Owners of plots intended for gardening strive to improve them as much as possible and build residential and utility buildings.
But before starting construction, it is worth studying the legality of the construction of various objects, existing requirements and standards.
If they are followed, citizens will not have problems when decorating buildings, as well as disagreements with neighbors.
Legal standards for construction
The main act regulating the development of garden plots, the creation of non-profit associations of owners, their management and protection of the rights of members is Federal Law No. 66-FZ.
This act is valid only until December 31, 2018. From the next day, a new law No. 217-FZ comes into force, in which summer cottages will be equated to garden plots , some provisions on non-profit partnerships will change, and the concept of common property will be introduced.
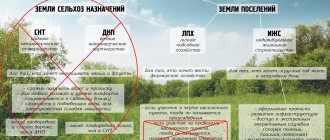
A site with permitted use for gardening may be located on agricultural land or within the boundaries of a populated area:
- For plots located within the boundaries of a populated area, it is necessary to study the design of the layout of a specific territory in accordance with Art. 42 Civil Code of the Russian Federation (if approved). The document delineates the zones of existing facilities, their characteristics, and areas where new buildings can be built. It is approved by a local authority after public hearings or by a regional executive authority without hearings.
- To build on agricultural land, you do not need to follow the red lines and rules defined by the territory planning.
It is imperative to take into account the type of territorial zone where the plot is located.
Horticultural plots are usually located in agricultural areas, but there are also plots in residential areas.
For different zones, different town planning regulations are established , which define:
- Basic, conditionally permitted and auxiliary VRI plots.
- Characteristics: maximum area of plots, distance of objects from boundaries, number of storeys, minimum share of landscaping on the plot and others.
You can become familiar with the town planning regulations, planning and development projects by contacting the authorized body of the local administration.
Category
Article 7 of the Land Code determined that the lands of the Russian Federation are divided into 7 categories, among which there are settlement lands (ZNP) and agricultural lands (ZSN).
According to the classifier, a land plot with a VRI “Gardening” may belong to either one or another category.
Objects on the land plot
The owner’s right to develop his plot is secured by the Land Code of the Russian Federation (Article 40) and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 263). All buildings that are allowed to be built and erected on lands for gardening can be divided into several groups.
Garden houses
The main difference between such buildings and residential ones is the seasonality of use . You can live in them only in the warm season, to take a break from gardening. Small houses can be used as a warehouse for equipment and crops. The buildings are not heated and are not supplied with communications.
You can live in such buildings, but you cannot register .
Exceptions are garden houses built on garden lands located in populated areas, which are equipped with all conditions for year-round living.
Such objects can be recognized as residential in court, and the owner will be allowed to register in it.
To do this, it is necessary that the objects meet the following requirements:
- Be in the full ownership of a citizen and not be the subject of a pledge.
- Compliance with all building codes, safety rules, sanitary requirements (level of sanitation).
- Fully equipped with all communications: heating, lighting, water supply and drainage, sewerage.
Garden houses should be used only by the owner's family ; dividing them into separate apartments is not allowed.
Individual residential
Houses recognized as residential must have all the necessary conditions for a comfortable life. The building is intended for individual use, not divided into apartments or blocks.
Recognition of a house built on a garden plot as residential is carried out in court or through local authorities .
Read more about the construction of residential and garden houses on lands for gardening in this article. Material about the characteristics of gardening sites located on agricultural land will also be useful.
Agricultural buildings
These include buildings that are intended for:
- cultivation,
- storage,
- storage
grown crop.
Also, this type includes structures, the construction and purpose of which is an auxiliary function for storing the necessary tools or equipment.
At the same time, the material of the walls and ceilings of which it consists is not important.
- Greenhouses are structures with a roof and walls that are used for growing seedlings and subsequently maintaining plants. The buildings may be equipped with a heating system.
- Sheds are covered utility rooms in which various property is stored and livestock are kept. Some barns have basements.
- Hangars , which are prefabricated structures of frame or frameless type. They can be used for storage, repair of agricultural machinery, as warehouses.
- A woodshed is a shed used for storing firewood and wood pellets for heating residential buildings.
Others
Other buildings include:
- bathhouse,
- garage,
- street toilet.
The buildings are not used for gardening purposes; they are necessary for the comfort of the owner of the plot.
Do I need to obtain permits?
Typically, special permits are required for the construction of any permanent structures.
A big advantage of building on dacha and garden lands is that there is no need to obtain permission to build a house in SNT, a dacha plot. This makes life easier for home owners when putting buildings into operation and registering them in the real estate register. However, unfortunately, this procedure is only valid until March 1, 2021. Theoretically, after this date the so-called “dacha amnesty” will not apply. Although, it is possible that the law will once again be extended into 2022.
Until this time, a construction permit in SNT (SPK, SNP, at dachas) for putting construction projects into operation, their registration is not required.
