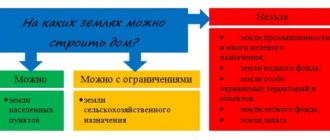
Is it possible to build a building on a rented plot of land?
The Land Code of the Russian Federation (Article 41) allows this. But it is necessary that the purpose of the building coincides with the category of land. In fact, the tenant of the site has similar rights to the construction of the object as its owner .
The only obstacle is the presence in the lease agreement of a clause that prohibits capital construction on the site. All work must be agreed upon with the owner of the site before construction begins. All nuances must be written down in the agreement to avoid future disputes and litigation.
On leased agricultural land
Often, farmers who cannot purchase a plot enter into a 49-year agricultural land lease agreement with the state. In the case of leasing agricultural land, construction is possible not only with the permission of municipal authorities, but also after agreement with the owner of the site.
It is advisable to include in the contract itself a clause regarding the possibility of constructing the necessary facilities on the site. The construction of residential and non-residential buildings, as well as the necessary infrastructure, is permitted (within the framework of the norms established by the Land Code and other laws).
What kind of real estate is allowed to be built?
First of all, a structure erected on leased land must be classified as real estate in accordance with Article 130 of the Civil Code. These are structures, buildings, unfinished residential construction, industrial and economic facilities. In this case, it is important that they are built on land of the appropriate category.
For example, you cannot build a residential building on forest lands (you can find out about the features of leasing forest plots and water bodies here?). If the land is for agricultural purposes, then the consent of the owner is required (what is the procedure for leasing agricultural land?).
Important! You can build any property. The main thing is the availability of permits from regulatory authorities.
To build a private house, it is necessary to include this condition in the land plot lease agreement (read about how to correctly draw up a house lease agreement with a land plot here). Before construction, you need to obtain permission from the municipal authorities and obtain a building design (read about the specifics of leasing a land plot for the construction of a residential building in a separate article).
However, due to the provisions of Article 48 (Part 3) of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, individuals building a house no higher than three floors for their own use do not have to draw up an architectural project. But an entrepreneur must definitely do this.
A development permit is issued for a period of 10 years in accordance with Article 51 (clause 19) of the Civil Code. And Article 55 of this legal act regulates the commissioning of the building. For structures and buildings for other purposes, it is necessary to draw up a project according to the architectural scheme in accordance with Federal Law No. 169-FZ of November 17, 1995 “On Architectural Activities”.
The construction of multi-storey buildings with infrastructure is permitted. Communications are provided in accordance with existing technical standards. And the construction site itself is leased by the municipality or a private investor.
The lease agreement may specify a specific period or an unlimited period.
It is allowed to build shared construction projects on leased land . In this case, the developers are commercial enterprises or housing cooperatives. Their activities must be insured without fail. You can learn about the risks when buying a home in an apartment building built on a rented plot in this article.
The process of shared construction is regulated by Federal Law No. 214 of December 30, 2004. For technical structures, it is necessary to obtain permission from the local administration and regulatory authorities. When constructing hydraulic structures, environmental safety standards should be adhered to.
There is no need to obtain permission to erect temporary buildings . Such structures include:
- hangars;
- household premises;
- outbuildings made of modular blocks.
The full list is presented in the Collection of estimated cost standards GSN 81-05-01-2001.
If you plan to build a permanent garage, a building permit will be required. Typically these are structures for commercial or industrial use. We also need a project that is agreed upon with the BTI.
A garage erected without permits may be demolished based on the request of the owner of the land plot.
- If the owner of the site agrees to the construction of a garage, then the developer himself must legitimize the construction.
- If the object is located on the territory of a gardening or dacha association, then it can be registered as an auxiliary premises.
- In other cases, legalization occurs in court. Evidence will be required that the structure does not pose a threat to the health and lives of people and does not infringe on the rights of those living in neighboring areas.
Find out how to rent land for a garage, pavilion or kiosk.
What buildings can be built
Owners of agricultural plots can erect a number of buildings and structures on their lands. This depends on the type of permitted use of the allotment (in accordance with Article 40 of the Land Code), each of which has its own types of buildings:
- Land for personal plots. The construction of cottages for permanent residence is allowed on them.
- Territories for gardening and summer cottage construction . Here you can build country houses, which are necessary for workers to live in the summer.
- Plots for running peasant farms (peasant farms). It is allowed to build a cottage in which the owners or hired workers will live during the season.
The issue of development on agricultural lands was defined in the Order of the Ministry of Economic Development (540), which provides a Classifier of sites. Please note that the legislation establishes administrative liability if the work leads to negative consequences (environmental pollution, etc.).
You can find out the permissible types of activities that can be carried out on the land in the cadastral passport for the object. It is better to do this in advance, since transferring a site from one category to another will take enough time and effort (it is carried out in accordance with Article 39 of the Civil Code).
The construction of non-residential buildings in which it is planned to store the received raw materials and products is permitted on all types of agricultural territories.
