Would you like to consult a lawyer for free? Write to the chat on the bottom right or call the hotline, calls within the Russian Federation are free. We accept questions any day of the week.
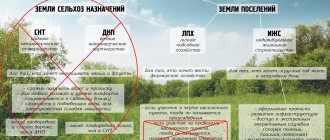
The Land Code of the Russian Federation strictly regulates the purpose of state lands and the types of activities permitted on them. A significant part of the country's territory is allocated to farmland. The owner of such a plot has the right to build any structures on his plot, depending on their intended purpose. A separate question is whether it is possible to build a house on agricultural land in 2021.
What can be built on agricultural land
Agricultural lands are located outside the boundaries of populated areas and are intended for agriculture and related purposes.
This definition is given in Art. 77 Land Code of the Russian Federation. A special legal regime for these lands has been established by law - priority in using for their intended purpose, preserving areas, and preventing erosion processes. On agricultural lands there are:
- Farmland (arable land, pastures, fallow lands, perennial plantings).
- Roads between farms.
- Forest plantations to protect land.
- Communications and water bodies.
- Buildings designed for storage and processing of agricultural products.
Taking into account the special regime for the use of agricultural land, and especially the best part of it - farmland, on the basis of Art. 77 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that the construction of residential buildings on these lands is not provided. Only structures and buildings necessary for production.
However, let us now turn to Federal Law No. 217-FZ of July 29, 2017, Art. 23, paragraph 11:
Click to enlarge image
Accordingly, the legislator does not introduce differences between garden plots of different categories. All current legislation regarding construction on garden plots, applicable to land in populated areas, equally applies to agricultural land.
Thus, the answer to the question whether it is permissible to build seasonal houses or houses for permanent residence on agricultural land depends on the type of permitted use of the site.
Currently, many residential and non-residential buildings located on garden plots, but included in agricultural land, are registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. And in connection with constant changes and additions to legislative acts, we clarify that on agricultural lands used for garden plots, it is still possible to build and register residential buildings, including under a simplified procedure.
Link to document:
Link to document:
VRI adjustment algorithm
The regulations for changing the classification of VRI are prescribed in Art. 39 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation:
- The interested party sends a petition to the local administration in charge of the site. the request is submitted with the mandatory attachment of documents for the allotment, as well as those necessary to identify the applicant.
- Based on local regulations in force in a particular area, a special commission is established to consider the request. In different regions of Russia, a different order from other territories is possible.
- The special commission conducts hearings to review the request and the advisability of issuing a permit. Hearings must be held publicly and with the participation of all persons who may be interested.
- After studying the issue, the commission makes a decision - refuse or allow - and makes recommendations on the intended use of a particular site.
- The decision must be published in the official publication for the publication of decisions of the local administration.
- After the commission makes a decision, the case falls under the jurisdiction of the head of the administration. Based on the recommendations and conclusions of the commission, the head makes his final decision - to allow or reject the request. A period of three days is given for this.
- Regardless of the result (refusal/permission), the outcome of the consideration of the issue by the head of the administration is also published.
For a sample application (see point 1) see here:
This method of obtaining permission is quite costly, since all costs necessary to conduct a hearing are borne by the person who requested the change in the VRI.
There are no guarantees that the decision of the commission and the head of the administration will be positive; they can always formally refuse. But in practice, local administrations usually do not object to issuing a building permit on agricultural land if a change in the VRI will have a positive impact on the general situation in the area.
This option for changing the purpose is good if it is necessary to carry out mass cottage or dacha construction on agricultural land that does not belong to code 2.1.
How to register a house on agricultural land
Let's consider the procedure for registering a house under the dacha amnesty, in accordance with Federal Law No. 267-FZ of 08/02/2019.
- Build a residential building. At the stage of inserted windows and doors, you can begin paperwork.
- Order a technical plan.
- Submit to Rosreestr through the MFC an application for registration of the house and the rights to it. You will need:
- technical plan;
- legal document for the land plot (if the right is not registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate);
- National tax.
If the right to land is confirmed in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, documents for the plot are not needed.
- You receive an extract from the USRN after 10-12 working days.
In connection with the extension of the dacha amnesty, until 2021, on agricultural land designated “for gardening,” it is possible to build and register a residential building without notification of the planned construction, without notification of the completion of construction, and without notification of the compliance of the constructed facility with acceptable parameters.
What will change in the near future?
In mid-2021, a new law No. 217-FZ was adopted, which will come into force at the beginning of 2021 and replace the current No. 66-FZ.
According to the document, plots with dacha VRI are classified as garden plots . Unlike another category of plots - garden plots, it is allowed to build real estate on garden plots.
Dacha consumer cooperatives will be reorganized into gardening partnerships.
At the local level, it is planned to create programs to support gardeners : providing territories with the necessary infrastructure, financing cadastral work.
For their part, gardeners will be required to pay membership fees. This applies to both members of partnerships and individual gardeners.
