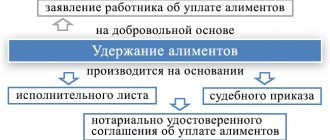
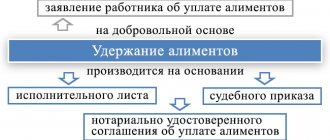
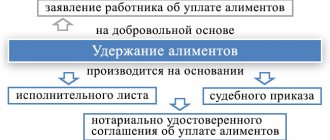
Grounds for deduction of alimony
An order to withhold and transfer alimony through the company’s accounting department is sent to the employee at his main place of work. The basis may be:
- performance list;
- court order;
- alimony agreement certified by a notary;
- resolution of the bailiff.
Accountants should be aware that alimony payments should only be withheld after income taxes have been withheld. That is, they are, as it were, second in line (Part 1 of Article 99 of the Federal Law of October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ “On Enforcement Proceedings”, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 229-FZ).
Settlement agreement on tax, alimony
The taxation of alimony may be addressed through a settlement agreement. In this case, a corresponding document is drawn up between the claimant and the debtor in the presence of a bailiff and at the stage of enforcement proceedings. In order to cancel coercive measures in relation to the fulfillment of alimony obligations, it will be necessary to file an application with the court and then submit it to the bailiff.
There is also a flip side to the coin. Alimony payments from the recipient who has entered into this agreement are subject to general income tax for individuals, since payments are not included in the category of those for which personal income tax is not charged; alimony withheld according to documents of an executive nature is not subject to income tax for individuals. A way out: at the time of applying to the court to approve a settlement agreement, indicate the need to divide the amounts of funds. One part will not be taxed (alimony due to the claimant), and the second will become the amount of withholding.
Deduction amounts
The writ of execution does not always indicate the specific amount of a fixed amount of alimony. Then the unfortunate spouse and his employer should know that they will have to pay:
- for one child – 25 percent of the amount of calculated earnings excluding personal income tax;
- for two children - a third of the same income according to the same calculations;
- for three or more children, you will have to share half of your income.
It should be noted that some individuals are deeply mired in paying child support. But keep in mind that Law 229-FZ contains a strict restriction: one person cannot be deducted for payments to other persons in an amount greater than 70 percent of his income minus income tax.
What is personal income tax and from what income is it taken?
One of the types of taxes that are levied in the Russian Federation on its citizens, as well as foreign persons receiving income on its territory, is personal income tax, or income tax. It is taken from various categories of earnings, both in cash and in kind. It can be:
- salary;
- bonus;
- sick leave;
- fee;
- winning;
- present;
- income from sales.
Personal income tax is calculated as a percentage of the total income received during the calendar year on an accrual basis. In some cases, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for deductions, as well as income, which are not the basis for personal income tax.
The basic income tax rate in the Russian Federation is 13%. But there are other sizes that correspond to different types of income and taxpayer statuses.
Thus, if a person is a tax resident, lower rates are usually provided for him. Tax residents are individuals who actually stay in Russia for no less than 183 days (calendar) within 12 consecutive months. At the same time, Russian citizenship, foreign or its absence does not affect the acquisition of resident status.
Basically, personal income tax is calculated and sent to the budget from wages at the place of work. Here the company acts as a tax agent. If income is obtained from the sale of property, you must fill out and submit a declaration to the tax authorities yourself.
Quick transfer
The same Law No. 229-FZ determines the period for payment (transfer) of alimony to the other parent of the child. It is three days after the accrual of wages and other payments. That is, taking into account all bonuses, vacation pay, sick leave pay.
A profitable loophole for alimony payers is travel accruals. The fact is that, according to the law, alimony is not withheld from them, since the entire amount goes to support the posted worker. In different years, the amounts of travel allowances were different. Sometimes their size was significant when the employee was sent on long business trips.
Employees are given a pay slip, which clearly states (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- the amount of calculated and transferred alimony;
- income tax;
- the balance of the amount received by the alimony holder.
Employers' liability
The main recipient of alimony for minors has the legal right to file claims in the form of a lawsuit against citizens who are the debtor's employers in the event of delays or incomplete transfers due to their fault. This issue is regulated by Article 118 of Federal Law 229.
The employer bears full responsibility for the timely deduction of alimony payments, starting from the moment the alimony payer submits the corresponding application, receives a court decision and other writ of execution. Failure to fulfill a monetary obligation may be brought against an employer who transfers alimony payments untimely or not in full.
The alimony collector has the right to file a claim against the organization/enterprise in order to receive interest for late payments (Article 395, paragraph 1 of the Civil Code of Russia).
If the income of the recipient of alimony payments is fixed in cash, then all interest received in the form of funds falls under the criteria of economic benefit, since the individual receives full right to dispose of them. Income received in the form of interest is subject to personal income tax on a general basis at a standard rate of 13%.
