In this article we will tell you about the key tools for tax-free (low-tax) transfer of property in business. Each of them has its own characteristics and limitations.
Why might a tax-free transfer of property be required? A change in the ownership of property by concluding a purchase and sale agreement is recognized as a sale and entails the need to pay VAT and income tax (if the general taxation system is applied). In the event that property is transferred within a single group of companies, the occurrence of tax obligations is extremely undesirable: in fact, the property remains the property of the same beneficiary, and taxes must be paid. In addition, a tax-free transfer (change of ownership) of property in a group may be required:
- To increase the level of property security. Obviously, assets that are “vital” to a business should not be located in the operating sector.
- To launch an investment project. It is more logical to start a new promising direction with a clean slate; it should not be subject to the risks and obligations of an existing business. In addition, partners who are not involved in your main business may participate in the implementation of the investment project. In this case, filling the new project with property (including money) should also occur with the most beneficial tax consequences for both the transferring and receiving parties.
- When refinancing in a group: redistribution of financial flows between related companies (entities) also requires the exclusion of unnecessary tax liabilities.
How to make a tax-free transfer of property?
- Capital contribution
- Contributions to property on the basis of subclause 3.7 and subclause 11 of clause 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, including “daughter gift”
- Reorganization in the form of spin-off
We have recorded the key points for you in a separate table.
| Nuances | Capital contribution | Contribution to property on the basis of subclause 3.7 clause 1 of article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | Gratuitous transfer of property on the basis of subclause 11, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | Selection procedure |
| Organizational and legal form of the company receiving the property | Any | Only business companies and partnerships | Any one that has an authorized/share capital or fund (JSC, LLC, business partnership/partnership) | Any |
| The size of shares/shares of the transferring party in the authorized capital of the recipient company | Any | Any | 50% or more. Not only direct but also indirect participation is taken into account | Any |
| Does the size of the transferring party’s share in the management company change? | Yes | No | No | No |
| Tax obligations | For organizations on OSN:
| For organizations on OSN:
| For organizations on OSN:
| For organizations on OSN:
|
| What can be conveyed | Cash, securities, other property, property and other rights that have a monetary value. This list should be in the charter | Property, property/non-property rights | Property and property rights. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, non-cash money refers to property rights. From 01/01/2019 to 22/11/2020, their transfer under this item was impossible. | Cash, securities, other property, property and other rights having a monetary value |
| Restrictions | Mandatory independent assessment of non-monetary contributions | Property cannot be transferred to third parties during the year, including under a lease agreement (except for cash) |
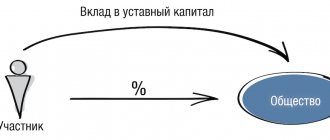
Capital contribution
This is the most well-known way of providing a company with property and property rights by its participants. A participant in any commercial organization (JSC, LLC, etc.) can make a contribution to the authorized capital (AC), both at the stage of registration of the company and during its activities.
In addition, a third party can make a contribution to the authorized capital of an LLC upon joining the company’s members. In a joint stock company, a third party can purchase shares during an additional issue, and this will constitute a contribution to the management company. Money, securities, other property or property rights can be contributed to pay for the authorized capital.
Tax consequences
A contribution to the authorized capital of a commercial organization is exempt from income tax (clause 3, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code). As for VAT, in a situation where the share in the management company is paid for with property, the transferring party to the OSN is obliged to restore the VAT previously accepted for deduction (clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) in an amount proportional to the residual (book) value without taking into account revaluation (in regarding fixed assets and intangible assets).
However, the receiving party, if it is also on the general taxation system, takes into account the same amount of tax as part of deductions after accepting the property for registration (clause 8 of Article 172, clause 11 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a result, the balance of VAT amounts paid and accepted for deduction is maintained, which actually means the absence of tax consequences for the business owner of the contribution of property to the authorized capital.
Naturally, if we make a contribution to the capital of a commercial organization under a special tax regime, it will not be possible to take VAT into account as expenses.
Additional expenses
To transfer property to the authorized capital, the law requires an independent monetary assessment of its value (clause 2 of Article 66.2 of the Civil Code).
