If the supplier has shipped a low-quality or incomplete product to the organization, the buyer can return it. There may also be other reasons for return, it depends on the terms of the supply agreement.
The Civil Legislation of the Russian Federation establishes several grounds on which goods can be returned. These are cases of non-compliance:
- quality;
- assortment;
- set;
- containers and packaging.
Thus, current legislation allows you to return goods to the supplier in the following cases:
- if the buyer has not received complete information about the characteristics of the product;
- The supplier did not ship the required quantity. In this case, the buyer may refuse the entire lot;
- the product is not fully completed;
- the supplier regularly violates delivery deadlines;
- the quality does not meet the terms of the contract;
- The products were shipped without packaging or containers.
In this article, we will consider what primary documents should be used to document the return of goods to the supplier.
How to arrange for a buyer to return goods to a supplier
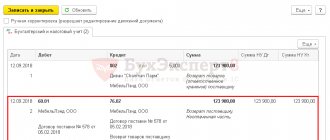
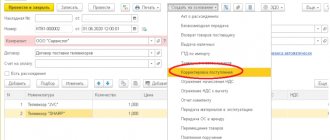
The return of goods to the supplier is accompanied by a return invoice (for example, in form N TORG-12 with the note: “Return of goods”) or an act of returning goods to the supplier.
Documents for returning goods from the buyer to the supplier are transferred along with the returned goods.
In addition, the buyer sends a letter (claim) to the supplier demanding acceptance of the returned goods, indicating the reason for their return.
If the goods are returned to the supplier by power of attorney, then in this case, when registering it, you can use form No. M-2 (clause 2.1.4 of the Methodological Recommendations, approved by Letter of the RF Committee on Trade dated July 10, 1996 N 1-794/32-5 ).
In this case, the buyer does not need to issue an invoice for the return of goods.
What documents are needed
To return a good quality product, you must provide an application, as well as additional papers.
These include:
- Russian passport or other identification document, for example, a driver's license;
- purchase and sale agreement for the return of a large batch of dishes (wholesale purchase);
- receipt, cash receipt for payment for goods.
Please note that a copy of the passport serves as a full-fledged document that can identify a person, so you do not need to present the original.
The cash receipt can be replaced with any other document that confirms the fact of the purchase, for example, witness statements, video recordings.
Letter of claim requesting the supplier to accept goods returned by the buyer
If, during the acceptance of the delivered goods or after its acceptance, it is revealed that the goods do not comply with the requirements for their quality, the buyer has the right, at his own discretion, to refuse to execute the sales contract, return the low-quality goods and demand a refund of the amount of money paid for it, or demand replacement of this product with a product of proper quality (clause 2 of Article 475 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The buyer sets out his requirements in the form of a claim, which is sent to the supplier (for example, for the return of goods). The norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation do not provide for an established form of claim for the return of goods to the supplier.
The letter of claim is drawn up in any form.
The letter states:
- full name and details of the buyer and supplier;
- number and date of the purchase and sale (supply) agreement;
- number and date of accompanying documents for the delivered goods;
- name of the product, its quantity and cost;
- detected discrepancy (malfunction);
- links to regulations;
- requirement to satisfy the claim (request for replacement, refund, reduction of amount, etc.).
The claim is signed by the head of the organization, indicating his position and his full name, and certified by the company seal (if any).
The letter of claim is handed over to the authorized representative of the supplier against signature or sent to him by registered mail with a list of the attachments.
Required documents
To return a defective product to the seller, the buyer must present a small package of documents:
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation or other document that can identify the individual;
- purchase and sale agreement (paper is not required to be presented, since contracts are usually not concluded for tableware, with the exception of wholesale purchases);
- receipt for the purchase of goods (if there is other evidence of purchase, you do not need to present a receipt).
The Federal Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” makes it possible to return purchases to the seller without having a cash receipt in hand.
VAT when returning goods to the supplier
VAT when returning goods to the supplier is required to be processed according to the following rules:
- The seller prepares an adjustment invoice and records it in the purchase ledger.
- The buyer registers the seller's adjustment invoice in the sales book (if he managed to accept VAT for deduction, if not, then he accepts the deduction in the non-refundable part).
Please note that it does not matter for what reason the return occurs.
This is how the return of both defective and high-quality goods is processed if it does not comply with the contract.
Is it possible to return quality dishes?
A quality product without defects can only be returned within two weeks from the date of purchase; this rule also applies to tableware.
