Taxi drivers, motorcyclists, and young drivers are increasingly encountering problems when applying for an electronic MTPL policy. Why insurance companies put a spoke in the wheels of some categories of citizens and how you can defend your right to take out a policy, Izvestia looked into it.
Put aside panic: why the unprofitability of MTPL is growing
Insurers blame snow and expensive parts
Statistics vs Statistics
Despite the growing popularity of e-MTPL, not everyone can purchase a policy online. This is evidenced by statistics on the execution of contracts through the E-Garant system, which is provided by the Sravni.ru aggregator. The system helps the car owner purchase an MTPL policy if he was unable to do so on the website of the selected insurer. Over the six months of 2021, 8.8 million electronic MTPL policies were sold, about 1 million through E-Garant. Compared to last year, the popularity of E-Garant increased by 47%. And every month more and more contracts are executed through the system. There are two reasons, according to Sravni.ru analysts. Firstly, the increase in cases of “temporary system inoperability” of insurance companies in certain regions. Secondly, more and more insurance agents are preparing compulsory motor liability insurance for problem clients.
OSAGO needs a “Guarantor”_5
Photo: TASS/Sergey Bobylev
The Russian Union of Auto Insurers (RUA) advised to treat these statistics with caution.
OSAGO fortress: insurance policy for drivers may rise in price by 5% in 2021
Why the market is waiting for insurance costs to rise
“The number of MTPL policies issued in the first half of 2021 amounted to 20.1 million, and in the first half of 2021 - 19.2 million, that is, the number of MTPL policies issued in the first half of 2021 increased by 4.7%, which indicates how about the increase in the vehicle fleet in the Russian Federation, and about the absence of problems with the availability of the mandatory “vehicle citizenship”. The E-Garant system contains MTPL policies of 39 companies. This is a technical service, so RSA does not provide statistics on the execution of contracts through E-Garant,” the press service of the union reported. And they warned: data from unofficial sources may be incorrect and used for manipulation purposes.
Everything you need to know about vehicle insurance
Everything you need to know about vehicle insurance
A car is subject to various dangers: it can get into an accident, it can be stolen, etc. To protect themselves from losses, companies insure their vehicles. Auto insurance contracts can be of two types: property insurance contract (Article 930 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and civil liability insurance contract (Article 931 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In the first case, the insurance company compensates for damage caused by damage or theft of the car, and in the second, damage caused by a car that belongs to you, another company or a citizen. In this article we will focus on the features of accounting and taxation of two types of car insurance.
Compulsory motor third party liability insurance
What is OSAGO?
This type of insurance is mandatory when an enterprise is forced to carry it out due to the fact that it is obligated to do so by some law (clause 3 of Article 3 of the Law of the Russian Federation of November 27, 1992 No. 4015–1 “On the organization of insurance business in RF").
Federal Law No. 40-FZ of April 25, 2002 “On compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners” obliges companies with vehicles to insure the risk of their civil liability. Civil liability may arise as a result of causing harm to the life, health or property of others when using vehicles.
Owners of vehicles are those companies that not only own a car, but also use vehicles by proxy or rent them.
There is an exception though. An organization will not have to insure civil liability if it rents a vehicle “with a crew” (the car is maintained by its owner). In this case, all costs of insuring both the vehicle itself and liability for damage caused by it are borne by the lessor.
If a company uses the car of its employee under a bareboat rental agreement or under a gratuitous use agreement, then the owner of the vehicle, and therefore the insured, is the organization.
If an organization pays compensation to an employee for using a personal car for business purposes, then the employee himself must insure his civil liability. Rules of "motor citizen"
It is necessary to insure civil liability no later than five days after the organization receives the right to own a vehicle (Clause 2, Article 4 of Law No. 40-FZ). Otherwise, the car will not be allowed for technical inspection and will not be registered with the traffic police.
The rules for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2003 No. 263.
