Find out why the debt has accumulated
Timely and full payment of housing and communal services is the responsibility of the owners of premises (Article 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). This obligation arises from the moment of registration of ownership of the premises.
Owners of apartments and non-residential premises do not always take responsibility for paying for housing and communal services. The reasons for non-payment of bills may vary. Some owners accumulate short-term debt due to the fact that they were temporarily absent from the premises and did not receive payment documents. For example, you were on a business trip or were treated in a medical facility.
Other residents do not pay their bills systematically and accumulate huge amounts of debt. Some believe that the management organization is not properly fulfilling its responsibilities, others believe that natural resources belong to all citizens on equal rights.
Depending on which group the debtor belongs to, the management organization can choose a mechanism for debt collection: awareness-raising, claims work, restriction or suspension of the provision of utility services. Let's discuss the basic techniques of each debt collection mechanism.
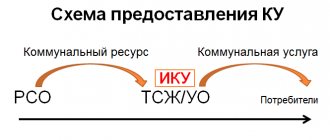
How to register partial repayment of debt for housing and communal services
Prohibition on collecting debts for housing and communal services
Until mid-2021, Law No. 230-FZ and the Housing Code of the Russian Federation did not directly prohibit the transfer of overdue housing and communal services debts to collectors. The indirect restriction was easily circumvented by management companies, homeowners' associations and housing and communal services enterprises by involving collection agencies as intermediaries (while the utility debt was not directly sold to collectors).
In July 2021, amendments to Art. 1 of Law No. 230-FZ and the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. Collection agencies included in the FSSP register are prohibited from collecting debts for all types of utility services
(gas, heat, electricity, solid waste, water supply and sanitation).
But management companies can involve third-party organizations in this work if their main activity is not professional debt collection within the framework of Law No. 230-FZ.
At the time of the adoption of amendments to Law No. 230-FZ, collection firms collected no more than 5% of the total volume of utility debts. Moreover, the involvement of legal collectors in collections gave many defaulters additional guarantees of protection.
Collection companies can act strictly within the law, including time periods and the number of calls, personal meetings, SMS. Employees of housing and communal services and management companies are not subject to Law No. 230-FZ, so they allowed themselves to abuse calls, home visits, and other methods of influence.
Ekaterina Uryvaeva
Bankruptcy Lawyer for Individuals
Outreach
A common way to motivate a resident to pay bills is to charge a penalty. Notify the debtor in writing that you are forced to charge him a penalty for late payment of housing and communal services. Explain that payment for residential premises must be paid no later than the date established in the management agreement or determined by the decision of the general meeting of owners of premises in the apartment building (Part 1 of Article 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
If the management agreement or the OSS have not determined the date for payment of payment for housing and communal services, then the last day of the payment period is considered to be the tenth day of the month (Article 190-192 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Payment will be considered overdue from the eleventh day in accordance with paragraph 30 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated June 27, 2017 No. 22.
There are residents who do not understand how the amount on the receipt is calculated, so they do not pay their bills. In this case, the debtor can be called and invited to an appointment with the head of the management organization or the chief accountant. During the conversation, tell the owner that non-payment of bills leads to the accrual of penalties, and failure to transmit meter readings leads to the accrual of amounts in receipts according to the standards.
Another option to resolve the problem peacefully is to enter into a debt repayment agreement with the debtor. This way, the consumer will be able to avoid restrictions and suspension of utility services and repay the debt in a manner convenient for him.
Tell the debtor about the terms under which you propose to enter into an agreement to repay the debt. Specify in the agreement:
- validity,
- consequences for violation of obligations,
- details of the parties.
Offer the consumer to choose how to pay the debt: in a lump sum or in installments. If the owner is ready to repay the debt in one payment, include in the agreement the amount of the debt, the period of its formation and the expected date of payment.
Not the most common way to work with debtors for housing and communal services is to offer the owner to work off the debt. Working off a debt instead of paying housing and communal services is considered a change in the payment method provided for in Art. 409 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The most convenient in this case is considered to be a mutual agreement concluded in writing in accordance with Art. 161 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Find out how to calculate penalties
Why do citizens become defaulters on utility bills?
As you can see, the above were subjective reasons why the apartment owner cannot pay utility bills on time. In addition to them, there are also objective reasons.
Subjective reasons for non-payment:
- low income;
- receiving income after the 10th;
- high level of seasonal expenses - New Year holidays, summer vacations, children getting ready for school, etc.;
- failure to collect payers, i.e. forgetting to pay payments on time;
- physical condition of the citizen - payment is impossible without outside help;
- temporary absence from the locality where the apartment is located.
Objective reasons for non-payment:
- high tariffs for utilities do not correspond to their quality, frequent changes in cost and payment details;
- incorrect accrual of amounts - the tenant has the right to receive full information for what and how the accrual is made and, in case of disagreement, to challenge it;
- weak notification system for payments - receipts did not reach the apartment owner;
- long registration of various benefits and subsidies - for several months, accrual may be made at the old tariffs;
- low level of public awareness about penalties for non-payment. This point is worth considering separately.
