On the territory of the Russian Federation, all citizens who belong to socially vulnerable segments of the population can count on state support.
Single mothers can also count on support from the state, which offers a wide range of benefits for this category of citizens. In particular, single mothers cannot lose their jobs in the event of layoffs, have priority rights when enrolling children in preschool institutions, and receive free vouchers. Privileges also apply to paying taxes. Let us consider the procedure for preferential taxation in more detail.
Features of income tax for single mothers
Let's start with the fact that not all women raising children on their own can count on preferential taxation.
For this, the status of a single mother is necessary. From a legal point of view, women are recognized as single mothers:
- those who gave birth to a child without being officially married, without recognizing the paternity of the baby: there is a dash in the birth certificate;
- who adopted a child without being legally married;
- raising a child whose paternity has been disputed.
If the father has recognized the child, the mother can no longer be considered single. In this case, the fact of living together does not play a significant role. If the status is confirmed, the woman becomes entitled to a number of tax breaks.
Options for submitting documents for deduction
The legislation provides for several ways to submit documents to the Federal Tax Service to receive the amount into the account after verification or from the employer.
| Conditions | Contacting the Federal Tax Service to receive the amount of overpaid tax into your account | Submission of documents through the government services website | Contacting the Federal Tax Service to obtain a deduction from the employer |
| Submission deadline | After a year of spending and receiving income | At the beginning of the year of receipt of the deduction | |
| Result of submitting documents | The Federal Tax Service does not provide additional information about the completion of the inspection. | You can find out about the verification process in your personal account. | Providing Notice to Employer |
| Form for receiving funds | To the person’s account after passing the verification and submitting the application | In the year of submission of notification upon receipt of income | |
| The amount of the deduction | In full | In full | Partially |
| Positive sides | Simplicity of document flow, possibility of consultation | Speed of document submission and ability to monitor verification stages | Efficiency of receiving benefits this year |
| Negative sides | Additional waste of time | The need to create a personal account and register an electronic signature | The remainder of the unreceived benefits is provided to the Federal Tax Service |
A person can receive a standard deduction and social and property benefit from the employer based on notification. To receive a notification, you must submit documents and a corresponding application. The notification is issued to the taxpayer within a month. Declaration 3-NDFL is submitted only when receiving the amount through the Federal Tax Service.
How are taxes deducted from the wages of single mothers?
Let's start with the fact that the right to tax breaks applies to all citizens raising children. According to the provisions of Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following amounts are established here:
- first and second child - 1,400 rubles;
- third and subsequent ones - 3,000 rubles;
- disabled children - 12,000 rubles (for a parent, spouse (and) parent, adoptive parent) and 6,000 rubles (for a guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, spouse (and) adoptive parent).
At the same time, deductions for disabled children are provided regardless of the order of birth of the children. Also, the deduction for a disabled child is summed up with the deduction that is provided for the child, taking into account the order of birth (clause 14 of the Review, approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on October 21, 2015).
When determining the amount of the deduction, the total number of children is taken into account, without taking into account the age of the children, that is, the order of birth is observed (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 23, 2012 N ED-4-3 / [email protected] ).
Single mothers are in a more privileged position, so they receive double tax deductions. In particular, for the first two children the rate is set at 2,800 rubles, for the third 6,000, for a disabled child - 24,000 rubles.
Download for viewing and printing:
Article 218. Standard tax deductions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
What deductions can a single mother receive?
Single mother tax deductions in 2021 can be divided into 2 main categories:
- Deductions that are guaranteed by law only for single mothers (and fathers raising their own or adopted children on their own). In fact, here we are talking about only one privilege - a standard social deduction for personal income tax, provided under special conditions (we will study it in more detail later in the article).
- Deductions that single mothers can apply for on the same basis as any other citizens.
The most common types of such deductions include:
- property;
- social.
Single mothers will also have access to any new tax deductions. In 2021, however, they did not appear.
At the same time, the registration of each of the “general civil” deductions may have features predetermined by the fact that their applicant will be a single mother.
First of all, let's study what the size of tax deductions in 2021 is for each parent or guardian who supports the child.
Required documents
Documents certifying the right to receive tax privileges are transferred to the accounting department of the organization where the single mother works.