If there is no need to create a partnership, obtaining utility resources is carried out by concluding individual contracts with resource supply organizations.
The document records
permission to build permanent houses in garden areas and carry out registration there .
Thus, if the owner of a summer cottage today has problems with registration in a built residential building, then after the act comes into force, the problem will be solved .
This applies only to places of permanent residence, since the document introduced a new term “garden house” , which refers to objects of a seasonal nature.
Is it possible to build houses on the lands of private household plots and peasant farms?
Now let’s look at what other lands can be used to build residential buildings.
Construction is strictly prohibited on farmland. There are no town planning regulations for land.
Lands intended for private plots can belong to both agricultural lands and lands of populated areas. At the same time, it is possible to build residential, industrial, and domestic buildings within the boundaries of a populated area, but taking into account compliance with urban planning, fire safety and environmental standards. And the same purpose within agricultural lands allows the construction only of reclamation structures and cattle pens.
In Art. 4 of Federal Law No. 112-FZ dated 07/07/2003 states that buildings and structures cannot be erected on plots for private household plots located outside cities and settlements.
Click to enlarge image
The issue of building residential buildings with the possibility of registering residence on peasant farm lands is not an easy one.
There are no direct instructions in the law to permit the construction of houses on peasant farm lands. But there are no prohibitions either. Indirectly, Articles 6 and 11 of the Federal Law on Peasant Farms No. 74-FZ indicate the possibility of building houses. From the content of individual paragraphs of the above articles, we can conclude that in order to carry out the activities of peasant farms, the presence of buildings for non-agricultural purposes is allowed.
At present, it is not recommended to build residential buildings on peasant farm lands, since it will not be possible to legitimize them and obtain registration.
In April 2021, a bill was introduced to the State Duma of the Russian Federation clarifying the provisions of the law regarding the construction of residential buildings on peasant farm lands. It is planned that on a plot of land owned by a farm, the construction of a residential building will be allowed, no more than 3 floors and an area not exceeding 500 square meters. m. But the house will be the property of a peasant farm, and a plot under it cannot be formed. This project is still under consideration.
Link to document: “On personal subsidiary plots”
Link to document: “On peasant (farm) farming”
What is needed for this?
Of course, we will not talk about boards and nails, but about the necessary documents. How to legally register this or that building on agricultural land? Let's consider the main list of documents for obtaining a permit to build a residential building:
- Certificate of ownership of the plot with a cadastral number and an indication of the permitted type of activity (for peasant farms).
- If the plot is in temporary use, then the charter of the dacha cooperative or SNT.
- Cadastral plan indicating boundaries.
- A document confirming the purchase of the site, for example, a purchase and sale agreement.
Reference. The list may differ depending on whether it is drawn up by a private individual or the founder of a peasant farm. With these documents, the owner must go to the local head for permission.
If the decision is positive, the paper must contain the following information:
- a period for construction and an obligation for the owner to register the building immediately upon expiration of this period. If the building is not ready, it will be registered as is;
- type of building and its purpose, for example, a residential building;
- date, signature and seal.
Before obtaining a building permit, you need to conduct an analysis of the site. To do this, you need to find your site in the municipality on the map of urban planning zones. It will indicate exactly what type of permitted use is appropriate for the site.
It would not be amiss to do the same with the general plan of the city, where the planned communications and roads are indicated. Based on these 2 factors, it will be clear whether it is possible to build a house on your site or not.
If the house has already been built, then it is necessary to recognize it as residential through the court. To do this, a commission is initiated, which confirms the compliance of the premises with the status of a residential building. Based on its results, they file a lawsuit to recognize the building as a residential building.
In order to erect other buildings, permission and registration are not required. A barn, garage, bathhouse, cellar, summer kitchen and even a large cattle pen can be built without the consent of anyone. There are restrictions only for summer cottages, where the volume of buildings should not occupy more than 30% of the site.
It will be useful for owners and users of agricultural plots to read the following articles:
- Changes in the type of permitted use.
- Cadastral valuation procedure.
- How to draw up a site reclamation project?
- Privatization process.
- How to calculate tax and how does the rate vary?
- How to avoid a fine for non-use of a site?
- Redistribution Fund.
- Legal regime and features of use.
- Transfer of allotment from one category to another.
- The nuances of concluding a lease agreement.
You can’t build it, but you really want to. What to do?
If the current purpose of the site does not include the construction of residential buildings, there are two possible ways to fix this:
- Change the type of permitted use of the site.
- Change the category of land.
To find out what the purpose of the land is for the site you are interested in, use the Rosreestr portal - Public Cadastral Map or reference information. Information about the purpose of the site is also contained in the extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, the land certificate and other documents.
If gardening is provided for in the urban planning zone where the site is located in the main or conditionally permitted types of use, then the purpose of the land can be changed in the manner prescribed by law. Information about use cases is given in the extract from the PPZ, which can be ordered at the MFC.
Changing a category is a rather complicated path, and it is not always permissible to transfer agricultural land to another category. However, practice on this issue exists.
