Although it is believed that in our country there is no discrimination based on gender, nevertheless, many employers are reluctant to hire young girls who do not have children. However, young mothers cannot relax either. For those who already have at least one child, HR specialists invariably ask whether more children are planned. This is due to the fact that employers do not want their employees to go on maternity leave. It is also possible to understand them: a valuable employee who is in her place and effectively performs her duties in the event of pregnancy will have to look for a replacement. And this is a waste of time, resources, paperwork, etc.
But if pregnancy does occur, what should the employer do in this case? Is it possible to fire an employee working under a fixed-term contract, part-time or on a probationary period? Let's look at these and some other situations in more detail.
Question: Can an employer fire a pregnant part-time employee in connection with the hiring of an employee for whom this work will be the main one? View answer
What does the law say about dismissing a pregnant woman?
Since the rights of women expecting a child are protected in a special way, from the point of view of the law, it is almost impossible to fire an employee who becomes pregnant, regardless of her position and status. That is, if a woman does not want to leave her job, then the opposite desire of the employer does not matter. However, this is clearly interpreted if a pregnant woman is on the staff of the enterprise, but what if not?
How to fire a pregnant woman during liquidation of an organization ?
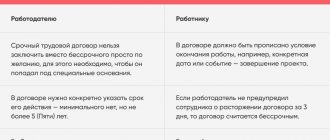
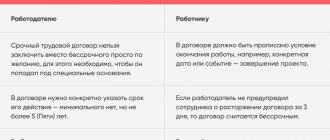
Dismissal of a pregnant woman working under a fixed-term contract
All of the above also applies to those pregnant women who previously entered into a fixed-term contract with their employer. It is strictly forbidden to fire a conscript if she:
- expressed in writing a desire to extend the validity of a fixed-term employment contract, that is, wrote a corresponding application;
- provided a certificate from a medical institution confirming pregnancy.
Important! A certificate of pregnancy must be brought to the employer every three months, until the birth.
In cases where a young woman on a fixed-term contract continues to work after the birth of a child, the employer has every right, on his own initiative, to terminate this contract with her due to its expiration.
Question: Is it legal to dismiss a pregnant woman due to the expiration of the employment contract (Clause 2, Part 1, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), if she did not apply for its extension and did not provide a medical certificate confirming pregnancy? View answer
conclusions
A fixed-term employment relationship cannot be terminated with a pregnant woman, unless, of course, she is hired to replace an absent permanent employee.
The agreement should be extended until the end of pregnancy or maternity leave, if it is issued. The maternity leave must be issued if the woman has provided sick leave and an application requesting leave.
For the entire period of maternity leave, a benefit should be assigned, the calculation of which is made in the standard manner on general terms.
Dismissal of a pregnant woman working part-time
If a pregnant woman works as a part-time worker, then in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is not possible to dismiss her on legal grounds.
When do courts allow the dismissal of pregnant women ?
However, if suddenly there is an employee in her place who is ready to work on a permanent basis, then the woman must be given an alternative in the form of another position.
Exception: in a situation where a part-time woman replaces another employee who is temporarily absent due to maternity leave, illness, business trip and for some other reasons, she can be fired as soon as the one at whose workplace she is returned.
Can they fire me?
Although the law protects expectant mothers from dismissal, in some cases the employer still has the right to terminate the employment relationship with an employee during her pregnancy. This is possible in exceptional cases:
- If the woman held the position of a temporarily absent employee who returned to her place of work (position) before the end of her pregnancy. But here the administration is obliged to offer the worker all available vacancies. Dismissal is permitted after receiving a written refusal of such proposals.
- When a company is in the process of being completely liquidated. Here the employment relationship is terminated without any offer. Even those who are on sick leave or on vacation can be fired.
- The fact of pregnancy will not be confirmed by a medical document. Here the norm of a previously concluded employment contract will simply work, where its expiration date will be indicated.
- Immediately after the end of pregnancy. Not only the birth of a baby is taken into account, but also artificial termination of pregnancy.
- When the seasonal contract is completed and the work is completely completed. Here the administration is obliged to suggest other vacancies at the enterprise. Dismissal is permitted in case of refusal or inconsistency with the existing level of qualifications (due to health reasons).
Remember, before parting with the expectant mother, the employer is obliged to take all measures to employ her in other positions until the end of the interesting position. Otherwise, such dismissal will be illegal.
Dismissal of a pregnant woman on probation
Obviously, it is almost impossible for a woman with a noticeably rounded tummy to get a job. But if a personnel employee did not immediately notice the signs of pregnancy, but paid attention to them already during the probationary period, what can be done in this case?