In order to insure civil liability, you need to enter into an agreement with an insurance company that has the appropriate license. To do this, the organization must submit the following documents or copies thereof to the insurance company:
- application for concluding a compulsory insurance agreement in the form given in Appendix No. 1 to the Insurance Rules;
- certificate of registration of a legal entity;
- passport or registration certificate of the vehicle specified in the application for concluding an insurance contract;
- driver's licenses of persons who are allowed to drive a car, as well as documents confirming the driver's right to drive this vehicle.
A vehicle may have several owners - owner, lessee, etc.
One of them has the right to insure the liability of all the others. To do this, they need to be listed in the contract with the insurance company. After the contract is signed, the insurance company must present the owner of the vehicle with an insurance policy in the form given in Appendix No. 2 to the Insurance Rules, as well as a special state-issued sign. This sign must be placed on the vehicle in the lower right corner of the windshield.
In the event that an insurance policy or a special sign is lost, the insurance company is obliged to issue a duplicate of these documents. This is done for a fee, the amount of which is determined by the cost of making duplicates.
The insurance company must also issue two accident notification forms to the organization.
It must be filled out in the event of an accident and handed over to the insurer within 5 days from the date of the accident. The civil liability insurance contract is concluded for a period of at least one year (Article 10 of Law No. 40-FZ). Then its validity will be extended until the policyholder notifies the insurance company of the termination of the contract. Moreover, he must do this no later than two months before the contract expires. On the other hand, the contract may be terminated if the vehicle owner is more than 30 days late in paying insurance premiums for the next year.
Insurance premium
Vehicle owners who have insured their civil liability must pay premiums to the insurance company. This is the so-called insurance premium, which is paid in one-time or partial payments. Its size is calculated based on insurance rates, which are established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 8, 2005 No. 739.
Insurance rates will be the base rate and odds. The insurance premium is equal to their product. The amount of insurance depends on the category of the owner of the car (individual, legal entity or taxi owner). The basic tariffs for them are 1,980 rubles, 2,375 rubles. and 2,965 rub. respectively.
In addition, the size of the tariff also depends on the age and experience of the driver, and the place of registration of the car. For example, in Moscow this coefficient is 2.
The make of the car and its age are not taken into account, but the term of the contract and the period of use of the car are taken into account.
The amount of insurance premium for cars, taxis (including minibuses) is today calculated using the following formula:
SP = TB x KT x KBM x KVS x KO x KM x KS x KP x KN,where TB is the base insurance rate in rubles (see Table 1).
Insurance rates coefficients depending on:
CT - from the territory of primary use of the vehicle;
KBM - on the presence or absence of insurance payments in the event of insured events that occurred through the fault of the policyholder during the period of validity of previous compulsory insurance contracts. If the insurance contract is concluded for the first time, then the BMR is taken equal to 1;
PIC - from the owner of the car (individual/legal entity), age and length of service of the driver;
KO - on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle;
KM - from the engine power of a passenger car (see Table 2);
KS - from the period of use of the vehicle; CP - from the insurance period (see Table 3);
KN - from the good faith of the policyholder. Its value depends on how reliably the person provided the information necessary to conclude a contract, or information about the circumstances of the case in an accident.
Table 1
Table 2
Coefficients applied depending on engine power
Table 3
Insurance rate coefficients depending on the insurance period
If the insurance company convicts the organization of providing it with false information, which resulted in the payment of an insurance premium in a smaller amount, then it will apply a CI coefficient of 1.5.
The same coefficient will be applied if the accident was committed intentionally or the circumstances of the accident were deliberately distorted in order to increase the insurance payment.
Finally, the insurance company can also apply the specified size of the KN coefficient when harm is caused under circumstances that were the basis for filing a regressive claim.
Example 1
The car belongs to Stalker LLC. The base rate of the insurance tariff (TB) for it is 2,375 rubles. The car was purchased and registered in 2006.
The territory of primary use is Moscow (CT = 2).
The contract of compulsory motor third party liability insurance is concluded for the first time (KBM = 1).
The age of the drivers indicated in the insurance policy is 27 years old, driving experience is 1.5 years (DIC = 1.15).
Two drivers specified in the compulsory insurance contract are allowed to drive the car (CO = 1).
Engine power is 119 hp. With. (KM = 1.3).
