1
After the death of citizens, property remains: movable and immovable. And if the personal belongings of the deceased are almost of little value, real estate attracts many heirs. Indeed, who doesn’t want to become the owner of a separate apartment or inherit a plot of land?
The law defines a strict procedure for inheriting real estate. The property cannot be received by strangers - according to the law, it is distributed among close relatives, but there are exceptions in the form of a will. Let's look at how to inherit real estate correctly, where to go, what to prepare and how much will it cost? The information in our article will be useful not only to heirs, but also to property owners.
What are the types of inheritance objects?
As stated in Article 1112 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the objects of inheritance include any property that belonged to the deceased during his lifetime. The inheritance estate can be formed by the following property:
- Real estate - land plots, residential buildings, apartments, dachas and other buildings. Real estate must be registered with government agencies in accordance with the established procedure.
- Vehicles – cars, motorcycles, boats, etc., officially registered.
- Things and objects acquired by the deceased during his lifetime - furniture, clothing, building materials, jewelry.
- Securities – shares, bills of exchange and other documents issued in the name of the testator.
- Bank deposits, including interest accrued on them.
- Borrowed amounts - funds lent to the deceased are subject to return to the heirs.
- Cash Savings – Applies to any cash savings, royalty payments, pension benefits and earnings.
- Compensation received by the deceased in connection with damage caused to life, health or property.
The deceased's ownership of the listed objects of inheritance must be documented. For real estate and vehicles, such confirmation is a purchase and sale agreement, for securities - the corresponding registration. The purchase of things and items can be confirmed by payment documents.
In accordance with the provisions of Art. 234 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is possible to obtain ownership of property by acquisitive prescription - if this or that thing belonged to a person for a certain period of time in compliance with the obligations provided for by law, amounting to:
- for real estate - from 15 years or more;
- for the rest – from 5 years.
In addition to movable and immovable property, cash savings and documents, there is a transfer into the possession of the heirs of the rights and obligations of the testator:
- unclosed loans and borrowings;
- arrears in payment for services of utility organizations;
- borrowed funds from individuals and legal entities.
In accordance with Art. 1175 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the liability of the heirs in relation to the material obligations of the testator extends to the extent of the value of the inheritance received from the deceased.
Art. 1112 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation excludes from the list of objects of inheritance property obligations assigned directly to the person of the deceased. This applies to alimony payments, payments for compensation for harm to life and health, and other obligations, the transfer of which by inheritance is not provided for by the norms of the current legislation.
The noted Article 1112 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that hereditary property does not provide for the attribution of non-property rights and intangible benefits to it.
The procedure for registering real estate as property by inheritance
Real estate objects undergo mandatory state registration with the authorities of Rosreestr (formerly the Cadastral Chamber). Documents can be submitted to one of the territorial branches of Rosreestr or choose an intermediary represented by the State Budgetary Institution “My Documents” (MFC). Such centers operate on the principle of a “one-stop shop” - documents are accepted from one specialist in the shortest possible time (5-10 minutes).
Procedure
Procedure for registering rights to real estate:
- Assess the property - find out its cadastral value to calculate the state duty.
- Prepare documents, pay the state fee, make an appointment with a notary.
- Obtain a certificate of inheritance.
- Submit an application and documents to the MFC or Rosreestr (at the location of the facility).
- Pay the state fee and wait for registration.
- Receive an extract from the Unified State Register of Property Rights.
Application (sample) 2021
Registration of rights occurs upon the application of a citizen. Samples of the required forms can be downloaded from the Rosreestr portal.
The application contains:
- name of the registering authority (State Registration Service);
- The requested legal action is to re-register ownership of an apartment or land;
- information about the copyright holder;
- the essence of the heir's request;
- the basis for registration of the right is a certificate of the right to inheritance;
- type of registered property;
- location of real estate - address, floor, building, living space, share in the right;
- method of submitting an application - paper or electronic version, through a representative;
- list of attached documents (appendices);
- date, signature of the next owner of the property.
Documentation
The application for registration of property rights must be accompanied by:
- a copy of the passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- title/technical documents for real estate - usually this is a privatization agreement, sale and purchase agreement, deed of gift;
- certificate of right to inheritance - with the seal and signature of a notary;
- agreement on the division of property between heirs (yes, yes).
