, a tax deduction is the right and opportunity for a taxpayer to reimburse part of the taxes paid through some other payments or to be completely exempt from paying them.
Professional tax deduction for individual entrepreneurs
Article 221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows individual entrepreneurs to reduce income received as part of commercial activities by the amount of expenses. That is, an individual entrepreneur can take advantage of the so-called professional tax deduction. Expenses for which the taxable income of individual entrepreneurs are adjusted are determined in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains criteria that must be taken into account when including expenses in the professional deduction:
- expenses must be supported by documents. Otherwise, the deduction is limited to 20 percent of the entrepreneur's income;
- the expenses were incurred for the commercial activities of the individual entrepreneur, that is, they are not related to his family expenses.
In addition, the professional deduction includes insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance and compulsory medical insurance, which were accrued and paid by the individual entrepreneur for the corresponding period, as well as the amount of property tax, provided that the object is used in the individual entrepreneur’s business.
It should be noted that an individual entrepreneur has the right to take into account the costs of using property acquired before the registration of an individual entrepreneur. It is important that the object be used in commercial activities in the future. The tax authorities are not against this (letter dated July 25, 2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
Terms and abbreviations used in the article
Tax deduction
- an amount that reduces the amount of taxable income. There are standard and calculated deductions.
Tax deduction according to the standard
- a deduction, the amount of which is determined as a percentage of the amount of income.
Tax deduction by calculation
- a deduction, the amount of which is equal to the expenses associated with generating income and confirmed by documents.
General taxation system (OSNO)
— the most complex type of taxation of organizations and entrepreneurs. Taxpayers on OSNO keep accounting records in full and pay all taxes.
Special taxation system (special regime)
— tax regime, which differs from OSNO in simplified accounting, fewer reports and fewer taxes. In order for the payer to apply the special regime, he must meet the conditions.
Simplified taxation system (STS)
- a special regime in which most taxes are replaced by one. The system is suitable for representatives of small and medium-sized businesses - both organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
Unified tax on imputed income (UTII)
- a special regime that is intended to tax certain types of activities, usually trade and services. The amount of tax depends not on real income, but on physical indicators. Such indicators could be, for example, the size of a retail outlet or the number of vehicles used for cargo transportation.
Patent tax system (PTS)
- a special regime in which the tax is replaced by a patent. The taxpayer purchases a patent that covers only one type of activity. The patent validity period is from 1 to 12 months. Suitable for individual entrepreneurs only.
Civil contract (civil agreement)
- an agreement between the customer and the contractor to perform certain one-time work or services. Common types of GPC agreements are author's agreements, contract agreements, and others.
Property tax deduction
The procedure for providing property deductions is regulated by Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. An individual entrepreneur has the right to receive a deduction when selling and purchasing property.
Let's look at it in order.
Tax deductions on the sale of property are provided in the following amounts:
- 1 million rubles - when selling housing that has been owned for less than five years;
- 250 thousand rubles - for the sale of other real estate, as well as the sale of movable property owned for less than 3 years.
Please note: this deduction is not available to individual entrepreneurs if the property was used in business.
Tax deductions for the purchase or construction of housing are limited to 2 million rubles . If real estate is purchased with a mortgage, then the taxpayer is entitled to a deduction for the interest paid to the bank. This deduction is provided in the amount of 3 million rubles. These deductions do not provide for their re-receipt. That is, if an individual entrepreneur previously took advantage of the deduction when purchasing an apartment, then it will no longer be possible to receive it when building a house.
Standard deduction for an individual entrepreneur
Standard deductions according to Art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are divided into:
- for deductions provided to the taxpayer (500 and 3 thousand rubles are allocated to certain categories of taxpayers, such as heroes of the USSR, heroes of the Russian Federation, persons who suffered illnesses as a result of the Chernobyl disaster, and others);
- for deductions provided for children (for the first and second child - 1,400 rubles, for the third and subsequent ones - 3 thousand rubles, for a disabled child - 12 thousand rubles).
In order to receive a child deduction, the following restrictions apply:
- The taxpayer’s income, calculated on an accrual basis, cannot exceed 350 thousand rubles. Starting from the month in which income exceeds the established limit, no deduction is provided;
- The child’s age is no more than 18 years (24 years if the child is studying full-time). In this case, the deduction is due until the end of the year in which the child reaches the specified age.
