When intending to purchase a plot of land, you should clearly understand what parameters it should have in order to ideally suit specific tasks: locating a house, running a subsidiary plot or creating a farm. This article will focus on the plot of private household plots as one of the most common types of land use.
What is private household plot
Private subsidiary plot (personal subsidiary plot) is a form of activity of a citizen and his family members aimed at the production of agricultural products and their processing.
In order for such activities to fall within the definition of private household plots, they must meet the following criteria:
- making a profit is not planned (this is why the activity is officially recognized as non-entrepreneurial - with all the ensuing consequences in the form of the possibility of not keeping accounting records and not paying taxes);
- there are no hired workers, all work is performed exclusively by one family (or even one person);
- products are produced for personal use, that is, to satisfy personal needs, and it is not prohibited to sell surplus products in any volume;
- the plot of land on which the activity is carried out is provided or acquired specifically for the management of private household plots and has a note about this in the documents.
Definition
The legislation does not contain a clear definition of a private plot. It follows from the Law on Private Private Farms that a plot of private household plots is a plot of land with a documented type of permitted use of the land - “for running private plots”, which was acquired and (or) provided to a citizen for running private plots.
Decoding
Lands in the Russian Federation are divided into categories, depending on their intended purpose, including agricultural lands (hereinafter referred to as agricultural lands) and lands of populated areas. The lands of each of these two categories are further subdivided according to the type of use of the land plot. The plot of private household plots is unique in that it can relate to both agricultural lands and lands of populated areas.
A plot of private household plot is called a household plot if it is located within the boundaries of a populated area, in which case the category of land is defined as “land of populated areas.” A plot of private household plot is called a field plot if it is located outside the boundaries of a populated area, in which case the plot falls into the category of agricultural land.
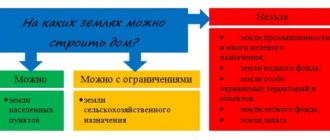
Possibility of development
This question can be answered after information is received regarding the location of the land plot. This suggests that if the plot is located within a populated area, then it is permissible to erect a building on it. It is noted that the types of buildings are not limited in any way, and permission is not required for their construction.
If a residential house is built on the site in question, then all necessary operations can be carried out in relation to it and residents can live on the grounds established in the legislation.
When the site is located outside a populated area, it will not be possible to obtain permission for its development. This is due to the fact that such plots have their own purpose for farming.
Purpose
The use permitted by law depends on whether the private plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area or beyond:
- On a private plot of land, you can build a residential building and any other buildings (subject to the rules that are the same for everyone - construction, fire safety, sanitary and hygienic and others, and you can also produce agricultural products (any kind: planting plants, raising animals and poultry, setting up an apiary) In a residential building built on a private plot of land, you can register at your place of residence, and it is also possible to receive a property tax deduction.
- On a field plot of land, you can only produce agricultural products and erect non-permanent buildings for this purpose (without a foundation). It is prohibited to build a residential building, and if it is built, it may be forced to demolish it. Naturally, there is no question of registration in such a house.
conclusions
Thanks to the import substitution program, private household plots have received a new round of development. Farming is now carried out not only by rural residents, but also by some urban residents and even the oligarchy. For example, the former mayor of Moscow Yuri Lushkov also took up agriculture - he grows buckwheat in the Kaliningrad region.
In the first half of this year, the volume of agricultural products in Russia increased by 3%, despite a general fall in GDP. Facts and figures create a favorable background for reducing loan rates and guaranteeing demand for the products of private farms in the future.
Minimum/maximum size of private plot
A plot of private household plots can be provided as a property or purchased.
If the land is issued by local governments or the state, then the size of the plot (minimum and maximum) will be limited by the standards established by the local governments. Thus, in Vladimir, a plot of land from 0.04 hectares to 0.15 hectares can be provided. In the city of Cheboksary - from 1200 to 1500 sq. m. m.