Remember! However, several conditions must be met:
- the appearance of the dishes has been preserved in its original form;
- the packaging is intact, not damaged, not torn, not wrinkled;
- the utensils have not previously been used for their intended purpose;
- The product has no chips, scratches or abrasions.
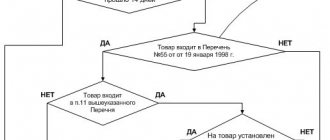
There are some types of goods that, in accordance with Government Regulations, cannot be returned to the seller. These include food items made from polymer materials. Even if part of the item is polymer, it is impossible to return the dishes.
A complete list of goods that are not subject to return or exchange can be found in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 55 “On approval of the Rules for the sale of certain types of goods, a list of durable goods that are not subject to the buyer’s requirement to provide him with a gratuitous supply for the period of repair or replacement of a similar product , and a list of non-food products of good quality that cannot be returned or exchanged.”
If the dishes are made of glass, ceramics, cast iron and other metals, you can safely contact the seller with a request to accept the goods and return the money for it.
If the seller refuses to accept a product that is not specified in the sixth paragraph of Government Decree No. 55, you should contact the management or the Russian consumer supervision.
Some non-stick frying pans are made using polymer materials. Before contacting the seller to return, check what the purchased cookware is made of.
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, it is impossible to get money back for a quality product if:
- there is a similar product on the store counter;
- The store has a similar product that can replace previously purchased dishes.
If the seller cannot replace the dish with another, then you can demand a refund.
To return, you should write a free-form application in two copies. Keep one for yourself, give the second to the seller. The store reserves the right to consider the request within ten calendar days. Most often, the replacement is made immediately after the request is sent.
Return of low-quality goods to the supplier if a defect is detected immediately upon acceptance of the goods
In this case, the purchasing organization may simply not accept the damaged goods.
In this case, it is enough to correct the invoice TORG-12 - without documenting the return of low-quality goods to the supplier.
That is, if the supplier is ready to take back expired products, then from the TORG-12 consignment note issued by the supplier, the purchasing organization deletes the necessary items - those items that are defective.
Please note that corrections in the receipt document must be made in the presence of the supplier or his representative - a forwarder or driver, vested with the rights of a financially responsible person.
The specified person must sign next to the crossed out item and pick up the defective product.
In addition, the supplier must not only accept the defect back, but also adjust the invoice for the purchasing organization downward and send it to the purchasing organization within 5 business days, since less goods were actually purchased.
At the same time, in the invoice, in the adjustment lines, the supplier indicates those goods that he must accept from the buyer.
Note that in practice another option is often used, namely, additional delivery of quality goods at another time, but without paperwork. That is, the purchasing organization accepts the entire delivery, signing the invoice without adjustments. And the supplier delivers the missing quality goods a little later. This is a common case when the buyer has established a trusting relationship with the supplier.
How to return poor quality dishes
The return of low-quality dishes occurs in accordance with the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”. The seller is obliged to accept the goods, if there are defects, during the entire shelf life. As a rule, it is not installed on dishes. In this case, the Law gives the right to return the purchase within two years from the date of purchase.
If the dishes are imported and expensive, then a sales receipt and a warranty card must be provided for it. Papers are provided with the purchase. They should be stored in a safe place with the packaging.
Dishes of poor quality may be damaged by the buyer or may have a manufacturing defect. If you yourself violated the integrity of the purchased product, then it is impossible to replace it or return the money. Responsibility lies entirely with the buyer.
To determine a manufacturing defect, an examination will be required. The implementation time depends on the location of the expert organization.
If a manufacturing defect is confirmed, the seller must:
- make a complete replacement of the product with a similar one, corresponding in color, size and cost;
- replace with a similar item and recalculate the cost (the buyer can return part of the money or, conversely, pay extra, it all depends on the cost of the chosen item);
- return part of the funds paid (in this case, the purchase remains with the buyer);
- return the cost of the product (this approach is welcome if the seller does not have a similar product for replacement).
The warranty gives the seller the right to correct existing defects. However, the dishes cannot be repaired, so the clause of the contract remains unheeded.
Please note! To file a claim, the seller must write a free-form application in two copies. You give the first one to the store employee, and keep the second one with the signature of the person in charge confirming acceptance of the request.
The seller is given ten days to consider the claim. Most often, conscientious stores replace low-quality goods on the same day.
Return of defective goods to the supplier after acceptance
There are situations when the purchasing organization cannot return the defective product to the supplier immediately, although the defect was discovered at the time of acceptance.
For example, the delivery was from another region, and the transport company - the seller's delivery contractor - does not accept anything back.
