Inheritance issues are always pressing and worrying for many. Especially if we are talking about significant property that can be divided between certain heirs. And all movements regarding the property of a deceased person must be determined by law.
The grounds for inheritance, Article 1111 of the RF IC, have undergone some changes and now read as follows: inheritance is carried out according to a will and law.
It occurs when and insofar as it is not changed by the will, as well as in other situations that are established in the Family Code.
Acceptance of inheritance by law
Inheritance, as follows from the provisions of Art. 1112 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is all, without exception, the property of a person that is transferred to other persons. The heir, in case of acceptance of the succession, becomes the absolute owner of all or part of the property.
The inheritance estate includes all movable and immovable property, a car, shares, shares, deposits, accounts, things, antiques, jewelry and other luxury items, intellectual property, etc. That is, everything that happened during the life of the testator on the day of death. This even includes debt obligations of the deceased.
Entering into an inheritance is personal right; he cannot sell or exchange it. In case of unwillingness to become the owner of the transferred property, the heir has the right to refuse simply or in someone else's favor (from the circle of successors).
The transfer of property may be based on law or will . The legal method is the most common; its implementation occurs if
- the person did not leave a will or was declared invalid;
- the testamentary document indicates only part of the property;
- if the citizen specified in the will refused what was intended for him.
For your information
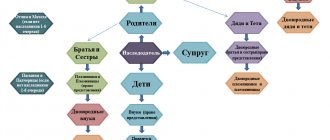
Inheritance on a legal basis is accompanied by a number of conditions. There are eight queues under civil law, each queue includes a group of relatives.
The heirs of each order, if their order occurs, must divide the entire inheritance mass equally among themselves.
The first priority is children, spouse, parents, grandchildren (by right of representation). Children are natural, adopted, born and not born in marriage, but if paternity has been established. The spouse must have been in registered marriage on the day of the testator's death.
If members of the first priority group of heirs are absent or they were disinherited, recognized as unworthy heirs, removed, or simply abandoned the inheritance, then the property goes to division among relatives of the next priority.
The second group is:
- the sisters and brothers of the deceased are full and not full, that is, at least one of the parents must be common.
- grandmothers, grandfathers.
- Nephews and nephews (by right of representation).
Third stage:
- Uncles and aunts of the testator.
- Cousins (by right of representation).
If all of the above groups of relatives do not enter into inheritance for any reason, then the remaining categories of relatives are accepted by law.
Other groups:
- fourth line - great-grandparents.
- fifth - great-aunts, grandfathers, granddaughters and grandchildren.
- sixth group - cousins, uncles, nephews, nieces, great-granddaughters, great-grandchildren.
- seventh order - stepmother, stepfather, stepsons and stepdaughters.
- The eighth group is the disabled dependents of the testator. In case of living with the deceased for at least a year (before the day of his death).
Civil law contains the concept of hereditary transmission . It, as an option for accepting inheritance, is relevant when the heir did not have time to accept the inheritance, which had already been opened before his death. The circle of applicants for the due share of the not accepted property is equal to the circle of queues.
Example
Citizen Ivanov P.R. is the father of O.P. Ivanov. The father died in an accident. The son (Ivanov O.P.), after opening the inheritance, died before it was re-registered. Ivanov P.R. there are two children (one of them Ivanov O.P.) and a wife, therefore, the inheritance mass of the main heir is divided into 3 parts. In this case, the share of the deceased heir should go to his first-degree heirs and be divided in equal shares. That is, the transition is carried out in order.
There is also the concept of inheritance by right of representation . The essence of the procedure is that the inheritance of a person who died along with the testator or before the opening of the inheritance passes to a descendant relative.
There are 3 categories of such relatives:
- grandchildren of the testator and descendants.
- nephews and nieces of the testator.
- cousins.
Example
Citizen Ivanov P.R. is the father of O.P. Ivanov. They died together in a car accident. Ivanov P.R. there are two children (one of them Ivanov O.P.) and a wife. Consequently, the inheritance of the main heir is divided into 3 parts, and the share that was due to O.P. Ivanov, who died along with his father, should be divided equally between his children, that is, the grandchildren of the heir. If they are not there, then between nephews and nieces, and if they are not there either, then between cousins of the deceased heir.
In order to inherit a fortune, you need to accept the inheritance within 6 months from its opening.
- The actual method of succession is characterized by the possession and disposal of property, protection from attacks by third parties. More suitable for close relatives who lived with the testator. The rights of the heir in such possession of property are not lost if the citizen missed the general deadline for entering into legal succession.
- The formal method is to visit a notary, submit an application for acceptance of the inheritance, and then apply for the issuance of an inheritance certificate. The entire procedure ends with receiving a certificate of inheritance. This occurs after six months from the date of opening of the inheritance. The notary will indicate what time you need to appear in order to receive the desired document.
