Starting from 04/13/2019, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 04/01/2019 No. 388, compensation for employee expenses for using a personal car for business purposes is excluded from the list of income from which the employer withholds alimony.
This news gave rise to a conversation about what payments alimony is withheld from, what is the basis for its withholding, and how to correctly fill out a payment order for its payment. Examples from judicial practice are given about payments to which the collection of alimony does not apply. Moreover, fines for violating legislation in this area reach 100 thousand rubles.
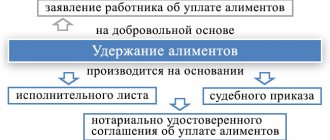
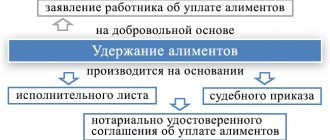
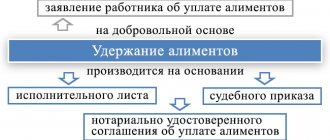
Voluntary payment of alimony
The responsibility of parents to support minor children is spelled out in paragraph 1 of Art.
80 IC RF. Child support can be paid voluntarily, both on the basis of an agreement concluded between the parents, and without it. The agreement must be in writing and certified by a notary. In this case, it has the force of a writ of execution. If the established form is not observed, the agreement is considered void.
The agreement can be changed or terminated at any time by mutual agreement of the parties, which must also be notarized. This follows from Art. 100–101 RF IC. If the agreement is presented at the place of work, the employer is obliged to withhold alimony from the salary or other income of the employee paying the alimony and transfer it to the recipient.
Payment of child support can occur voluntarily and in the absence of a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony, but only on the basis of an application from the employee with a request to withhold alimony from him.
Editor's note: at the request of the employee, it is allowed to withhold any amounts without restrictions, but only after withholding personal income tax and amounts under executive documents (letter of Rostrud dated September 26, 2012 No. PG/7156-6-1).
How much alimony is collected?
If agreement on the payment of alimony is not reached between the parents, alimony is collected by the court.
Their size is determined in paragraph 1 of Art. 81 of the RF IC: for one child - 1/4, for two children - 1/3, for three or more children - 1/2 of the earnings or other income of the parents. The size of these shares may be reduced or increased by the court, taking into account the financial or family situation of the parties and other noteworthy circumstances (clause 2). Collection of alimony for the maintenance of minor children in court can be carried out not only in shares of the earnings of the parent from whom alimony is collected, but also in a fixed sum of money.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 83 of the RF IC, the court has the right to determine the amount of alimony collected monthly in a fixed sum of money (or simultaneously in shares and a fixed sum of money), if the parent obligated to pay alimony:
- has irregular, fluctuating earnings or other income;
- receives earnings or other income wholly or partially in kind or in foreign currency;
- has no earnings or other income;
- in other cases, when the collection of alimony in proportion to the earnings or other income of the parent is impossible, difficult or significantly violates the interests of one of the parties.
From what income can alimony be deducted?
The full list of income from which alimony is withheld is approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 18, 1996 No. 841. It indicates the following types of income:
- wage;
- vacation pay;
- amounts of financial assistance;
- severance pay;
- all types of pensions (except for survivor's pension);
- scholarships paid to categories of students specified in the list;
- benefits for temporary disability, unemployment - only by court decision and court order for the collection of alimony or a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony;
- income from entrepreneurial activities, determined minus the amounts of expenses incurred related to its implementation;
- income from the rental of property;
- income from equity participation in the organization (dividends);
- from other payments made by the employer in accordance with labor legislation.
According to paragraph 4 of the list, the collection of alimony from wages and other income is carried out after taxes are withheld from these amounts.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 18, 1996 No. 841 “On the List of types of wages and other income from which alimony for minor children is withheld”
Editor's note : a parent who pays alimony for the maintenance of his minor children is entitled to a standard child deduction for personal income tax. This is possible due to compliance with the conditions of paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the fact that the child is supported by the parents or the spouse of the parent. Payment of alimony confirms this fact (letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 7, 2018 No. 03-04-05/80099, dated August 10, 2016 No. 03-04-05/46762).
Alimony is withheld from severance pay
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation answered the question about the withholding of alimony from severance pay and average earnings for the period of employment, paid upon dismissal of an employee.
