Women raising children on their own, without the support of their husbands, have a number of benefits provided by the state. Raising a child in a single-parent family not only leaves a psychological impact, but also causes financial difficulties. It is more difficult to deal with them alone. There are different situations in life, so divorced women require social protection, which, among other things, is expressed financially.
Government support is provided to both divorced women and single mothers. According to the law, these concepts are not identical. You still need to obtain single mother status. Therefore, a divorced woman is not considered a single mother.
The state supports citizens in difficult life circumstances. And although there are general regulations and conditions for receiving benefits, their assignment is made on a strictly individual basis. There are too many requirements to consider. Specialists from social security authorities provide advice on all questions that arise regarding benefits and benefits.
Benefits for divorced women with children
Women after divorce who are raising minor children themselves and do not have the status of a single mother are not entitled to assistance. They need to first resolve the issue of paying child support. Even if the child's father has been deprived of parental rights, the mother does not receive any benefits in connection with this. The basis is taken from the provisions of the Family Code, which clearly states that both parents must financially provide for the child, regardless of personal relationships.
The only way out of this situation will be a court order for the father to collect alimony.
If we consider an incomplete family from the perspective of poverty, there is a chance to receive financial assistance. You can achieve both cash payments in the form of child benefits and the provision of essential goods, medicines, clothing, food, and stationery.
For low-income single-parent families, there is financial assistance for children from three to seven years old and from eight to sixteen years old.
If a family meets the conditions of the program, then there is a chance to receive financial support in the form of an amount from fifty to one hundred percent of the subsistence level in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation where a woman and a child live on a permanent basis (based on registration).
Required documents
According to current legislation, the applicant must provide:
- passport of the candidate for status;
- child's birth certificate;
- certificate F-25 (issued at the registry office);
- information about those living in an apartment or individual house (the mother must live with the child);
- income certificate in form 2-NDFL;
- a copy of the work book.
It is worth understanding that the validity of the family composition certificate and income information have a limited period of validity.
Therefore, they must be received last.
To obtain a certificate from the registry office, you must contact any department of this organization. However, by contacting the place where the birth certificate was issued, you can save time. Then you won’t have to make a request to another department (the time to clarify the data is up to 30 days).
Who is a single mother
A woman who has given birth to a child and is raising him independently, without a biological father, is considered a single mother according to documents. At the same time, in the child’s documents (in the certificate) there is a dash in the line “father”. This status is also given to a woman who gave birth to a child ten months after the divorce, since it is logical that the biological ex-husband is not his father. The registry office issues a certificate to confirm your status.
Important!
Even after getting married, the status of a single mother is not lost. This applies if the new husband does not legally adopt the child.
Who can apply for single mother status?
According to domestic legislation, not every woman who raises a child on her own is recognized as a single mother. You should know that in order to obtain this status, the column in the birth certificate of a minor that indicates information about the father must be empty. It is also allowed to have the note “recorded from the mother’s words.”
The concept of “single mother” can be interpreted from two points of view:
- in the context of labor law;
- from social security.
Find out more about who can qualify for single mother status.
Social guarantees for single mothers
The laws of the Russian Federation provide for material support for this category of citizens. Large non-material assistance from the state makes it possible not to spend money on purchasing items necessary for life. From the birth of a child, he is entitled to a set of things. If the doctor writes a prescription for baby food, then the mother will be able to receive free dairy products for the child for the first two years.
If a child gets sick, he will be given the necessary medications. This support is provided until the child is three years old. A discount on utilities is also a good help in the household. For example, until the baby is one and a half years old, some types of utility bills are not calculated for him, which significantly saves a single mother’s finances.
To stimulate productivity, single women are able to register their children in preschool institutions without waiting in line.
The family is obliged to pay no more than half of the parental contribution for the child’s stay in kindergarten. There is also a thirty percent discount for children who attend extracurricular classes in music, art, and sports.
When entering school, children of single mothers are provided with meals twice a day in the school canteen and are provided with writing materials: notebooks, pens, pencils, etc. Free trips to children's camps and sanatoriums are also available to preferential families. These benefits apply mostly to children. But the presence of these factors removes the financial burden from the mother.
In addition to the above benefits in material form, there are also legislative provisions that protect single mothers. For example, according to the Labor Code, it is believed that it is impossible to fire a single mother raising a child under fourteen years of age. This can only happen if the activity of the enterprise is stopped - during reorganization and liquidation. In this case, the employer is obliged to find a new place of work.
Naturally, cases are not discussed when an employee, represented by a single mother, constantly violates labor discipline and commits illegal actions. Here it is not possible to hide behind a dependent minor child. Violation of the law will result in dismissal.
