Grounds for filing a claim
Registration of inheritance is carried out through a notary office. However, if there are controversial issues, the notary cannot issue a certificate of inheritance rights; in this case, the situation will be resolved in court.
Recognition of property rights by inheritance is the granting of ownership rights to the property of the deceased to the applicant in court. This option is used if there is a controversial situation in inheritance.
The requirement for recognition of property rights is often associated with other requirements:
- recognition of actual inheritance;
- inclusion of an object in the hereditary mass;
- restoration of missed deadlines for entering into inheritance;
- contesting a will;
- redistribute shares in inherited property.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Evseev
Lawyer. Experience 12 years. Specialization: civil, family, inheritance law.
Let's consider the situation. Family members live in the same apartment. After the death of one of the owners, the remaining relatives continue to use the property without thinking about the need to put the papers in order. They accept the inheritance after the fact. Problems usually arise when there are other applicants or if an urgent sale of the home is required. Relatives turn to a notary, who explains that registration of an inheritance is required.
To do this, you need to provide evidence of actual acceptance of ownership.
Heirs must present the following documents:
- on ensuring measures to protect property;
- about paying bills;
- on repayment of loans of the deceased;
- on accepting debts from the debtors of the deceased;
- about carrying out repair work and others.
However, if citizens are co-owners, then their living in the apartment and paying bills may not be evidence of actual acceptance. Because they are using their property. If there is no irrefutable evidence of the actual acceptance of the inheritance, then the heirs will have to go to court.
What does a court decision provide? In fact, a judicial act replaces a certificate issued by a notary. The document allows you to register property in the name of the heir and receive funds from deposits.
What is actual acceptance of inheritance?
The situation with the actual acceptance of an inheritance arises if citizens lived together with the deceased and ran a common household. They did not open an inheritance case within the prescribed period for various reasons: lack of finances, unwillingness to waste time on a lawyer, etc. Usually, the actual acceptance of property is spoken of when the heirs are the first-priority heirs; other than them, no one lays claim to the property of the deceased.
The actual acceptance of the inheritance is characterized by the scope of actions of the persons acting as heirs:
- entry into the management of inherited property;
- taking measures to preserve the inheritance;
- protection of the property of the deceased from attacks by third parties;
- payment of expenses for maintaining the inheritance;
- payment of the testator's debts.
The measures described above are named in the Civil Code as grounds for accepting an inheritance in actual order. But the list is not exhaustive, which means that actions of potential heirs that are similar in meaning may be recognized as the actual acceptance of the property of the deceased.
Out-of-court settlement
The heirs have the right to resolve the dispute peacefully, without trial.
Almost every dispute can be resolved without going to court:
- Recognition of actual entry into inheritance - if there is sufficient evidence through a notary's office, even after the deadline for entry into inheritance has expired.
- Restoration of missed deadlines for entering into inheritance - by agreement with other heirs who accepted the property in a timely manner. For this purpose, written consent of the recipients is provided. The notary will cancel the issued certificates and issue new ones.
- Redistribution of shares in inherited property - for this, the heirs can independently draw up an agreement. The document is submitted to the notary and he issues certificates based on the decision made by the recipients.
However, not all disputes can be resolved peacefully. A will can be contested and an object without title documents can be included in the estate only through the courts.
To avoid re-applying to a notary, a citizen can include in the claim a requirement for recognition of property rights by inheritance.
Author of the document
| Contract-Yurist.Ru offline Status: Legal company rating460 84 / 6 Private message Order a consultation | number of consultations: |
| noted as the best: | 5 |
| answers to documents: | |
| documents posted: | 927 |
| positive feedback: | |
| negative reviews: |
To court
Plaintiff: ______________________________
Address: __________________________________
Respondent: Administration _________________
Address: __________________________________
Who is the defendant in a claim for recognition of the right to inheritance?
To determine the defendant, you need to start from the reason for filing the claim:
- The recipient missed the deadline for accepting the inheritance - the defendants will be the persons who accepted the property.
- If the property is accepted after the fact, then the defendants are the relatives of the deceased citizen. Let's say a son inherits property. If at the time of the testator’s death the spouses were alive or there were other children, then they are potential claimants to the property. Therefore, these persons are defendants.
- If the deceased citizen did not have time to draw up papers for the property, then when filing a claim, the defendants are the applicants for his assets. This situation often occurs with privatized housing. In this case, the defendant is the municipality.
- When challenging a will, the defendant is the heir specified in the order - an individual or an enterprise.