What to do if you can’t build
If the construction of a residential building on your garden plot of land is impossible for some reason, it is worth finding out whether it is possible to change the VRI to the following:
- Individual housing construction. Advantages in creating infrastructure and utility networks at the expense of the budget. But construction will require a design, permission and subsequent approvals from various authorities. And the land plot must have the category “Land of populated areas”.
- For running a dacha farm. The plot will have a lower cadastral value and a lower taxation level. The building can be registered under the “dacha amnesty”.
- Private household plot located within the boundaries of a populated area. May have a significant area, simplified procedure for registering a structure.
- A peasant farm is suitable for owners running a farming business. The plot area can be large.
Horticultural plots are characterized by high soil fertility, so to change the VRI, you may need to prove its deterioration, or have another compelling reason for the transfer.
What is allowed to build in gardening (SNT, SNP, SPK)
The answer to the pressing question of whether it is possible to build a house on a garden plot has already been found. Now you need to find out what nuances need to be taken into account for this. Land for gardening is allocated to people for recreation and growing various agricultural plants.
The provisions of the law (“On gardening, vegetable gardening and dacha non-profit associations of citizens” dated April 15, 1998) allow the construction of a residential building on a garden plot.
This can be done with any form of the association itself (SNT, SNP or SPK). Both in horticultural non-profit partnerships (SNT), and in horticultural cooperatives (SPK) and partnerships (SNP), not only economic but also residential buildings can be carried out for gardening. According to the law, it is impossible to register (register residence) in such buildings. However, recently, thanks to the position of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, this can be done through going to court. In gardening, a house can be considered a permanent place of residence with all the ensuing consequences.
Prohibited structures
The change in VRI occurs in accordance with the type of territorial zone in which the plot is located.
Those objects that do not correspond to the category of land can neither be erected nor used after construction.
Therefore, on a garden plot belonging to an agricultural or residential zone,
you cannot build:
- industrial facilities,
- business, commercial, domestic and communal buildings,
- healthcare, social, cultural facilities,
- shopping malls and shops,
- infrastructure facilities.
Requirements for buildings
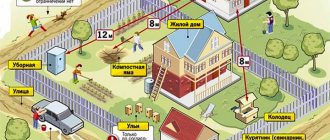
The rules of the Housing Code establish the distance between all objects, as well as the distance from the object to the boundaries of the allotment.
According to current sanitary and fire safety standards, the distance from the walls of the house to the border of the allotment is at least 3 meters, for outbuildings from 1 meter.
The distance from the walls of the house to the cellar or cesspool is at least 12 meters, to a well, bathhouse or outbuildings is 8 meters or more.
Construction is permitted only on marked areas. If land surveying has not been carried out, it is not permitted to place buildings, with the exception of auxiliary ones.
Approvals and permissions
The Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Article 51) stipulates that a building permit is not required for the following objects:
- garages on garden plots,
- auxiliary structures not related to permanent buildings (sheds, sheds, hangars).
Obtaining a permit for the construction of a garden or residential building is also not required. However, when placing an allotment on the territory of a gardening non-profit association, the owner is obliged to follow Art. 34 Federal Law No. 66-FZ and SP 53.13330.2011, i.e. take into account the territorial planning or land surveying project.
The set of rules for the development of gardening associations, approved at the meeting, defines many parameters, including:
- planning solutions for individual plots,
- type and quality of fencing,
- distance of objects from the fence and from each other,
- arrangement of a compost pit,
- remoteness of residential buildings from roads.
Due to membership and entrance fees, the territory of the non-profit association is being developed.
Also, at the expense of the general fund, security of the territory and areas of the partnership, a checkpoint or barrier is organized.
If necessary, the meeting can decide where and when to install waste bins and how to remove them.
If the owner does not adhere to these rules, then his buildings may be recognized as unauthorized , and he will be obliged to demolish them in court (Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Limit dimensions
Article 11.9 of the Land Code determined that the minimum and maximum dimensions of a plot are established by local town planning regulations .
This is also confirmed by Article 38 of the Town Planning Code, which states that, among other things, town planning regulations must contain:
- Limit sizes of allotment;
- Minimum setback from the property line to the building (house, barn, garage, etc.);
- Maximum number of floors (heights) of the building;
- Possible percentage of development of the site.
That is, the maximum and minimum sizes of plots are established by the administration in charge of these lands. This could be the administration of a village, the administration of a city, the administration of an entire subject of the Russian Federation, etc.
Most often, only the minimum plot size ; it makes no sense to determine the maximum, since one person can purchase several plots at once, thereby doubling their area.
Taking into account the requirements put forward by the main regulatory documents (SNiP, fire service requirements), the minimum area of the garden plot is 3 acres . This area allows you to move the house to the required distance from the neighboring plot and from the road.