Single-parent family
An incomplete family has the status of a family where children are raised with one of the parents,
mostly with my mother. Typically, such families arise in the following situations:
- The baby was born at a time when the parents were living together, but after the divorce, the mother and him were left alone and did not receive help from the ex-husband.
- The father does not live with the family for various reasons - he died, is serving a sentence in prison, has been documented as missing, and is incompetent for medical reasons.
- The woman gave birth to a baby without being married, and then paternity was officially established, but the real father does not take part in the child’s life and does not help financially.
- A man who is not the biological father of the children adopted them after marriage to a woman, but subsequently does not live with this family, does not maintain a relationship, and does not help financially.
Labor guarantees for single mothers
The legislation prescribes a loyal attitude towards mothers with children under five years of age. Without written confirmation of consent from the employee, you cannot send her on business trips, give them night shifts and overtime assignments, and you cannot involve them in work on weekends. Mothers with children under fourteen years of age have the right to request a part-time work schedule.
Working single mothers can ask for additional leave at their own expense, up to two weeks, at a time convenient for her, if such a clause is provided for in the collective agreement. Also, single mothers cannot be subject to discrimination in employment for the sole reason that they are raising a child on their own.
If there is a child with a disease, a single mother has a more advantageous position in terms of payments and treatment compared to a similar situation for a woman after a divorce.
List of benefits provided
When a woman receives the status of Single Mother after a divorce, what benefits she will receive are indicated in the legislation of the Russian Federation. These questions concern many mothers who have to raise children on their own. The state provides various benefits to divorced women. Every family where a single mother has children under 1 year of age receives benefits.
A single woman with a child after separating from her husband has certain types of government support, namely labor benefits and subsidies for improving housing conditions.
Labor benefits will include the following additional rights and benefits:
- women who have the status of single mothers and raise children on their own cannot be laid off or dismissed from their positions until the child reaches the age of 14:
- during the reorganization or closure of an enterprise, the employer is obliged to offer such a single employee a new place, otherwise, until she is hired, she will receive a monthly amount of her income for three months;
- sick leave for caring for a child of such an employee must be paid in full until he reaches the age of 7;
- a woman is entitled to an additional two-week leave;
- The work schedule in the evening and at night is established only with a written application from such an employee;
- Long business trips are made only with the consent of a single mother.
When a woman is divorced and lives with a child, additional benefits give her the right to receive subsidies out of turn for the purchase of real estate for herself and her children.
She receives such rights in the following situations:
- large families need to improve their living conditions;
- a mother, as a single parent with two or more children, can participate in the “Young Family” program, which is aimed at obtaining new apartments;
- family members have less living space than required by law and local standards.
Payments to mothers in the Russian Federation
All types of assistance are regulated by federal laws and apply to all Russian citizens. Benefits are calculated using a single mechanism in all regions.
Every mother: married, divorced, and single mother is guaranteed to receive these types of assistance - benefits for pregnant women, at the birth of a child and for caring for him up to eighteen months. These types of payments do not depend on social status.
Women with single mother status are provided with additional types of assistance, which are accepted and established by regional municipalities. The mother may be paid compensation for a child from eighteen to thirty-six months at the place of work. Regional authorities of the competent departments can calculate benefits for large families with three or more children. This takes into account the cost of living.
For a child from 0 to sixteen years old, and in the case of continuing education in a comprehensive school - up to eighteen years old, there is also the opportunity to receive financial assistance at the regional level from social protection.
Its purpose depends on the income level of a single-parent family. The assistance that a family receives every month is usually larger than the standard norms for low-income families (instead of 500-1000 rubles - 700-1500 rubles or more).
Social protection authorities take into account the amount of compensation for food products. This is a monthly type of benefit, and it is calculated for a child under three years of age. Due to the rising cost of living, a type of assistance is also provided for children under sixteen years of age. And for those who study in general education institutions, this assistance is prescribed for a period of up to eighteen years. The main criterion for calculating benefits in this case is the income of a single mother. An example would be a situation where two women of the same status received different amounts of child benefit. One is 350 rubles, and the second is 700 rubles. When clarifying the circumstances, it was discovered that the woman with a smaller amount had an income level that exceeded the subsistence level per person, and the woman with a larger amount had an income less than the minimum established in the region.
Non-working mothers who can prove a low level of subsistence can receive benefits for a child aged 14-18 years.
The amounts received for this type of assistance are not very large - from one hundred fifty to one and a half thousand rubles per month.