With the received certificate of the right to inheritance, you must contact Rosreestr if you need to register real estate that was inherited as an inherited property.
The fact of opening a will
The inheritance case is initiated at the request of the applicant. The basis for inheritance is a handwritten application submitted to a notary office. The package is printed and the conditions are announced. The notary carries out legal monitoring, checking the accuracy of the information, the correctness of the documentation and the presence of sufficient grounds for acceptance. The result is the issuance of a certificate on the basis of which the heir re-registers the property.
Terms of inheritance
The general period of inheritance is six months after disclosure. The reference date is:
- The day of the decedent's death as indicated on the death certificate.
- The moment of issuance of the certificate of recognition as dead, if the fact was established by the court.
- The date indicated in the judicial act declaring him dead, if it is actually impossible to establish it.
When there are no other applicants, the time frame is reduced to three months. Delay in completing the case is grounds for filing an appropriate claim to restore the right of inheritance. This situation is exceptional. The judge assigns additional time for inheritance - 3 or 6 calendar months. They are added to the main six.
Acceptance of inheritance by will
If the law itself outlines the circle of relatives who will receive the property of the deceased and even determines the equality of shares, then a citizen, at his personal request, can change this order and independently decide who will get what.
A will is an administrative document, in fact, a unilateral transaction, regarding a person’s property in the event of death. A citizen has the right to leave all his property to any person, regardless of family ties.
Important
By an administrative document, the testator can not only leave his property to anyone, but also deprive one or all legal heirs of succession to his property.
deprive will not be valid :
- children under 18 years of age, or reached but not able to work;
- non-able-bodied parents and spouse.
Obligatory heirs cannot be deprived of property. Neither on a testamentary basis, nor on a legal basis for accepting an inheritance. In any case, they will receive half of what they would have been legally entitled to. The testator has the right to cancel, change, or draw up a new document, since it comes into force only after the death of the testator.
A will refers to transactions that must be completed independently, without representatives. Only a legally capable citizen can dispose of personal property. Such a document cannot be drawn up jointly even by spouses who have common property.
The convenience of the document is that, through an early expressed desire, disputes between claimants for property are prevented. The manager has the right not to give reasons for his decision.
The testator can express his will not only in relation to the entire existing estate, but also make a reservation about what he will acquire in the future. You can make one will, or several. Let’s say one thing for an apartment, another for a car. And if the same property appears in several wills, then the valid one is the one drawn up last .
In case the person designated in the document dies or for other reasons is unable to inherit, a sub-heir . In addition, the will must be written, signed personally. This act can be canceled at any time.
Legal features of the grounds of inheritance
The grounds of inheritance are circumstances that regulate a specific range of legal relations related to the transfer of rights by inheritance.
Mainly, the existing grounds of inheritance differ in a specific fact, namely whether there was an expression of the will of the deceased person regarding his property. When there is an expression of will, then the choice of method of inheritance is made by will , and when there is no will, then a different type of inheritance is used - by law .
Russia is a democratic country, so legislators strive to take into account the will of the owner of the property and respect his actions towards it. Intestate inheritance applies only when the inheritance procedure has not been changed in any way.
Certain provisions of the Civil Code regarding methods of inheritance
Certain provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are designed to regulate inheritance legal relations. In particular, Article 1110 expresses the specifics of universal inheritance . First of all, the inherited property is transferred unchanged. That is, the entire inheritance is transferred to the owner in the form of “one whole”. Another feature is that the obligations of law must transfer at the same time, that is, at the same time.
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the chapter that regulates inheritance by will is located in the Civil Code higher than inheritance carried out by law. This approach creates a priority of the first type over the second, which was done on purpose.
Acceptance of inheritance simultaneously by law and by will
Clause 2 Art. 1152 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation regulates the acceptance of part of the property as the acceptance of everything that was the property of the testator. Moreover, in addition to the existing inherited property, that which is discovered after entering into inheritance rights will also be considered accepted.
Information
If a citizen is called upon to inherit simultaneously on several types of grounds, he has the right to accept on all or one basis at once.
Let’s say the deceased has a daughter and a son, and the property consists of a house and an apartment. He assigned the house to his son, but did not indicate his daughter in the administrative document. After his death, the son takes over the house based on the will. He still has the right to purchase half of the apartment (since the second part must by law go to his sister), he can refuse to purchase it by law or accept it. In the second case, he will receive the property for all reasons.
The choice of one type of succession does not serve as a refusal of inheritance under other provisions. This rule occurs upon actual acceptance of property. The notary must explain that in the application for acceptance of the inheritance it is necessary to indicate that the property is accepted for all reasons, if this does not contradict the will of the applicant.