One family (one private household plot) may own (or otherwise have) a limited amount of land, as a general rule - 0.5 hectares. Regional legislation may increase this number, but not more than 5 times. In the Vladimir region, a private plot can be up to 2.5 hectares in size, in the Chuvash Republic it should not be more than one hectare.
Differences between private household plots and individual housing construction
Individual housing construction (individual housing construction) is a type of use of a land plot in which a citizen either independently builds a house on this plot, or the house is built entirely for him. At the same time, the built house has legally established restrictions on the number of floors (no more than three) and the composition of residents (one family).
Both private household plots and private housing construction are intended for non-commercial use, i.e. do not involve making a profit.
However, there are differences:
- On any plot of individual housing construction, the construction of a residential building is permitted with further registration at the place of residence. On a private plot, the construction of a residential building is permitted only if the plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area (registration at the place of residence in such a house is also possible).
- The land tax on an individual housing construction plot is much higher than the similar tax on agricultural land. In terms of this parameter, a household plot of land does not differ fundamentally from an individual housing construction plot (the interest rate is either the same or differs slightly - for example, the land tax rate in the city of Vladimir is 0.3% for both individual housing construction plots and private household plots), and only field a plot of land without the right to build will be cheaper.
- Growing agricultural crops is allowed on the individual housing construction site. On a private plot, you can engage in not only crop production, but also livestock farming on any scale.
- On an individual housing construction site, the construction of a residential building is the responsibility of the owner (work must begin within at least three years, otherwise the owner can be held liable for misuse of the land), while on a private household plot, the construction of a residential building is only the right of the owner.
Which to choose
The choice between private plots and individual housing construction depends on a number of conditions:
- Category of land and main purpose of use. For the construction of a residential building, either a plot of individual housing construction or a plot of private household plots from the lands of populated areas is suitable; for crop production - both individual housing construction and private plots; for livestock farming - only private household plots.
- Location of the site and availability of utility networks. When providing a site for individual housing construction, local governments are obliged to provide the necessary set of infrastructure: roads cleared in winter, electricity, water supply, gasification, public transport, hospitals, shops, schools - all according to the standards established by law. The owner of a private plot runs the risk of finding himself in a situation where he will have to pay for the creation of engineering and technical support networks; local governments do not bear such responsibility. Therefore, if there are no utility networks near the site, its low price in most cases will result in huge costs for the installation of utilities, and this should be taken into account.
- Maintenance costs. For private household plots, such costs will be lower (of course, if communications are not required), for individual housing construction sites they will be significantly higher, especially in terms of costs for gas and electricity prices.
What to consider when choosing a site
When choosing a private plot, you should consider:
- Plot size. It must fit within the maximum size of the total area of land plots (0.5 hectares, if the law of the subject of the Russian Federation does not increase the specified area).
- Location of the site. For a private plot of land, it is important to have communications, for a field plot - access roads, for any plot of private household plot - the suitability of the plot for use, which is intended for breeding farm animals, growing plants, etc.
- Special programs to support private household plots adopted by local governments, i.e. those that are taken in addition to government support measures. If such programs exist, this moment may become decisive when choosing between two private plots located within the boundaries of different settlements.
Ownership Features
Land plots that are allocated for the purpose of running subsidiary farming are recognized as the most profitable category of land. This is due to the fact that the possibility of their development is allowed, as well as on plots intended for individual construction. This rule applies to areas located within populated areas.
When a person decides to purchase land of the category in question, he bears less tax responsibilities than when purchasing land in the individual housing category. On plots allocated for construction, construction work is allowed, but if we are talking about subsidiary farming, then both construction and farming are allowed.
If we compare the category under consideration with lands allocated for agriculture, the former have significant limitations in size. The advantage is the possibility of constructing buildings.
Products obtained through the use of the allotment become the property of the user. When a person decides to sell land through sale, he does not need to pay taxes. This is a significant advantage of this category.
