Withholding part of the money earned by a citizen is permitted in situations and amounts determined by certain federal laws and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If deductions made from a citizen’s earned income are unlawful, the latter has the right to send a corresponding application to the court. Therefore, responsible employees of the organization must make all deductions from the income of workers in strict compliance with legislative norms, and information on possible options for deductions can be included in a document on the rules of remuneration or other internal act regulating issues of remuneration in the organization.
In what cases does an employer have the right to make deductions from wages ?
What are the grounds for salary deductions?
To withhold part of an employee's salary, there must be a legal basis. For example:
- Art. 137 of the Labor Code: reimbursement of advance payment unspent on a business trip, accounting error, unearned vacation pay.
- Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - transfer of personal income tax by a tax agent.
- Art. 109 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation - withholding alimony from an employee.
- Art. 98 of the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” No. 229-FZ - foreclosure of the debtor’s income by a bailiff.
All grounds, except for personal income tax withholding, must be documented.
Penalty deductions for failure to comply with plan or misconduct
For disciplinary offenses such as tardiness or absenteeism, the labor code provides for a number of punishments: reprimand, reprimand and dismissal. But no amounts can be withheld from the salary (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
But in many enterprises, employees also receive a bonus in addition to a monthly salary. Bonus rules are prescribed in the employer’s internal documents or in the employment contract and additional agreements thereto. The rules indicate what rewards will be rewarded for and what bonuses will be deprived of.
It turns out that deprivation of a bonus is a kind of deduction of money from the variable part of the salary.
Types of deductions
All deductions can be grouped into mandatory by law, optional at the initiative of the employer, or voluntary at the request of the employee.
The first group of withholdings is mandatory - withholding 13% of the personal income tax, the amounts specified in the court decision, writ of execution or order of the bailiff.
The employee’s consent or the employer’s permission is not required to produce them.
The second group of deductions - at the initiative of the employer - can be in 6 cases.
1. The employee received an advance, but did not work the allotted time and quit . Some employers pay a fixed advance - 50% of the salary. They take into account the actual number of shifts worked only when calculating at the end of the month. If an employee worked few shifts, received an advance and immediately quit, he received too much.
The employer can withhold the money during the final payment or reclassify it as compensation for unused vacation.
2. The employee received advance travel allowances, but did not spend them all and did not return them upon returning from the business trip . For example, Ivanov was given 10,000 rubles in advance to cover the cost of paying for a hotel room. But Ivanov finished his business earlier, returned home, and from 10,000 rubles he still had 1,500 rubles unspent.
The employer can withhold 1,500 rubles from the next salary.
3. A counting error has occurred . This is a very controversial basis, since the law does not define the concept of “counting error”. There is an opinion from Rostrud that the counting error is an arithmetic one.
Whether a technical error is considered a counting error is also unclear - the law does not say anything, the courts say different things (see the ruling of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated 04/21/2016 in case No. 33-7642/2016, the Samara Regional Court ruling dated 01/18/2012 No. 33-302/ 2012).
In any case, the law has such a basis, which means the employer has the right to use it to withhold, for example, overpaid wages.
4. The employee did not fulfill the work standard through his own fault, and the labor dispute commission or court confirmed this . For example, an employee must produce 50 products a week, for which he is paid 5,000 rubles. For unknown reasons, he produced only 40 items.
The employer organized a commission on labor disputes, at the meeting they recorded the fact of shortcomings, and the manager had the right to withhold wages from the employee on account of unmanufactured products.
5. The employee took 28 days off, but did not work for a full year . For example, Ivanov got a job in March, worked for six months and went on full leave. After his vacation, Ivanov worked for another 2 months and quit. He received 4 months of vacation pay in excess, so the employer can withhold this money when calculating.
6. The employee caused material damage to the employer . For example, an employee spilled coffee on the keyboard and it stopped working. He caused damage to the employer, so the latter can deduct wages.
The third group of deductions is at the request of the employee. For example, an employee asked an accountant to send part of his salary to the bank to pay off a loan. The Ministry of Labor believes that this cannot be done: the law allows deductions only in certain cases, and this is not on the list.
In what cases is it possible to deduct funds from wages?
Labor legislation clearly lists the cases in which the employer has the right to withhold funds:
- At the initiative of the employee himself.
- The employee did not actually work out the money he received. Most companies have adopted an advance payroll system, and this is one of the unpleasant consequences it can lead to.
- A business trip or relocation of an employee was planned (with a budget allocated), but it did not take place.
- If the enterprise has established production standards, and the employee has not met them.
- If the employee is at fault that there was an error in the accounting documents in favor of increasing the funds allocated for his salary.
- If the working year was not completed due to vacation.
- If, as a result of the employee’s actions or inaction, there is downtime at work.
In addition to these situations (they can be challenged), there are cases of mandatory retention. Specifically, these are court orders. If an employee is a debtor of alimony payments, a defaulter of traffic police fines, etc., then his salary must be reduced by the appropriate amount.
The only exception to the rule is the last “peaceful” month of cooperation between employer and employee. That is, the employee leaves, but only due to a reduction in staff, being sent to military service, due to the return to work of the previous employee, etc.
When deduction from salary is not possible
An accountant withholds tax or debt from a salary by order of a bailiff without completing other documents. He only needs to remember the restrictions from Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, two conditions must be met:
- The one-month period established for debt repayment has not expired (Part 3 of Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The employee gave written consent to the deductions.
If at least one of these conditions is not met, the employer will have to go to court to return the overpaid money.
There is no need to obtain consent from the resigning employee to withhold for unworked vacation days. But if there is not enough money to cover overpaid vacation pay, the employer will not be able to recover the remaining amount through the court. Because there is no such basis in the law.