Restriction or suspension of provision of CG
If the owner’s debt exceeds the sum of two monthly payments for utility services, calculated from the standards for its consumption, the management organization has the right to limit or suspend the provision of utility services in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354.
For debts, you can limit the supply of hot water, electricity, gas or sewerage services.
The management organization must inform the debtor about the restriction or suspension of utility services by sending him a written notice. The provision of CG may be limited within 20 days from the date the owner receives such notice.
At the same time, the management organization needs to remember that the restriction or suspension of the provision of utility services should not lead to a violation of the rights and interests of other residents of the apartment building who fully fulfill their obligations (Section 11 of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 6, 2011 No. 354).
The technical features of the house do not always allow suspending or limiting the provision of utilities in one room.
Owners of non-residential premises and fees for maintaining public buildings in apartment buildings
Writing off debts for utilities: all the details!
According to statistics, the debt of Russians for housing and communal services in 2019 and the beginning of 2021 reached a record value of 1.3 trillion rubles! Officials note: the reason for the situation is the unreasonable and opaque tariffs of service providers, and the lack of a culture of resource consumption. The financial and legal illiteracy of the population leaves its mark, hence these shocking figures. But some obligations of citizens to management companies are sometimes actually recognized as unfounded, and residents do not have enough information about this, hence such debts.
In our article we will talk about the features and intricacies of writing off debts for utility services, outline the situations in which write-off is possible, and the conditions for executing the procedure.
How and when is it possible to write off debts for housing and communal services?
The legislation does not provide for debt write-off only at the request of the owner (tenant). But the rules have exceptions, and in this case it is advisable to outline the conditions for writing off debts for utility services.
The most common factors include:
- changes in legislation affecting certain categories of citizens;
- expiration of the statute of limitations;
- through bankruptcy;
- death of the owner;
- impossibility of execution of the decision.
Let us consider each case separately, identifying the features, specific mechanisms and accessibility.
Law 2020
Writing off debts for housing and communal services in 2021 is regulated by laws and regulations.
At the beginning of 2021, according to current legislation, it is permissible to write off service debts in several cases:
- The court declares an individual bankrupt.
- The management company missed the statute of limitations for debt collection.
- The organization providing utility services has been liquidated and (or) excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
- Loss of the payer's ability to work as a result of an industrial accident, obtaining the status of a disabled person and other serious illness.
The return of the writ of execution by the bailiff and the closure of enforcement proceedings are considered methods of writing off debts for housing and communal services.
However, a case can only be closed in a number of cases:
- the debtor's complete lack of property and funds to repay the debt;
- the debtor is listed as missing;
- The bailiff service does not have information about the location of the debtor and his property that can be foreclosed on.
The presence of valid reasons should prompt a person to contact the management company with an official application for restructuring. Refusal by the Criminal Code is a reason to go to court. Courts make positive decisions in favor of the consumer. The main thing is timely contacting the authorities and the desire to assist them. Then you have a chance not only to write off part of the debt, but also to avoid the accrual of penalties in the form of penalties. Responsible authorities go to meet conscientious people halfway, even if they find themselves in a difficult life situation, and the debt for utility bills has already accumulated.
Expiration of the statute of limitations
Writing off housing and communal services debts based on the statute of limitations is the most common procedure. In the event of a debt, the Criminal Code acts on its own, and only then directly goes to court. As a result, the statute of limitations is missed. For this reason, claims after 3 years are declared invalid in court, which means they are not satisfied.
However, debt write-off is subject to several more significant conditions:
- an application in court to apply the statute of limitations - the court does not automatically recognize the fact of omission, so the applicant should immediately indicate the aspect;
- not to acknowledge or confirm the existence of a debt to the management company.
Confirmation of the fact of recognition of the amount of debt - agreement on debt recognition, application for deferment, restructuring agreement, partial payment of bills.
Write-off of debts after the statute of limitations has expired without legal proceedings is carried out in the following cases:
- death of the debtor, provided there is no heir;
- liquidation of the service provider - that is, liquidation of the management company.
Bankruptcy
Another option is to write off housing and communal services debts in bankruptcy. A citizen submits an application for declaring himself bankrupt to the arbitration court. This happens when the total debt on accounts reaches an amount of 500 thousand rubles, and the owner’s income does not allow him to pay debts on time and in full and make current payments.
Debts amounting to half a million rubles are rare, so the law understands the amount as different debts, but the rules are established uniformly. By the way, an additional condition was recently introduced - the delay in payment for services and other obligations exceeds 90 days. The debtor himself can submit an application to the court for recognition of the fact of insolvency. Creditors must be notified in writing of the start of the procedure. Otherwise, the debt, including penalties, will grow. Bankruptcy status has both its pros and cons.
Positive consequences of status:
- during the procedure, the amount of debt will not increase;
- as a result of obtaining the status, debt obligations are written off;
- there is no threat of administrative or criminal prosecution for failure to comply with a court decision to pay the debt;
- the housing remains in the possession of the debtor.
