Who is entitled to social benefits for education?
When receiving income, any individual is obliged to pay tax on this income to the state budget. For individuals, this is the personal income tax – personal income tax. The state provides its citizens with various tax benefits. One of these personal income tax benefits is the right to receive a social deduction for training (Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is worth considering that personal income tax rates are not the same for every type of income. The basic personal income tax rate is 13%. But there are others:
- 30% – for non-residents;
- 15% – for income over 5 million rubles;
- 35% – for income in the form of winnings, etc.
IMPORTANT!
A tax deduction for education can only be obtained if you have income taxed at a rate of 13% personal income tax.
Thus, if in one tax period (calendar year) you received income taxed at a rate of 13% and studied for a fee, then you have the right to receive a deduction for education.
You also have the right to a deduction if you child (ward), brother or sister was trained . At the same time, you also paid for the training.
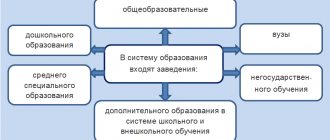
Let us summarize in the diagram who is entitled to a social deduction for education and who is not.
How to get a set of documents at the Russian School of Management
If you have completed a professional development program (lasting 16 hours or more), then, subject to other conditions, you have the right to receive a tax deduction within three years from the date of payment. Save all the papers that remain: the agreement and payment documents. A copy of the license of the Russian School of Management can be downloaded here.
For questions related to documents for studying at the Russian School of Management, please contact | 8 800 100-02-03
The essence of the personal income tax deduction
What is the meaning of the personal income tax deduction? There are several types of personal income tax deductions, but the essence of their application is the same.
Personal income tax is calculated as a percentage of the tax base. A deduction is an amount by which the tax base can be reduced.
IMPORTANT!
A deduction is not an amount that can be returned, but an amount by which the tax base is reduced.
Let's look at an example. The income for the year amounted to 100,000 rubles. Deduction – 20,000 rubles. What will be the tax without applying the deduction and with applying the deduction?
Thus, when applying the personal income tax deduction, it becomes less. If the tax base for the year was calculated without taking into account the deduction, then personal income tax was overpaid, and the overpayment can be returned.
The next question is what amount of tax deduction can be applied.
Rights of the student and expert
Training in online courses falls under the category of services. The Civil Code gives the customer (student) the right to refuse services (course training) at any time. At the same time, he must reimburse the contractor (author or organizer of the course) for the expenses incurred.
This is a general rule, but there are nuances in its application that depend on the focus of training.
Why do people buy your information product? Want to satisfy personal needs? Or do you plan to earn more from the knowledge gained, develop your personality, or create a business?
Whether your relationship will be regulated by consumer protection law or not depends on the content of the course and the purpose of its purchase.
Limit on the amount of social deduction for training
The deduction is equal to the amount actually incurred (subclause 2, clause 1, article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This amount must be paid during the tax period (calendar year). However, there is a limit for it. Moreover, there are 2 types of limits:
Thus, the maximum possible return from the use of a social deduction is the overpayment of personal income tax in the amount of: 120,000 × 13% = 15,600 rubles.
Let us repeat that in addition to the deduction for training, there is also a deduction for treatment, pension contributions and other types of social deductions. The limit of 120,000 rubles applies in total to all social deductions (except for expensive treatment and education of children).
If suddenly the tax base for personal income tax for the year is less than the deduction amount, then the tax payable for the year is 0, and the balance is not carried over to the next tax period (calendar year).
How can you return overpaid personal income tax taking into account the deduction for training?
When you can't get a tax refund
It will not be possible to return personal income tax from the cost of training if (for example):
- the spouse paid for his wife’s education (and vice versa) - the law does not provide for such an opportunity;
- Tuition was paid for using maternity capital funds - para. 5 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- a non-working student used a survivor's pension as payment - there is no income subject to personal income tax (13%);
- payment documents are lost and cannot be restored - one of the prerequisites for providing a deduction and refund of personal income tax under paragraph. 3 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is the availability of documents confirming payment for studies;
- the child’s education was paid for by a person who is not his father according to documents and who did not officially adopt him - there is no such provision in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- in other cases.
