Financial assistance is one-time in nature, carried out by order of the manager on the basis of an application received from the employee, and is associated with:
- with the birth of a child;
- with the death of an employee’s family member;
- with damage caused by a natural disaster;
- with retirement upon reaching the appropriate age or due to disability;
- for other reasons.
Financial assistance cannot be classified as wages, since it is not of a stimulating or compensatory nature, but is aimed at supporting an employee in a difficult life situation. This circumstance is taken into account in the current legislation.
The answer to the question whether alimony is withheld or not from financial assistance depends on the basis for the allocation of funds. Calculation of alimony from amounts of financial assistance is not carried out in all cases.
How is child support paid?
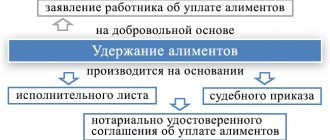
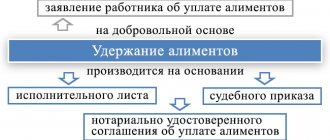
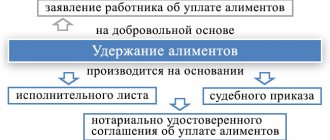
If the parents of the children fail to reach an agreement on the substance, then alimony must be collected in court from the parent who refuses to voluntarily support his children.
In case of judicial collection, alimony can be withheld in two ways:
- In the form of a fixed amount paid monthly;
- In the form of a percentage (share) of all types of parent’s earnings.
In cases of shared collection, alimony will be deducted from the official income of the parent or, if it is collected in a fixed amount, will be paid to him voluntarily. Also, a fixed amount can be withheld by the employer from wages and other due payments.
The procedure for deducting alimony payments from MP
In exactly the same way as from any other type of income, alimony is withheld from material support. The procedure is the same for everyone.
All that matters is the basis on which the payment is made.
This can be considered an alimony agreement, which both parents voluntarily agreed upon, one paying alimony, the other receiving it. By the way, the Family Code provides for such an agreement with a person who, by law, is not at all obliged to do this. And then both parties negotiate among themselves the types of income, including MP, the amount of deductions (a share or a specified specific amount), methods of payment and the frequency of receipt of funds.
The second option is a court decision - payments under a writ of execution, which stipulates obligations in relation to a minor child, or a court order issued by a single judge. Payments, which may be shares of earnings, lump sums, or a combination of options, are made every month (or one-time) in accordance with the decision made by the court on this issue, as prescribed by current legislation.
The employer's accounting department is responsible for deducting designated amounts from the income of a person officially employed, starting from the very month when the writ of execution was received. In all other cases, the citizen will have to make payments independently.
How are the types of income for which alimony is taken regulated?
Before answering the question of how you can withhold part of the paid financial assistance in favor of alimony, you need to understand what legal acts regulate the admissibility of collecting alimony payments from one or another type of financial assistance. Such acts are:
- Government Decree No. 841 of June 18, 1996, which contains information about all types of wages and other income, including received financial assistance, from which alimony can be withheld for the maintenance of minor children. This document was adopted back in 1996, however, after quite a lot of time, it still has not lost its relevance.
- Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings”. This regulatory legal act also reflects the types of income from which alimony payments can be calculated, as well as income from the amount of which any deduction is prohibited by law.
Note: The legislation on enforcement proceedings also establishes what property can be seized to pay off a debt (including alimony).
Find out more about what income is and is not subject to alimony.
Is alimony deducted from financial assistance?
The procedure for withholding alimony is based on the principle of the impossibility of unlawful enrichment of the party receiving alimony in the event that such payments may worsen the financial situation of the alimony payer.
Current legislation allows deduction only from a certain list of types of material assistance, namely from assistance that does not have a social purpose.
Thus, if the payments provided should be used to eliminate the consequences caused by emergency events such as a fire, earthquake, death of a close relative, or are intended to provide the necessary care for a seriously ill person, then the funds allocated for these purposes are not subject to withholding alimony payments.
If the specified assistance is targeted in nature and allocated to cover specific expenses, then such monetary payments should go precisely to their designated purposes. In this case, the legislator also prohibits retention. For example:
- financial assistance provided to meet the needs of a newborn child should be spent exclusively on providing such a child with all the necessary things such as clothing, baby food, etc.
- Financial assistance for the treatment or burial of a relative is similarly targeted.
A more detailed list of types of financial assistance from which alimony is not deducted is disclosed in paragraph “L” of Article 2 of the previously mentioned Government Resolution No. 841.
Payments allocated for a person's vacation are those that the recipient has the right to dispose of at his own discretion, and therefore there are no restrictions on the collection of alimony payments from vacation.
