Regulatory base of deductions
All types of legal deductions from employee income are enshrined in current legislation. First of all, the specifics of applying deductions from wages are prescribed in the Labor Code of Russia, namely in Articles 130, 136–138 and 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition to labor legislation, the procedure for withdrawals is regulated in the Tax and Family Codes of the Russian Federation, as well as in some federal laws:
- Law of October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ “On Enforcement Proceedings”.
- Law of July 21, 1997 No. 118-FZ “On Bailiffs”.
- Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity.”
- Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ “On state benefits for citizens with children.”
It is these legal acts that provide the legislative basis for regulating issues related to deductions from the earnings of Russian citizens.
Recalculation if there is guilt in non-compliance with established labor standards or simple
To apply this basis, it is important to know:
- what is non-compliance with labor standards (Article 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- what is meant by downtime (part 3 of article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Art. 160 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, labor standards mean various (temporary, quantitative, etc.) standards provided for by a given employer.
From Part 3 of Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation follows: if an employee has not met the standard due to his own fault, he is paid a part of the salary corresponding to the fulfilled part of the standard.
For information on how work not completed is paid for, read the article “Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers.”
According to Part 3 of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, downtime is understood as a temporary cessation of work for various reasons.
Based on Part 3 of Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee’s guilt during downtime is a reason for the employer not to pay him.
Examples when an employee is guilty of downtime:
- got into an accident, violating traffic rules;
- refused training in occupational safety rules and was suspended from work.
Such cases may lead to salary recalculation.
Types of deductions from wages
The current regulatory framework provides for the following types:
1. Mandatory deductions from wages are types of investigations from the wages of Russian citizens, which are carried out on the basis of legislative norms. For example, personal income tax, which must be withheld from almost all types of income and receipts in favor of individuals.
Mandatory deductions include not only personal income tax, but also deductions from wages based on a writ of execution: alimony, deductions from the earnings of convicted citizens. The key difference from other types is the presence of a legislative or administrative document on the basis of which deductions are made from debtors. An administrative document means a court decision, enforcement proceedings, a writ of execution, etc.
2. Optional - this is a type of deduction from earnings that is made by order of the employer, by agreement between the employer and the employee.
By decision of the employer, amounts excessively transferred to citizens, for example, as a result of a counting error, may be withheld from the income of subordinates. Also, money may be withheld from workers’ earnings in the following cases:
- by order of the body for resolving individual labor disputes, if the employee’s guilt in causing damage, failure to perform duties, or downtime has been established;
- a court ruling established that the employee’s wages were paid in excess due to his failure to fulfill his official duties;
- by decision of the employer, the unearned advance payment transferred towards future wages is withheld;
- by order of the employer, unspent and (or) unconfirmed advances for travel expenses, accountable amounts, and similar payments are withheld;
- compensation to the employer for material damage by financially responsible persons, etc.
There are many reasons for unnecessary wage garnishments. Let's look at some situations in more detail.
3. Voluntary - any type of deduction from earnings made at the employee’s own request, be it the transfer of additional insurance contributions to the funded part of a labor pension, trade union dues or amounts of voluntary donations.
The main difference from other types is the presence of a statement from the employee, which indicates the conditions, amounts and purposes of the withheld amounts. An approximate sample can be downloaded at the end of the article.
4. Special or individual - this is a separate type of penalties that are provided for by local regulations of employers. For example, a company has introduced a penalty for being late. Please note that such penalties are not provided for in current legislation. Officials consider such deductions illegal. However, some employers continue to introduce a system of fines into the wage system.