After receiving ownership of a plot, the owner is also given the corresponding responsibilities. This is the use of the allotment strictly in accordance with the permitted use. Before purchasing a property, you should study its pros and cons.
How to register a private subsidiary plot
Citizens can run private plots from the moment of state registration of rights to a land plot and automatically stop running them in the event of termination of rights to the land plot on which private plots are maintained. Registration of personal subsidiary plot is not required.
However, in order to receive various subsidies, it is in the interests of the citizen running the private household plot to register the private plot with the local government, where a household book will be kept for the private plot. When registering, you will need to present a passport (passports of family members, if any) and title documents for the land plot (the type of permitted use of the land is “for running private household plots”).
The following information is entered into the household book according to the owner of the private household plot:
- about persons who run private household plots;
- about the area occupied by various plantings of agricultural crops;
- about the number of farm animals, birds and bees;
- about vehicles and agricultural machinery.
The specified information is entered at the time of initial registration, and subsequently - annually as of July 1 by visiting farms by representatives of local government bodies and on other dates at the initiative of members of private household plots.
Advantages of personal subsidiary farming
- Simplicity of organization (LPH does not require legal registration);
- lack of registration with the tax office and tax reporting (accounting is maintained in household books by local authorities based on information provided by the owners);
- various benefits (exemption from personal income tax under certain conditions, preferential transport tax on equipment, etc.);
- the possibility of making an independent decision on pension insurance (the owner of a private household plot decides whether to pay contributions to the Pension Fund).
Advantages and disadvantages of private household plots
Advantages:
- maintaining private household plots is not a business activity, that is, registration of an individual entrepreneur is not required;
- there is no need to pay income tax (NDFL) if the following conditions are met: the size of the plot is not larger than that established by law;
- Only family members work in private household plots; hired labor is not used.
Flaws:
- The combination of a high rate of land tax on private plots within the boundaries of a populated area and a ban on the construction of residential buildings on private plots outside such boundaries. That is, everyone faces a choice: either it is prohibited to build, or high taxes.
What taxes will you have to pay?
Proceeds from the sale of products produced in private household plots are not subject to taxes. You also won’t have to pay VAT, since this tax only applies to individual entrepreneurs and organizations. The only regular payment is land tax, approximately 0.3% of the cadastral value of the site.
According to current legislation, income from the sale of products of animal and plant origin is not taxed, however, to be exempt from taxes, two conditions must be met:
- The area of the land plot should not exceed that established by Law No. 112-FZ. The permissible plot size is 0.5 hectares, unless a larger plot is allocated by decision of the local administration.
- Personal subsidiary farming is carried out without the involvement of hired workers.
To be exempt from taxes, you must obtain a document confirming that crops, meat and other products were produced on a plot of land permitted by law. The certificate must be issued by the local administration or the board of the dacha (gardening) partnership.
However, there are nuances that are worth paying attention to:
- If you decide to produce vermicompost, biosoil, etc. on your site. and sell it wholesale or retail, you may be required to pay taxes. Fertilizers are not considered a product of livestock production; their production is considered as a result of business activity, and therefore is subject to taxation. Also, the legislator does not classify turf and soil mixtures as crop products.
- To obtain tax exemption, you only need a certificate from the administration of the locality or the board of a non-profit association (gardening, dacha). A document issued by another organization is invalid.
- Only income from the sale of products produced in private household plots is exempt from tax. If you manage to get a government subsidy, you will have to pay taxes. Amounts received from the budget to reimburse interest on a targeted loan are not taxed; the remaining funds for subsidies are subject to taxation.
Construction on a private plot
When planning to build a residential building on a private plot, you need to clearly understand what documents will then be required to obtain a certificate of ownership.
The “dacha amnesty” has been extended until 2021, so for state registration of rights to a house on a private plot within the boundaries of a populated area, one document is needed - a title document for a land plot.