- If the property is recognized as escheat, then the defendant is the state represented by the Federal Property Management Agency (Article 5 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court No. 9).
Procedural features of this category of cases
Regardless of the composition of participants or the type of property, all cases are considered by courts at the district and city levels.
After acceptance of the inheritance, all disputes that arise from the fact of transfer of the deceased’s property to the heirs are dealt with in accordance with the general procedure. It all depends on the amount of the claim: up to 50,000 rubles, the case is considered by a magistrate, more than 50,000 rubles - by a city or district court.
Claims are brought at the place where the defendant lives, if he is an individual. If this party in the process is a legal entity, then the claim is filed at its location.
Disputes about rights to real estate that are inherited are resolved at the location of the objects.
How to recognize property rights by inheritance
Ownership rights can be recognized by inheritance only in court. To do this, the person whose rights have been violated must apply to the district or city court.
The claim is submitted:
- at the place of registration of the defendant;
- at the location of the disputed object (if the dispute concerns real estate);
- At the place where the inheritance case was opened, the testator's creditors submit an application.
Procedure
Algorithm of actions for an applicant for the testator's property:
- Prepare a package of documents.
- Pay the state fee.
- Submit a claim.
- Wait for a summons to appear in court.
- Provide available evidence of the stated facts.
- Obtain a court order.
- Register ownership.
How to file a claim correctly
When preparing a claim, you must be guided by the provisions of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation:
- The application must be submitted in writing.
- The document must contain an introductory, descriptive, motivational, pleading part.
- The application is also accompanied by a list of documents substantiating the plaintiff’s claims.
Important! Failure to comply with the established form may lead to immobilization of the document. Courts often leave the document without consideration, giving the plaintiff a period to eliminate the shortcomings. Failure to respond appropriately on the part of the plaintiff results in the return of the claim.
Claim details
| Name of the document part | Name of the statement item | Content |
| Introductory part (header) | Name of district or city court | Full name |
| Information about the plaintiff | Full name, passport details, place of permanent and temporary registration, telephone number | |
| Respondent details (if there are several respondents, they are listed one by one) | Similar to information about the plaintiff | |
| Information about third parties | Notary, guardianship and trusteeship authority | |
| Cost of claim | The amount is indicated based on the estimated value of assets for the disputed share of property | |
| Name of the document (Statement of Claim) | If the applicant needs to recognize ownership, then the corresponding wording is displayed immediately under the title of the claim. | |
| Descriptive part | Circumstances of the case and facts that support the plaintiff’s position | The stated circumstances must be confirmed by documents and/or testimony of witnesses. |
| Motivational part | Links to regulations | The plaintiff must refer to articles of law that correspond to his situation and give the court a basis for satisfying the claim |
| Petition part | Statement of the plaintiff's request | Recognize ownership. It must be understood that the court cannot go beyond the limits of the claims. The pleading part is reflected in the court decision, and later in the writ of execution. Therefore, you need to think through not only the structure of the document, but also the final request. In some cases, it is possible to clarify the claims during the trial. For example, if new circumstances open up. |
| List of documentation | Documents must be directly relevant to the case | |
| Date and signature of the applicant | The claim is signed by the plaintiff or his representative |
The text must be consistent. The descriptive and motivational parts of the document can be combined into one whole or written one after the other. The main thing is that the logic is visible, and the facts presented are relevant to the case.
The document must clearly indicate a violation of the applicant's civil rights. The plaintiff must also refer to the pre-trial settlement of the dispute.
If there are several requirements, you can combine them. At the end, documents confirming the stated facts are attached to the claim.
When writing an application, it is advisable to write briefly and to the point. The optimal document size is 2–3 pages.
Sample statement of claim for recognition of property rights by inheritance
The document can be used as a basis. However, the circumstances in which the plaintiff found himself must be taken into account. If necessary, the statement of claim may be supplemented with new sections.
Sample statement of claim for recognition of property rights by inheritance
Documentation
The following documents must be attached to the statement of claim:
- passport;
- evidence of the death of the testator (death certificate, court order);
- will (if any);
- evidence of relationship with the deceased citizen (birth/marriage certificate);
- a document confirming the last address of residence of the testator;
- documents of title to the property of the deceased citizen;
- written refusal of the notary;
- report on the value of the inheritance;
- receipt of payment of the fee.
The statement of claim is filed according to the number of participants in the trial. If the statement of claim is filed by a representative of the plaintiff, then a notarized power of attorney will need to be attached.
