Happy owners of garden plots located in picturesque areas often decide to build a residential or garden house on their land.
Some people need a place to relax while gardening, others dream of a cottage where it will be comfortable to stay all year round.
how legal such construction is and what difficulties may be encountered.
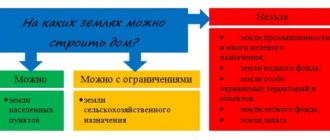
Legal norms for the use of garden land
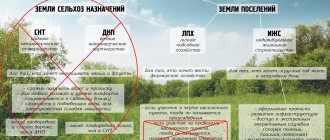
In accordance with the modern classification, there are 2 types of permitted use of land related to gardening:
- Type 1.5 involves conducting activities for the industrial cultivation of perennial crops.
- Type 13.2, in addition to agricultural activities, allows the construction of outbuildings and a garden house on the site.
Thus, only owners of plots with VRI 13.2 “Gardening” .
The category of land is also important: it is better if the plot is located on the territory of populated areas.
Additional information on garden plots located within the boundaries of populated areas can be obtained here.
If the category of land on the gardening plot is agricultural, then it will be very difficult to register there; only a garden house for recreation is allowed to be built there.
Detailed information can be found in the feature article.
Differences in the construction of a building for permanent and seasonal residence
The set of rules SNiP 30-02-97*, regulating garden buildings, highlights the difference between a garden and a residential building, in the possibility of registering residence in the latter.
Garden
Let's take a closer look at the features of a garden house:
- Is a residential property used for recreation
- Living inside it is temporary
- Such a residential building cannot be divided into separate apartments
- Construction is possible without obtaining a permit
A garden house can be considered suitable for living if the following are met:
- fire safety requirements,
- building codes and regulations (intact floors and walls, reliable foundation, protection from melt water),
- sanitary requirements (sufficient insolation, the presence of thermal insulation of walls to maintain optimal temperature inside the building),
- provision of engineering infrastructure (heating, lighting, water supply, sewerage, ventilation).
Residential
A residential building can be used as a permanent residence . Registration is permitted there.
When starting construction, it is necessary to clearly determine whether the building will later be designated as residential. Since the cost of refurbishment of a summer house practically corresponds to the construction of a new residential property.
There are currently several problems:
- many garden plots are not used for their intended purpose,
- owners do not develop plots due to the great difficulties with subsequent registration.
To solve them, Law No. 217-FZ was developed, which expands the concept of a garden plot and prescribes the possibility of building a garden or residential building on it.
At the same time, there are no restrictions on the category of land.
The law comes into force on January 1, 2019, after which unregistered seasonal country houses are also recognized as garden houses .
Re-registration of documents for constructed objects is carried out at the request of the owner.
The VRIs covered by the law include 13.2 and 13.3. Thus, owners of plots with such permitted use can construct garden and residential buildings.
Bringing the old VRI to the current classification is carried out at the initiative of the owner, but is not mandatory.
What kind of houses can be built
Many people, having purchased a dacha, begin construction on it. At the same time, they do not think about what kind of buildings can be erected on such land plots. And in vain! After all, unauthorized construction of buildings, even on land that is private property, can cause problems with the law.
It is important! To build a residential building on country land, you must obtain permission from the construction services, providing a design. Ignoring this rule can lead to the imposition of various sanctions on the owner of the house, including the demolition of the structure.
A summer cottage plot is primarily intended for growing cultivated plants. Despite this, it is permitted to erect residential buildings on the territory of such an allotment. However, it is important to consider that according to the law, all buildings in a dacha should not occupy more than 30% of the total area of the territory. The rest of the land should be used for its intended purpose, that is, planted with plants.
There are a number of buildings that can be erected at the dacha. At the same time, when choosing a building of one type or another, it is necessary to study all the requirements for it.
What kind of houses can be built in the country:
- Residential building up to three floors high;
- Garage;
- Bath;
- Various utility buildings.
At the same time, when constructing a residential building, it is necessary to comply with all SNiP requirements for residential buildings. Otherwise, you will not be able to register with it.
Is it possible to get a registration?
Current law No. 66-FZ does not provide for temporary or permanent registration in a garden house . However, the decision of the Constitutional Court changed the current situation and made it possible to register through the court.
If registration is necessary, the owner can act in one of two ways:
- Convert a non-residential property to a residential one by contacting the authorized body of the local administration. A redevelopment project will be required, agreed upon by several authorities.
- Recognize the garden house as residential, suitable for living, in court. After a positive decision, registration is possible.
The most popular method is a court decision ; it requires less financial costs and time.
For a property to be recognized as residential, it must comply with all
- sanitary,
- construction,
- firefighters
standards.
If the garden house is the only available place for permanent residence, the likelihood of a positive court decision increases.
The package of documents attached to the claim for filing a lawsuit includes:
- The conclusion of an expert organization on the compliance of the object with SNiPs, issued on the basis of title documents and a technical passport.
- Conclusion of the SES on the compliance of the facility with sanitary standards. If the authority does not issue the required certificate, it can be replaced with a similar expert opinion.
- Conclusion of OGPN on compliance with fire safety standards or a similar conclusion of a third-party organization.
- A document confirming the actual residence of a citizen in a garden house, for example, a certificate from the chairman of the SNT.
After a positive court decision is made, you must obtain a mailing address . To do this, contact the local administration.
If the plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area, then assigning an address does not cause difficulties. If the plot is located at a short distance, the owner can initiate its inclusion within the boundaries of the locality. This decision is made at the local leadership level.
It is also possible to obtain an address without including the plot of land in the boundaries of the settlement, but the procedure is more complicated. The postal address of such houses will coincide with the address of the site on which it is located.