After the expiration of the “dacha amnesty” period, as a general rule, in addition to the document for the land plot, you will need a document confirming the fact of the creation of a residential building and containing its description, that is, either permission from the local government to put the object into operation, or a construction permit (for an unfinished construction project ).
Disadvantages of personal farming
- Restrictions on the area of land for private household plots. The size of the plot cannot be more than 0.5 hectares, although the local administration has the right to decide on a fivefold expansion of the plot.
- The state does not support private household plots by providing preferential loans and subsidies:
- Some types of activities subject to certification are prohibited, and declarations of conformity are not issued.
Commercial cattle breeding on private plots will be problematic
Getting permission
A building permit is not required when registering the right to a house, but it is still better to obtain one. The Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Parts 1 and 2 of Article 51) still provides for the need to build only with a construction permit, and the Code of Administrative Offenses (Part 1 of Article 9.5) establishes liability for the construction of a capital construction project without permission.
A violator, an individual, is subject to a fine of 2 to 5 thousand rubles, and such a fine can be imposed repeatedly throughout the entire construction period.
To obtain a construction permit, an application for a permit and three documents accompanying it are submitted to the local administration:
- title document for land;
- urban planning plan of the site, it must first be obtained from the same administration by writing an application for issuance, the administration collects documents for registration independently, the urban planning plan is issued free of charge within thirty days from the date of submission of the application;
- a planning organization diagram, which is prepared by the developer to the best of his ability - usually the proposed development scheme is drawn with a pen on a copy of the cadastral plan.
If these three documents are available, a building permit is issued no later than 10 days after submitting the application.
Rules for keeping cattle (cattle) in 2021
A citizen who decides to take care of cows must comply with the following rules for keeping livestock:
- It is imperative to create conditions for keeping animals: build an appropriate room where it should be heated in winter. It is also necessary to provide electricity to the barn;
- animals should have free access to water; they must have it constantly;
- the owner of a private household plot is obliged to comply with veterinary, sanitary, hygienic standards, and general principles of humane treatment of animals;
- Manure contamination of the surrounding area should not be allowed. The barn must be cleaned and new straw laid;
- animals must undergo routine vaccinations against parasitic and infectious diseases;
- Animals must be slaughtered in special slaughterhouses. It is prohibited to carry it out in places not intended for slaughter;
- the owner must organize the grazing of cows. In winter, he must ensure that the cows are kept in stalls;
- to feed cattle you need to use special feed, hay, straw, silage, compound feed, milk (for calves);
- water for drinking cattle must be clean and potable;
- Cows should graze on pastures, which should be located at a distance of no more than 2.5 km from a watering hole (river, stream, canal, etc.).
How many cows can be kept on a private farm according to the law in 2021?
The law does not establish a standard or maximum number of cattle that can be kept and used in private household plots.
How justified is it to invest in such a business?
I'll give an example of my friends. They have a small mini-farm of 8 heads of cattle (cows), 4 adult pigs and 7 piglets, 30 chickens, 15 rabbits, as well as purebred German shepherds for sale of puppies. There are 5 people in the family. 2 adults, 3 children (25, 22 and 10 years old). The head of the family is a livestock specialist by training.
Adults and children are involved in the work. The main income is the sale of dairy products: cheeses, feta cheese, cottage cheese, sour cream, butter. They also sell eggs, fresh pork, and rabbit. Place of sale: a trading place in the city market, rented jointly with other “mini-farmers”.
If the volume of dairy products produced by their farm decreases, they buy additional milk from local residents. This mini-business gives the family a stable income and allows them to live in abundance. Its profitability is obvious.
To confirm my opinion, another story about a mini-business in the countryside:
Opening a business based on your own personal plot is a great idea for entrepreneurs who do not have much initial capital and want to organize a business from scratch.
This is a chance to try your hand at the agricultural industry and decide for sure whether it’s for me or not. In 2021, the import substitution program continues to operate, thanks to which the agricultural industry opens up new opportunities for aspiring businessmen and investors.