True, the letter is about alimony for the maintenance of parents, not children. The agency indicated that alimony should be withheld from these amounts; this is expressly provided for by law. Specifically, in paragraphs “k” and “e” of the list of types of wages and other income from which alimony for minor children is withheld. Moreover, from these payments, alimony is withheld both for the maintenance of minor children and for the maintenance of parents.
Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2017 No. 11-1/OOG-1816
Results
So, the answer to the question of whether alimony is withheld from financial assistance depends, first of all, on the grounds for its payment. As a general rule, due to regulatory regulation, the amount of assistance is issued to the recipient minus alimony obligations. At the same time, there are a number of exceptions, which, firstly, are provided for in the List approved by the government, and secondly, follow from the specifics of the payment (for medical treatment, drugs).
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
From what income can alimony be withheld?
All types of income for which alimony cannot be collected are listed in Art. 101 of the law on enforcement proceedings. Let's name some of them. These are, for example, compensation payments provided for by the Russian labor legislation:
- in connection with a business trip, transfer, employment or assignment to work in another area;
- due to wear and tear of a tool belonging to the employee;
- in connection with the birth of a child, the death of relatives, and the registration of marriage.
In addition, these payments also include benefits from the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, in addition to sick leave benefits, and various compensation payments from the budget.
Remuneration system
Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly determines that the remuneration system is reflected in the local acts of the organization (Regulations on remuneration), agreement or collective agreement. Local acts are developed and approved within the enterprise. They are put into effect by order of the manager, in some cases they are agreed upon with the trade union organization.
In fact, the payment system is a unified list of payments with an approved procedure and conditions for the accrual of funds.
Individual entrepreneurs who use hired workers regulate the payment system with an employment contract.
Alimony established in a fixed amount must be indexed
If alimony is established in a monetary amount, then its size must be periodically indexed.
This helps to protect, on the one hand, alimony payments from inflation, and on the other hand, to avoid repeated appeals to the court to change the amount of alimony. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation reminded of this obligation. Namely, when the cost of living increases, the organization indexes alimony, established in a fixed monetary amount. Indexation is carried out in proportion to the increase in the cost of living for children in the region where the recipient of alimony lives. If there is no regional minimum, alimony is indexed in proportion to the increase in the national subsistence minimum.
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 3, 2018 No. 03-05-06-02/62540
Editor's note : indexation of alimony collected in a fixed sum of money is provided only in proportion to the increase in the cost of living, therefore, if the cost of living decreases, indexation is not carried out.
It is the employer who is obliged to index alimony payments established in a fixed amount.
Previously, the obligation to independently index alimony collected from the debtor by court decision in a fixed sum of money was provided only if the writ of execution was brought to the accounting department of the enterprise by the claimant. In all other cases, indexing was the concern of the bailiffs. They had to calculate the amount of indexation, make an appropriate decision and send it to the debtor’s place of work. The accounting department could only accept this resolution for execution. But from November 25, 2017, with the entry into force of amendments to the RF IC introduced by Law No. 321-FZ of November 14, 2017, it became unimportant from whom the employer received the writ of execution with a fixed amount of alimony - from the claimant or from the bailiff service.
Failure to fulfill the obligation to index alimony risks a considerable fine from bailiffs under Part 3 of Art. 17.14 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- for an organization - from 50 to 100 thousand rubles;
- for its manager (or individual entrepreneur) - from 15 to 20 thousand rubles.
We receive information from the bailiff.
The bailiff is obliged to ensure proper execution of the judicial act and stop the debtor from concealing his income. Bailiffs have quite broad powers, but in most cases they work carelessly. How to force the bailiff to conduct an “investigation”?
First of all, it is important to understand that without constant contact the bailiff will most likely let your case take its course. According to statistics, one bailiff in Moscow handles up to 3,700 enforcement proceedings. Therefore, prepare a clear algorithm of actions for the bailiff and show that his possible inaction will be appealed. Perhaps the bailiff’s problem will be the physical impossibility of effectively working on your case. In this case, demonstrate that you can help him prepare the necessary documents. If we take Moscow and the Moscow region, then in the current situation, the work of a claimant “for a bailiff” is sometimes the only guarantee of the progress of your case.
