All this is very convenient and great, but many people, when starting to register, do not even realize that this is a taxable . But in what amount and in what cases you can be exempt from paying it - read in our article.
Read on the website about the features of exchanging an old apartment for a new building, as well as how to exchange a room or apartment for a house and land with an additional payment.
general information
Let's take a little dip into history.
Twenty years ago, during the existence of the Soviet Union, such a thing as private property did not exist at all.
All real estate was state-owned, which means that all transactions that took place with it were also carried out at the expense of the state (read about the possibility of exchanging municipal housing).
It was during the Soviet Union that the exchange of apartments was widespread, since it was impossible to sell what did not belong to you by right of ownership.
After the Union ceased to exist and a new state called the Russian Federation appeared on the map, the situation changed somewhat.
Now citizens have the opportunity to purchase real estate as their own, and at the same time, own, manage and use it at their own discretion. Apartments can now be alienated by any transaction known to the Civil Code (read about the exchange of a privatized apartment).
Of course, now the costs of conducting a transaction, namely the execution of relevant documents by government agencies and checking the transaction for legality, are carried out for a certain fee .
This is a kind of payment towards the country’s budget for the opportunity to own this or that real estate under the right of ownership.
A question of cost
Let us also clarify the procedure for accounting for goods received in exchange for our own products. First you need to decide at what cost they are reflected in accounting. To do this, let's turn to PBU 5/01. According to clause 10 of this document, the actual cost of inventories received under contracts providing for payment in kind is the cost of assets transferred or to be transferred by the organization. In turn, the value of the latter is established based on the price at which, in comparable circumstances, the company usually determines the value of similar assets.
If the MPZ are received before the transfer of ownership, then, in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 8 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ, they must be reflected separately. Since the inventories received by the organization do not belong to it, they are considered accepted for safekeeping and are recorded in off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” (clause 155 of the Guidelines for accounting of inventories). The latter were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n.
Board size
Unfortunately, the Tax Code does not establish the amount of tax for such a transaction as the exchange of real estate. There is no mention of this in the Civil Code.
By the way, you can find out the details of the transaction in Article 567 and subsequent norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. But how then can a common man know what kind of monetary contributions to the state he can count on?
If we turn to the Civil Code, one of the articles contains the following definition.
Thus, barter is equivalent to the well-known purchase and sale agreement .
Many citizens will throw up their hands, because there is nothing similar in these procedures. Actually this is not true.
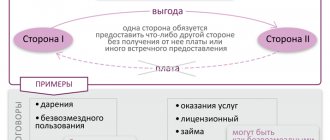
In a purchase and sale transaction, we can observe the presence of two parties - the seller's side , transferring ownership of the property in favor of another person, and the buyer's side , acquiring ownership for money.
There are also two parties to an exchange agreement, but each of them is automatically both a seller and a buyer . This means that these transactions can be compared almost equally.
The Tax Code in Article 217 establishes a tax of 13 percent of personal income tax on a purchase and sale transaction . Consequently, this figure is also relevant for barter transactions.
What to agree on when exchanging goods
For barter to take place, you need to sign an exchange agreement, draw up specifications and transfer the goods using invoices. Let's fill out all the documents together.
Template for an agreement for the exchange of goods between individual entrepreneurs
You need to check the following in the contract.
Subject of the agreement
The subject is what the parties agreed on.
The subject is written in the first paragraph of the contract. Under a barter agreement, entrepreneurs exchange goods for good. In the text it will sound like this:
In accordance with this agreement, each party undertakes to transfer ownership of one product to the other party in exchange for another.
Each entrepreneur is considered a seller of his goods and a buyer of the counter. In practice, this means that if there is a defect in the product, the rules for purchase and sale will be activated. The supplier of a defective product will be obliged to replace it with a normal one or compensate for repairs.
Description of goods
It should be clear from the barter agreement what goods are being exchanged.
It is more convenient to describe the product in detail in a separate document - specifications. We have two products, so the specifications must be filled out for each. Both entrepreneurs sign for each specification.
For a sample, we filled out a specification for coffee beans. The jam specification will be the same.
Sample of filling out the specification
If it is not clear from the contract what goods are being exchanged, the barter is considered inconsistent. Either party can give back at any time without fines or penalties. But here it may turn out that one product has already been given away. It must be returned. Or pay in money - if the product has already been processed, for example, jam was used for pies.
Are the goods equivalent or not?
By default, barter goods are of equal value. Even if their cost does not match figure for figure.
According to the specification, coffee beans from our example cost 50,000 rubles. Let's imagine that a batch of jam cost 48,500 rubles. Different prices do not mean that you have to pay extra for a more expensive product. In our case, jam and grains are equivalent.
For insurance we write the following phrase:
Goods to be exchanged are assumed to be of equal value; goods are exchanged without additional payment.
❗ In order for goods to be considered unequal, this must be stated in plain text in the contract. Plus indicate how much and when the party pays extra. For example, we write in the specifications that grains cost 50,000 rubles, and jam costs 30,000 rubles. And the recipient of the grains is obliged to pay an additional 20,000 rubles.
In the contract, this condition will look like this:
Party-2 undertakes to transfer to Party-1 the difference in the cost of the exchanged goods in the amount of 20,000 rubles within two days from the date of signing this agreement.
If the recipient of an expensive product delays making an additional payment, interest will accrue on the debt at the key rate, starting from the next day after delivery.
Who pays for shipping and packaging
By default, each party bears all costs of transfer of its goods.
For example, Ivanov is obliged to pay for the transportation of goods to Petrov’s warehouse himself. And Petrov - transportation and packaging of cans in special containers for glass.
But if necessary, all costs can be transferred to one of the parties. For example, Ivanov brings grain and picks up jam in his car.
Delivery time and place of delivery
Goods can be exchanged on the same day or at different times. For example, Ivanov brings grain now, and Petrov brings his goods only in a month. So it is possible. The place of delivery is also agreed upon.
Example:
Party-1 is obliged to deliver the goods by July 30, 2021 to Party-2 at the warehouse address: Yekaterinburg, Lenin Street, building 5.
The same point will be for delivery of the second product.
A delivery note is issued for the transfer of each product.
Invoice template TORG-12 + instructions for filling
The timing of delivery of goods is very important.
If the goods are not delivered at the same time, a so-called counter-fulfillment occurs. And this is where this rule comes into play. If the first item is late, the delivery of the second item can be delayed or the barter can be canceled altogether. With one-time barter, it is impossible to refuse the goods on the move.