The period of use of the car is 12 months a year (KS = 1).
The insured is recognized as being in good faith, therefore the KN coefficient is not applied.
SP = 2,375 rub. ? 2? 1 ? 1.15? 1 ? 1.3? 1 = 7,101.25 rub. (in year).
Note! The amount of the insurance premium cannot exceed three times the base rate of insurance tariffs, adjusted by the regional coefficient. In the example given, the maximum amount of the insurance premium should not exceed RUB 14,250. (RUB 2,375 ? 2 ? 3).
In tax accounting, expenses for compulsory types of insurance are included in other expenses within the limits of insurance tariffs, which are approved in accordance with Russian legislation.
This is established by paragraph 2 of Article 263 of the Tax Code. Thus, as part of other expenses, an enterprise can include the amount of insurance calculated for it at the established rate.
If the tariffs are not approved, then the costs of compulsory insurance are included in other expenses in the amount in which they were actually paid.
Please note: in some cases, tax authorities take the exact opposite position. Article 263 of the Tax Code does not directly indicate that it applies not only to the costs of property insurance, but also to the costs of compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicle owners. This gives tax authorities reason to believe that vehicle insurance costs do not reduce taxable profit. They believe that an organization can reduce its taxable profit only by the amount of expenses for compulsory types of property insurance.
New information about insurance coefficients
At the end of last year (November 8, 2006), the State Duma of the Russian Federation adopted in the third reading amendments to the law “On compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners,” which establish the procedure for applying the coefficient depending on the presence or absence of insurance payments (“ bonus-malus"). The new law will come into force 90 days after its publication.
The current version of the “Law on Compulsory Civil Liability Insurance of Vehicle Owners” (No. 40-FZ) provides the following description of the KBM coefficient:
"2. The coefficients included in the insurance tariffs are set depending on: ... the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers when carrying out compulsory civil liability insurance of the owners of the specified vehicle in previous periods.”
The version of the bill adopted in the second reading proposes the following option:
"2. The coefficients included in the insurance tariffs are set depending on: ... the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers in previous periods when implementing compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owners of this vehicle, and in the case of compulsory insurance for limited use of the vehicle, which involves driving means only by the drivers specified by the policyholder - the presence or absence of insurance payments made by insurers in previous periods when implementing compulsory civil liability insurance for each of these drivers.”
According to the deputies, this innovation will help eliminate injustices in the application of the bonus-malus coefficient, namely when the accumulated bonus was lost when the policyholder, an individual, changed the vehicle.
In fact, now accident records must be kept for each driver separately, that is, all accidents that a driver commits in any car will increase the cost of compulsory motor insurance for him. For example, a driver violated traffic rules at work (driving a Kamaz) and got into an accident - now even when insuring his personal car, he will pay an increasing bonus-malus coefficient.
Moreover, the tariff will be increased for all cars where our “emergency” driver is listed as a person allowed to drive. Today, the average Russian driver is allowed to drive three cars. Consequently, on average, an insurance company, having made one payment under MTPL, will have the opportunity to increase the rate under three contracts at once.
If this bill is adopted, the meaning of the Insurance Certificates, which insurers must issue to policyholders upon termination of a contract, will be lost. After all, a driver can be simultaneously insured by several insurance companies (included in the policies of different cars). Therefore, to prove your positive insurance history, you need to bring certificates from all insurance companies! This problem can be solved with the help of a single computer database, but will insurers be able to implement this database within 90 days after the adoption of the law, and most importantly, ensure access to it for all selling divisions and agents throughout the country?
Information about the policyholder history of each driver will now be needed not only when moving from one insurance company to another, but also when renewing a contract in the same insurance company, making changes to the contract, or adding a new driver to the policy. All this will significantly complicate these procedures and, accordingly, increase the time required for processing documents. For example, if today almost every agent can add a new driver to the policy, then after changes in the law this can only be done after receiving a request from the database - most likely, the time frame for making changes to MTPL policies will increase to 2 days.