An application for preferential taxation is submitted from the moment the grounds arise, for example, if a woman gave birth to or adopted a child without being in an officially registered marriage and without establishing paternity. If a tax deduction was provided at your previous job, a 2-NDFL certificate is sent to the accounting department. This document clearly confirms what tax has been withheld since the beginning of the year. In addition to the application, the following documents will be required:
- birth certificate;
- act of establishing guardianship;
- passport: photocopy of pages confirming that the applicant is not officially married;
- medical report if the child is disabled;
- certificate from the place of study - if the child is over 18 years old, but continues to receive education.
Important! The application and the listed documents are submitted only once during employment, however, if the grounds for receiving a tax deduction change. This may include situations when a second child is born or a woman gets married and her husband adopts children. In such cases, the documents are collected again.
Persons entitled to use the deduction
Benefits in the form of deductions are provided upon fulfillment of a certain list of requirements.
| Condition | Emergence of law | Lack of right |
| Person status | Resident | Non-resident |
| Taxable income | Available | Absent |
| Taxation | Personal income tax at a rate of 13% | Application of a different rate to income |
| Compliance with the requirements | Yes, different in each case | Absent |
| Confirmation | Submitting a declaration, application and documentary evidence of entitlement | No deduction was applied for |
How is the tax deduction applied?
In general, a single mother should not ask this question: the required deductions are made by the company’s accounting department. However, it would be useful to know the mechanism for using such calculations. Let's consider the principles of making such deductions.
How much can you expect?
As discussed above, a tax deduction is available to all parents and guardians raising children under the age of 18.
However, single mothers are entitled to a double deduction, so the amount of reduction in the tax base will be doubled. Currently, single mothers receive payments in the following amounts:
- one child - 2,800 rubles;
- two children - 2,800 rubles;
- three or more children - 6,000 rubles;
- for a disabled child - 12,000 rubles.
Let us remind you that the deduction is provided until the age of 18. In cases where a child of a single mother enters a full-time department of a university, the period for granting tax privileges is extended to 24 years.
How are calculations made?
The tax deduction is quite simple: the tax base is reduced by a fixed amount, after which income tax is charged. However, a number of nuances need to be taken into account here.
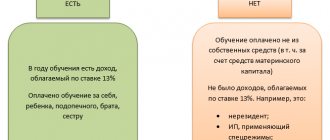
In particular, the privileges accrued are cumulative. For greater clarity, we give a small example of calculations. Let’s say that a certain citizen Alexandrova is raising three children born out of wedlock; paternity of the children has not been established. Considering that the relationship was not registered and there is a dash in the “Father” column, Alexandrova is considered a single mother, and therefore has the right to a double tax deduction.
So, for the first two children, a woman is entitled to a tax privilege in the amount of 2,800 rubles, for the third child - 6,000. By adding, the total tax deduction will be 11,600 rubles. Let’s imagine that Alexandrova’s monthly salary is 50,000 rubles. Tax-free income is subtracted from this amount: 50,000 - 11,600 = 38,400 rubles. This is the tax base from which income tax will be withheld in the amount of 13% or 4,992 rubles.
After paying taxes, 33,408 rubles remain, to which the tax-free amount is added. As a result, a single mother will receive 45,008 rubles. If the woman had not exercised the right of tax deduction, after withholding 13%, her salary would have been 43,500 rubles. At first glance, the difference is insignificant, but for a single mother, an amount of 1.5 thousand rubles can be a good help.
The principle of reducing tax deductions
Today, the upper financial limit of preferential taxation is set at 350,000 rubles. If the total amount of privileges granted reaches this threshold, the preferential taxation ceases to apply until the end of the calendar year.
Single mother status.
A woman caring for a child without the support of a father is not always a single mother in the legal sense.
To be assigned official status, you must contact government agencies with documents confirming the absence of the second parent.
The mother can apply for a certificate either immediately after the birth of the baby or after a while. In some cases, you will need to confirm your status through the courts.
Labor legislation provides a large number of benefits for those who raise a child without the help of a second parent.
This could include additional days of vacation, shortened working hours, or financial compensation. The latter include benefits when paying income tax.