The listed situations of impossibility of returning personal income tax when paying for education are mainly related to:
- with the degree of relationship between the student and the person paying for the education - the tax can be returned only if the education of an individual is paid for by close relatives (father, mother, brother, sister);
- lack of properly executed necessary supporting documents;
- with the legal origin of the income of the person who paid for the education - these must be legally earned funds, from the amount of which personal income tax is transferred to the budget.
The article “Distance Worker Abroad: We Pay Fees, But Not Personal Income Tax” will help you understand why a person working remotely abroad will not be able to return personal income tax for training.
Since we are talking about paying for education, a logical question arises: does the content of the training program and (or) the form of the educational institution affect the possibility of returning personal income tax? Find out about this in the next section.
Methods for returning personal income tax - applying deductions
So, without applying the deduction, the result is an overpayment of personal income tax to the budget. How can I return this overpayment? There are 2 ways to receive a deduction:
- through the employer - tax agent,
- on one's own.
The employer pays wages and withholds personal income tax from it monthly and transfers it to the budget. If you receive a deduction through your employer, he will reduce the tax base by the deduction every month. Accordingly, reduce personal income tax payable to the budget. And in fact, you will receive a larger amount in your hands.
In the second case, the employer calculates personal income tax without taking into account the deduction, which results in an overpayment of personal income tax. At the end of the tax period, you independently contact the tax office, confirm your right to deduction, and the tax office returns the amount of overpayment for personal income tax.
Thus, you can receive a personal income tax deduction gradually throughout the year through your employer or all at once in the next tax period.
Where can I complain about poor quality training?
Initially, you need to understand whether the complaint will help you get your money back? The answer is clear - it will help.
Verification by a government agency often encourages pre-trial payment. The test results will be strong evidence in court proceedings.
When protecting consumer rights in the provision of paid educational services, a complaint is submitted to the following authorities:
- Rospotrebnadzor
- Department of Education
- Prosecutor's office
- Ministry of Education
- Traffic police (in the case of a driving school)
- and etc.
It is important to complete the agreed documents correctly. An error in filing a claim, complaint, or even more so a lawsuit in court can significantly delay the process of returning money. In the worst case, the result of such errors may be the impossibility of returning money at all.
USEFUL: watch our video for additional tips on filing a complaint
Necessary conditions for the return of personal income tax for training
We have already given some important conditions. Let’s add a few more and summarize all the important nuances of receiving a deduction for education.
One of the main conditions for obtaining a tax deduction for education is the presence of an appropriate license from an educational organization or an entry in the Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs stating that an individual entrepreneur is engaged in educational activities (since individual entrepreneurs engaged in education without the involvement of third parties have the right not to obtain a license) .
Let’s put the main conditions for receiving a deduction for education on the diagram:
The year 2020 was marked by the coronavirus pandemic, due to which all educational institutions switched to distance learning. Is it possible to consider distance learning full-time and receive a deduction for such education for a child? Yes, it is possible, since full-time and correspondence forms of education differ in the format of student-teacher communication. During distance learning, the face-to-face format did not stop, it only moved into another form – online.
Where can I study?
You can receive a deduction for training expenses:
- at a university (university, institute, academy);
- in colleges, vocational schools, technical schools;
- in schools (including in the form of external studies);
- in kindergartens (a deduction can be claimed specifically for tuition fees);
- in institutions of additional education for adults (for example, in advanced training courses, driving schools, foreign language courses, etc.);
- in institutions of additional education for children (for example, in art schools, music schools, sports schools, hockey, football clubs, ballroom dancing schools, development centers, preparatory groups, clubs, sections, etc.);
- from an individual entrepreneur who provides tutoring services, from a speech therapist.
Procedure for receiving a deduction
As already mentioned, there are 2 ways to apply the social tax deduction. Let's consider the procedure for obtaining it for each method.