Procedure for receiving insurance compensation
To receive insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance, an organization must notify insurers of the occurrence of an insured event within five working days after an accident. To do this, you need to submit to the insurance company:
- an application for insurance compensation in any form;
- notification of an accident (the form of this document was approved by order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation dated June 14, 2003 No. 414);
- certificate of participation in an accident (Appendix No. 12 to the Methodological Recommendations for organizing the activities of traffic police units in proceedings on cases of administrative offenses (letter of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation dated June 18, 2003 No. 13/ts-72));
- a copy of the protocol on the administrative offense (Appendix No. 1 or No. 2 to the Methodological Recommendations).
After the injured party receives the remaining documents, they are also transferred to the insurance company. This is about:
- certificate of participants in the accident (Appendix No. 31 to the Methodological Recommendations);
- copies of the resolution in the case of an administrative offense in the event of an administrative offense;
- documents confirming the organization’s ownership of damaged property or the right to insurance payment in case of damage to property owned by another person;
- the conclusion of an independent examination on the amount of damage caused;
- documents confirming payment for the services of an independent expert, if payment was made by the victim;
- documents confirming the provision and payment of services for the evacuation of a damaged vehicle from the scene of an accident to the place of its repair or storage;
- documents confirming the provision and payment for services for storing damaged property from the day of the accident until the day the insurer conducts an inspection or independent examination.
If property was damaged during an accident, then its remains must be submitted to the insurance company.
She, in turn, must conduct an inspection and independent examination of the damaged property. To do this, she is given 5 working days from the date of receipt of the application for insurance payment from the victim. If the vehicle is severely damaged as a result of an accident and it is impossible to deliver it to the insurance company, then the inspection and assessment of such property within the same time frame is carried out at its location.
Please note that insurance compensation will be paid to the organization only after providing a complete package of documents.
Within 15 days from the date of receipt of documents confirming the insured event, the insurance company must compensate the losses to the injured party or send a reasoned refusal to pay insurance compensation.
Amount of insurance compensation
If damage is caused to life and health, then the victim must be compensated for the lost earnings (income) that he had or could have had on the day the harm was caused to him. In addition, the insurance company must compensate for additional expenses incurred:
- for treatment;
- additional food;
- purchasing medicines;
- prosthetics;
- outside care;
- Spa treatment;
- acquisition of special vehicles;
- preparation for another profession.
As part of the insurance payments, damage caused as a result of the loss of a breadwinner, as well as funeral expenses, are also compensated.
If damage is caused to property, the insurance company must compensate the victim for its real value, which is determined depending on the condition of the property. In case of complete loss of property, expenses can be reimbursed in the amount of its actual value on the day of the accident. This also applies to those cases when the cost of restorative repairs of a vehicle involved in an accident is equal to or greater than its value before the accident.
If the car is not completely damaged, then the damage is compensated in the amount of restoration costs, that is, those costs that are necessary to bring the property to the condition in which it was before the insured event. These include:
- materials and spare parts necessary for repair work;
- expenses for vehicle repair work.
If, as a result of an accident, not only the vehicle, but also real estate located at the site of the accident is damaged, then the organization’s expenses for the delivery of material and spare parts to the place of repair of this property, as well as the costs of delivering repair crews to the place of repair and back, are also subject to compensation. .
The insurance organization determines the amount of expenses taking into account the wear and tear of parts, assemblies, assemblies and parts used during restoration work. Vehicle repair costs are paid based on the average prices prevailing in the relevant region.
In addition, the insurance company will reimburse the organization for the costs of evacuating the vehicle from the scene of the accident to the place of repair or storage, as well as the costs of storing it from the day of the accident until the day of inspection by the insurer or until the day of an independent examination.
The maximum insured amount under compulsory motor liability insurance, within which the insurer will compensate the insured for the damage caused, is 400,000 rubles. (Article 7 of the Law on Compulsory Insurance). From this amount to compensate for damage caused:
- life or health, if there are several victims, 240,000 rubles, one victim - no more than 160,000 rubles;
- property, if there are several victims - 160,000 rubles, one victim - no more than 120,000 rubles.