Compensation for damage
The employer has the right to recover compensation from the subordinate for damage caused.
In fact, it is not very simple, but it is still possible. First of all, the employer needs to assemble a commission and organize an inspection to identify those responsible and calculate the damage. The employee is asked to draw up an explanatory note, and if he does not want to write it, then the commission draws up an act of refusal (Article 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on the results of the inspection, the employer can determine the exact amount of damage based on market prices. Well, for example, an employee broke a machine in production. This happened because he violated the operating instructions. First, you need to calculate the cost of repairing the equipment, and if it cannot be restored, then calculate the amount of damage equal to the cost of a similar machine (Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is possible to withhold compensation for damage from an employee’s salary without his consent. But only if two conditions (Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
By the way, the Labor Code provides for agreements between the employee and the employer on installment plans to pay off damages. And with the consent of the employer, the employee can fix what he broke himself or give the organization equivalent property for replacement.
How to withhold money from an employee
For mandatory deductions, orders from the manager or statements from the employee are not needed; a writ of execution or a copy of it with the order of the bailiff is sufficient.
For deductions initiated by the employer, the list of documents depends on the situation. For example, when withholding an overpaid advance, written consent must be obtained from the employee and an order from the manager to withhold. If a shortage occurs, in addition to these documents, a deficiency report must be drawn up, signed by the commission, and an explanatory note from the financially responsible employee.
Reflection of deductions in accounting
The amounts accrued on wages are indicated in the accounting records. 70. Deductions must also be reflected in accounting, therefore, accrued on the debit of the account. 70 amounts will be reduced:
- when deducting personal income tax - on an account loan. 68;
- when deducting contributions to the Pension Fund - on an account loan. 69;
- when paying according to writs of execution - on an account loan. 76;
- to compensate for losses from marriage - on an account loan. 28;
- for reimbursement of unreturned accountable amounts - on an account loan. 71;
- when withholding funds in favor of third parties - on an account loan. 76.
After all necessary deductions have been made, wages are paid in cash through the cash register (Debit account 70/Credit account 50) or credited to the employee (Debit account 70/Credit account 51).
When can employees challenge wage deductions?
Let us once again draw your attention to the fact that money must be withheld from an employee’s salary strictly in accordance with labor laws.
This applies not only to the registration of the employee’s consent and the employer’s order to withhold; it is necessary to correctly draw up the documents that form the basis of these withholdings.
If the employer incorrectly prepares the supporting documents, there is a high probability that the employee will challenge all “deductions”.
For example, you need to prove that this particular employee is to blame for the breakdown of this particular item, or that there was a shortage, and it occurred precisely because of this employee. For each case, the employer should carry out a number of activities and prepare the necessary documents. Otherwise, the deductions are illegal.
Retention application - sample
If an employee has asked to make any payments from his salary, you need to fill out an application for deduction from wages - a sample is presented here.
It is written in the name of the manager and must contain his full name. and the employee’s position, passport details and registration address. The application should indicate the type of deduction, amount, frequency of payment, details of the recipient and the basis document. It must have the date of compilation and the signature of the employee with a transcript. The application is marked with an instruction from the manager to accept it for execution.
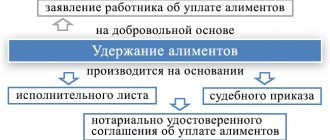
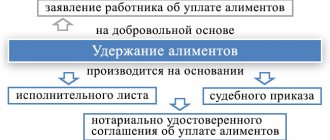
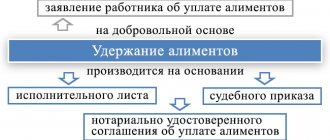
IMPORTANT! The agreement to pay alimony must be notarized and has the force of a writ of execution in accordance with paragraphs. 1, 2 tbsp. 100 of the RF IC, therefore, after the employee writes an application, payment becomes mandatory.
Deduction based on writs of execution
The employer is obliged, and the employee does not have the right, to prevent the employer from withholding from the salary the amounts specified in the writs of execution issued on the basis of a court decision (sentence).
The amount of deductions from wages is calculated from the amount remaining after taxes have been deducted. In this case, the withholding and tax are summed up. Their amount should not exceed 20 (50, 70) percent of earnings.
As an exception to the general rule, the amount of deductions can reach 70% of earnings if:
— the employee serving correctional labor,
- collection of alimony for minor children,
- compensation for harm caused to the health of another person,
- compensation for damage to persons who suffered damage due to the death of the breadwinner,
- compensation for damage caused by the crime.
The employer is prohibited from making deductions from the following payments due to the employee:
- monetary amounts for damages;
- payments in connection with a business trip, transfer, admission or assignment to work in another area;
— payments in connection with the wear and tear of tools belonging to the employee;
- amounts of money paid by the organization in connection with the birth of a child;
- amounts of money paid by the organization in connection with the registration of marriage;
- amounts of money paid by the organization in connection with the death of relatives.
Exceptions to the rules
If an agreement on financial liability has been concluded, the employer has the right to recover the entire amount from the employee. By mutual agreement, you can pay in installments, deducting gradually from each subsequent salary.
The same is done if, during the trial, the employee was found guilty of any administrative offense that resulted in material damage to the organization.
The employee may also express a desire not to receive part of the funds. He can, for example, transfer his finances immediately to repay the loan, to a charitable organization, trade union, insurance fund, etc. It is worth keeping in mind that in order to carry out such actions, the company’s accounting service will need to have a written statement from the employee himself. It must clearly indicate that this is his initiative and he fully agrees with these actions.