Basic definitions
Help
This is considered a one-time cash receipt that is not of a production nature and is in no way interconnected with the results of the enterprise’s work, the size and quality of a person’s performance of his professional tasks and compliance with labor regulations. It is also called monetary support.
The circumstances that give rise to such support may vary:
- difficult financial situation;
- disaster;
- loss of ability to work due to illness;
- addition to the family;
- death of a relative;
- vacation or treatment;
- theft of property;
- anniversary, wedding, etc.
It is the purpose of the payment that determines whether it is additional income or material support. The first option is a basis for collecting alimony, the second is not.
Alimony
This is mandatory cash support that must be paid by one relative to another disabled family member (child or parent) living separately. How these payments are made is determined by legislative acts.
Material assistance in difficult situations (fire, death of relatives)
Money accrued to the alimony payer as assistance in critical situations, such as the death of a close relative, fire, etc. are of a direct social nature, since these payments are intended to financially support a person during one of the most difficult periods of his life. These targeted funds are aimed specifically at solving socially important problems of a person, and therefore alimony is not withheld from them.
Situations similar to those mentioned above may also include:
- Financial assistance in connection with a natural disaster;
- Funds paid in connection with an injury or injury;
- Payments taken by the payer to repay material damage, for example, associated with theft of property;
- Compensations related to moral damage.
List of payments on which interest is withheld in favor of the child
Child support must be paid from funds that are not of a social nature and are aimed at improving the quality of life of an employee of the organization, who already feels pretty good. In essence, such payments are a kind of bonus that is not directly related to results or success in work activity for a certain period.
You can set out a list of assistance with which alimony is paid, it will be open, because the payment of money to an employee can, by and large, be timed to coincide with any event. So:
- Help on the occasion of a public holiday . For example, a payment for Russia Day. Money is transferred to the employee not because some changes have occurred in his life, but to emphasize the importance of the event and so that the person can better celebrate the holiday. That is, the money does not go to any social purposes. Therefore, it is necessary to withhold alimony from them.
- Holiday payments. In essence, this is a bonus that the employer rewards a good employee of the company. In such a situation, the owner of the company wants the employee to fully enjoy his vacation and not rest without money. That is, again, there are no social purposes for the payment.
In case of vacation, it is necessary to withhold alimony so that it is good not only for the employee who pays the funds, but for their recipient, a child or several children.We wrote about whether alimony is calculated from vacation pay here.
- Help for health purposes .
In the vast majority of cases, about exceptions - a little lower, alimony from such payments will be withheld (is alimony calculated from sick leave?). Logic of the post: yes, we can assume that money, in the situation described, is a kind of social support. Health is a concept that relates specifically to this area. But, if you look at it, most of these payments do not have a specific purpose. That is, the employer gives money to an employee of the organization and says: “Take it, get some treatment.” The employee goes to a sanatorium, where measures are taken aimed at the general health of the body, and not at rehabilitation, say, after a work injury. The social character seems to be present. But there is no specific goal.
Thus, in order for the withholding of alimony from financial assistance to be legal, you need to make sure that the payments:
- do not have a social character;
- aimed at achieving a specific goal.
To be exempt from withholding alimony in a particular case, it is necessary to prove that both of the above signs of financial assistance occur. Assistance can be considered as income, therefore alimony from financial assistance for vacation can be collected in accordance with the general procedure.
Read about what income and how alimony is calculated here.
Maternity assistance during vacation
The case of payment of compensation when an employee goes on vacation does not have any social basis. This payment serves only the purpose of making the vacation more comfortable for its recipient. Thus, deduction of alimony from such payments is not prohibited.
However, it should be understood that according to the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, vacation pay must be paid no later than three days before the alimony payer goes on vacation. If the payment was made later, then it will be necessary to clarify the question of the real purpose of such assistance.
Financial assistance for treatment
As a rule, funds provided for health improvement are equated to those intended to improve a person’s quality of life, since they are mainly allocated for the completion of health procedures for such a person in specialized sanatoriums. In this case, alimony may be withheld from the amount provided.
However, there are situations when the employer provides financial assistance not just for health improvement or rehabilitation. Thus, if the alimony payer received a serious injury at work, and a specific amount of financial assistance was allocated for his treatment, aimed specifically at such recovery procedures, then it would be unlawful to withhold alimony from such payments.
Help at the birth of a child
Money intended to improve the quality of life of a child does not count as income from which child support payments can be recovered. The fact is that such payments in the literal sense do not bring any benefit to the general family budget, since the state allocates a specific amount of money for certain purposes, namely, to meet the needs of the newborn.