The Law on the Turnover of Agricultural Land establishes the possibility of building other infrastructure necessary for farming. For example, roads within the site, fences, pipes, etc.
Articles of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (77-81) state that agricultural lands are areas outside the boundaries of urban/rural settlements where it is allowed to engage only in agriculture and agricultural processing activities. It also regulates the types of activities in agricultural territories that are permitted by law:
- Agricultural production.
- Engagement in scientific activities and research in the field of agriculture.
- Storage and processing of agricultural products.
Accordingly, a certain infrastructure is required to conduct such activities. The legislation allows the construction of necessary buildings and structures in these territories. But before this, it is necessary to coordinate the construction with local authorities, draw up permitting documentation, and then register the rights to the new facility.
The permit issued by local authorities shall indicate the following information:
- Construction start and completion dates. Upon completion, the owner of the site must register the structure (even if the construction work has not been completed).
- Type and purpose of the desired structure.
- Signature of the person who issued the permit.
How to do this legally?
The legality of erecting a building on a rented plot is determined by the availability of a building permit.
Writing an application
Since the law does not establish a specific form of application, it is drawn up arbitrarily. But it must indicate:
- Full name, address, position, organization/institution;
- information about the applicant - full name, registration and/or residence address, contact details;
- document title – “Application”;
- submit a request for a permit to develop the site, indicating the name of the object, address, and the validity period of the permit;
- information about the plot of land;
- characteristics of the constructed object.
At the end of the document there is a list of appendices.
Collection of documents
The following documents will be required:
- applicant's passport;
- if a development permit is obtained through a representative, then in addition to a passport, he will need a notarized power of attorney;
- land lease agreement;
- a diagram of the site indicating the location where the real estate will be located;
- urban planning plan.
For capital construction projects, design documentation will be required. It is subject to examination. It can be prepared by both government agencies and commercial enterprises. Then it is necessary to provide documentary evidence that this legal entity can conduct an examination.
Innings
Documents are submitted to the local government authority in whose territory the site is located. The applicant can do this in person, through a representative or using the services of a multifunctional center.
Commission decision
The tenant will be given a positive decision if the building being constructed fully meets the technical requirements and has all the necessary documents. You have 10 days to accept it. If you receive a refusal, you can appeal it in court.
Buying land for individual housing construction: how to do everything right?
Transactions on the land market are often challenged in the courts. And not only by the participants, but also by local authorities.
When purchasing a plot for individual housing construction, you should be wary of:
- old documents for land (for example, before 1998), not reissued at the right time;
- indication in the USRN extract of any other type of permitted use other than individual housing construction;
- encumbrances, for example, bank pledge, judicial arrest in connection with a lawsuit filed by former owners (checked through the Unified State Register of Real Estate and by sending requests to the court in the area where the site is located);
- the presence of power lines, heating networks, communication nodes (this is always noted in the USRN extract as a restriction in use);
- the presence of any formal easement with authorities or services;
- unauthorized construction on the site or a waste dump;
- the site is located next to a military camp, a sanitary area, in a zone with special conditions, near the state border.
All these little things can turn into lawsuits or bans in the future. “I bought a plot of land for individual housing construction, but it turned out that there was a heating main on it. Construction of a house according to the project in compliance with the norms on the distance between networks and residential buildings becomes impossible. I was forced to file a lawsuit against the seller, since he hid this fact from me, and no official easement was issued and no restrictions were registered,” says the land buyer.
The court found that the seller, despite having documents for the plot, did not have the right to sell it for individual housing construction, since its purpose was a blocked residential development. The buyer did not know anything about these nuances and was planning a large-scale construction of a separate building with different approaches.
Buyers often learn about the prohibitions after purchasing a plot and starting the notification procedure with local authorities regarding individual housing construction. “I purchased a plot of land for individual housing construction and sent a notification to the District Administration about the planned reconstruction of an unfinished house that was located there. I received a refusal due to the location of the facility in the power supply security zone,” said one of the victims. He tried to obtain a notice for reconstruction through the court, but his claim was denied.
You also always need to find out whether there is a tenant at the house or unfinished site on the site for individual housing construction, since by law he has the right to use the site plus he has the right of first refusal. If his interests are circumvented, he may go to court and demand termination of the contract.
The owner of the site is obliged to inform the buyer about the restrictions on its use. But in practice, information rarely occurs, because it always affects the price. If, after purchasing the land, it turns out that construction is not prohibited on it, then the new owner has the right to demand termination of the contract and the return of money through the court.
In an effort to save money, buyers also agree to purchase land for a different purpose, hoping to change its status to individual housing construction. Only lawyers specializing in land law should agree to such transactions. For example, land cannot be transferred if it is located far outside the city and is not adjacent to any settlement. There may also be a moratorium on the transfer of agricultural land to individual housing construction, for example, if there is a shortage of plots for growing crops in the region. If all these nuances are unknown to you, then it is better not to take risks and choose to buy land with the possibility of residential development.