Alimony for 1st child
Parent Kovalenko V.P. pays child support for one child. In May, he received a salary with all additional payments in the amount of 36 thousand rubles. According to the law, 25 percent of income must be withheld from each child.
Income tax for 36 thousand is 4680 rubles. (36,000 x 13:100).
The amount that remains after paying personal income tax: 36,000 – 4680 = 31,320 rubles. This is the indicator from which the amount of alimony is calculated.
In our case, child support for one child will be: 31,320 x 25:100 = 7,830 rubles. This amount will be transferred to the other parent within 3 days for the maintenance of their son or daughter.
Kovalenko V.P. will receive a salary minus income tax, alimony, other deductions for social and pension insurance, and union dues. If we do not take into account other deductions, the amount in hand will be:
36,000 – 4680 – 7830 = 23,490 rubles.
Why aren't taxes paid on alimony payments?
The legislator does not classify alimony payments as income from which taxes are withheld.
This is due to the fact that alimony is assigned to citizens in need of financial support. For example, both parents are required to support their children. After a divorce, financial obligations between the mother and father are distributed in accordance with the law. The parent with whom the child remains to live receives alimony
s for the maintenance of their common offspring.
It turns out that this is not the recipient’s personal money, which is why it is not required to pay tax
.
Moreover, the man has already had personal income tax withheld from his salary .
One child
In our case, with a salary of 36,000 rubles while supporting one child, income tax is taken not from the indicated amount, but from the amount:
36,000 – 1400 = 34,600 rub.
The tax from this amount will be equal to 4498 rubles. (34,600 x 13:100), and not 4,680 rubles without taking into account the deduction.
Then alimony will be calculated based on the amount of 31,502 rubles. (36,000 – 4498).
The amount of alimony is 7875.50 rubles. (31,502 x 25:100).
The employee will receive: 36,000 – 4498 – 7875.50 = 23,626.50 rubles.
Let's compare the amounts received by the worker in different cases: 23,490 and 23,626.50 rubles.
The difference with the tax deduction refund is only 136.50 rubles. (23,626.50 – 23,490).
Thus, with a tax deduction, a person will receive 136.50 rubles more than without its use.
How to correctly reflect alimony in 6 personal income taxes?
Since 2021, a second form of reporting has been introduced for the calculation and withholding of personal income tax from employees by tax agents.
On a quarterly basis, employers draw up and submit to the tax office a report on Form 6 Personal Income Tax, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] dated 10/14/2015.
In the first section, they are indicated as a cumulative total:
- line 020 - the sum of all income of the tax agent’s employees;
- line 030 - the sum of all tax deductions that reduce the tax base;
- line 040 - calculated personal income tax amount;
- line 070 - personal income tax amount withheld.
Not a single line mentions alimony, so it is not reflected in section 1.
In the second section, quarterly indicators:
- line 130 - the sum of all income. This reflects the amount calculated and not issued in person, i.e. until the moment of deduction of personal income tax, standard, property and other deductions.
- line 140 - personal income tax actually withheld from line 130 minus tax deductions.
As you can see, alimony is not highlighted in any of the paragraphs, so they do not fit separately in Form 6 of the personal income tax.
ATTENTION! Along with the 6th personal income tax report, every year before April 1, a 2nd personal income tax certificate is submitted, which has not been cancelled.
For 2 children
Income tax is calculated from the amount: 36,000 – 1,400 x 2 = 33,200 rubles.
Personal income tax is taken from this amount and amounts to: 33,200 x 13: 100 = 4,316 rubles.
In the first case, excluding tax deductions, the amount of alimony was 10,440 rubles. In our case, this is: 36,000 – 4316 = 31,684 rubles. A third is taken from this amount. Then the alimony will be:
31,684: 3 = 10,561.3 rub.
The employee will receive: 36,000 – 4316 – 10,561.3 = 21,122.7 rubles.
The difference with and without the deduction is: 21,122.7 – 20,880 = 242.7 rubles.
Taxpayer status when transferring alimony
Payment of alimony is not a tax payment, which is paid into a non-budget system.
The Ministry of Finance has developed rules for filling out payment slips only for money transfers to the budget (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 107n dated November 12, 2013):
- taxes;
- insurance premiums;
- fees;
- customs payments, etc.
In Appendix No. 5 to this order there is a list of statuses from two-digit codes, which must be entered in field 101.
But, since the transfer of alimony is a transfer not to the state budget, these rules in the preparation of a payment order do not apply to it, and nothing is entered in the payer status; the field remains empty.
In this case, the “Purpose of payment” field contains information:
- the purpose of the payment is the transfer of alimony;
- object of deduction - from the salary, full name of the employee;
- employee tax identification number;
- for what period is the transfer;
- basis - number and date of the writ of execution.