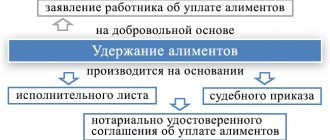
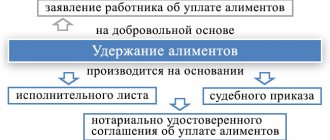
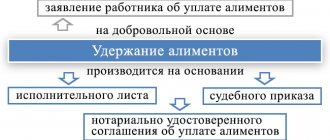
Deductions according to writ of execution
Deduction from wages under a writ of execution is made from the date the document is received by the organization and continues until the obligations are repaid, the employee is dismissed, the claimant refuses, or by order of the bailiff. In this case, it is necessary to return the writ of execution to the claimant or a copy of it to the bailiff no later than the next working day with a note on the amounts paid (clause 4.1 of Article 98 of Law No. 229-FZ), otherwise the employer will face a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles, and officials - from 15,000 to 20,000 rubles. (Article 17.14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Since payments are made on the basis of the law, additional orders from the manager or statements from the employee are not required - a writ of execution or a copy thereof is sufficient.
General rules and restrictions
The responsibility to withhold funds from citizens' earnings is assigned to persons who accrue and pay income. For the most part, this function is performed by employers.
Withhold money from earnings based on key principles:
- Calculate personal income tax taking into account the requirements of fiscal legislation. Consider the taxpayer’s right to benefits, refunds, tax deductions and concessions.
- Income tax calculated on material benefits or income in kind cannot exceed 50% of earnings. This opinion was expressed by the Federal Tax Service in Letter No. BS-4-11 dated October 26, 2016/ [email protected]
- Calculate the amount to be collected (except for tax) from the amount of salary minus personal income tax. That is, income tax is withheld first. And only then are all other types of enforcement proceedings applied to the amount received.
- The maximum amount of recovery under writs of execution in terms of alimony, compensation for harm to health or damage in connection with the death of the breadwinner is 70%.
- The maximum amount of penalties for writs of execution on other grounds is set at 50% of income.
- When withholding at the request of the employee, no maximum restrictions are established. Any amount specified in the application may be collected. Such standards were outlined by Rostrud in Letter No. PG/7156-6-1 dated September 26, 2012.
- The maximum amount of any other penalties is 20%.
Example. An accounting error was made regarding the employee (a shortage was identified, the advance was overpaid, the report was not confirmed). The employer can withhold no more than 20% of the salary per month until the debt is fully repaid. However, if enforcement proceedings are already in force against this employee, for example, 25% for alimony, then it is unlawful to withhold the overpayment. Maximum withholding limits are not cumulative.
When can employees challenge wage deductions?
Let us once again draw your attention to the fact that money must be withheld from an employee’s salary strictly in accordance with labor laws.
This applies not only to the registration of the employee’s consent and the employer’s order to withhold; it is necessary to correctly draw up the documents that form the basis of these withholdings.
If the employer incorrectly prepares the supporting documents, there is a high probability that the employee will challenge all “deductions”.
For example, you need to prove that this particular employee is to blame for the breakdown of this particular item, or that there was a shortage, and it occurred precisely because of this employee. For each case, the employer should carry out a number of activities and prepare the necessary documents. Otherwise, the deductions are illegal.
Collection procedure: table
What is the correct way and in what order to collect amounts from the earnings of subordinates? The table will help you figure it out:
| Queue number | Types of deductions | Maximum amount of deduction (based on the employee’s income minus personal income tax) |
| First of all | Alimony according to executive documents in favor of minor children, unemployed spouses or elderly parents | 70 % |
| Writs of execution for compensation for harm caused to health | ||
| Enforcement proceedings for compensation of damages in connection with the death of the breadwinner | ||
| Writs of execution for compensation of damage caused by a crime | ||
| First of all | Enforcement proceedings for compensation for moral damage | 50 % |
| Second stage | Enforcement papers and proceedings for withholding severance pay and wages of persons working (working) under an employment contract | |
| Withholding in enforcement cases of payments of remuneration to the authors of the results of intellectual activity | ||
| Third stage | Enforcement proceedings on mandatory payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds | |
| Fourth stage | Withholding under enforcement documents for all other claims (for example, collection of a bank loan debt, collection of an administrative penalty in the form of a fine, compensation for property or material damage to the employer) |
If several sheets have been initiated against one individual, follow the rules:
- the requirements of each subsequent queue are satisfied only after the requirements of the previous queue are satisfied in full;
- within one queue (including in the presence of several writs of execution), claims are satisfied in proportion to the amount due to each claimant.
