Any person has the right to engage in personal subsidiary or peasant farming to create agricultural products. It is intended for own consumption or sale. There are significant differences between peasant farms and private household plots, and before starting work, the intended purpose of the land plot is taken into account.
The concept and nuances of peasant farming
The peasant farm is represented by a peasant farm. This type of activity consists of agricultural entrepreneurship. The process is carried out by people who are relatives. All co-owners of the plot have equal rights in relation to the territory, and also bear equal responsibility for violation of the requirements of the Land Code.
Common property refers only to a plot of land. If there is any property on the territory, represented by equipment, equipment or buildings, then the rules for its use are given in a special agreement drawn up between the co-owners of the land. This document is certified by a notary.
If one person wants to leave the farm, he receives material compensation, and the amount depends on the size of the share in the plot. It is allowed to replace a monetary amount with material assets represented by products, equipment or equipment, but only with the permission of the participant himself.
Deprivation of property rights
Alienation of property is carried out within the framework of Russian legislation. A plot may be seized in the following cases:
- cluttering of the allocated land;
- release of toxic substances into the ground;
- violation of soil fertility;
- soil damage.
To prove that these events occur, an official examination is carried out. A positive result may be observed if chemical or toxic waste is found on the site.
The authorities have the right to take away the site if it is not used for its intended purpose. In this case, it is easy to correct the situation by planting several fruit trees on it.
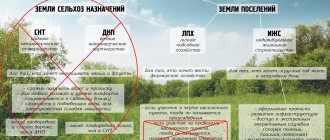
Differences between peasant farms and private household plots
These types of farms have some differences:
- peasant farming is intended to make a profit, and private household plots are used to obtain products for own consumption, and not for resale, although it is allowed to sell surpluses;
- for subsidiary farming, preliminary registration as an entrepreneur is not required, and when choosing a peasant farm, the owners or tenants of the land must register an individual entrepreneur;
- Personal income tax or other types of tax are not paid on income received from private household plots, and for peasant farms, fees are paid based on the chosen taxation system.
Each form has both pros and cons, so before choosing a suitable farming option, its features are taken into account.
Insurance payments
Insurance contributions are paid from salaries to pension and extra-budgetary funds. The percentage of deductions is determined by the selected fee payment mode. Reporting is submitted to the Federal Tax Service. Deductions for cases of injuries and occupational diseases are sent to the Social Insurance Fund in the form of an abbreviated report.
Let's consider the types of reporting and place of submission:
- the final report is submitted to the Social Insurance Fund;
- data on deductions for injuries and occupational illnesses are provided to the Social Insurance Fund;
- the RSV-1 calculation is submitted to the Pension Fund;
- a report type SZV-M is submitted to the pension fund every month.
Today, all reports are accepted by the tax service quarterly.
What plots of land are allowed for running private household plots or peasant farms?
Only plots that have the appropriate purpose can be used for growing agricultural products. The following actions are performed on them:
- cultivation of crops necessary for consumption or processing;
- grazing.
It is allowed to use not only purchased land, but also territories issued by the local administration or leased from the owner. Not only the lessor, but also his family members have the right to use the plots. But it is not allowed to involve outsiders in this activity who receive a salary for their work.
To conduct activities, any plots with the appropriate category are used, so they can be located in the city or outside its borders. The soil must be black soil, therefore it is prohibited to build buildings with foundations or residential buildings in such an area.
Plots allocated for agriculture cannot exceed 0.5 hectares in size, but there are exceptions, so some families can use an area of up to 2.5 hectares.
For private household plots or peasant farms, plots with developed infrastructure are used, so water supply, electricity and road surfaces are supplied to them.
Legislative regulation
The activities of peasant farms are regulated by the provisions of civil legislation and Federal Law-74 of June 11, 2003.
They determine the possibility of creating a farming enterprise for individual entrepreneurs and organizations, and accordingly the plot is transferred to organizations and entrepreneurs.
The main areas of activity of farmers are established:
- Production and processing of agricultural products and livestock products;
- Their transportation, preservation, sale.
On lands owned by peasant farms, the following can be carried out:
- Crop farming (growing grain, fodder and other crops, tobacco, etc.);
- Animal husbandry (breeding various animals - horses, goats, sheep, pigs, rabbits, raising poultry, deer, camels, silkworms, beekeeping);
- Vegetable growing (picking nuts, mushrooms, berries, growing fruits and grapes).
IMPORTANT! The farm's land can be used by all the people included in its composition to produce products for their own consumption. In this case, registration of a company or individual entrepreneur is not required.
Farm property means:
- Earth;
- Structures and buildings;
- Outbuildings (warehouses, sheds, etc.);
- Reclamation structures and irrigators;
- Agricultural equipment and special equipment;
- Draft animals and poultry;
- Machines and equipment.
The procedure for providing plots for peasant farms, the requirements for them and their purpose are determined in the Land Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On the turnover of agricultural land”.
Pros and cons of farms
Private household plots and peasant farms have significant advantages, although they have some disadvantages. The positive aspects of subsidiary farming include:
- ease of starting a business;
- state registration is not required;
- infrastructure is improved at the expense of the state;
- grown products can be sold, bringing high profits;
- no need to pay taxes;
- receiving government benefits;
- Part of the land is allowed to be rented.