- proof of tax payment - a receipt (not required in all cases).
If the papers are submitted by a representative of the applicant, then an additional notarized power of attorney to conduct the inheritance case will be required. In case of redevelopment, appropriate permission from the BTI will be required.
If a minor child inherits property, legal representatives act in his interests. When submitting an application, you will additionally need identification of the parent/guardian and the child's birth certificate.
After submitting a package of documents, the applicant is given a receipt. It indicates the date of issue of the extract from the Unified State Register, i.e. the day when you can come and pick up the completed title document. The heir must provide a receipt when re-applying to the registration authority.
Expenses
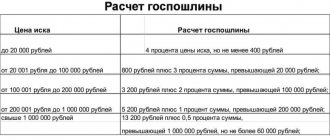
A state fee is withheld for registration actions. Its size depends on the type of property and the action that needs to be taken in relation to it. Basic rates are fixed in Art. 333.33 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Prices for registering property rights:
- Ownership rights for citizens – 2,000 rubles.
- Registration of a dacha plot of land – 350 rubles.
- Organizations – 22,000 rubles.
If a citizen is entitled to benefits, then when submitting an application to Rosreestr he needs to attach papers confirming the existence of such a right. For example, a certificate of disability, a certificate from the social service.
Deadlines
What is the deadline for submitting documents to register property rights? The law does not establish a specific time frame. Delaying the renewal of documents is disadvantageous for the heir himself.
How long does it take to register property rights? The procedure takes from 7 to 14 days . The deadline depends on the volume of registration actions, completeness of documents, and workload of the government agency. An employee of Rosreestr sets a date for issuing title papers immediately upon receipt of the application.
If documents are submitted through the MFC, the registration period may increase by 2-3 days. This is due to the fact that the State Budgetary Institution “My Documents” accepts documents, but does not register property rights. Only Rosreestr has such powers.
If the applicant submits an incomplete list of documents, a Rosreestr employee may extend the registration period or refuse to provide the service (Article 26 of Federal Law No. 218). Similar consequences occur if there are contradictions in the papers or in the case of open legal proceedings in relation to real estate.
Objects of inheritance under a will
In accordance with the provisions of Art. 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of objects of inheritance can be carried out in two ways:
- as required by law;
- according to the inheritance document left by the deceased - a will.
A will, if there is one, has a priority right. During his lifetime, the testator has the right to dispose of the property belonging to him, determining the circle of possible heirs.
According to Art. 1118 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a will can only be drawn up by a legally competent citizen and must be notarized.
During his lifetime, the deceased has the right to independently distribute the property belonging to him among legal successors, without any notification to them of such intentions.
A testamentary document may provide for the transfer by inheritance not only of property belonging to the deceased, but also of things (real estate, cars, etc.) planned for acquisition.
In accordance with Art. 1122 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, if the testator did not indicate in the will the procedure for dividing the inherited property, its division is made equally between the applicants. In the absence of the possibility of division, each of the heirs can receive their share after the sale or payment by one of the new owners of the remaining value.
If controversial situations arise, disagreements are settled in court.
A will may be declared invalid by a court decision if the following grounds exist (Article 1131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- the court will indicate the contestable nature of the document, provided that it contradicts the requirements of the current legislation;
- the nullity of a testamentary document – in the event of an initial deviation from the norms of the law at the time of preparation.
Any person whose interests are violated by the will of the deceased, as noted in the will, has the right to file a claim.
What can you do with real estate?
After registration of property rights, a person becomes the full owner of the testator's property. Now you can make any transactions with real estate that are not prohibited by law.
How can you dispose of inherited property:
- sell (purchase agreement);
- rent out (agreement for renting a residential premises or renting a land plot);
- donate (donation agreement for any person);
- bequeath to heirs;
- exchange (exchange agreement);
- pledge (an agreement with a bank to pledge an apartment).