IMPORTANT!
No taxes, fees or contributions need to be withheld from amounts due to the claimant, unless otherwise provided by the requirements of the writs of execution.
Retain without fail
These types of deductions include all amounts withheld by the employer from the earnings of a subordinate on the basis of legislation. That is, part of the earnings was withheld by force of law.
Personal income tax
The employer in this case acts as a tax agent and withholds the calculated income tax in the amount provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For Russian citizens (residents of the Russian Federation) the tax rate is 13%.
Example 1.
Let's look at an example of how income tax is withheld from wages.
In September 2021, the following were accrued in favor of Ivan Petrovich Berezkin:
- salary in the amount of 50,000 rubles;
- disability benefits - 17,500 rubles;
- vacation pay - 45,000 rubles;
- financial assistance - 4000 rubles.
Berezkin does not have the right to tax deductions from wages.
Personal income tax calculation:
- For salary: 50,000 × 13% = 6,500 rubles.
- For sick leave: 17,500 × 13% = 2,275 rubles.
- For vacation pay: 45,000 × 13% = 5850 rubles.
- Financial assistance up to 4000 rubles. inclusive of personal income tax. Read more: “Is material assistance subject to personal income tax?”
In total, from Berezkin’s total income of 116,500 rubles (50,000 + 17,500 + 45,000 + 4000), 14,625 rubles will be withheld.
IMPORTANT!
Insurance contributions are not deducted from wages. The rule applies to all types of standard insurance coverage for citizens (OPS, OPS, VNiM and NS and PZ). Voluntary contributions, on the contrary, are deducted directly from the salary and other income of a specialist.
Deductions under a writ of execution from wages
Let us note that in terms of seizures under writs of execution we are talking not only about the collection of alimony in favor of minor children or elderly parents, but also about collections in favor of paying off overdue accounts payable (for example, proceedings on a mortgage or consumer loan), payment of administrative fines and other forms deductions under a writ of execution from wages in favor of legal entities and (or) individuals.
IMPORTANT!
In accordance with Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, art. 99 of Law No. 229-FZ, deductions under writs of execution in terms of alimony, compensation for harm to the life and health of citizens, compensation for loss of a breadwinner cannot exceed 70% of total income. Research for other types of writs of execution - no more than 50% (writ of execution for repayment of debt under an agreement, loan, compensation for moral damage). Other types of deductions cannot exceed 20% of earnings (for example, compensation for shortfalls, correction of accounting errors, etc.).
Example 2. Writ of execution, alimony.
Let's look at a similar example of how to withhold alimony from your salary.
At the end of August 2021, the employer received three writs of execution against employee Kreditovaya Irina Pavlovna. The total debt amounted to 410,000 rubles, including in favor of:
- enforcement proceedings of Bank of Russia OJSC - 210,000 rubles;
- enforcement case of OJSC "Credit to everyone" - 120,000 rubles;
- executive papers of JSC "Loans bystry" - 80,000 rubles.
According to the terms of the writ of execution, deductions should be made monthly until the loan debt to the bank is fully repaid, but not more than 50% of the amount of income per month.
Earnings for September amounted to 46,500 rubles.
IMPORTANT!
The calculation of the amount of how much to withhold under writs of execution is made after calculating personal income tax! There is no need to issue additional orders or obtain the employee’s consent.
Calculation of deductions:
46,500 – (personal income tax 46,500 × 13%) = 40,455 rubles.
Amount of deductions: 40,455 × 50% = 20,227.50 rubles.
We distribute the amount between banks as a percentage of the total amount of debt:
- Writ of execution of OJSC Bank of Russia: 20,227.5 × (210,000 / 410,000 × 100%) = 20,227.5 × 51.2% = 10,356.48 rubles.
- Executive documentation of Credit to Everyone OJSC: 20,227.5 × (120,000 / 410,000 × 100%) = 20,227.5 × 29.3% = 5926.66 rubles.