The specified insurance amounts are paid in each insured event. This means that if a car is involved in several accidents within a few hours, then for each of them the maximum insured amount will be 400,000 rubles.
If a criminal or civil case is opened as a result of an accident, the amount of payment may depend on the results of the proceedings in these cases. The period of insurance payment in this case is extended until the end of this proceeding and the entry into force of the court decision. The same mechanism applies when initiating a case of administrative violations. At the request of the policyholder, the insurer must issue a calculation on the basis of which the amount of the insurance premium was determined.
Voluntary car insurance
Features of voluntary car insurance
Insurance, which the company carries out at its own discretion, is voluntary. The company can insure the car against theft or damage. To do this, you need to conclude a property insurance agreement with an insurance company. The contract must indicate the following main points:
1. Duration of the contract (usually one year).
2. The amount of insurance premiums and the procedure for their payment.
3. Insured events (situations in which the insurance company pays compensation).
4. Sum insured (the maximum amount that can be paid in an insured event). It should not be more than the value of the insured vehicle.
The insurance contract begins to be valid on the day the organization pays the first installment (Clause 1, Article 957 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the company is issued an insurance policy. It will need to be presented to the insurer in the event that something happens to the car.
The company can also insure a rented vehicle if its owner has not done so. After all, it is the tenant who will have to reimburse expenses in the event of damage (Article 669 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting and taxation
Expenses for voluntary insurance of vehicles that are used to generate income are also taken into account when calculating the tax base for income tax (subclause 1, clause 1, article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, this fully applies to rented cars.
The terms of the insurance contract may provide for payment of the insurance premium in a one-time payment. Then, for contracts that are concluded for more than one tax period, expenses are recognized evenly over the term of the contract.
In accounting, vehicle insurance costs are expenses for ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 10/99). Insurance costs must be reflected in the accounting period to which they relate, regardless of the time of their actual payment. The enterprise reflects a one-time payment for the year on account 97 “Deferred expenses”, and then monthly writes off 1/12 of its part to the accounts of production and sales costs.
The amount of insurance compensation received by an organization upon the occurrence of an insured event is not subject to VAT.
Taxable profit can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums (Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It does not matter which vehicle the organization insured - its own or a rented one. The main thing is that it is used in production activities. A prerequisite for recognizing such expenses is the actual payment of the insurance premium.
The procedure for tax accounting of insurance premiums depends on the method by which the organization accounts for income and expenses. If the accrual method is used, then in tax accounting, as well as in accounting, insurance premiums must be included in expenses in the reporting period to which they relate. This means that when paying an insurance premium in a one-time payment, insurance costs are included in other expenses evenly throughout the entire term of the contract.
Tax accounting of vehicle insurance costs can be maintained using accounting data.
Example 2
On November 1, 2006, Zigzag LLC entered into an agreement to insure a passenger car against theft for a period of one year with a one-time payment of an insurance premium in the amount of 18,000 rubles. The organization determines income and expenses using the accrual method. The monthly amount, which is included in expenses, both in tax and accounting, will beRUB 18,000: 12 months. = 1,500 rub.
The following entries were made in the accounting records of Zigzag LLC:
Debit 97 Credit 76 subaccount “Calculation for property insurance” - 18,000 rubles. — the enterprise’s debt under the insurance contract is reflected;
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculation for property insurance” Credit 51 - 18,000 rubles. — reflects the enterprise’s debt under the property insurance contract.
Monthly:
Debit 26 Credit 97 - 1,500 rub. — part of the costs of car insurance is included in general business expenses.
In tax accounting for 2006, the amount of insurance payments in the amount of 3,000 rubles must be included in other expenses. (RUB 1,500 = 2 months). And in 2007, the amount of 15,000 rubles will be included in other expenses. (18,000 rubles - 3,000 rubles).
Organizations that use the cash method to determine income and expenses can reduce their taxable profit by the entire amount of insurance expenses in the month when the premium was paid (clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, tax accounting data will not coincide with accounting data. Compulsory motor third party liability insurance allows you to transfer compensation for damage caused to third parties to the insurance company. This means that if the organization’s vehicle causes harm to the life, health or property of the victim, then the insurance company will compensate for the damage caused.