DEDUCTION FROM EMPLOYER
To receive a deduction for training from an employer, you must confirm your right to it with the tax authority and only then contact the employer. Let's present the algorithm of actions in the table.
| ACTIONS | REQUIRED DOCUMENTS | RESULT |
| 1. Applying to the tax authority for confirmation of the right to receive a social tax deduction. This can be done either in person or through the taxpayer’s personal account. | 1. Application for confirmation of the right to deduction in the form recommended in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 16, 2017 No. BS-4-11/500. 2. Agreement with an educational institution. 3. License. 4. Documents confirming payment in cash by the taxpayer. To receive a deduction for the education of children and a brother/sister, you additionally need:
| Receiving a notification from the tax office within 30 days confirming the right to deduction. The notification is drawn up on a specific form recommended in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 16, 2017 No. BS-4-11/500. |
| 2. Contacting the employer | 1. Notification from the tax office. 2. Application in free form. | The employer, starting from the month of contacting him, begins to provide a social deduction. That is, he reduces the tax base, transfers personal income tax in a smaller amount, and the taxpayer receives a salary greater than before the deduction was issued. |
If the employer does not apply the deduction, he will have to recalculate the tax and return the excess withheld.
If the employer did not manage to include the entire required deduction amount in the calculation of the tax base (for example, the taxpayer contacted him at the end of the year), then the unused portion cannot be , but you can return the unused balance by independently contacting the tax office.
INDEPENDENT RECEIPT OF DEDUCTION
If the taxpayer did not apply to the employer to apply for a deduction for training, he can return the overpayment of taxes on his own. We present the action algorithm in the table.
| ACTIONS | REQUIRED DOCUMENTS | RESULT |
| Applying to the tax authority to receive a social deduction for education. You can provide documents either in person or through the State Services portal (you must have a verified account), as well as through the taxpayer’s personal account | 1. Declaration 3-NDFL. 2. Certificates of income of an individual (2-NDFL). 3. Agreement with an educational institution. 4. License. 5. Documents confirming payment in cash by the taxpayer. To receive a deduction for the education of children and a brother/sister, you additionally need:
| The desk audit of the declaration takes place within 3 months . Upon successful completion of the audit and confirmation of the right to deduction, the tax authority transfers funds to the payer’s account specified in the 3-NDFL declaration (application). |
If you missed the deadline for filing a 3-NDFL declaration to receive a deduction for education, you can do this for the previous 3 years. For example, if in 2021 you met all the conditions for receiving a deduction, but for some reason you did not use it, then in 2021 you can still do this. But it’s too late to receive a deduction for 2021.
IMPORTANT!
If in the year of study there was no income taxed at a rate of 13%, and later they appeared, this does not mean that you can reduce the tax for later periods by deducting training completed in previous tax periods. Income and training must be within the same tax period (calendar year).
Next, we will consider in more detail the procedure for filling out the 3-NDFL declaration to receive a social deduction for education in 2021.
Cases when you can get a refund
You can compensate for part of the money spent on your own education under the following conditions:
- When studying in an educational institution that is officially registered.
- The student was officially employed during his studies and paid taxes on his salary.
There are no limits on refunds for personal training. The type of training can be any: full-time, part-time, evening or distance learning. The general rule is that studies took place on a paid basis.
How to fill out and submit 3-NDFL for a refund of tuition fees
The most convenient and fastest way to tell the tax office about your right to deduction is to fill out a declaration online on the Federal Tax Service website:
- there is guaranteed to be the latest current declaration form (and they change annually);
- The data of 2-NDFL certificates is automatically pulled up (they do not need to be taken from the employer);
- the program displays only necessary to fill out (in the paper 3-NDFL declaration there are a lot of sections that are simply not needed to receive a deduction).
What documents will be required?
One declaration will not be enough for tax authorities. It is necessary to attach documents confirming payment of tax and expenses of the taxpayer to the 3-NDFL for training:
- certificates of 2-NDFL income from the place of work (they can be downloaded from the “Taxpayer’s Personal Account” on the Federal Tax Service website);
- agreement with an organization (IP) providing educational services;
- a license for educational services, if its details are not specified in the contract;
- payment documents - receipts, checks, etc.;
- if your own child is studying - a birth certificate, a ward - a guardianship/trusteeship agreement, a sister or brother - documents on kinship (birth certificates of the taxpayer himself and the studying relative);
- a certificate from the place of study of a relative or ward, if the contract does not indicate full-time study.