Risks
The guaranteed amount of liability of a legal entity for its obligations to creditors is equal to the amount of the authorized capital. Also, a large management company can make the company attractive to unscrupulous third parties (for example, raiders).
However, a participant has the right to make a contribution to the management company in an amount exceeding the nominal value of his share. For example, to pay for a share in the authorized capital of an LLC of 10 thousand rubles, a participant may well contribute, for example, 15 million rubles. In this case, the nominal value of his share will be 10,000 rubles. This is exactly what will be indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. And this contribution (including in terms of the excess of the real amount of the contribution over the nominal value of the share) is not included in the tax base of the receiving party (paragraph 3, paragraph 1, paragraph 3, Article 170, paragraph 11, Article 171, paragraph 8 Article 172 of the Tax Code; paragraph 3, paragraph 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code).
You can read more here.
Tax consequences upon subsequent sale of a share or exit from the company
It is important not only to provide the company with property without taxes, but also to take into account the costs of its acquisition or creation during the further alienation of the share in the company.
In this case, income will arise (from the sale of the share, in the form of the actual value of the share upon leaving the LLC, or in the form of property remaining after liquidation), which can be reduced for tax purposes:
- when selling a share - for expenses associated with its acquisition (for legal entities - clause 2.1, clause 1, article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for individuals - clause 2, clause 2, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- upon exit - for the amount of the contribution to the authorized capital (clause 4, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for legal entities, clause 2, clause 2, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for individuals);
- upon liquidation - in the amount of the actually paid cost of the share (clause 2 of Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for legal entities, clause 2 of clause 2 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for individuals).
If the owner has made a contribution to the company's management company that exceeds the nominal value of his share, the income received upon sale (exit, liquidation) can also be reduced by the amount of expenses for acquiring the share in full. If the payment was in property - for the amount of expenses for acquiring the property.
If you or your organization has continuously owned shares in the company for more than 5 years, then the entire amount of income from the sale of such shares will be:
- be exempt from personal income tax for individuals (clause 17.2, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- subject to a tax rate of 0% for income tax for legal entities (Article 284.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Is it possible to donate a share of a company in 2021?
A limited liability company or LLC is one of the main forms of business organization in the Russian Federation. An LLC is formed as a result of a group of people expressing their desire to combine their own aspirations and capabilities (for example, financial assets) for the purpose of making a profit.
However, it often happens that the idyll reigning in a company in the first stages of development is replaced by disagreements and conflicts, as a result of which one or more founders may wish to leave the LLC. As a rule, in such cases, a citizen offers to buy out his share to the remaining participants, but this does not mean that his part of the company cannot be transferred to a third party. For example, one of the founders has the legal right to draw up an agreement for donating a share to a relative or another person, which often does not suit the other co-owners.
Therefore, experienced lawyers of the website “Legal Ambulance” recommend that when forming a company, stipulate in the terms of the contract a certain condition, according to which the possibility of transferring the LLC’s share as a gift becomes possible only after approval of this by all owners of the common business.
Indirect share of participation
Subclause 11, clause 1, Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation makes it possible to make a contribution to property not only from a direct participant, but also from a person who has an indirect share of participation through an intermediate company. For a contribution to be exempt from taxation, the share of indirect participation must also be at least 50%.
To calculate the share of indirect participation, it is necessary to multiply the shares of direct participation in each organization along the ownership chain. For example:
In this case, the share of indirect participation of the Participant in Organization No. 3 will be 63%. Accordingly, he can directly, bypassing the intermediate Organization, transfer funds, other property or property rights. When it comes to real estate, this saves time on registration activities and compliance with corporate procedures.
The rules for determining the share of indirect participation are spelled out in detail in clause 3 of Art. 105.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
"Daughter's Gift"
At the same time, according to paragraphs. 11 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code, not only the parent company can contribute to the property. The opposite situation is possible - the “daughter” transfers the property to the “mother” (the so-called “Daughter’s gift”). And even “grandmother” - taking into account the rules on indirect participation.