A request to call witnesses can be attached to the claim or submitted during the court hearing. Here it is necessary to proceed from the amount of evidence that the applicant can provide.
If the available documents indisputably confirm the rights of the plaintiff, then you can do without witnesses. The same applies to cases where the defendant admits claims. In such circumstances, no additional evidence is needed.
Proof
The burden of proof lies with the applicant. The necessary information can be obtained from the explanations of the plaintiff, defendant or third parties.
However, the basis of any claim is written evidence, audio-video recordings, and opinions of specialized experts. The plaintiff needs to confirm the actual acceptance of the inheritance within the time period allotted for entering into inheritance rights.
However, the evidence in the trial does not directly relate to the recognition of ownership. The citizen must prove a related claim:
- taking actions aimed at actually entering into inheritance;
- the deceased citizen has ownership rights to the object;
- existence of grounds for challenging the will;
- validity of the reasons for missing the deadlines for entering into inheritance;
- grounds for redistribution of shares in inherited property.
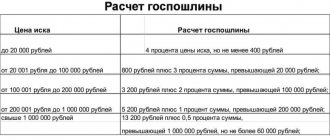
State duty
When filing a claim, a state fee is usually withheld. Only privileged categories of citizens are exempt from paying tax.
The amount of the fee is determined by Tax legislation. The amount of tax is calculated based on the cost of the claim (Article 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
However, the plaintiff cannot indicate an arbitrary figure. Therefore, you will first need to evaluate the accepted inheritance.
- up to 20 thousand rubles - 4%. The minimum payment amount is 400 rubles;
- from 20,001 to 100,000 rub. – 800 + 3% of the minimum threshold;
- from 100,001 to 200,000 rub. – 3200 + 2% of the minimum threshold;
- from 200,001 to 1,000,000 rub. – 5200 + 1% of the minimum threshold;
- from 1,000,000 rub. – 13200 + 0.5% of the minimum threshold. The maximum collection amount is 60 thousand rubles.
Example. As a result of the death of citizen K., an inheritance was opened. The object of inheritance was an apartment. The claimants to the property are the wife and son of the deceased man. The testator's parents renounced their rights. No will was made. There are no benefits for heirs. The estimated value of the property is 2.7 million rubles. The amount of state duty is 21,700 (13,200+8,500) rubles. Each heir must pay 10,850 rubles.
Additional costs
Additional costs arise when assessing property (apartment, car, house, securities). For example, the valuation of an apartment in 2021 is 3,000 rubles. To determine the market value of a car you need to pay from 2 to 5,000 rubles.
Costs for notary registration
According to Art. 22 Fundamentals of legislation on notaries, all notarial actions are subject to payment in accordance with the requirements of the legislation on taxes and fees, state fees or notarial tariffs.
However, the state fee for registering an inheritance with a notary is far from the only payment. Not only that, such a fee can consist of several amounts depending on the actions performed by the notary. The cost of legal and technical services should also be added to it. The right to pay them is guaranteed to the notary by Art. 23 Fundamentals of legislation on notaries.
Unlike state fees and notary fees, the cost of these services is not regulated by law, and therefore is set by the notary at his own discretion.
Such services may include legal advice, drafting and production of documents, mediation in obtaining the necessary certificates, and the like.
The article “How much does it cost to enter into an inheritance from a notary” will help you find out more about this.
Deadlines for filing a claim
The limitation period is 3 years . However, the countdown of time does not begin from the moment the event occurs (the death of the testator).
The connection goes to the moment when the heir became aware of the violation of his civil rights or the person who should be the defendant in the case. During the specified period, the beneficiary may file a claim in court. The rule applies if there are controversial issues between the heirs.
The timing also depends on the reason for filing the claim. Let's consider several options:
- Missing deadlines. Reasons: the person did not maintain contact with the deceased citizen, prolonged illness, business trip abroad, imprisonment. The applicant is given 6 months to file a claim. The countdown begins after the cause disappears. If a person was in the hospital, then the connection goes to the moment of discharge. In the case of a foreign business trip, the starting point is the moment of return to the country of residence. If the plaintiff is an heir who was a minor on the day of the death of a relative, then the application is submitted after he reaches the age of 18.
- Acceptance of assets upon the fact. The reason is that family members lived with the testator. After his death, the children or spouse continue to use the property. The law does not contain fixed deadlines for protecting rights. You can file a claim at any time.