Please note that the insurance company will not compensate for damage that was caused as a result of force majeure or as a result of the intent of the victim.
Thus, insurance compensation is the amount that is paid in the event that the vehicle is damaged due to extraordinary circumstances. The fact that extraordinary events actually occurred must be documented.
Accounting and tax accounting of insurance payments
The expenses incurred by the organization in an insured event are extraordinary expenses (clause 13 of PBU 10/99). Therefore, they need to be taken into account in account 99 of the “Extraordinary Expenses” subaccount. Insurance compensation paid to an organization is considered extraordinary income. It must be taken into account in account 99 of the “Extraordinary Income” subaccount. The amount of compensation depends on the damage caused to the vehicle.
In tax accounting, compensation is included in non-operating income that increases taxable profit (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the expenses incurred by the enterprise due to an insured event are included in non-operating expenses (subclause 6, paragraph 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 3
In September 2006, Grom LLC insured its car in case of an accident in the amount of 290,000 rubles. In December of the same year, the car was badly damaged in an accident. The car cannot be repaired or restored. This is confirmed by an accident report issued by the traffic police, as well as a certificate received from an independent appraiser. The company decided to write off the car. An insurance claim was received from the insurance company.
The initial cost of the car in accounting and tax accounting is 400,000 rubles. The amount of depreciation accrued at the time of the accident, both in accounting and tax accounting, is 100,000 rubles. Grom LLC paid 2,000 rubles for conducting an independent examination.
In tax accounting, Grom LLC uses the accrual method to determine income and expenses.
The following entries were made in accounting:
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance” Credit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary income” - 290,000 rubles. — insurance compensation has been accrued;
Debit 51 Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance” - 290,000 rubles. — insurance compensation has been transferred;
Debit 01 subaccount “Retirement of fixed assets” Credit 01 subaccount “Fixed assets in operation” - 400,000 rubles. — the original cost of the car has been written off;
Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 100,000 rubles. — the amount of depreciation accrued at the time of the accident is written off;
Debit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary expenses” Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 300,000 rubles. (400,000 rubles - 100,000 rubles) - the residual value of the car is written off;
Debit 99 subaccount “Extraordinary expenses” Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with other creditors” - 2,000 rubles. — the cost of an independent examination is taken into account;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with other creditors” Credit 51 - 2,000 rubles. — paid expert services.
In tax accounting, insurance compensation (290,000 rubles) is included in non-operating income. And the residual value of the car and the cost of the examination (300,000 rubles + 2,000 rubles) are included in non-operating expenses. Consequently, in December 2002, the taxable profit of Grom LLC will be reduced by 12,000 rubles.
When rental property is insured, the accounting for compensation depends on who the contract is in favor of.
After all, an insurance contract can be concluded both in favor of the tenant and in favor of the lessor (Article 930 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If insurance is paid to the landlord, it is not reflected in the tenant's accounting. If the insurance compensation is received by the tenant, then the accounting and tax accounting of this operation is exactly the same as in the case when one’s own property was damaged.
F.N. Filina, economist-analyst
Unlock access to the private part of Clerk with a Premium subscription. Get hundreds of webinars and online courses, unlimited consultations and other proprietary content for accountants.
Hurry up to subscribe with a 20% discount until October 15, 2021. Read more about “Premium” here.
Technical glitches occur constantly
Meanwhile, problematic categories still exist. The head of the MotoMoscow movement, Andrei “Prorector” Ivanov, notes that difficulties with obtaining compulsory motor insurance are traditional for all bikers without exception, regardless of age, motorcycle model and region.
OSAGO needs a “Guarantor”_2
Photo: IZVESTIA/Tatyana Polevaya
Bottom line: the Supreme Court decided to pay a record penalty under compulsory motor liability insurance
Will the decision be the basis for changing judicial practice?