Registration of a share for another owner
Any redistribution of shares, the emergence of new co-owners must be recorded in the charter. Such changes are registered in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Information about them is transmitted to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration of the company within three days by the notary certifying the transaction. After receiving the data, the registrar makes changes to the register and generates a new extract.
It will contain information about:
- the new owner of the share;
- full composition of LLC participants;
- the size of the shares of each of them and their nominal value.
Reorganization in the form of spin-off
Reorganization in the form of separation (Article 57 of the Civil Code; clause 8 of Article 50 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is the most universal method of transferring property that does not have organizational and legal restrictions (applicable to both JSC, LLC, and partnerships).
During the spin-off, a second legal entity is formed, which is not the legal successor of the reorganized organization in terms of its tax obligations, except in cases where the tax authority proves that the sole purpose of the spin-off was to evade repayment of debt to the budget (clause 8 of Article 50 of the Tax Code).
Tax consequences
Income tax
A spin-off involves the “spinning off” of an old company into a new company. The property is transferred under a transfer deed and its value is not an expense for the old legal entity and is not income for the new company. That is, there are no income tax consequences.
VAT
The transfer of property within the framework of the allocation is not a sale; the company on the OSN does not have the obligation to charge VAT.
If the legal successor switches to UTII or the simplified tax system, then he is obliged to restore the VAT previously accepted for deduction by the reorganized organization in proportion to the residual (book) value. Clause 3.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation This obligation has been in effect since 2020.
Who can become a participant in the spun-off company?
During the procedure of separation from an LLC, the participants of the new legal entity may become:
- reorganized company;
- participants of the reorganized company in the same composition and in the same proportions;
- part of the participants of the reorganized company (in other proportions) or other third parties.
The main condition is that this third party independently pays for the authorized capital, at least in the minimum amount of 10 thousand rubles.
In the case of a joint stock company, only the first two options are possible during the spin-off. Either the new company becomes a 100% subsidiary of the reorganized company, or the same shareholders in the same proportions become participants in the spun-off company.
In addition, mixed reorganizations in the form of spin-off are allowed, when it is possible to spin off an LLC from a JSC or vice versa.
Risks
The separation must be carried out in strict accordance with the principle of fair distribution of rights and obligations between the old and new legal entity. It means that:
- The assets of the spun-off company must be balanced by liabilities. In other words, it is impossible to transfer fixed assets without transferring the debt on the loans with which these fixed assets were acquired. If the old company has a large amount of accounts payable, then it is fair to transfer to the spun-off company part of such debt associated with the transferred property;
- the spin-off must meet the criteria of the business purpose concept (transfer of part of the assets to organize a new line of activity, business restructuring with the aim of creating several independent business units on the basis of former divisions, etc.).
When separating, the transfer of property and/or obligations to the new organization occurs under a transfer deed.
Consent of partners when donating
According to Federal Law No. 14, for a share donation agreement, it is not necessary to seek permission for such actions from other co-owners of the business. However, when such a question is raised, the priority is those conditions that are spelled out in the organization’s Charter. And if such a topic is not raised in this document, therefore, the company’s participants have the rights to independently dispose of their shares in the company.
An agreement for the gift of a share in an LLC, which consists of one founder, in almost all cases there is a risk of its participant leaving. Therefore, a correctly drawn up Charter will prevent unwanted actions, and also indicate on what grounds alienation of a part may occur:
- Transfer of a part within the organization. According to Russian legislation, a gift of a share in an LLC to a partner can occur without the consent of the other co-owners. But then the procedure begins to re-register rights and the level of power. If this point is important, then it must be reflected in the constituent document (Charter).
- A deed of gift in an LLC to an outsider often results in an undesirable development of the situation for the company. Therefore, it is typical for the constituent document to have a clause prohibiting outsiders or imposing restrictions.
- The procedure and period for notifying company participants about the upcoming donation, incl. The deadlines within which the founders give a response are not mandatory clauses of the Charter. However, if they are not spelled out in it, then you need to act within the framework of Federal Law No. 14 (Article No. 21, paragraph 10).