Please note: if the individual entrepreneur is the only parent, then he can receive a double deduction. It is important to remember that from the moment of marriage the entrepreneur loses the right to deduction. After a divorce, the corresponding right resumes its validity (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 2, 2012 No. 03-04-05/3-410).
In addition, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not prohibit one of the parents from refusing a deduction in favor of the other. However, as officials note, this is only possible if you have the appropriate right to deduct, which is documented (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 14, 2018 No. 03-04-05/91182).
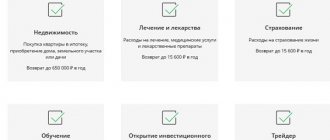
Social tax deduction
An individual entrepreneur can count on social deductions, the rules for receiving which are prescribed in Art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. By virtue of this norm, deductions are provided for expenses:
- for education;
- for treatment;
- for donations;
- for non-state pension provision and (or) voluntary pension insurance and (or) voluntary life insurance;
- to pay additional contributions to the funded pension;
- to undergo an independent assessment of their qualifications.
There is a total limit of 120 thousand rubles for all types of social payments. The exception is deductions for children's education and expensive treatment.
Let's consider these types of social payments in more detail.
An individual entrepreneur can receive a deduction for personal education, as well as for the education of his children under 24 years of age, as well as his brother and sister. In the latter case, the deduction amount is 50 thousand rubles for each child (sister, brother) in the total amount for both parents.
To receive a deduction for the education of children, wards, as well as siblings, it is important that the form of education is exclusively full-time (for yourself, it does not matter). Also, a deduction will not be given if it turns out that the educational institution does not have the appropriate license.
The medical deduction can be used for expenses on medical services provided personally to the individual entrepreneur, as well as to his children, spouse and parents. In addition, an entrepreneur can receive personal income tax preferences on the costs of purchasing medications prescribed by a doctor.
If an individual entrepreneur donates money to citizens, medical, educational organizations, social service institutions, charitable and scientific communities, foundations, museums and other organizations, then he has the right to receive a deduction for donations. The amount of deduction is limited to no more than 25 percent of annual income. If an entrepreneur makes donations to cultural institutions and non-profit organizations in this area, then the maximum deduction amount is 30 percent.
A deduction for pension insurance is due to an individual entrepreneur when paying pension contributions under an agreement with a non-state pension fund (NPF), when paying insurance premiums under a voluntary pension insurance agreement concluded with an insurance organization, when paying contributions under a voluntary life insurance agreement for a period of at least 5 years.
If an individual entrepreneur pays additional contributions to a funded pension, then he is entitled to a corresponding deduction. An individual entrepreneur has the right to reduce his tax base by the amount of additional insurance contributions paid for a funded pension.
Right to deduct personal income tax
Most of the deductions are provided for by the personal income tax. It is paid by all citizens working under labor and civil contracts. In addition, personal income tax is subject to certain other types of income, for example, received from renting or selling property, from investing, under insurance contracts, and others.
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneurs in the main tax regime (OSNO) also pay personal income tax. Can an individual entrepreneur receive a tax deduction if he uses this tax system? Of course, it can, since all the rights of a taxpayer apply to it. But those individual entrepreneurs who have chosen preferential regimes (USN, UTII, PSN, Unified Agricultural Tax) do not have the right to deductions for personal income tax. They are not payers of this tax, they have no tax base, which means they have nothing to reduce.
At the same time, it cannot be said that entrepreneurs in special regimes are completely deprived of the right to tax deductions for personal income tax. After all, at the same time as their business, they can receive other income that is subject to this tax. For example, if an individual entrepreneur on a simplified system simultaneously works for hire or rents out real estate, then he retains the right to deduction. But it can only be applied to income subject to personal income tax.
Thus, the rule is very simple: if an individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax at a rate of 13%, then he can receive the deductions provided for in its calculation.