In this case, despite the defect, the purchasing organization will have to accept the products according to the TORG-12 invoice, draw up a statement of discrepancies in quantity and quality, and place the inventory items in its warehouse.
And only after this the purchasing organization can write a claim and wait for its consideration by the supplier.
Is it possible to return dishes after two weeks?
It is impossible to return quality dishes to the seller after fourteen days. The legislation does not provide the opportunity to first use an item and then return it to the store.
However, if the dishes are defective, the return period is extended for the entire warranty period. If this is not established, then the exchange of goods occurs within two years.
If the buyer, without leaving the store, changes his mind about purchasing the goods, the seller is obliged to immediately return the money paid.
Legal assistance
If the management of the retail outlet does not want to resolve the issue amicably or ignores the return request, the buyer can go to court. In this case, the store will pay not only the money you spent, but also a fine for failure to comply with consumer requirements. Our lawyers have accumulated extensive experience in resolving such issues. If the store refuses to issue a return of goods without a sales receipt, call us! Specialists will provide a free consultation and advise you on what to do in this situation.
The legislative framework
The buyer has the right to return the product to the supplier even if it is not defective or damaged. This rule is established by Article 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. There are the following reasons for a return:
- All necessary documents are missing.
- Defect detected.
- The product has expired.
- The supplier sent products in a smaller volume than was agreed upon, or the wrong product was delivered (according to Articles 466 and 468 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Unsatisfactory product quality (Article 475 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- There is no container if there should be one (Article 482 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Upon acceptance of the goods, the buyer must carefully inspect it. If any defects are found, a refund will be issued.
How is VAT charged to the buyer when returning goods to the seller ?
Complaint to the store
If the seller refuses to accept the goods, it is worth making a written complaint in free form. It is issued in two identical copies. One remains with the buyer, the second is sent to the store manager.
Be sure to reflect in your claim the sequence of purchasing the dishes, making a decision to return and the actions of the seller when trying to exchange.
Next is to reflect the requirements. Please note that the store management is obliged to pay compensation for the inconvenience.
The product is described in accordance with its purpose, model, style. It is also advisable to indicate the color, volume, and cost of the dishes in the application.
If a product is returned with a manufacturing defect, it is worth describing in detail what defects are present and how the buyer discovered them.
If the buyer conducted an independent examination, its results should be attached to the application. An assessment is not necessary at the buyer’s expense; the store independently determines the time of occurrence, as well as the nature of the damage.
Please note! Be sure to refer to the regulations establishing the procedure for returning goods:
- Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”;
- Article 309 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 310 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 503 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
If there is no receipt for the purchase, this will be indicated in the claim. It is worth notifying management that if the solution is unsatisfactory, you intend to send a complaint to the Russian consumer supervision or court.
On your copy of the claim, ask for the signature and date of acceptance from the seller. If he refuses, send the application by registered mail with notification.
Returns without a cash receipt: fines on all sides
Alena ANDROPOVA
A retail buyer demands a refund for a defective product. But he doesn't have a cash receipt. What to do? Accept the goods without a receipt or refuse the buyer? Whatever you do, you risk breaking the law.
Seller: “We won’t give out money without a receipt!”
The seller needs a receipt for the returned goods. Without it, he will not be able to process all operations to return goods and issue money from the cash register.
Thus, when returning goods on the day of purchase, the seller is obliged to draw up a report in form No. KM-3 (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of December 25, 1998 No. 132). Moreover, the seller draws up this act precisely on the basis of a canceled cash receipt, since the document must indicate the check number and the amount entered on it.
To give the buyer money from the cash register, the cashier also needs a returned check. Moreover, with the authorization signature of the director of the company, his deputy or the manager of the store. This rule is established by clause 4.2 of the Standard Rules for the Operation of Cash Register Machines (approved by letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 30, 1993 No. 104). Canceled checks must be submitted to the accounting department along with the act in form No. KM-3. Based on these documents, the cashier enters the amounts issued to customers for returned goods in column 15 of the cashier-operator's journal. The total amount of revenue for the day, which the accountant accepts according to the receipt order and records in the cash book, is reduced by the total amount.
Buyer: “I’ll go to court!”
However, the buyer insists that you must return his money for the goods without a receipt. He has the right to do so. On his side is the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300-1 “On the Protection of Consumer Rights.”
This law clearly states: the seller cannot refuse to accept low-quality goods from the buyer and return the money to him due to the fact that he did not present a cash receipt (Clause 5 of Article 18 of the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300-1).