Legislation
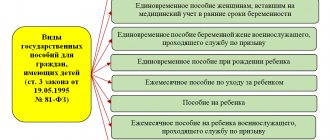
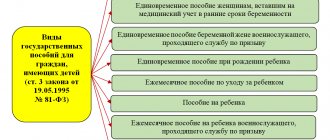
The most complete definition of the concept of “single mother” is contained in Resolution No. 1 of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2017. In turn, certain benefits for this category of the population are provided for by the Labor, Tax and Housing Codes of the Russian Federation. Financial benefits are regulated by Federal Law No. 81-FZ of May 19, 1995 “On state benefits for citizens with children.”
In the regions, single mothers receive some privileges in accordance with by-laws. For example, the Moscow Government is adopting a whole comprehensive program of social protection measures for the population, as well as regulations regulating this issue in certain areas of citizens’ lives.
Is it possible to become a single father or mother after a divorce?
Yes, this is possible. The law describes everything in detail. Divorce is not a reason for automatic approval. The possibility of obtaining status must be documented.
There are several reasons for granting the status of interest:
- There should not be a note about the presence of a father on the baby’s birth certificate. Instead, there should be a dash, or the full name should be indicated according to the mother’s words.
- The fact that the baby was born during marriage or within 300 days after its termination, but the father was able to prove that he is not the biological father in court.
- During the adoption of a child out of wedlock.
The status is not granted in a number of cases:
- After the termination of the marriage bond, if the father refuses to fulfill his parental obligations, but was involved in the birth. At the same time, his full name is indicated in the main document confirming the child’s identity.
- When the birth occurred before 300 days after the divorce or after the death of the father. In the latter case, it is possible to apply for a survivor's benefit, but you will need to provide quite a lot of different documents.
- If the birth of the child was not in marriage, but the biological father does not abandon the baby, or paternity was established through the court.
- When the father is deprived of parental rights.
Thus, it is necessary to understand whether it is possible in a particular case to obtain the desired status before starting to collect documents and waste your time. If a woman does not meet the above criteria, she will receive a refusal. Marriage is considered grounds for termination of benefits and payments.
Payment of alimony
If a woman is divorced from her husband, what benefits she can claim also depends on how she managed to resolve the issue of alimony. A property claim during the divorce process also involves determining the amount of payments for child support. After the end of the trial, the court makes a decision indicating what monetary benefit the spouse will pay for his children until they reach adulthood.
There are two forms of requesting alimony - voluntary and forced. If the ex-spouses mutually agree on how much money will be paid to the children each month, they can either agree verbally, based on goodwill towards each other, or draw up a written alimony agreement.
In order for the spouse to understand whether there are benefits after a divorce in the form of financial assistance, the agreement must specify all the mandatory nuances - in what form the assistance will be provided, its size, the number of payments per month, the frequency of execution of the agreement. Such an agreement certified by a notary has the force of a writ of execution and is subject to strict implementation.
Legislative consolidation of status
As of 2021, there is no legal definition of a single mother.
There is a definition of a person with family responsibilities and a single parent raising a child on their own. These concepts are enshrined in the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of 2014, which regulates the work of persons with family responsibilities raising young children on their own. The main signs of the status of a single mother, according to the above document:
- the presence of responsibilities for the upbringing and development of the child;
- providing actual child care;
- the father died, was deprived of parental rights, had limited parental rights, was declared missing, and incompetent.
Attention! Legally, the definition of a single mother is applied only in the field of labor law; it does not allow a woman to receive social benefits.
The key point for using benefits in the field of labor law for mothers is that she alone raises, educates, and feeds her children. She doesn't even need to have an ID to enjoy these privileges.
In 2021, the Labor Code provides many benefits for single mothers. For example, when reducing the number of employees, it has an advantage, and there are also many incentives and benefits when organizing the working day.
Who cannot apply for status
Women who are not eligible to receive this status:
- if she was left alone after the divorce, the father is recorded in the corresponding column in the birth certificate;
- the paternity of the children was established in court or voluntarily;
- the child appeared before the expiration of 300 days from the date of divorce or other circumstances, for example, the death of a spouse (Part 2 of Article 48 of the Family Code of Russia).
Procedure for obtaining status
Receiving benefits for single mothers in 2021 in the Russian Federation is more profitable and easier than trying to establish paternity and seeking to formalize child support obligations for the father.
How to obtain single mother status? Some believe that receiving a certificate in Form No. 25 is already the basis for recognizing such status, but everything is not so simple.
To assign the status of a single mother and receive her benefits and other payments, you need to contact the social protection department or MFC with a certain list of documents. A certificate in form No. 25 will only be confirmation that a woman can be classified as a single mother.