Material costs
The future owner of the land plot will have to bear the following expenses:
- The provided copies of documents must be certified by a notary. The cost will be 200-500 rubles, depending on the region and the tariffs of the notary’s office.
- Individuals pay a state duty in the amount of 2000 rubles, legal entities - 22 thousand rubles.
- The transfer of land ownership depends on its location. In large cities this is 10-20% of the cadastral value, in local entities - no more than 3%. For cities with a population of more than 3 million people, you should focus on the upper limit, i.e. 19-20%.
In addition, it should be noted that in some cases it is necessary to obtain permission before starting construction. This document will cost 15-50 thousand rubles. depending on the region and type of building being constructed.
How to transfer ownership of a plot after registration of real estate?
You can register ownership of land when a building has already been erected on it, either on a paid or free basis. They enter into ownership for a fee if the land plots were leased after 2001. Free transfer is provided in the following cases:
- ownership of the property was registered earlier than 2001, and the land was leased at that time;
- the lease agreement for the plot was concluded before 2001 for the purpose of constructing a private house or for organizing a personal subsidiary plot;
- buildings are transferred to individuals for lifelong inheritable ownership or for permanent use;
- land plots belong to a garage, construction or gardening cooperative.
You can find out whether it is possible to buy land from lease into ownership and how to do it here.
Reference. The land lease agreement may stipulate the parties’ decision to transfer the land into ownership to the developer free of charge.
Necessary:
- construct the building within the time limits specified in the agreement;
- obtain ownership of the building in the manner prescribed by law;
- with a document confirming ownership, contact the local administration.
After this, the site will be transferred to the ownership of the current tenant.
What should you be wary of when purchasing a building if it is located on a leased area?
The main risk in this case is that the new property owner does not have the right to buy the land . He can only acquire the right to lease. But it may be limited in time. Often such buildings are sold closer to the expiration date of the contract.
After this, the site will have to be vacated, since local authorities will not necessarily agree to sign an agreement with the new owner. And in general this is done only through the bidding procedure.
As for the agreement for the purchase and sale of real estate, if its terms are fully met, the transaction cannot be terminated. Consequently, the buyer will simply lose money.
Another nuance is the payment arrears of the previous tenant. This should be clarified before purchasing real estate (you can find out about how to find out about debts and write a claim for debt collection under a land lease agreement in this article). The fact is that the land owner has the right to terminate the agreement after money for the use of the site has not been received two times in a row or more.
Any buildings can be erected on the rented plot. The main requirement is that their purpose coincides with the category of land. In addition, for capital projects you need to obtain a development permit. Once the building is ready, ownership is issued to it. Only after this is it possible to transfer the land from lease to ownership. This can be done for money or free of charge - it all depends on the specific situation and what is specified in the lease agreement.
Is it possible to build a house
Lands for peasant farms are usually large in size (at least 3 hectares). The construction of a residential building (cottage) on such plots is permitted, but only after its owner proves to municipal authorities that he is engaged in peasant farming activities (according to Article 11 of Federal Law No. 74).
However, exact terms are not established: the owner of the plot does not have to be a farmer; he can rent the plot to another person who will conduct farming activities. The owner is required to register as a farmer if he produces (wants to produce) agricultural products for sale. Registration is carried out in a simplified manner, plus you do not need to pay taxes for the first 5 years after registration.
This can be confirmed by the presence of a livestock farm on the site: the animals need constant care from the farmer, and, therefore, they need housing in which the workers will live.
Before starting construction work, the owner of the site must obtain permission to erect a building from the local authorities by submitting:
- Statement.
- Your passport and contact details.
- The right establishing a document for a plot, this can be a purchase and sale agreement, donation, inheritance, etc.
- Cadastral passport, which indicates the boundaries of the territory and the fact that the neighbors have no claims.
- Project of a house that is planned to be built. It must indicate that the owner wants to erect a residential building.
- Other documentation confirming the fact that the CF is engaged in activities. These include receipts for the purchase of feed, contracts for the supply of equipment, livestock, etc.
Theoretically, you can register in the cottages, but this can only be done in accordance with a court decision. This will require a series of examinations. The catch is that the legislation does not provide clear criteria based on which one can accurately determine that a building is residential and can be used for year-round living. Therefore, everything depends on the personal decision of the expert himself, which may not satisfy the court.
The law allows for the demolition of a building if:
- It was proven that this object caused damage to the property of neighbors.
- The structure was erected in a nature-protected area controlled by the state (this applies to nature reserves, nurseries, areas with drinking ponds, etc.).
- The house is located close to utility lines (gas pipes, water supply lines, electrical cables) and a road (highway, etc.). This is reflected in the construction documentation for the site on which the owner wishes to build a building.
This can only be done in accordance with a court decision, and the municipality will not compensate for the losses caused.