- Implementation requirements of JSC Loans bystro: 20,275.5 × (80,000 / 410,000 × 100%) = 20,227.5 × 19.5% = 3944.36 rubles.
Next, the employer will repay debts to banking organizations until the resulting debt in enforcement cases is fully repaid.
Alimony by agreement
The provision of minor children is not always paid by parents according to writs of execution. In some situations, the employer withholds money from the employee's earnings under a notarial agreement. This agreement is concluded between the parents of a minor child in the presence of a notary. It specifies the amounts, frequency of payments, as well as other conditions.
How to withhold alimony from your salary, example 3.
Sergey Nikiforovich Ivanov entered into a notarial agreement with his wife Ivanova Marya Yakovlevna to pay alimony for their minor children Alena and Peter. The amount of monthly payments in favor of children is 35% of S.N. Ivanov’s income.
Official salary of Ivanov S.N. — 100,000 rubles, worked for a full month.
Calculation:
100,000 – personal income tax 13% = 87,000 rubles.
87,000 × 35% = 30,450 rub. - transferred alimony in favor of minor children.
Let us note that it is possible to withhold alimony in favor of an employee’s minor children on the basis of his application, and not only by agreement or enforcement proceedings.
Application for deduction from wages (sample)
Income from which deductions cannot be made
At the everyday level, the concept of earnings includes all payments made by the employer, but part of this income is not subject to deduction. Deductions cannot be made from funds received as:
- compensation for injury to health or death of an employee;
- compensation for business trips and transfers, wear and tear of the employee’s personal tools;
- payments on the occasion of marriage, birth of a child and death of loved ones;
- insurance coverage for compulsory insurance, except for amounts paid on sick leave;
- one-time financial assistance in cases of natural disasters and similar emergency circumstances;
- compensation for the cost of a trip to a sanatorium, as well as travel to and from the place of treatment.
If we are talking about the payment of alimony, then amounts compensating for harm to health and benefits for temporary disability are excluded from this list. Withholding of alimony payments can be made from them.
Voluntary contributions
Some amounts may be withheld from employees on a voluntary basis. For example, trade union dues that an employee decided to transfer to a trade union organization. Or voluntary contributions for insurance coverage of citizens. The most common option is to pay contributions to form the funded part of the pension to non-state pension funds.
The group also includes amounts withheld from an employee in order to repay loans, credits and credits previously issued by the enterprise. For example, a specialist received an interest-free loan from an employer. It is repaid through deductions from accrued wages in a fixed amount.
Withholding of any amounts based on a written statement by the employee, as well as by agreement between the employee and his employer, also falls into the group of voluntary penalties.
Committing illegal actions that resulted in excessive payment
This is one of the most difficult grounds for an employer, since the legislation does not contain specific criteria for unlawful actions. Consequently, any illegal acts that result in receiving a salary in a larger amount than required can be recognized as such. The illegality must be confirmed in court. Therefore, in order to use this basis, the employer must have appropriate evidence.
For example, if an employee falsified documents confirming the fact of his employment, the employer will have the right to demand the return of unlawfully received wages.
In each specific case, the relevant criteria for the illegality of an employee’s actions are subject to consideration by the court, taking into account all the circumstances of the case.
How to recover accountable amounts
Overpayment of an advance on travel expenses or on accountable money is a common situation. It is almost impossible to plan future expenses down to the penny, so unspent accountable funds are constantly encountered in the work of an accountant.
In fact, the employee must return the money himself. But this is ideal. If a subordinate does not want to return the accountable money on his own, the employer can withhold the overpayment from his earnings.
IMPORTANT!
You can deduct from your salary not only the amount of overpayment, but also the debt on an unapproved advance report. For example, if the employer did not approve the advance report due to the lack of supporting documentation.
The action plan is outlined in the Letter of Rostrud dated 08/09/2007 No. 3044-6-0. To make deductions from wages of accountable amounts:
- within one month from the date of expiration of the period for compensation of the resulting overpayment, issue an order to withhold money from the employee’s salary.
IMPORTANT!
If the deadline is missed, then it is unlawful to collect accountable amounts from earnings. In such a situation, the overpayment can only be reimbursed through the court.