Example 1
Citizen Smirnov worked in a company and received a salary of 40 thousand rubles, from which his employer withheld monthly and transferred personal income tax to the budget. When calculating the tax, a standard deduction per child was used in the amount of 1,400 rubles. The tax was calculated as follows: (40,000 - 1,400) * 13% = 5,018 rubles.
Smirnov decided to try his hand at business, for this he registered an individual entrepreneur and immediately switched to a simplified tax regime. However, he had not yet quit his job, meaning he still received wages. The employer still continued to calculate personal income tax from her and apply the child tax deduction. The entrepreneur must calculate the tax on business income under the simplified tax system himself; deductions are not applied in this case.
A few months later, Smirnov decided to devote his time entirely to a new business and left his job. He no longer had income that was subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. Accordingly, Smirnov no longer has the right to apply a personal income tax deduction.
Starting from the next calendar year, the businessman decided to change the tax regime from simplified to basic - it was more profitable for the business. He began to pay personal income tax, since it is provided for by the basic taxation regime, which means that the right to apply tax deductions has arisen again.
There are several types of personal income tax deductions. Articles 218-221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are devoted to them. Let's look at the most common ones in more detail.
Investment deduction for individual entrepreneurs
The right to investment deductions is fixed in Art. 219.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The deduction is due in the following cases:
1. When selling securities traded on the securities market. The difference between income and expenses received from the sale of securities is exempt from tax. The amount of the deduction is calculated as the product of 3 million rubles and the number of full years that the sold securities were owned. A deduction is due if securities (stocks, bonds, shares) are traded on the Russian organized securities market, were owned for more than three years and were acquired after 01/01/2014.
2. When depositing money into an individual investment account (IIA). The amount deposited into an IIS during the year within the limits of 400 thousand rubles is exempt from personal income tax. You can take advantage of the deduction if the taxpayer has only one valid agreement with a Russian broker or trustee for the maintenance of personal investment information, concluded after 01/01/2014 for a period of at least three years.
3. Upon receipt of financial results from transactions reflected on the IIS. The deduction is provided for the entire amount of income received from transactions accounted for on the IIS. It is possible to apply the deduction if the taxpayer has only one valid agreement with a Russian broker or trustee for maintaining an individual investment information system, concluded after 01/01/2014 for a period of at least three years. The deduction can be used one-time, upon expiration of the contract for maintaining an IIS.
The procedure for obtaining a tax deduction
In order to take advantage of personal income tax deductions, an individual entrepreneur must submit a declaration in Form 3-NDFL to the tax office at his place of residence. Documents giving the right to receive one or another deduction should be attached to the declaration.
Thus, for a property deduction, a package of documents confirming the purchase or sale of an object is required. The right to a standard deduction will be confirmed by the child’s birth certificate and a document certifying the right to the benefit. The professional deduction will be confirmed by all expense documents, an investment deduction, an agreement for maintaining an individual investment account or an agreement on brokerage services.
Unlock access to the private part of Clerk with a Premium subscription. Get hundreds of webinars and online courses, unlimited consultations and other proprietary content for accountants.
Hurry up to subscribe with a 20% discount until October 15, 2021. Read more about “Premium” here.
Nuances of filling out 3-NDFL when buying an apartment
The correct preparation of the declaration is recognized as a mandatory condition for tax refund. Features of working with form 3-NDFL follow from the content. Each page of the report is dedicated to a specific deduction. In the case of purchasing housing, you need to fill out the title page, sections 1–2, pages A, B and D1.
Detailed instructions are given in order No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] On the first sheet of the form, indicate the applicant’s personal data, tax period, adjustment number, and put a personal signature.
Sections 1 and 2 are general in nature. This reflects the total amount of income, the amount of property deduction and tax to be refunded.
Sheet A indicates the source of earnings, subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%, as well as the total amount of income in favor of the declarant.
Entrepreneurs on OSNO will also need to fill out page B. Here you should reflect income from commercial activities, business maintenance costs and advance payments.
Experts recommend paying the most attention to sheet D1. It is important not to make a mistake with the type of property, to accurately enter the address of the purchased apartment and the amount of costs. The guidelines will be the appendices to the instructions of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
Note! Special programs will help you avoid mistakes when drawing up a declaration. A service for automatically generating a 3-NDFL report has been launched on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. You can use the tool for free.