The negative consequences of bankruptcy are expressed as follows:
- the services of the arbitration manager, as well as procedural features, are paid by the debtor;
- control is established over the debtor’s income and family members;
- a ban is imposed on receiving loans and microloans;
- lack of the right to register as an entrepreneur (both as an individual entrepreneur and as a founder).
Death
The death of a debtor is a valid reason according to which housing and communal services debts are written off. Relatives are required to send a copy of the debtor’s death certificate to the Criminal Code. In addition to the Criminal Code, the second option is to send a copy to the RSO if a direct agreement was concluded. Sometimes the management company is not aware of the fact of death and continues the proceedings by filing an application with the court to recover funds. Having received a copy of the certificate, the court issues a special “Decree to terminate proceedings in connection with death.” The management company writes off the debt after receiving the Determination.
Impossibility of execution of the decision
Enforcement of the decision is impossible when the debtor has no money and property. In this case, the bailiffs make a decision to end the enforcement proceedings. But here it is necessary to collect documents and 100% prove the insolvency, otherwise the court decision will be made clearly not in favor of the debtor.
How to reduce rent payments
There are many options for reducing utility bills. Perhaps the main ones are savings in housing and utility services provided and their timely payment. The method is completely legal and does not cause unnecessary trouble. In the table below we list a few more truly suitable and effective methods:
| Way | Peculiarities |
| Installation of meters | We recommend investing once every few years. A conventional device is designed to operate for 3 years, but the device helps to save significantly and pays for itself within 5-6 months. For example, many people are registered in an apartment, and everyone has to pay for it. But the counter records the actual consumption of volumes of resources. The difference sometimes reaches five times! |
| Use energy-saving light bulbs and devices | Electricity is not a cheap pleasure; its costs are enormous. Unlike other expensive services, such as drainage and heating, reducing electricity consumption is within the power of everyone. You shouldn’t give up on devices completely, but you can choose your equipment responsibly. |
| Review your daily habits | For example, use the dishwasher and washing machine at night (if you have special consumption tariffs). Don’t start the equipment half empty, but load it to the maximum. |
| Avoid delays | For delays, a penalty is charged - a waste of money. |
Is it possible not to pay for utilities at all and what will happen?
You should not experiment and take on the role of a debtor. Depositing amounts on time will save your nerves and wallet. Are you experiencing difficulties? Contact the management company yourself and warn specialists about your difficult financial situation. As a rule, organizations also do not benefit from your delays, so they will meet you halfway and provide assistance.
Declaring the HOA bankrupt
As in the case of legal entities, the bankruptcy procedure of an HOA takes place in several stages:
- observation;
- financial recovery;
- external management;
- bankruptcy proceedings.
In relation to homeowners' associations, as practice shows, the first stage is applied - observation. The appointed temporary manager assesses the amount of the HOA's debt, its assets, draws up a register of creditors to whom the organization has a debt, and then immediately follows the procedure for liquidating the HOA, seizing the property and selling it at auction to pay debts to creditors (bankruptcy proceedings).
Responsibility of the chairman of the partnership
A homeowners' association is equated to a legal entity, therefore, the responsibility of the chairman of the HOA in the event of bankruptcy of the HOA is, first of all, to check by special bodies the activities of the organization for deliberate bankruptcy. If signs of such a violation of the law are detected, the chairman may be brought to administrative or criminal liability.
If no signs of deliberate bankruptcy are detected, the chairman will not be held liable - the debt will be repaid from the property of the partnership. At the same time, members of the HOA have the right to file a complaint against the chairman if his activities are seen as a violation of the law.
Features of HOA liquidation
Previously, there was no bankruptcy procedure for HOAs as such, since the organization was one of the structures that were not subject to the bankruptcy law. Despite changes in legislation, there is NO special procedure for bankruptcy of a homeowners association , so in this situation it is necessary to be guided by the following elements of the regulatory framework:
- Bankruptcy Law;
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Partnership property
Property owned by a partnership means movable or immovable objects that were acquired with the joint funds of members of the organization or with the funds of third parties, and are in the possession and use of the partnership.
If the HOA goes bankrupt in any case (voluntary or at the request of a creditor), the property is subject to seizure and sale at auction. The funds received from its sale will be used to repay debts to creditors in an equal manner according to the compiled register. In this case, the arbitration manager has the priority right to collect the debt.
The property of the HOA includes:
- transport for personal or public use owned by the partnership;
- office equipment;
- organization bank accounts;
In some cases, the organization may also own real estate objects acquired with the common funds of the HOA members, with the funds of one of them, or with the help of third parties. Such objects are also subject to seizure and sale at auction.
It is important to note that if, in the event of full sale of the partnership’s property, the organization’s debt is not repaid in full, the court notifies the creditor of the inability to return the debt and closes the case. Personal property of HOA members or the chairman is not subject to seizure.
Advantages of contacting Legal Bureau No. 1
We employ competent specialists who know how to act competently in the current circumstances. Other important points:
- each request, regardless of the client’s status, is considered in detail;
- documentation is collected promptly;
- the debtor's prospects are assessed objectively.
Are you unable to repay your debts to creditors? Contact Legal Bureau No. 1 immediately! We will help you avoid debt bondage and provide assistance in resolving the most difficult issues.