If there are several co-owners (heirs), alienation of property occurs only with their consent. If one of the owners is against the sale of property, the remaining co-owners can offer him to buy out their parts, and vice versa - the pre-emptive right to purchase (Article 250 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Such actions are carried out in writing. The offer must contain the value of the share of the property and the terms of sale.
The owner is given 30 days to make a decision on the redemption of shares . If the bidder fails to act, the co-owners can sell their parts to third parties. If a written refusal was received earlier, then the co-owners can draw up a purchase and sale agreement without waiting for the expiration of the month. Such transactions require notarization.
Is the sale of real estate subject to tax? If the heir registered ownership less than three years ago, then he must pay personal income tax. If the property is owned for more than three years, then the tax is not withheld (Article 217.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read more about this in the article “Tax on the sale of an apartment received by inheritance.”
Inheritance of real estate occurs in accordance with the general procedure. Applicants need to contact a notary, submit an application, and pay a state fee. Registration of rights occurs after receipt of the certificate. The basis for succession is relationship with the testator or the terms of the will. Possible problems are the lack of documents for the property, missed deadlines, or a dispute between the heirs. Such issues are resolved in court. In order not to violate the procedure, collect all the documents and competent evidence - contact the lawyers of our portal for help. Having received a preliminary consultation, you will be able to assess your strengths, outline an action plan and a list of tasks. Lawyers will help you understand your case from a professional point of view. Leave a request in the online form or call the hotline!
Objects of inheritance by law
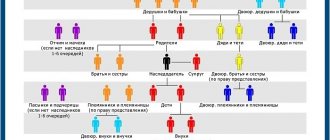
In the absence of a testamentary document, the transfer of objects of inheritance is carried out according to law. The right of applicants to receive inherited property depends on the order of priority determined by the degree of relationship to the deceased:
- the first (Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) - applies to children, parents or spouses of the deceased;
- the second refers to brothers and sisters, grandparents on both lines;
- the third includes uncles and aunts.
More distant relatives are included in the absence of the above applicants. If disputes arise during the division of inheritance objects, the problem is resolved by appealing to a judicial authority.
Object of inheritance upon transfer of a mandatory share
In accordance with Art. 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, freedom of testament is limited to the testamentary share, which is at least half of the part that the heirs would receive, according to legal norms. This rule applies to the following persons:
- children of the deceased who have not reached the age of majority and are disabled;
- disabled spouses, mother or father of the testator;
- dependents and other people supported by the deceased.
The listed categories of heirs have the right to receive at least half of the inherited property due to them by law, regardless of the presence and content of a will.
Who can be the heir
Legal heirs can be individuals who are alive on the day the inheritance is opened, or who were conceived during the life of the testator and born after the opening of the inheritance. Also, the state may be called upon to inherit an inheritance if the inheritance is recognized as escheatable property.
In addition to individuals, legal entities, municipalities, states, including foreign and international organizations can also be involved in inheritance under a will.
Features of inheritance of individual objects
It is necessary to clarify the inheritance features of some objects:
- The transfer of insurance amounts under personal contracts is excluded from the property transferred to the heirs (Article 4 of the Law “On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation”). But, on the basis of clause 2 of Art. 934 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, if the insured citizen dies and there is no other beneficiary in the policy, the insurance money goes to the legal successors.
- The spouse of the deceased, in addition to her part of the property laid down by the will, has the right to claim a share of the remaining property (Article 256 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- If there is a marriage contract, the distribution of objects of inheritance in relation to the husband or wife of the testator is carried out in accordance with this document (Article 42 of the RF IC).
- When dividing a piece of real estate or a vehicle by heirs, various distribution options are possible - joint use, sale with subsequent division of the proceeds, or compensation by one of the owners (Article 1165 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- The heir who lived with him at the time of the testator’s death (Article 1169 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) receives priority in receiving household items.
- The transfer by inheritance of objects of shares in cooperative or other communities is made subject to the consent of the remaining participants (Article 1176 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Inheritance of items of limited circulation (weapons, drugs, etc.) occurs on a general basis, with the recipient taking measures to ensure the rules for handling this property (Article 1180 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- State awards, which are subject to the provisions of the relevant legislative acts, are excluded from the number of hereditary objects (Article 1185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
With regard to land plots, it is necessary to take into account that the division of plots by inheritance is allowed within the limits provided by law. Otherwise, the heirs should decide on the order of their division, using methods that ensure the preservation of integrity.