Required documents
To obtain the status of a single mother, you need to contact the department of social protection of the population or the MFC for registration with a certain list of documents. Such documents include:
- a statement written by a woman demanding that she receive this status;
- children's birth certificates;
- the applicant's passport or other identification document;
- a certificate stating that the child lives with his mother, and not with his father or another person (can be ordered at the passport office);
- documents indicating the applicant’s income for the last three months preceding the date of application;
- a certificate in form No. 25, a decision of a judicial authority or another document confirming the fact that this person belongs to the category of single mothers;
- documents confirming the presence/absence of other family income (certificates from school/kindergarten);
- account details for transferring benefits;
- documents confirming the absence of a father in children.
After submitting documents to obtain single status, she will have to wait for the decision of the authority’s employees, which they must make no later than 10 days from the date of their receipt.
If the applicant’s request receives a positive response, a certificate will be issued that will confirm the rights of a single mother.
Who is eligible to receive the status?
The clear concept of “single mother” is not fixed by law. When determining who has the right to count on acquiring such status, it is worth focusing on the requirements provided for acquiring benefits in a particular area.
In order to receive the benefits provided by labor legislation, the mother must meet the requirements provided for in paragraph 2 of clause 28 of the Resolution of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 1 of January 28, 2014. In particular, a single parent is obliged to raise and provide for the child independently, without the participation of the father . The father may be absent due to:
- Death.
- Deprivation or restriction of rights to education.
- Official declaration of missing persons.
- The presence of incapacity.
- Serious health problems that do not allow him to take responsibility for financial support and participation in the life of his daughter/son.
- Convictions of stay in correctional institutions.
- Evasion (refusal) from paying financial resources for the maintenance of a minor.
At the same time, labor legal acts do not consider it mandatory for the father to be absent from the birth certificate. A parent may be included in the certificate, but avoid paying child support, or do not have the physical ability to do so.
To receive tax benefits, a woman will need to meet the requirements described in Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-05/78050 dated October 30, 2018. According to the criteria specified in the regulatory act, a mother can receive single status if:
- The father is not included in the birth document.
- The parent died or was officially declared dead.
- The pope is missing in action, about which there is a court order.
For tax benefits, therefore, the criteria are stricter than for labor benefits.
Divorce and failure to fulfill parental responsibilities are not considered grounds for recognizing a mother as single.
Allowances and other social compensations and benefits are established by regional legislative acts. Therefore, the requirements for a mother to obtain single status may vary significantly. However, most laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are guided in determining the mandatory criteria of Art. 17 of Law No. 143-FZ of October 22, 1997 and the Family Code.
In particular, social benefits will be provided if the father is not identified and there is a dash in the corresponding metric column. It is also considered acceptable to indicate the father from the words of the mother. In this case, it is legally considered that the father does not exist and has no rights or obligations in relation to the child. This entry is made if:
- The marriage has not been officially concluded, the parents have not submitted a joint application to indicate paternity, and there is no decision from the judicial authorities.
- There is an appeal from an unmarried woman about the need to include the pope in the documents from her words, the man himself did not show any initiative to establish kinship.
- The mother was married, but the marriage was dissolved more than 300 days before the birth of the baby; other candidates did not file applications to indicate paternity.
- The woman’s husband passed away (died, died, was declared missing) more than 300 days before the birth of the child.
Svetlana Anokhina
Family lawyer, website expert
In the social sphere, the mother will be recognized as the only parent only if the father is not legally established. Divorce, incapacity, conviction or failure to pay alimony are not grounds for establishing status!
How to become a single mother after divorce?
Many people want to know whether it is possible to become a single mother after a divorce in 2021. The fact of marriage is not a fundamental reason for rejecting an application for benefits.
If the father is not indicated on the birth certificate, but the mother was married, then in this case it is possible to be considered a single mother.
But if the father is indicated on the birth certificate, then it is impossible to purchase such benefits.
Is it possible?
There are some nuances to this procedure. They are all connected with the procedure for adopting a child during marriage without the consent of the spouse. There are also legal issues that affect the status.
After a divorce, it is possible to obtain status in the following situations:
- the child was born without a father, when the mother married after the fact of birth or when paternity was not established;
- at the birth of a baby in a marriage, but the father challenged his paternity through the court;
- at the birth of a child after 300 days of divorce, paternity is challenged in court;
- when adopting a child without the consent of the second spouse.
Normative base
Several laws regulate the issue:
- Federal Law No. 81 of May 19, 1995 on benefits to citizens in this status.
- Article 6 regulates the question of who exactly is entitled to receive maternity benefits.
- Article 7 regulates the time period for receiving benefits.
- Article 8 regulates the amount of the benefit.
- Article 9 regulates who exactly is entitled to receive benefits and benefits of a one-time nature.
- Article 11 regulates benefits for the birth of a baby.
- Article 12 regulates the issue of the amount of benefits.
- Article 13 regulates the issue of citizens who are entitled to receive child care benefits.
- Article 14 specifies the payment period.