Features of deductions for preferential categories.
The Tax Code (Article 218) provides for the return of part of the cash payments paid from official income for parents of minors.
However, there are some peculiarities of income tax for single mothers.
Women assigned this status are entitled to a double deduction. This privilege is enshrined in law (Plenum Resolution No. 1012).
It is tied to the fact that if both parents are present, both the mother and father receive the deduction.
In the event that one of the parents is absent, the refund that he could have received should be sent to the mother raising the baby.
If the woman remarried
It is noteworthy, but the fact that the mother of the children is officially married deprives her of the right to receive a double tax deduction.
So, paragraph 12, paragraph 4, paragraph 1 of Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the provision of a double deduction to a single parent ceases from the month following the month of his marriage. Note that in this case, the woman retains the right to tax deduction on a general basis. In particular, the amount of 1,400 rubles is established for the first and second child, 3,000 rubles for the third, and 6,000 rubles for disabled children. Documents about changes in status are transferred to the accounting department of the enterprise.
Benefits for single mothers: property deductions
Probably the most common property deduction, a single mother has the right to receive on the same basis as other citizens. In this case, obtaining a deduction will be possible even if the apartment was purchased for a child and registered in his name. The child, in turn, does not lose the right to his deduction.
In 2020-2021 The size of the tax deduction limits for an apartment and the procedure for registering it for single mothers are the same as for other citizens. The applicant can claim an amount of 13% of the cost of purchasing an apartment (but not more than 260,000 rubles). A tax deduction on mortgage interest in 2021 is, of course, also possible, and payment for it:
- will not be limited if the apartment was purchased before 2014;
- will be limited to 390,000 rubles if the apartment was purchased in 2014 or later.
The documents for deduction submitted to the Federal Tax Service are the same as usual (but they include the child’s birth certificate).
Individual nuances characterize the payment of personal income tax (when it is calculated) if an apartment owned by a child is sold.
If the child is not yet 14 years old, then only the mother can sell his apartment on her own behalf (Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2015 No. 25), and in this case she will pay personal income tax. If the child’s age is from 14 to 18 years, then he will be able to sell the apartment himself with the consent of the mother and will have to pay personal income tax.
At the same time, since parents are obliged to support their children, as well as to protect their rights and interests (clause 1 of article 80 of the RF IC, clause 1 of article 64 of the RF IC), the child has the right to expect that when all proceeds from the sale of the apartment are spent, monetary His mother will provide him with funds to pay taxes.
Until what age is the child deduction allowed in 2021?
The standard tax deduction is paid until your 18th birthday. But this does not mean that the last payment will occur in the month when the child turns 18 years old - your right remains until the end of the calendar year.
If the child is a full-time student, the tax refund continues throughout the entire period of study or until he turns 24 years old, whichever comes first.
If the child is 24 years old and has not yet graduated, the standard tax deduction is provided until the end of the current year (or earlier if the diploma is issued in the same year). If the child has completed his studies and is not yet 24 years old, then the tax benefit ceases after receiving the diploma.
Example:
After school, your 17-year-old son entered a full-time university and graduated in four years. Despite the fact that the boy is not yet 24 years old, starting from the next month after receiving his diploma, you will no longer receive a tax deduction.
Example:
Your daughter finished school, then graduated from a full-time university and entered graduate school full-time. Even before graduation, she turned 24 years old. You will continue to receive the standard tax deduction until the end of the current year or until your daughter graduates, whichever comes first.
Receive a tax deduction within a week with the Quick Deduction service!
Get a service
Registration procedure
If a woman is officially employed, the registration process will not be difficult. You will need to write an application using a special form and provide personal documents; the accounting staff will do the rest.
If a woman works in several companies at the same time, it will be possible to apply for the required deduction in only one of them!
It is necessary to act through the Federal Tax Service if the tax benefit was not provided at the place of official employment or was not transferred in full. In such a situation, a woman should perform the following manipulations:
- The declaration is filled out.
- A certificate in form 2-NDFL is obtained from the head of the enterprise. If a woman is employed in several organizations, this certificate is taken from each of them.
- The required papers are collected.
- The package of collected documents is handed over to the Federal Tax Service specialists.