But this type of activity has the following disadvantages:
- collective responsibility, therefore, if one family member violates the requirements of the law or causes damage to the land through his actions, then penalties are applied to all co-owners;
- to obtain a harvest you have to spend a lot of time and effort;
- restrictions on the size of the plot used for farming;
- lack of opportunity to hire workers;
- establishing certain limits on the quantity of products received.
When choosing a peasant farm, there are the following advantages:
- providing a grace period of up to 5 years, during which the entrepreneur is exempt from paying taxes;
- banks offer preferential conditions when applying for a loan;
- lack of regular and complex inspections by Federal Tax Service inspectors;
- the ability to choose simplified taxation systems that do not require accounting;
- accrual of length of service for all participants in the farm;
- provision of benefits and concessions from the state;
- a decision regarding the use of an existing allotment can be applied without first holding a meeting of owners.
The disadvantages of growing agricultural products through peasant farms include:
- there is no opportunity to hire additional workers who are not related to the participants;
- it is impossible to build a capital facility on the territory intended for storing inventory, equipment or collected products;
- a person can be a member of only one peasant farm;
- Significant costs are required to register a farm;
- the land can be used exclusively for its intended purpose;
- the infrastructure is formed at its own expense, and this is a mandatory process if the plot is used for agricultural activities, otherwise the owner will be held administratively liable by paying a large fine.
Since each option has its own pros and cons, it is recommended to choose the optimal type of farming before starting work. To do this, it takes into account whether the products will be grown for consumption or profit.
Cows
Specific primary
Accounting in a farm involves processing primary documents, reflecting financial and economic transactions in the database, maintaining registers, making entries, generating and submitting reports. It’s worth looking at the primary in more detail.
The use of a number of documents is due to the peculiarities of farming activities. Thus, a peasant farm accountant has to deal with waybills F412 of the agro-industrial complex, registers for sending grain from the field, accumulative statements of harvest receipts, records of the movement of raw materials, acts for sorting, drying, etc. Limit-fence cards, acts of write-off of materials, acts of posting of offspring (relevant for livestock farming) are also accepted for accounting.
A peasant farm accountant must have the appropriate competencies and experience in accounting for an agricultural producer. Otherwise, serious mistakes and associated tax, financial, legal and reputational consequences cannot be avoided.
Which farm is better
It is impossible to answer this question, since the choice of private household plots or peasant farms depends on the purpose of the activity. If people want to do business, making a profit from sowing and harvesting, then they choose peasant farms. They will not have to register a large company, since it is enough to register an individual entrepreneur and choose the optimal taxation system.
If people plan to use the resulting products themselves, selling only a small amount of surplus, then private household plots are chosen. Citizens will not have to pay taxes even on income received from the sale of grown products. They do not need to prepare special reports submitted to the Federal Tax Service. But they will face some restrictions regarding plot size and will also not be able to obtain product certificates.
The disadvantages of private household plots include the difficulty of obtaining a loan from a banking institution. This is due to the fact that subsidiary farming cannot be developed to a large scale. Therefore, if you plan to work from scratch, you will have to use only your own and not borrowed funds.
When choosing a specific type of farm, the purpose of the activity is taken into account. If you plan to receive a permanent and only income, then a peasant farm is chosen.
Inventory
Accounting in agricultural companies is complicated by the constant circulation of assets, recalculation of production costs, and natural loss of property. To obtain up-to-date information about the condition of assets, an inventory is carried out. The list of property being inspected and the frequency of inspections are determined by the farmer, taking into account the nature of the activity.
Usually the status is checked:
- property assets as part of fixed/current assets;
- livestock in the main herd and young animals;
- grain crops, seeds for sowing;
- reporting on transactions with counterparties;
- other assets of the company.
The inventory is carried out by a special commission, which is approved by the management of the organization. The data obtained during the verification process is noted in the inventory list.
Features of taxation for subsidiary farming
Based on Art. 217 of the Tax Code and the provisions of Federal Law No. 112, owners of private household plots may not pay personal income tax or other types of taxes. But for this the conditions must be met:
- the area of land owned by a citizen on the basis of property rights does not exceed 0.5 hectares;
- work on the land is carried out only with one’s own hands or with the involvement of relatives, but other specialists are not hired;
- Most of the products received are used for personal consumption rather than sale.
Owners of private household plots are required to pay land tax, although they have the right to apply for a benefit.
Demolition of unauthorized buildings
Illegal construction on peasant farm lands may lead to the demolition of the erected buildings based on a decision made by the court.
This happens if:
- Damage is caused to nearby buildings or people living nearby.
- The building is located in close proximity to a railway, gas or electric main, as well as next to residential or other infrastructure.
- The building is located in a sanitary, protective or any other zone of encumbrance, as well as in a protected natural area, for example, in a protected zone of a reservoir.
In all other cases, a decision on the demolition of a building made by a court cannot be made. If such a decision is made by the court, it is subject to execution by the owner of the building. At the same time, no one compensates him for the expenses incurred.
If you have any questions, you can ask our land dispute lawyer.
Is it possible to organize a farm on the territory for private plots?
Under some conditions this is allowed, but you will first have to contact the local administration to obtain permission. Another significant condition is the location of the land outside the city.
The translation process begins with the preparation of a package of documents. It includes an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate confirming ownership of the land plot, an application in the form of the local administration, a passport of the owner of the territory, as well as documents confirming that the applicant is the founder or participant of the peasant farm. The documentation is transferred to the city municipality, after which it is necessary to wait for a decision.
A positive decision is made only if there are compelling reasons set out in the application.