- Contesting a will. The reason is that the testator was very ill and could not fully understand the consequences of his actions and/or suddenly made an order to a stranger. If the heirs contest the will due to violence or threat, the statute of limitations is 1 year . If the reasons are different, then the statute of limitations is 3 years . The countdown begins from the moment the heir receives information about the violation of his rights, and who should be the defendant in the case.
When is the state duty paid?
In each case, the state fee, regardless of what actions it is paid for, must be paid before they are performed. Ignoring this rule will become an obstacle to taking the necessary actions. For example, a notarial act is considered completed by law only after the state fee has been paid for it.
If we are talking about judicial review, the court will leave the claim without progress until payment of the state fee (except for cases of deferment of payment).
As for Rosreestr, the lack of information about the payment of state duty is grounds for returning submitted documents without consideration.
Arbitrage practice
If there is written evidence of acceptance of the inheritance, the courts satisfy the stated requirements.
Example. The court received a statement of claim. The plaintiff asked to recognize his ownership of the land. The defendant was the Administration of the municipality. The heir claimed that after the death of his two grandmothers, an inheritance in the form of land plots opened up. He is the only contender for both sites. However, at one time the testators did not register ownership of the land. Although they used the plots and paid taxes for them. The plaintiff accepted the property in fact and has been using the land all this time. The court agreed with the plaintiff’s opinion and recognized the claims (Decision of the Pochinsky District Court of the Smolensk Region dated January 12, 2012, case No. 2-25/2012).
At the same time, a lack of evidentiary documentation may become a reason for refusal to satisfy the requirements.
Example. The citizen filed a claim for recognition of property rights. The man asked to include part of the residential building, land plot and outbuildings in the inheritance. The essence of the requirements is that after the death of a relative, an inheritance was opened. He was actually accepted by two people - the wife and daughter of the deceased man. However, the daughter soon died. No documents were issued in her name. The son of a deceased woman found out about her death after the deadline for registering an inheritance had expired. The notary refused to issue the certificate to the plaintiff. The deadline for accepting the inheritance was restored by court decision. However, the court was unable to satisfy the requirements for recognition of property rights by inheritance due to the lack of documents in the name of the deceased heiress.
Inclusion in the hereditary mass
The concept of “estate” means all property that can pass to the heirs after the death of the testator. Therefore, for each individual thing, evidence of the ownership of the testator must be presented.
Inclusion in the estate is the addition of part of the property to an existing inheritance . This action is justified by new documents or a court decision proving the legality of the testator’s ownership of the property.
When submitting an application, the notary will have to find out whether the testator made a will during his lifetime or not. If such a document is missing, then inheritance is carried out according to law.
First degree relatives include father, mother, children and spouse. Each of them has equal rights . The identified property will be divided between them in equal shares. The exception is joint property of spouses.
Therefore, from such property, a part of the co-owner is first allocated. The distribution of the second half of the assets occurs among the declared heirs.
If the applicants do not contact a notary, then the succession passes to second-line relatives. In this case, the heirs are given an additional six months to take over their rights.
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction of claims determines in which court the case should be heard. Cases of this nature are considered in the court at the place where the inheritance was opened. Such a place is where the deceased officially resided .
If there is no such place or there is no information about it, the place of opening of the inheritance is recognized as the area in which the majority of the testator’s property is located. When property falls under the jurisdiction of several districts, a claim can be filed in any district court.
The jurisdiction of such claims does not provide for the right of choice of court by the plaintiff or the other party.
Rules for drawing up an application
A well-drafted claim is a guarantee that it will be accepted the first time and you will not have to write it again, pay fees, and so on.
Let's consider what our statement of claim should look like. What needs to be written in the application, in order.
- To which court was the statement of claim sent?
- Plaintiff's details - f. And. O. and address. If necessary, the details of the plaintiff’s representative.
- Defendant's details - name of organization or f. And. O. and address.
- If available, third party data. Name/f. And. O. and address.
- The claim price is in rubles.
- The amount of state duty in rubles.
- Title of the claim.
- Information about the acquisition of property rights by the deceased (information about the property itself, the method and date of acquisition, indicating all documents and their numbers).
- Information about the death of the testator.
- Detailed information about the problem that occurred.
- References to the articles of the relevant codes under which the plaintiff’s rights were violated.
- Claim.
- List of attached documents.
- Date and signature of the person making the application.
The statement of claim must include as complete information as possible - names, names of organizations, telephone numbers, etc.
It is advisable to draw up a claim using a sample to avoid inaccuracies.
You can download a sample claim here.