- Two competent applications are written according to the sample - for a refund of funds and for the transfer of the required amount to a card or account.
Deadlines for receiving a deduction through the Federal Tax Service
When contacting the tax office to recalculate the taxable income base and receive the overpaid tax into your account, the procedure is carried out within the established time frame. Before receiving the right to a refund of the amount upon application, the declaration and documents must undergo a desk audit. The control period is 3 months.
The verification period is calculated from the next day after receipt of the declaration. The deadline for sending documents by mail is counted on the 7th day after sending a registered letter with notification and inventory. The amount of overpaid tax is credited to the person’s account within one month after submitting the application. The person's account must belong to the applicant.
Income limit for child deductions
In 2021, deductions for children are provided only until the employee’s income, taxed at a rate of 13%, from the beginning of the year does not exceed 350,000 rubles . There was a proposal from officials to increase the limit to 400,000 rubles, but so far it has been rejected. Starting from the month when the employee’s income exceeds the specified amount, the provision of these deductions ceases. Payments not subject to personal income tax are not taken into account as income when providing standard deductions.
Example of calculating deduction for a child
An employee of the organization, Ivan Petrov, is the parent of a minor child. He is provided with a standard deduction of 1,400 rubles. Petrov got a job with the organization in April. His income from his previous place of work from January to March was 75,000 rubles.
Petrov’s salary is set at 40,000 rubles per month, which means in this case his income will exceed 350,000 rubles in October (including income from his previous place of work). From April to September he is provided with a deduction of 1,400 rubles, but from October this deduction is not provided.
To determine the income limit, take into account only the income of residents, subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13% (except for dividends). Income that is partially exempt from personal income tax should be included in the calculation only in the taxable portion. For example, the provision of financial assistance in the amount of up to 4,000 rubles per year is not subject to personal income tax. If you gave the employee more, then include the excess amounts in the base. Do the same with daily allowances over 700 rubles, gifts over 4,000 rubles, and financial assistance at the birth of a child over 50,000 rubles for each child.
Special rules apply for external part-time workers. Such employees can choose for themselves which place of work to receive the deduction. To do this, they must submit to the employer a written application and documents confirming his right to the deduction. There is no need to take into account the income that the employee receives in another place of work. You simply calculate the personal income tax from his salary in your company and reduce it by the amount of the deduction, transferring it to the employee.
Is it necessary to provide a deduction if the employee has no income? If in certain months the employee did not receive income taxed at a rate of 13%, then deductions should be provided to him in subsequent months, including for those months in which income was not received. Moreover, if the payment of income is completely stopped and does not resume until the end of the year, no deduction is allowed for such months (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 30, 2018 No. 03-04-05/78020, dated September 4, 2017 No. 03-04-06/56583). If an employee is on parental leave, the deduction is not provided from the beginning of the year until the month in which the employee returns from leave.
conclusions
The main standard tax deduction is “children’s”, the amount of which can be single or double. The amount increases by 2 times if the child’s parent has the status of the only one or one of the spouses renounced his right in favor of the other.
In all other cases, the benefit is provided in a single amount.
If the mother or father is raising a child alone, but there is a second parent, then the deduction is also given in a single amount. The same rule applies in case of deprivation of rights.
Legal provisions
The issue of receiving a double deduction by a single mother is regulated by several legal regulations:
- Resolution of the Plenum No. 81 of 1995. It regulates the very concept of the status of a mother raising children independently and the procedure for its registration.
- Resolution of the Plenum No. 1012 of 2009. This provision regulates the possibility of receiving and annually increasing the established ratio of payments made.
- Many issues are regulated by the Labor and Tax Codes.
Refusal to provide a deduction to a person
When applying for a benefit at the place of employment, a refusal may occur in the absence of supporting documents or notification, if the benefit requires permission from the Federal Tax Service. If a person applies to the Federal Tax Service to recalculate the base, a refusal will follow in the following cases:
- Submission of the 3-NDFL declaration on a form that is not valid for the period.
- Missing the deadline for filing a return after 3 years after the period of tax withholding and expenses.
- Absence of documents in full or discrepancies in taxpayer data.
A person receives information in writing about a refusal to recalculate the tax base or to provide a notification.