This also includes:
- Incentive payment in connection with the birth of a child;
- A one-time payment for a child from social security or an employer.
Any attempts to foreclose on financial assistance in favor of alimony at the birth of a child will entail an actual deterioration in the child’s living conditions, and such actions are prohibited by current legislation.
If the bailiff demands withholding of alimony from any of the types of financial aid prohibited from withholding, then you can safely file a complaint against the official.
Procedure for taxation of financial assistance
Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of income paid to employees that is not subject to taxation. This includes financial assistance, the amount of which does not exceed 4,000 rubles. in year.
But alimony for financial assistance of 4,000 rubles will be charged, since alimony obligations are not related to tax obligations. For them, there are separate lists of income from which collections are made and from which alimony payments cannot be deducted.
How alimony is withheld from financial assistance: terms of transfer, before and after taxes
If the financial assistance provided to the alimony payer does not have a social purpose and is considered to improve the general financial condition of the debtor, then according to Art. 99 of the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings”, alimony is withheld from these payments in accordance with the general procedure. As in the case of wages, only after personal income tax has been withheld, and only then is interest paid from the remaining amount, which goes towards repaying alimony payments.
Also, according to the regulations of the RF IC, namely Art. 109, alimony must be accrued to the recipient of such payments no later than three days from the moment the alimony payer receives wages or other income, including material assistance.
Important! Personal income tax is not withheld from the final amount of alimony. This rule is provided for in paragraph 5 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, according to the mentioned Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are many types of material assistance that are not subject to taxes at all. These include:
- Compensations made on a one-time basis to family members of a deceased employee;
- Payments provided in connection with a natural disaster or other emergency situations;
- Compensation provided to victims of terrorist attacks;
- Funds intended for persons who are members of public organizations of disabled people;
- Monthly benefits that are issued at the birth of a child (first and second), etc.
Cost and terms
If the parties decided to peacefully conclude an agreement on the withholding of alimony obligations from financial assistance, then in accordance with clause 9 of Art. 333.24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, you must pay 250 rubles for certification of a document by a notary. Moreover, if the project was drawn up not by the parties, but by a notary, the specialist may increase the cost of services. 250 rubles only includes certification of the completed agreement. Regarding deadlines, no rules have been established at the legislative level. In practice, everything depends on the workload of the specialist; on average, the procedure for concluding an agreement on alimony with financial assistance takes no more than 2 days.
For your information
In a situation where citizens have not agreed peacefully to provide for their offspring and they have to go to court, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of Art. 333.36 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Item 2, part 1, art. 333.36 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates that for applications related to the collection of alimony, the plaintiff is exempt from paying money. The financial burden falls on the defendant after the case is decided. According to the rules of clause 14, part 1, art. 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of the duty in this situation will be 150 rubles. The time frame for consideration of a case on the collection of alimony from financial assistance is reflected in Art. 154 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, this is 2 months. In complex cases, the duration of the trial may increase by 1 month, which means a total of 3 months.
Example of calculating alimony with financial assistance
Ivanov A., in connection with his departure on regular leave from July 15, received the following payments at his main place of work:
- Vacation pay in the amount of 16,000 rubles;
- Salary from July 1 to July 14 in the amount of 14,000 rubles;
- A one-time payment for vacation, provided for by internal regulations and called “material assistance for vacation in the amount of 10,000 rubles.
All of these funds were credited to him on July 13 shortly before he left for vacation. The amount of all funds received was 40,000 rubles. For the child, ¼ of all types of earnings is withheld from Ivanov.
Thus, the total amount of alimony payable will be:
- We subtract personal income tax: 40,000 rubles – 13% = 34,800 rubles;
- We calculate alimony: 34800 * 25% (1/4) = 8700 rubles.
Please note that in this case, there is no need to separately calculate alimony from financial assistance. The employer's accounting department itself will calculate them at the same time as deducting mandatory payments from vacation pay and wages.
If the payer pays child support in a fixed amount, then the amount of financial assistance will not matter at all - the required amount will be withheld either from vacation pay, or from the balance of wages for the month, or from financial assistance. Typically, accounting tries to evenly distribute the burden of alimony in a fixed amount across the payer’s income.
Deduction amount
Working citizens, as a rule, pay alimony in the form of a share (percentage) of their earnings and other income received both at work and outside of work.
The amount of deductions depends on the number of children of the payer.
So, for one child, funds are withheld in the amount of ¼ of the salary, as well as other payments to the employee, including bonuses, vacation pay, and so on. For two children, 1/3 is withheld, for three or more – ½.
If an employee has an alimony debt, it is also withheld from wages and other payments. At the same time, the law prohibits withholding more than 70% of funds from an employee’s earnings.