“It is impossible to independently issue a policy on the RSA website, as well as on the websites of the insurance companies themselves; technical glitches constantly occur there. I didn't manage to do it myself. The sites confidently refused to remember what was typed, forcing me to enter the same thing a dozen times, or lost the data of the policy or diagnostic card. As a result, everyone is forced to turn to familiar agents who take over the registration, constantly emphasizing that they are experiencing difficulties with processing and transferring the policy to the company. They also say that they are criticized for the large number of policies for two-wheelers,” states the motorcyclist.
Ivanov notes that even when his colleagues try to apply for insurance offline, that is, they come to the office of the insurance company, they are given a referral for an examination at the other end of the city, or even to New Moscow, if we are talking about the capital.
Who can be a car insurer under the motor insurance policy?
Any OSAGO insurance form has special lines in which you need to enter information about the owner of the vehicle and the insured. In this regard, the person taking out the insurance may not be the owner.
Related article: Do I need to change insurance when changing numbers?
The following have the opportunity to obtain auto insurance for a specific car:
- master;
- trusted person (family member, colleague, friend);
- driver driving a car for work.
Therefore, it does not matter who the policyholder is in the insurance and MTPL policy, because any person acts as such. There are no special instructions in the regulations regarding the type of persons who have the opportunity to insure a vehicle, therefore insurance organizations accept applications from individuals. and legal persons The insured is any individual. and legal the person who provided the documentation and paid the premium to the insurer.
Taxi drivers also have difficulties
Taxi drivers face the same problems. For example, Facebook user Alla Zefirova asks for help from the Internet community:
“...It took a week to issue compulsory motor liability insurance for taxis. Unsuccessfully.<…> Everything is aimed at not taking out a policy. <…> Share contacts who insures taxis. <…> Two insurance companies are conducting inspections in Zelenograd and Troitsk.”
OSAGO needs a “Guarantor”_3
Photo: IZVESTIA/Konstantin Kokoshkin
Simple things: OSAGO was untied from technical inspection
The policy can be purchased without a diagnostic card
In such situations, experts advise immediately writing a complaint to the Central Bank of Russia, which supervises, among other things, the insurance market.
How to get a policy without the owner of the vehicle
The owner's visit to the insurance company is not required. But his data is certainly recorded in the document.
To purchase a policy you will need the following documents:
- statement;
- Driver's UI;
- passport of the driver and owner of the vehicle;
- PTS;
- previously issued policy;
- power of attorney.
To purchase a policy, you do not need to provide transport for inspection. It must be remembered that it is not the vehicle that is subject to insurance, but the liability of the person insured to other participants in the vehicle liability.
Armenian registration, Russian owner
Another problematic category of car owners are Russian owners of cars with Armenian license plates. Some time ago, a Russian citizen could purchase a car in Armenia at a very favorable price, pay duties at Armenian rates, which were much lower than Russian ones, and calmly cross the border without declaring the car or registering for temporary import. Some also liked the fact that the Armenian registration plate gave immunity against traffic cameras. In addition, there was no need to pay Russian transport tax. At some point, there were a lot of such cars, and in 2021, massive claims from the traffic police and customs authorities began against their owners.
OSAGO needs a “Guarantor”_1
Photo: IZVESTIA/Andrey Ershtrem
They will answer without wear and tear: how to get more for repairs under MTPL
Car owners have a chance to receive their full cost of repairs without taking into account wear and tear under MTPL
“In most cases, cars with Armenian license plates belong to citizens of the Russian Federation permanently residing in the Russian Federation. As far as I know, electronic policies are not issued for such cars. A limited number of insurance companies issue paper forms. But since there is a point that the car is registered in another state, but belongs to a Russian citizen, insurers use increased coefficients,” comments international law expert, lawyer Yuri Demin.
Their main difference
The main differences between the beneficiary and the mortgagor are due to the following:
- the policyholder is considered to be a person who has entered into an agreement with the agency; registration of compulsory motor insurance by a non-owner who has paid the motor third party liability insurance premium can buy compulsory motor insurance without a driver's license;
- the owner of the car is not given the rights to adjust, make changes, extend or terminate the contract, but he receives a cash payment or other material compensation.