1) In order for the bailiff to take active action, contact the bailiff department at the place of registration of the alimony payer with a written statement about the need to verify the real amount of the debtor’s income. In it, state all your suspicions with reference to sources: certificates from the Unified State Register, traffic police, printouts of posts on social networks, etc.
Indicate the sources of regular payments (for example, a loan opened in a certain bank) and income (if the spouse trades on the stock exchange or is engaged in forex trading).
2) Within 10 days, the bailiff must consider your application. Based on the results of this, he will issue a decision to refuse or satisfy your requirements. The decision must be sent to you no later than the next day.
3) The decision on refusal can be appealed - to the prosecutor's office, the head of the bailiff department and to the court in accordance with the CAS of the Russian Federation.
You can read more about this in our post dated July 11, 2019 (“Enforcement proceedings”).
The amount of deductions from income is limited by law
When withholding alimony, it is necessary to take into account the requirements established by Art.
138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Namely, the amount of deductions from wages when collecting alimony for minor children cannot exceed 70 percent. Moreover, this refers to the total amount of all deductions, since in addition to alimony, the employee may have other grounds for collection. Editor's note : Exceeding the maximum amount of deductions from wages is subject to criminal, administrative and disciplinary liability. Criminal liability, according to Art. 145.1, is expressed in the imposition of fines, deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities, forced labor and imprisonment. Administrative liability for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs provides for fines under Parts 6 and 7 of Art. 5.27, which can reach a maximum amount of up to 100 thousand rubles for legal entities. In addition, a prosecutorial audit and a labor inspectorate audit may be initiated against the employer.
If compensation is established by law, alimony cannot be withheld from it
An employee of the Murmansk sea trade port filed a claim against the employer for the recovery of funds and compensation for moral damage.
In terms of recovery of funds, the court satisfied his demands. The reason for the claim was the illegal deduction of alimony from the amount of compensation for travel expenses to the vacation spot and back. According to the plaintiff, these actions of the employer violate his rights, since the said compensation payment does not relate to the employee’s income and compensation from which alimony can be withheld by force of law.
The port, in turn, decided to file an appeal to overturn the court decision. The appeal upheld the decision. The court justified the illegality of deduction from compensation amounts with the following arguments:
- in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, deductions are not allowed from payments that are not subject to foreclosure in accordance with federal law;
- the list of income from which alimony is withheld for minor children is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- despite the fact that this compensation is not named in the specified list, it is indicated in another legislative document - Law of February 19, 1993 No. 4520-1 “On state guarantees and compensation for persons working and living in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas” . Therefore, compensation is a measure of state support for citizens living in extreme climatic conditions of the north, and not income at all.
Moreover, according to Art. 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, persons who work in organizations located in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas have the right to pay once every two years at the expense of the employer the cost of travel and luggage transportation within the territory of Russia to the place of vacation use and back. This right arises for the employee simultaneously with the right to receive annual paid leave for the first year of work in this organization.
Thus, the deduction of child support from the specified payment is illegal and violates the plaintiff’s rights to receive compensation for travel expenses incurred to the place of use of the vacation and back in full.
Appeal ruling of the Murmansk Regional Court dated May 20, 2015 No. 33-1457/2015
Alimony is not deducted from compensation for rental housing expenses.
An employee of a machine-building plant filed a lawsuit against the bailiff to declare his actions illegal, which resulted in the plant’s accounting department being obliged to calculate and withhold alimony from the amounts of compensation payments for renting housing and to determine the amount of arrears he had accumulated in the payment of alimony in the amount of 71 thousand. rubles
The man indicated that housing rental compensation is not his income, so it cannot be taken into account when calculating and withholding alimony.
The citizen was hired from another area, and he did not have living space. According to the regulation on rental compensation approved by the general director, the plant compensated the costs of renting residential premises to employees who do not have permanent housing or permanent registration.
The court of first instance satisfied the citizen's demands. However, the appeal overturned the decision. The cassation returned the case for consideration to the previous instance for the following reasons:
- compensation was established by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and, in accordance with clause 1 of the list of types of wages and other income from which alimony for minor children is withheld, alimony is not collected from them;
- compensation for the cost of housing is not stimulating in nature and, therefore, does not relate to the income of the debtor from whom alimony is subject to deduction. A non-resident specialist with special experience and qualifications was invited to work, that is, his invitation was made in the interests of the organization, and not in order to increase the motivation and efficiency of the employee’s work function;
- Taking into account the direction of the employer's expenses, the mere circumstance that, as a result of compensation to the employee for his expenses for renting residential premises, his personal needs are satisfied to a certain extent, is not sufficient to conclude that he has income from which alimony is subject to deduction.