If the buyer goes to court, the judges will support his demands and force the seller to accept the goods without a receipt. And in addition to everything, the company will be obligated to pay a penalty to the buyer for the delay in his demands. The amount of the penalty is 1 percent of the cost of the goods for each day of delay (Article 23 of the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300-1).
Some sellers are trying to challenge these regulations. As an argument, they refer to Article 493 of the Civil Code. It says that sales or cash receipts confirm the fact of purchase. And without them, the buyer cannot talk about the seller’s obligations to him. It would seem that if there is no receipt, there is no reason to return the money. “However, the same article 493 of the Civil Code allows the buyer to make a reference to witness testimony,” warns the director of the auditing firm Finstatus, Alexey Beklemeshev. “In addition, the buyer can provide other documents proving that the purchase and sale of goods actually took place.”
Whatever one may say, you will have to give the buyer money without a cash receipt.
Inspection: “No receipt - get a fine”
But in this case, the seller may face another danger - a fine from the tax office for not posting money to the cash register (Article 15.1 of the Administrative Code). When checking the cash register, inspectors may consider that since canceled cash receipts are not attached to the acts in form No. KM-3, the company does not have evidence that money was issued for the returned goods. They justify their position as follows.
Firstly, tax officials recall clause 4.2 of the Standard Rules for Operating Cash Register Machines: the cashier must issue money from the cash register using a returned check that has been canceled and signed by the director.
Secondly, according to the inspectors, in this case the company violates paragraph 12 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). It says that every operation of the company must be supported by supporting documents. “The returned cash receipt is just such a document,” the inspectors say.
It turns out that the money “left” the cash register without reason, instead of being credited to the cash register. And this is a reason for a fine of 40 thousand rubles for the company and four thousand rubles for the management (Article 15.1 of the Administrative Code).
Judges: “You can’t fine!”
This is exactly the situation I found myself in from St. Petersburg. She refused to pay the fine issued by the inspectorate and went to court.
The arbitrators rejected the inspectors' request. They disagreed that the lack of bounced checks meant the company had not cashed in the money. After all, the company executed acts in form No. KM-3 (even without canceled cash receipts) and made all the necessary entries in the cash book. This means that the inspection had enough documents to understand on what basis the company issued money from the cash register.
The inspector's decision to collect the fine was declared illegal by the judges (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated June 16, 2005 No. A56-2903/05 - Clerk.Ru wrote about this on July 22).
Judges of the Federal Arbitration Court of the East Siberian District considered a similar case in 2004. The inspectors wanted to collect a fine from both the selling company and its chief accountant. The reason is that cash receipts were not attached to the cash return acts. This means that they cannot be considered correctly issued, the inspectors decided. And accordingly, it cannot be said that the company has supporting documents for the amounts issued to customers.
The arbitrators did not support the inspection findings. The absence of a canceled cash receipt does not in itself confirm that the company did not receive cash into the cash register. To document a cash transaction, acts in form No. KM-Z are sufficient,” they indicated in their decision. Moreover, according to the Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights”, the seller cannot refuse to return money if the buyer does not provide him with a cash receipt. The inspector’s decision to collect fines in this case was also canceled by the judges (resolution dated February 25, 2004 No. A33-15332/03-S6-F02-468/04-S1).
The next day - the same
The buyer can return the goods not on the day of purchase. In this case, the company issues money for low-quality goods from the cash register in a different order and draws up other documents. The buyer writes an application and presents his passport. The selling company draws up a cash order and according to it issues money from the cash register (Procedure for conducting cash transactions, approved by letter of the Central Bank dated October 4, 1993 No. 18). It is not stated anywhere that a canceled cash receipt must be attached to the consumable.
However, sellers in this case also ask buyers for cash receipts. At least so that they can prove that the product was purchased in this particular store, from this company.
Buyers, as in the case of returning goods on the day of purchase, have the right to demand that their money be returned to them even without a cash receipt (clause 5 of Article 18 of the Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights”). Having fulfilled their requirements, the company may again face accusations from inspectors of “failure to report.” The arguments in defense of the company in this case will be similar to those that help companies when returning money to the buyer on the day of purchase (see “Judges: “You can’t fine!”).
The buyer has the right to return the goods without a sales receipt. For the company, such a situation can result in a fine.
Unlock access to the private part of Clerk with a Premium subscription. Get hundreds of webinars and online courses, unlimited consultations and other proprietary content for accountants.
Hurry up to subscribe with a 20% discount until October 15, 2021. Read more about “Premium” here.