The original 2-NDFL certificate and copies of other documents are attached to the paper copy of the declaration. Scans of all documents are attached to the electronic version. Inspectors may require original attached documents to be presented for verification.
FILLING 3-NDFL WITH DEDUCTION FOR TRAINING
If you still decide to fill out the form on paper, you can download the form used in 2021 for the 2020 report here:
Let us remind you: for 2021 and 2021, forms different from those presented were used. If you submit data for several years, for each year you need to use Form 3-NDFL, which is valid specifically for that year.
We have given the 3-NDFL declaration in full. We will consider below which sheets to use and how to fill them out to receive a deduction for education. Let’s assume that no other deductions or additional income are claimed.
Here are the sheets that must be filled out to receive a tuition deduction.
| SHEET | COMMENTS ON COMPLETION |
| Title page | Here you indicate information about the taxpayer: INN, full name, date and place of birth, telephone number and passport, code of the tax authority where you are filing the declaration (usually at the place of registration of the individual). The primary declaration is submitted with the adjustment number “0–”. All subsequent ones are adjustments. They are numbered in order: “1–”, “2–” and so on. Tax period – 34, reporting year – 2021, taxpayer category code – 760, taxpayer status code – 1. |
| In the header of each sheet indicate the TIN and full name. taxpayer | |
| Section 1 | Here you only need to fill out item 1, since you need a refund of the overpaid tax. Line 010 – “2 – return from the budget” Line 020 – KBK NDFL 182 1 01 02 010 01 1000 110 Line 030 - indicate the OKTMO according to which the excess personal income tax was paid (the tax agent's OKTMO can be found in the 2-NDFL certificate). If there are several of them, then fill in several blocks of lines 010 – 050 Line 040 – not filled in Line 050 = line 160 of section 2 (calculated amount to be returned from the budget) |
| Appendix to section 1 | This is an application for a refund of overpaid tax. It has been included in the 3-NDFL declaration since 2021. Previously, it had to be written separately. Here only the second part “about the return” is filled out. The first part “about the test” is left empty. Line 095 – serial number of the application data for lines 100 (return amount), 110 (KBK), 120 (OKTMO) - taken from the corresponding lines of section 1 Line 130 – GD.00.2020 Next, enter the details of the bank account to which the money should be transferred. Here it is important to enter the current account number, not the bank card number. |
| Section 2 | Here the total amount to be refunded is calculated. Line 002 – “3 – other” Line 010 – contains the total amount of income from all 2-NDFL certificates Line 020 – fill in if Appendix 4 is completed Line 030 = line 010 – line 020 Line 040 = sum of all deductions (page 200 of Appendix 5) Line 060 = line 030 – line 040 Line 070 = line 060 × 13% Line 080 = the amount of tax withheld by the employer (taken from 2-NDFL certificates) Line 160 = line 080 – line 070. This means that when calculating tax using a deduction, its amount is less than that withheld by the employer. Therefore, an overpayment occurs (indicated on page 160), and this amount must be returned from the budget. |
| Annex 1 | Here they enter data from income certificates (2-NDFL) issued by the employer. All fields specified in the application are in 2-NDFL. If there were several sources of income, fill out some application sections. Line 020 – “07” for income from employment contracts |
| Appendix 4 | Fill in only if there was non-taxable income specified in this application and a certificate from the employer (for example, financial assistance in the amount of 4,000 rubles) |
| Appendix 5 | This reflects the deductions to which the taxpayer is entitled. Since we are talking about the tuition deduction, let’s focus on it. Let's assume that there are no other deductions. Section 1. Employer tax agents usually provide standard child tax deductions. Data on standard deductions provided by the employer are indicated in the income certificate (2-NDFL). They should be transferred to line 070. If you do not add other standard deductions, then line 080 = line 070. Section 2. Line 100 reflects the costs of training children (wards), but not more than 50,000 rubles for each child (i.e., if there are two children studying, put no more than 100,000 rubles, etc.). It must be remembered that the deduction is total for both parents. Line 120 = line 100 Section 3. In line 130 enter the amount of payment for your education (brother, sister), but not more than 120,000 (we remind you that the limit of 120,000 rubles applies to the entire amount of social deductions specified in this section). Line 180 = line 130 (provided there are no other deductions) Line 181 indicates the social deductions provided by the tax agent (for example, if the declaration is filled out when additionally applying for a social deduction for training, when part of it was provided by the tax agent - the employer). If, after deduction, the employer was not contacted, this line is not filled out. Line 190 = line 181 + line 130 Line 200 = line 190 + line 120 + line 080 |
Now let’s look at a sample of filling out the 3-NDFL declaration using an example.