Read: Registering a house in SNT in 2021: step-by-step instructions
Consequences of misuse of allocated land
The state strictly monitors the intended use of land. And if we are talking about agricultural plots, then it is understood that the owner will cultivate these lands, grow crops or raise livestock.
If the territory is used inappropriately, a considerable fine will follow. Moreover, it will have to be paid not only by the owner, but also by all legal entities and officials who were caught illegally using the land. Illegal construction is punishable by fines based on percentage. The law has corresponding minimums for each of the citizens’ positions.
The land may also be confiscated. The court has the right to order the demolition of buildings if damage has been caused to property, the environment or third parties.
Let's sum it up
Summarizing the above, we can conclude:
- On agricultural lands designated “for gardening”, residential buildings can be built without approval from government agencies until 2021. Registration of the right to such a house is carried out only according to the technical plan for the structure and if there is a right to the land. If you do not have time to complete construction by 2021, you will need to carry out all necessary approvals with the administration by sending notifications. At the same time, the construction will be subject to requirements for compliance with urban planning and fire safety standards.
- Construction is not allowed on lands for private plots.
- There are no residential buildings on peasant farm lands.
- It is strictly forbidden to build on agricultural land.
Purposes of using agricultural land
In addition to the production of agricultural products and plant raw materials, agricultural plots are intended for:
- running a personal subsidiary plot;
- gardening;
- farms;
- breeding fish in isolated reservoirs.
This list does not include the construction of residential buildings or technical buildings . However, agriculture is impossible without infrastructure development.
Within the framework of certain legislative norms, the construction of barns, cowsheds, warehouses, barns, roads, and vehicle hangars is allowed.
Transfer of a plot of land from agricultural use to another status
If you are wondering about transferring land from one category to another, then be prepared to face financial costs. The authorities are not always willing to change the status of land, as this may affect the cadastral value of the site. If it decreases during the transfer, you may be asked to reimburse the difference in this cost.
A transfer requires compelling reasons. For example, if the site is located near a settlement and has long been used for residential development, or these lands are planned to be included in the settlement in the future.
Transferring a land plot to individual housing construction status opens up a number of advantages for its owner:
- your piece of land can be included in the plan for gasification, electrification, and can connect you to central heating, water supply and sewerage;
- They are required to build a road to your site and make access roads;
- the site will be included in the plan for the construction of other infrastructure.
Owners of plots classified as agricultural land are forced to carry out all communications and build roads at their own expense.
We recommend
Land for agricultural purposes and for gardening: legislation and practice. Seminar in Moscow + Online broadcast
Interest in agricultural lands has again intensified with the latest changes about them: Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 21, 2020 No. 1509 on the cultivation and use of forests on agricultural lands, including those not for agriculture; dated September 18, 2020 No. 1482 with new signs of non-use of agricultural land. As a result of legislative changes, starting from 2021, a more or less clear procedure has emerged for the registration of fish farming in ponds on agricultural land. During the same period, new regulations regarding garden plots and houses came into force. It is impossible to call certain other issues regarding agricultural land, for which regulations have not changed in recent years, unambiguously resolved. Current and problematic issues about agricultural land are discussed at this seminar.
Grounds for refusal
Your application may be denied for several reasons:
- the presence of restrictions that do not allow the transfer of land to another category in accordance with the law;
- ecologists did not give a positive conclusion based on the results of measurements of the necessary parameters;
- the intended purpose of the land does not correspond to the documents;
- The site is classified as special purpose land.
There are other reasons that may be an obstacle to transferring land to another category. However, you always have the right to go to court to challenge the refusal received.
Before buying a plot, carefully read the documents to find out whether the previous owner violated the intended purpose of the land. However, it is not always possible to purchase land for individual housing construction, so we have to decide on the transfer of agricultural land to a new status.
Cost and terms of translation
The most important cost item is compensation for the difference in cadastral value between an agricultural plot and a plot intended for individual housing construction. The tax base may also change, which will change the amount of the tax payment. You may also need to pay a state fee. Include here the costs of preparing documents and the costs of environmental assessment. These costs may vary in different regions, and in the Moscow region they will not be the smallest.
The time frame for consideration of the application is about 3 months. It depends on how much work there is at the moment in the administration, whether there are national holidays, etc. However, if you receive a refusal, such an answer will come within a month.
What is the difference between a garden and a residential house
The concept of a garden house was introduced by Law 217-FZ. You cannot register in such a house. It is intended for seasonal use and auxiliary use.
A house intended for year-round use will be considered residential. It must comply with the limit parameters specified in paragraph 39 of Art. 1 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation.
There are a number of common requirements for residential and non-residential buildings:
- the minimum distance from the boundaries of the site is 3 meters;
- height - no more than 20 meters;
- no more than 3 floors.
The house is not allowed to be divided into apartments, and during construction the norms and requirements for insolation and structural strength must be met.
The procedure for recognizing a garden house as a residential building was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2021 No. 1653 “On amendments to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 28, 2006 No. 47.”