When there is separate will for each object of disposal, the heir can indicate that he is acquiring an inheritance for each of them. It is impossible to accept an inheritance under conditions . Within 6 months, the successor has the right to refuse what was received or change the basis for the acquisition without specifying reasons or motives.
Testator's rights
What rights does the testator have:
- Transfer property by inheritance to any entity.
- Divide property into parts.
- Include any valuables in the inheritance mass.
- Assign shares to successors in the inheritance procedure.
- Deprive inheritance rights without specifying reasons.
- Cancel and change the terms of the transaction.
- Demand compensation in case of early disclosure.
- Appoint a secondary successor in the event of the death of the primary one.
- Transfer the right to sign in the presence of a notary if it is physically impossible to do it yourself.
- Entrust the execution of inheritance to an executor (third party).
- Determine the obligations of the successor (refusal, non-fulfillment - grounds for deprivation).
- Required to take care of pets.
A full list of rights and obligations in testamentary inheritance is stipulated in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Judicial practice under Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Determination of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 26, 2019 N 5-КГ19-33
In accordance with Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, inheritance is carried out by will and by law. Inheritance by law takes place when and insofar as it is not changed by a will, as well as in other cases established by the said code. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 1152 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in order to acquire an inheritance, the heir must accept it.
Determination of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 06.08.2019 N 64-KG19-3
Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as amended in force at the time of the emergence of controversial legal relations, establishes that inheritance is carried out by will and by law. Inheritance by law takes place when and insofar as it is not changed by a will, as well as in other cases established by this Code.
Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated February 28, 2017 N 391-O
According to the applicant, this legal provision - applied by the courts when considering a specific civil case without taking into account the interrelated provisions of paragraph two of paragraph 2 of Article 218 and Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation - insofar as it, in the meaning given to it by law enforcement practice, allows for the possibility of the emergence of preferential the rights of some participants in civil legal relations arising from a purchase and sale agreement before the rights of other participants in civil legal relations arising from a will, violates his rights guaranteed by Articles 6 (Part 2), 8 (Part 2), 19 (Part 1), 35 ( parts 1, 2 and 4) and 46 (part 1) of the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Determination of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 01.08.2017 N 18-КГ17-116
According to Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, inheritance is carried out by will and by law. Inheritance by law takes place when and insofar as it is not changed by a will, as well as in other cases established by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Determination of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 21, 2017 N 18-КГ17-202
Inheritance by law takes place when and insofar as it is not changed by a will, as well as in other cases established by the said code (paragraph two of Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). By virtue of the first paragraph of paragraph 1 of Article 1117 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, citizens who, by their deliberate unlawful actions directed against the testator, any of his heirs or against the implementation of the last will of the testator expressed in the will, do not inherit either by law or by will. contributed or tried to promote the calling of themselves or other persons to inherit, or contributed or attempted to increase the share of the inheritance due to them or other persons, if these circumstances are confirmed in court.
Determination of the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 5, 2019 N 5-КГ19-181
By virtue of Article 1111 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, inheritance is carried out by will and by law. Inheritance by law takes place when and insofar as it is not changed by a will, as well as in other cases established by the Code. The heirs of the first priority according to the law are the children, spouse and parents of the testator (clause 1 of Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Deadlines in inheritance
The death of the testator must chronologically precede the opening of proceedings along one of the paths of inheritance. After its completion, the notary is obliged to notify all potential participants about the event. If the announcement of the death of a citizen is made as part of a legal battle, the discovery date will be the day on which the act drawn up by the judge comes into force.
The time allotted for citizens to enter into an inheritance (regardless of the type of transfer of property) is six months. Missing the deadline entails losing the chance to receive a share. In this case, their share passes to other participants in the case. But the rule has an important nuance: the citizen must argue in court that the reason for the absence was valid. Then we will talk about restoring rights and reviewing the inheritance case.
The question of the correct determination of jurisdiction is decided in a particular court. As a rule, the place of commencement of proceedings is the last place of residence of the deceased testator. If difficulties arise in determining the location, the notary initiates a review at the location of the most expensive part of the property.
Statements of claim are sometimes returned to the court with a note indicating that jurisdiction has been incorrectly determined. The reason is that the dispute affects the interests of other parties, so the claim should be filed at the place of residence of the defendant (one of the participants in the inheritance process).
Inheritance of certain types of property
This type of inheritance is discussed in a separate chapter of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. We have already completed an abstract
The courts of the Russian Federation provide more details and include the following categories of inherited property:
- the right to participate in a joint-stock company, production cooperative or other organization;
- the right to participate in a consumer cooperative;
- right of inheritance of an enterprise;
- property of a peasant (farm) enterprise;
- items restricted in circulation (weapons, etc.);
- land plot;
- memorable, honorary signs, medals, orders;
- amounts unpaid to the testator;
- property that was provided by the state on preferential terms.
Get paid for your student work
Coursework, abstracts or other works