Alimony deduction code in certificate 2-NDFL
All income received by an individual is reflected in the certificate. The line contains rewards. The accounting employee also indicates the code for deducting alimony withholding and transferring personal income tax to the state treasury. When filling out the document, take into account the following points:
- alimony refers to part of the employee’s officially earned funds, they are included in the general code 2000;
- A tax of 13% is deducted from the total portion of income.
There is no special deduction code for child support payments. The security consists of a group of general remunerations. It is not reflected separately in the certificate in any way, since document 2-NDFL is recorded in relation to the money earned by the employee at the enterprise.
In addition, alimony is not a source for calculating income tax.
Income tax rate
First of all, the rate is affected by residency status . Resident - a person who has been in Russia for more than 183 days and does not leave it during this period. Otherwise, the payer will be recognized as a non-resident.
13% of income is deducted from residents' salaries . However, there are also more specific rates. For example, 35% - for winnings over 4,000 rubles, for interest on deposits and coupons on bonds, and so on. Personal income tax of 30% is taxed on income from certain securities. The lowest rate of 9% is available for mortgage-backed bonds that were issued before 01/01/2007, and for the income of the founders of the mortgage-backed trust.
For non-residents, 30% is deducted from their income, but there are exceptions . For example, a rate of 15% is relevant for non-residents who receive dividends from domestic companies. Foreigners can claim 13% personal income tax under the following conditions:
- they are highly qualified specialists;
- they are crew members of sea vessels flying the flag of the Russian Federation;
- they are refugees;
- they are participants in the state program for the resettlement of compatriots;
- they work for hire under a patent.
Controversial issues
It is worth highlighting some points:
- Alimony is not calculated from travel allowances, the lifting part of payments when an employee is transferred or sent to another region, subsidies paid at a wedding, the birth of a child, or in the event of the death of a loved one.
- If the alimony worker does not work, this is not a reason to refuse to pay payments. This is clearly reflected in Article 80 of the SK. The security is set in the form of a fixed amount. According to the claim document, it is possible to obtain the recovery of funds from the non-payer.
- The total debt is calculated for the last three years that preceded the date of the court decision. When an agreement is concluded between divorced parents, the calculation occurs in accordance with the points specified in it.
- There are situations in which you can ask for more money from the payer: a serious illness that requires expensive treatment, the purchase of medications, surgery, or injury to the baby.
- If the father of the child is a foreigner, then you can demand payment of funds in court through the bailiffs.
If the parents are not divorced and are fully raising and raising the child, the question of the procedure for calculating and withholding alimony payments does not arise. The material describes in detail the aspects of calculating and transferring payments to a child.
Income not subject to taxation
The types of income that are exempt from the tax burden are established and include:
- benefits and payments as compensation, with the exception of temporary disability benefits;
- various types of pension payments;
- monthly payments provided for the first child, according to the new legislation on providing benefits to low-income families with children;
- income from volunteer activities;
- rewards provided to donors of blood, plasma or breast milk, as well as other donors;
- alimony payments, regardless of who they are paid to;
- grants and awards received by citizens of the Russian Federation;
- financial assistance from federal, regional or municipal budgets;
- scholarship transfers to students;
- other categories of income established by federal regulations, including the provisions of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that alimony payments should not be subject to income tax. In addition, alimony cannot be fully considered the income of the custodial parent. In fact, these funds are intended for a minor child as material support, which the parents provide in equal shares: one parent is involved in financial support, education, and care for the child on an ongoing basis, the second helps only financially with minor care, for example, when spending time together weekends or holidays.
Amount of alimony paid
After we have found out whether alimony is calculated from “clean” or “dirty” wages, we will figure out the minimum and maximum amounts of enforcement payments.
Article 81 of the RF IC stipulates that one dependent receives 25% of wages, two dependants receive 33% of labor income (from ordinary or patent activities), and three dependants receive 50% of remuneration for labor. In this case, the amount can be increased by court decision, but the total amount of alimony from wages should not exceed 70%.
If certain grounds arise, a citizen also has the right to go to court to reduce the amount of payments. If the payer has dependents from different marriages, then alimony from the salary will be transferred in equal shares for each minor child.
Personal income tax benefit if the employee pays alimony
Alimony non-payments have long become a global social problem. Since the main breadwinner in the family, as a rule, is the father, with his departure the remaining family members lose their previous level of material well-being and have every chance of sliding down the social ladder. It was to prevent mass impoverishment of the population and increased social tension that, on the basis of foreign experience, the concept of tax benefits appeared in Russian legislation.
How are taxes calculated?
According to the Tax Code, taxpayers with children are entitled to tax deductions:
- if there are 1 or 2 children, compensation in the amount of 1,400 rubles is provided for each of them;
- for the third child and subsequent payments will be 3,000 rubles;
- for a disabled child, the deduction is 3,000 rubles;
- For a child studying full-time, under the age of 24, deductions of 3000 are allowed.