| EXAMPLE. Let Kazeeva A.A. paid for my education in the amount of 50,000 rubles and my daughter’s education in the amount of 10,000 rubles in 2020. Let’s assume that Kazeeva collected and provided all supporting documents (agreement, license, etc.). Kazeeva’s income in 2021 from her work at Spectr LLC amounted to 340,000 rubles. |
| 1. From her employer, Kazeeva received a standard tax deduction for a child of 1,400 rubles for each month. Thus, the deduction amount was 1,400 × 12 = 16,800 rubles. 340,000 – 16,800 = 323,200 × 13% = 42,016 – tax withheld by the employer in 2021. 2. In addition, Kazeeva has the right to receive a social deduction for the education of her child and her own education: 10,000 + 50,000 = 60,000. These deductions can be applied in full , since they do not exceed the established limits (Kazeeva is entitled to other deductions does not have in this tax period). Kazeeva did not apply for social deductions for training from her employer, so she will receive them independently from the tax office in 2021. 3. Let's calculate the amount of tax overpayment for 2021. 340,000 – 16,800 – 50,000 – 10,000 = 263,200 rubles. (the tax base is calculated using all required deductions). Tax payable: 263,200 × 13% = 34,216. And the employer withheld 42,016 rubles from Kazeeva. Thus, the overpayment to be refunded is: 42,016 – 34,216 = 7800. This is the amount Kazeeva should receive from the tax office. |
For a sample of a 3-NDFL declaration for educational deductions completed based on the example in 2021, see below:
SAMPLE DECLARATION 3-NDFL 2021 FOR DEDUCTION FOR TRAINING
We remind you that there is no need to print, number or provide blank declaration sheets.
If you fill out the paper form 3-NDFL by hand or use MS Office tools, you need to additionally observe some points. We talked about them in the article “How to fill out a declaration on paper: rules.”
Compensation without official employment
There are situations when a citizen did not work anywhere during the year of payment for training and did not receive an official salary, from which an income tax of 13% would be withheld. If this tax was not paid, then the person does not have the right to monetary compensation. Types of income that are not subject to income tax include:
- payments for the period of maternity leave;
- pensions;
- benefits.
Regarding compensation for training, a refund can only be issued for the year in which the citizen paid for the service. It is impossible to transfer compensation to other years, as with a property deduction.
In a situation where a citizen paid for study, and in the same year sold property for which tax must be paid, then income tax or part of it can be covered using a deduction for education.
about the author
Klavdiya Treskova - higher education with qualification “Economist”, with specializations “Economics and Management” and “Computer Technologies” at PSU. She worked in a bank in positions from operator to acting. Head of the Department for servicing private and corporate clients. Every year she successfully passed certifications, education and training in banking services. Total work experience in the bank is more than 15 years. [email protected]
Is this article useful? Not really
Help us find out how much this article helped you. If something is missing or the information is not accurate, please report it below in the comments or write to us by email
Courses for business purposes
If your course has a business theme and is aimed at developing your business (for example, how to increase sales), in this case it is purchased for business purposes and the Consumer Protection Law does not apply to your relationship.
For example, in case No. 33-48505/2017, the Moscow City Court refused to collect a penalty, compensation for moral damage, and a fine provided for by the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, because a course on training in doing business on a state confiscation was purchased for carrying out entrepreneurial activities.
What is impossible with consumers is possible with entrepreneurs. This means that the contract can provide for a fee for unilateral refusal to attend the course (clause 3 of Article 310 of the Civil Code).
Compensation for cancellation can be determined as a percentage of the cost of the course, as a non-refundable prepayment, or depend on the period of cancellation of the course. You can also set differentiated prices for lessons when selling business courses.