- After issuing a deduction order, familiarize the debtor with the order against signature. The employee must state in the order that he agrees with the collections from the salary. Otherwise you will have to go to court.
Accountable money that is not returned to the employer is not the employee’s income and is not subject to personal income tax, since it is a debt to the employer.
If the employee does not repay the debt on accountable money within a month from the date of expiration of the period established for their return, charge insurance premiums on the unreturned amount. The premiums can then be offset if the employee does not repay the money. Or return it if the accountant provides supporting documents (Letters from the Social Insurance Fund dated April 14, 2015 No. 02-09-11/06-5250, Ministry of Labor dated December 12, 2014 No. 17-3/B-609).
When deduction from salary is not possible
An accountant withholds tax or debt from a salary by order of a bailiff without completing other documents. He only needs to remember the restrictions from Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, two conditions must be met:
- The one-month period established for debt repayment has not expired (Part 3 of Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The employee gave written consent to the deductions.
If at least one of these conditions is not met, the employer will have to go to court to return the overpaid money.
There is no need to obtain consent from the resigning employee to withhold for unworked vacation days. But if there is not enough money to cover overpaid vacation pay, the employer will not be able to recover the remaining amount through the court. Because there is no such basis in the law.
How to keep records
Account for deductions from wages using the following standard entries:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Salary accrued | 20 | 70 |
| Personal income tax withheld | 70 | 68 |
| The amount under the writ of execution was withheld | 70 | 76.41 |
| The amount under the writ of execution is transferred in favor of the recipient | 76.41 | 51 |
| Amounts of unused sub-report are withheld | 70 | 71 |
| Repayment of the issued loan is reflected | 70 | 73.1 |
| Union dues withheld | 70 | 76 |
How to reflect deduction on a payslip
Another “personnel” issue that arises in this situation is related to the preparation of pay slips. As you know, Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires them to be issued when paying wages. At the same time, as stated in paragraph 3 of this article, the payslip must contain information about the amount and reasons for the deductions made. Is it necessary to reflect on the payslip the amounts that are withheld at the request of the employee?
Unfortunately, neither legislation nor regulatory agencies give a clear answer to this question. But from the analysis of judicial practice it follows that the pay slip must also indicate those deductions from wages that are carried out with the consent of the employee (see, for example, the appeal ruling of the Omsk Regional Court dated 05.08.15 in case No. 33-5198/2015). In particular, the pay slip should reflect the deduction, formalized as a deposit into the organization’s cash desk of funds just issued to the employee as a salary (see, for example, the appeal ruling of the Krasnoyarsk Regional Court dated November 24, 2014 in case No. 33-10088).
Thus, regardless of the wording of the employee’s application (whether he asks to withhold money from his salary or transfer it to the organization’s account), this operation must be reflected in the pay slip. It should indicate the basis for the deduction (employee statement) and its amounts.
Calculate advance and salary taking into account all current indicators
Special types of deductions
Some employers provide a bonus labor system to motivate employees. For example, a guaranteed salary is only a small part of earnings, the rest of the amount is determined based on the specialist’s performance indicators.
The system of fines for employees is becoming increasingly popular (example: wages in large corporations, supermarket chains, holding companies, etc.). This remuneration system is aimed at motivating specialists to achieve their goals. In other words, if the employee did not fulfill the plan or committed any misconduct, the employer has the right to punish the specialist with a ruble.
However, according to the labor inspectorate, such a system is considered illegal, since collecting a fine from an employee is equivalent to non-payment of part of the salary, even if the punishment itself is supported by an order and other documents. For this, the employer can be punished under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences.
Withholding of unearned advances issued on account of wages
The employer has the right to withhold the unearned advance payment no later than one month from the date of expiration of the period established for its return.
Since withholding is possible only if the employee does not dispute its grounds and amounts, the employer must obtain the employee’s written consent. Such consent to retention is drawn up in free form.
The decision to withhold is formalized by order (instruction). Since there is no unified form for such an order (instruction), it is issued in free form.