After assigning a postal address, the owner initiates cadastral changes and receives a new technical passport for the garden house as a residential property.
Why do they want to extend the dacha amnesty again? How many unregistered dachas are there today?
The dacha amnesty, in fact, ended ahead of schedule on March 1, 2021, when the transition period for the new rules that introduced amendments to the Town Planning Code of August 4, 2021 ended. True, a bill has already been introduced to the State Duma to extend the dacha amnesty until March 1, 2022.
“Neither Rosreestr nor the Cadastral Chamber has such data. Local authorities should have information about how many unregistered individual houses and dachas there are.
Because the Unified State Register of Real Estate (USRN) contains information only about real estate objects registered for cadastral registration and registered rights to them. Since 2006, about 13 million property rights have been registered using a simplified procedure.”
Permission to build a residential building
A special document that allows the developer to carry out reconstruction and construction of permanent buildings is called a building permit.
Based on the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (subclause 1, clause 17), it is not required for construction on garden plots.
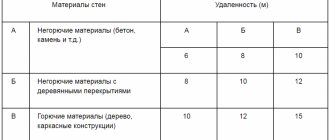
In order to avoid problems with neighbors during the construction of objects, it is necessary to take into account the rules for the location of buildings from borders, roads, and other objects according to SNiPs.
If it is planned to build an object, subsequently registered as an individual residential property, then the owner can obtain permission in a simplified manner in accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Part 9, Article 51).
To do this, he needs to contact the body authorized in the field of urban planning and submit the following documents:
- of a legal nature,
- urban plan,
- plot layout diagram with the designated location of the facility under construction.
The obtained permission will be submitted to the court.
Do greenhouses need to be registered?
Let's start with perhaps the most pressing issue in the last three months.
As soon as the owners of gardens and vegetable gardens learned about the mandatory registration (and, accordingly, taxes) of outbuildings on a foundation, questions began to pour in about what to do with greenhouses and sheds, toilets, etc. The resonance was so high that at the end of April the deputy chairman of the State Duma Irina Yarovaya asked the head of the Federal Tax Service Mikhail Mishustin to check the information and once again clarify “to pay or not to pay.” Specialists from BTI and Rosreestr responded as follows:
The need to register outbuildings, including greenhouses and sheds, depends on the purpose of the site.
“If the land is intended for vegetable gardening, then the construction of capital construction projects is not allowed on such plots. This means that all outbuildings (sheds, bathhouses, greenhouses, sheds, cellars, wells and other structures) cannot be erected as capital ones - on a solid foundation.
But garden plots can accommodate capital outbuildings that are firmly connected to the ground, that is, objects that cannot be moved without compromising their purpose. Rights to such objects are subject to registration.”
Conclusion: if greenhouses on a permanent foundation appear on garden plots, they will have to be demolished; if on garden plots, they will have to be registered.
Please note that the Russian Ministry of Economic Development is currently developing a bill that clarifies the criteria for classifying objects as immovable or movable things. According to the draft law, auxiliary buildings - sheds, greenhouses, etc. - will be considered improvements to the land plot or the main facility, for example, a residential building. Previously registered buildings can be excluded from the Unified State Register of Real Estate in a simplified manner at the request of the copyright holder.
Advantages and disadvantages
When deciding to start building your garden plot, it is important to understand all its pros and cons, and not act under the influence of a trend for your own country houses.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons, especially if you have no previous experience of living in a private home and caring for it.
What benefits does the owner receive when building a house on garden land:
- The plot is already owned or is much cheaper than for individual housing construction.
- Low payments for the use of utility infrastructure.
- No noisy neighbors or freeways outside your windows.
- Your own home is built in accordance with personal concepts of beauty, including exterior and interior decoration. Compliance with building codes is mandatory.
- The progress and speed of construction depends on your desire and financial capabilities.
- Favorable environmental conditions: clean air, water, land, natural sounds of wildlife around.
What are the main disadvantages of living on a garden plot:
- Building a house that meets all requirements and standards is expensive.
- SNT members pay considerable annual fees, which go towards maintaining infrastructure facilities.
- Low transport accessibility. Public transport outside the city runs on schedule, with large intervals. This leads to the need for each family member to have their own car.
- The infrastructure is poorly developed. Troubleshooting (broken wires, broken water tower) takes a lot of time.
- The peculiarities of the winter climate with heavy snow drifts impose restrictions on physical activity.
- Maintaining your home during the cold winter months requires significant effort.
- Registration in a garden house is possible only through the court.
- The arrangement of social and transport infrastructure, even for garden villages located within the boundaries of a populated area, is carried out at the expense of the owner-gardeners. The new law No. 217-FZ provides for co-financing programs for such expenses, but it is not yet known whether there will be funds for them in the regional budgets.
In some cases, the owner may initiate changes to the VRI of his plot. More details about the procedure can be found in a special article.
Read more about the main differences between garden land and individual housing construction in a separate article.
Approximate prices for country houses
When choosing the option with a frame or frame-panel house, the approximate price will be from 11 thousand rubles per square meter. Construction of a wooden house box will cost about 13,000 rubles. for one m2. For a building made of foam concrete blocks you will have to pay from 15 thousand rubles. for 1 m2. Brick house – 18,000/m2. Thus, knowing the total area of the designed house, it will not be difficult to calculate the final cost of construction. But these are only the costs of building walls. To this amount it will be necessary to add funds for laying the foundation, insulation, costs of laying the roof, and interior decoration of the premises.
In Moscow and the Moscow region there are a huge number of offers for the sale of ready-made turnkey country houses. Example: a house with dimensions width/depth/height - 6000/6000/3020 made of laminated veneer lumber is sold at a price of 367,000 rubles.
The final cost of the house depends on your preferences regarding the choice of additional options and can double or even triple.