In human terms, the policyholder is the owner of the contract, and the owner is the owner of the car. However, if a road accident occurs, the latter receives the compensation amount from the bailor.
Internal order or program ban
When applying through E-Garant, 95% of policyholders receive compulsory motor liability insurance. The remaining 5% are refusals due to incorrect data entry or invalid documents, a source in the insurance brokerage business told Izvestia.
The algorithms of insurance company websites, according to the source, are configured in such a way as to weed out unprofitable categories of citizens. Out of ten applications from the “non-segment”, only three are approved, and seven are redirected to E-Garant to transfer the application to another insurance company. Thus, the total number of unprofitable users is evenly distributed across all insurance companies.
OSAGO needs a “Guarantor”_4
Photo: TASS/Alexander Ryumin
The “non-segment” includes young drivers under the age of 23 and with a total experience of less than three years, as well as taxis, motorcycles, special equipment and trucks owned by individuals. These categories of drivers will also have problems with offline registration of a policy. Many insurance agents have a ban on processing “non-segments” - this may be an internal order or a program ban. If a broker or insurance agent continues to work with such clients, he may be fined, deprived of bonuses, or even terminate the contractual relationship, the source said.
Point of deception: insurance companies named the most popular fraud schemes
In 2021, the activity of attackers will increase to the level of 2019
Comments: 1
Your comment (question) If you have questions about this article, you can tell us. Our team consists of only experienced experts and specialists with specialized education. We will try to help you in this topic:
Author of the article Irina Rusanova
Consultant, author Popovich Anna
Financial author Olga Pikhotskaya
- Alexandra Nikolaevna
08/07/2021 at 21:23 Has the age limit of the policyholder and the life insurance period been established?
This seems natural, because there are statistical data on average life expectancy, survival, etc. Reply ↓
"Come tomorrow"
In offices, there is also an unspoken rule not to issue policies to unprofitable categories. Under any pretext, managers will try to escort such a driver out.
“There can be many ways: “come back tomorrow”, “we have run out of policies”, “the database is not working”, etc. If a person is smart, he will ask for a written refusal. Most likely, at this moment the manager will understand that it is better to issue a policy and not enter into a conflict situation, since he had no right to refuse the person. If the insurance representative stays until the last minute, the car owner asks to justify why he was refused in writing. If there is a refusal again, he writes a complaint with the content: “Please sort it out. I, my name, came to the office to get a compulsory motor liability insurance policy,” and they are required to supply the incoming number. Then they answer him with an outgoing number, and with it you can go to court or, more often, to get your MTPL policy, since the answer will come with a polite invitation to the office for registration,” concludes a source in the insurance brokerage business.
Who can renew insurance
The vehicle can be operated not only by its owner or policyholder, but also by a third party who has a notarized power of attorney for the right to drive it. In addition, it must have insurance.
The agreement can be signed for a period of one year, or a shorter period with its extension. Here the question also arises about the extension of compulsory motor insurance by the owner of the vehicle. He will be able to do this only if he is a party to signing the insurance contract.
A significant role is played by the change of ownership of the car. Therefore, doubts about whether it is necessary to reissue the policy when the owner changes should be put aside.
The owner of the insurance document can renew it online. To do this, you need to go to the insurance company’s page and go through the policy renewal procedure. He can also change the owner’s electronic form or make other adjustments.
Policy upon sale
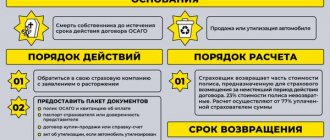
After the sale of the vehicle, part of the insurance price is allowed to be returned. This is provided for by the Federal Law on Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance during the period of contract termination. Cases of termination of the agreement are considered in clauses 1.13-1.16 of the car insurance rules.
In this article, a refund of part of the insurance price is possible if:
- sale of the vehicle by the owner;
- loss of a car;
- restriction of the work of the insurance organization.
The procedure for returning money most often does not cause any difficulties; disputes arise only over the amount of the amount to be returned.
To return part of the funds unused under insurance, a person needs to contact the insurance company where the policy was purchased and submit an application.