Provisions of other laws that do not allow inheritance of rights and obligations
Examples of other legal provisions that prohibit inheritance of certain types of property (both rights and obligations) are the following.
- the obligation to pay a tax and (or) fee terminates with the death of an individual - the taxpayer or with the declaration of his death in the manner established by the civil procedural legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 3 of clause 3 of Article 44 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the debt of a deceased person or a person declared dead for transport tax, land tax and personal income tax is repaid by the heirs within the limits of the value of the inherited property;
- wages not received by the day of the employee’s death are issued to members of his family or to a person who was dependent on the deceased on the day of his death. Payment of wages is made no later than a week from the date of submission of the relevant documents to the employer (Article 141 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- payment of alimony collected in court is terminated by the death of the person receiving alimony or the person obligated to pay alimony (clause 2 of Article 120 of the RF IC);
- the social rental contract for residential premises is terminated due to the loss (destruction) of the residential premises, with the death of the tenant who lived alone (clause 5 of Article 83 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation);
- subsoil plots cannot be the subject of inheritance (Article 1.2 of the Law of the Russian Federation of February 21, 1992 N 2395-1 “On Subsoil”);
- accrued amounts of funded pension due to the insured person in the current month and remaining not received due to his death in the specified month are not included in the inheritance and are paid to those members of his family who belong to the persons specified in Part 2 of Article 10 of the Federal Law " On insurance pensions” and lived together with this insured person on the day of his death, if the application for the unreceived amounts of the specified pension followed no later than six months from the date of death of the insured person. When several family members apply for the specified amounts of funded pension, the amounts of funded pension due to them are divided equally between them (clause 3 of Article 13 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 424-FZ (as amended on March 7, 2018) “On Funded Pension”) ;
- sale, donation and inheritance of combat short-barreled hand-held award weapons are not allowed (Article 20.1 of the Federal Law of December 13, 1996 N 150-FZ (as amended on March 7, 2018) “On Weapons”). At the same time, donation and inheritance of civilian weapons registered with the federal executive body authorized in the field of arms trafficking, or its territorial body, are carried out in the manner determined by the legislation of the Russian Federation, if the heir or the person in whose favor the donation is made, licenses for the purchase of civilian weapons (Article 20 of Law No. 150-FZ “On Weapons”).
Nuances
When entering into the right of inheritance of objects, the following nuances must be taken into account:
- the possibility of registering objects of inheritance appears six months after the death of the testator (Article 1154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- to obtain an inheritance certificate, it is necessary to pay a state duty, the amount of which depends on the degree of relationship with the deceased and the value of the property (Article 333.25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the deadline for applying for an inheritance has expired, restoration is carried out in court, providing justified reasons for absence - illness, business trip, etc. (Article 1155 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- entry into inheritance without filing a claim with a judicial authority is permitted if this is done in fact, with the submission of the relevant grounds to the notary - housing and communal services payment receipts, payment of the testator's debts and other documents (Article 1153 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- in the absence of applicants for the inherited property, the latter is recognized as escheated and transferred to the state (Article 1151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
To avoid problems in registering inheritance objects, you need to know and comply with the requirements of current legislation. Given the complexity of this issue, especially if the division of property is accompanied by disputes with other claimants, it would not hurt to contact a qualified lawyer.
Deadlines in inheritance
The inheritance opens with the death of the testator; the day of opening is the day of the citizen’s death. When the testator is declared deceased by the court, the day of opening of the inheritance is the day the court decision enters into legal force.
A citizen must enter into inheritance rights within 6 months from the date of opening of the inheritance; at the end of this period, the heir loses the right to receive the inheritance, except in cases where he can voice a valid reason for non-compliance with the legal deadlines for entering into the inheritance, then the court can restore the deadline inheritance of property.
It is also worth noting that the place of opening of the inheritance is the immediate last place of residence of the deceased; if it is unknown or is located outside the territory of the Russian Federation, then the place of opening of the inheritance is considered to be the location of the inherited property.