Resolution of the Presidium of the Moscow Regional Court of October 18, 2017 No. 546 No. 44GA-279/2017
Calculation example
As noted above, alimony will be deducted only from bonuses, which are an integral part of the salary and are provided for by a personal or collective agreement. So, the formula for calculating monetary obligations in this case will be as follows:
- Calculation of the total amount of income, which consists of salary (50,000 rubles), monthly bonus (12,000), as well as an allowance for night work (7,000). Thus, the monthly salary of the alimony worker was 69,000 rubles.
- Of all types of official profit, mandatory income tax deductions are made to the state budget in the amount of 13%; if taxation is subtracted, the person’s “net” earnings is 60,030 rubles.
- The court ordered deductions in favor of the child in the amount of 25% of income. Therefore, every month the child’s legal guardian will receive 15 thousand rubles.
In judicial practice, there are situations when the alimony payer protests the amount of deductions made. But only 5% of such claims are satisfied if there are actual violations on the part of the accountant. In this case, the child’s finances are not taken away, but child support is reduced until the illegal difference in transfers is compensated.
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation explained how to fill out a payment form for the transfer of alimony
The Ministry has issued detailed instructions for filling out a payment order for alimony payments. The document must reflect:
- number and date;
- amount (in numbers and words);
- details of the organization sending the payment (name, tax identification number, checkpoint, address, bank details);
- details of the payment recipient (full name, address of residence and bank details);
- the purpose of the payment, which indicates the data of the writ of execution or agreement on the payment of alimony (information about the organization that issued the writ of execution, the date of issue, the number of the case or materials on the basis of which the writ of execution was issued, the period for which the money is withheld, and the amount of payment);
- priority and type of payment (according to clause 2 of Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, alimony is a payment of the first priority, therefore in the corresponding field “21” of the order you must enter the number 1).
The agency explained why these details are required to be filled out:
- according to Art. 109 of the RF IC, the organization at the place of work of the alimony payer is obliged to withhold and transfer alimony monthly from his salary or other income. The basis for payment is either a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony, or a writ of execution;
- To pay alimony, three days are given from the date of payment of wages. This requirement is established by Part 3 of Art. 98 of the Law of October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ and Art. 109 RF IC.
If the address of the recipient of alimony is unknown, it should be transferred to the bank account of a structural unit of the territorial body of the FSSP of the Russian Federation (clause 9 of clause II of Appendix No. 1 to the methodological recommendations on the procedure for fulfilling the requirements of executive documents on the collection of alimony (approved by the FSSP of the Russian Federation on June 19, 2012 No. 01 -16).If
alimony is transferred to an individual’s bank card, then the recipient must clarify the bank details and personal account number.
Unlock access to the private part of Clerk with a Premium subscription. Get hundreds of webinars and online courses, unlimited consultations and other proprietary content for accountants.
Hurry up to subscribe with a 20% discount until October 15, 2021. Read more about “Premium” here.
Insurance premiums from premium
According to Federal Law No. 212, payments to employees working on the basis of an employment contract are subject to insurance contributions. Deductions for insurance premiums from remuneration proceed in the same manner as with wages. Contributions must be paid to the Federal Tax Service, Social Insurance Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
Important! Insurance premiums are accrued in the same month in which the monetary reward was accrued. For example, an annual premium for 2021 accrued in January 2021 is included in the base for calculating contributions for January 2021.
According to the Ministry of Finance, bonuses for holidays, anniversaries and one-time payments are subject to contributions in the standard manner. However, companies that did not agree with this position and went to court were able to win against the tax office and defend their right not to charge contributions for such payments (Definitions of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2017 N 310-KG17-19622, dated April 6, 2017 N 306 -KG17-2349, dated 10/13/2016 N 306-KG16-13002). It turns out that it is possible not to pay contributions on such premiums, but you should be prepared for the fact that the tax office will charge them additionally and the dispute will have to be resolved in court.