So, from the above it is clear that if written consent of the parties is needed, then the donor must notify the director of the company about the upcoming procedure. The written notice is drawn up in 2 copies and handed over from hand to hand and obtaining a signature. Receipt stamp is required. You can also send a notification through the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Russian Post" with an attached inventory. From the date of dispatch or delivery, it is considered that all co-owners are familiar with it.
The co-owners also give consent or refusal in the format of a written agreement. Your decision is expressed within a calendar month, starting from the date of delivery/reception of the notice. Those who did not have time to do this are regarded as agreeing in absentia.
Does the Charter specify priority for the purchase of shares by community members? Then they can use it within 30 days. If there is no such desire, a refusal is provided in the form of a letter. Otherwise, you must wait the specified period. Only after this can a donation of a share in the common property of the company be made.
By the way, a legal spouse may also be interested in donating a share in an LLC. The Civil Code of Russia states that if the co-founder is a spouse, then on the basis of Article No. 578, paragraph 2, written consent must be obtained.
Exceptional situations are those specified in the marriage contract.
In order to do everything correctly, from the legal side, we recommend using the sample deed of gift given in the next section, which describes the process of registering such a transaction.
Selection with appendix
Within the framework of one reorganization, the law allows you to combine two procedures at once (Article 57 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation): separation and merger, which can significantly save time and costs for reorganization. First there is separation, then attachment. The intermediate company resulting from the spin-off is virtual in nature, as it is used solely to transfer assets and liabilities to the acquiring company. The period of existence of this legal entity is not defined by law, but we can say that it tends to zero.
Documents are drawn up first for the separation of the company. According to the transfer deed, part of the assets and liabilities of the reorganized company is transferred to it, which are then added to the balance sheet of another legal entity (“Company 2” in the diagram above).
Of course, real life cannot always be “shoved” into the framework of the above-described methods of transferring property. There are a great many options for property consolidation; most often they are a combination of tax-free and low-tax methods of property redistribution, the set of which is always unique.
A database of other business tools and comprehensive developments of the taxCOACH Center - at the seminar “STAY ALIVE-2021” in Yekaterinburg, December 10-12.
Scheme for registering the fact of donating a share of an LLC
- The notary certifies the donation agreement and the application.
- Sends data on form P14001 to the Federal Tax Service.
- Issues a letter to the donor with an inspector's note confirming its receipt. You can receive completed documents by proxy.
- LLC documents are sent to the address specified by the donor or received by him personally (or by proxy).
- After this, a copy of the donation agreement, a certificate of amendments to the register and a document confirming the entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities are transferred to the general director of the company.
Legal basis
Article 128 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation recognizes property rights as full-fledged objects of civil circulation. Shares in the authorized capital may become the subject of contracts after full payment by the participants. The actual making of a contribution is a key condition for the validity of such transactions (clause 3 of Article 21 of Law 14-FZ of 02/08/98). Confirmation of the fulfillment of obligations are deeds of transfer, accounting certificates, payment orders or other documents.
The procedure for donating a share becomes more complicated in the following cases:
- Transfer of property rights as collateral. Sometimes participants use an asset as collateral for debts. In this situation, it is permitted to conclude an agreement only with the written approval of the mortgagee (Article 346 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Prohibition on alienation of shares to third parties. Trying to protect the business from attacks, the founders prescribe special conditions in the charter. Agreements drawn up in violation of the ban are declared invalid (Resolution of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 10590/11 of December 13, 2011).
- Coordination of the entry of the new owner into the structure. This option serves as an alternative to a complete ban on the alienation of shares. Participants may transfer property rights to third parties. However, approval of the agreement by the general meeting of the LLC becomes a prerequisite (Article 21 of Law 14-FZ).
The special legal status of commercial assets does not conflict with the official definition of property. The prohibition of alienation of shares to third parties does not deprive the owner of the right of disposal. At any time, the owner can withdraw from the LLC with payment of the actual value. The same mechanism applies if the general meeting refuses to approve the transaction (Article 21, Law 14-FZ).