As the law says, if the fact of pregnancy was discovered while the woman was on probation, then she cannot be fired.
However, to confirm pregnancy, a woman must present a corresponding certificate from a doctor. Thus, the employer organization will have to cancel the probationary period and maintain the woman as a staff member until the birth.
What are the features of dismissing a pregnant woman upon expiration of a fixed-term employment contract ?
Holiday to care for the child
The law stipulates that a woman who has given birth to a baby, upon her application, must be granted leave due to the need to look after the baby until he turns 3 years old. In this case, there are also some peculiarities that you need to know about even before this date:
Such leave is provided to existing employees. In other words, at the time of writing the application for this leave, the employment agreement should not terminate. Otherwise, the employer will simply formalize your dismissal and leave your application for another vacation without consideration.
If an employee working under a fixed-term employment agreement wants to immediately go on maternity leave after giving birth, it is better to immediately discuss this issue with the employer. Even during the period of the first extension of the employment contract, which is due to expire. This will save nerves and time for both parties and not waste time sorting things out.
The father, grandparents, guardians and other relatives also have the right to inspect the baby. In this case, the woman is not entitled to rest, and immediately after the end of the pregnancy, she becomes an ordinary employee, relations with whom can be terminated at any time.
Is it possible to fire a pregnant woman at the initiative of the employer?
There are often situations when, for some reason, a pregnant woman cannot cope with her responsibilities or makes her doubt her competence. It is not surprising that in these cases, the employer prefers to see in her place a more successful and efficient employee who performs the job fruitfully.
However, in accordance with the law, regardless of the reasons prompting the employer to voluntarily part with an employee who is expecting a child, this is impossible.
Thus, as can be seen from all of the above, it is impossible to fire a pregnant woman:
- not in case of poor quality work performed during the probationary period;
- not in case of termination of a fixed-term employment contract;
- not when working part-time;
- not at the will of the employer unilaterally;
- not even if the employee fails to fulfill her job duties.
If the dismissal does occur, the pregnant woman has the right to sue the employer . As practice shows, the courts almost always side with the plaintiff, and the employer, in addition to everything, also bears administrative responsibility.
Features of registration of maternity leave
Pregnant workers have their rights
Even when working under a time-limited employment contract, you can enjoy all the rights granted to pregnant women.
In order to go on maternity leave calmly, you need to state all your wishes in a statement. Then, after 30 weeks of pregnancy, they calmly go on maternity leave. These norms are contained in Article 261.
Receiving maternity benefits
For women signed up for a fixed-term contract, maternity benefits are calculated according to the usual principles. They receive all the money they are legally entitled to until the end of their maternity leave. Employees employed under a fixed-term contract are entitled to the following payments:
- a special benefit that is paid for early registration;
- lump sum benefit for pregnancy and childbirth;
- benefits (as the average salary for 140 days) for pregnancy and childbirth.
All payments are made to the account of the pregnant woman / woman in labor.
When and under what conditions can you fire a pregnant employee?
Force majeure and unforeseen situations occur in the work of every enterprise. Now let's consider those cases when the dismissal of a lady in an interesting position is possible, regardless of her opinion and desire. There are a number of objective reasons for this:
- If a pregnant woman worked for an Individual Entrepreneur, and he ceases his commercial activities due to the expiration of the state registration certificate;
- Dismissal of a pregnant employee is also possible if the employer company is liquidated. In this case, a certain procedure must be followed.
Firstly, you need to warn the pregnant employee about the upcoming fact in advance, or rather two months before the closure of the organization, against signature. Secondly, pay severance pay in the amount of the average monthly salary. In addition, it is necessary to maintain her average monthly salary for the duration of her job search (but not more than two months).If everything is carried out in strict accordance with the letter of the law, then no sanctions from the labor inspectorate should follow in the event of claims from a pregnant employee.
- Liquidation of a branch or representative office is also a legal basis for terminating the employment relationship with a lady in an interesting position. Even if the head office continues to operate as usual, employees of branches and representative offices are subject to dismissal in full. At the same time, the employer, in order to avoid violations, must be guided by the same recommendations as in the previous paragraph.
- Dismissal at your own request. If a pregnant employee expresses her own will for dismissal, then the employer has no right to contradict her. To do this, the lady just needs to write a written statement requesting her resignation, and after two weeks this fact can be considered accomplished. However, if for some reason a woman changes her mind about quitting, she has every right to withdraw her application. In this case, you just need to write an application to withdraw your resignation letter and set a specific date. You can withdraw your resignation letter only before the expiration of the two-week “working off period”.
Based on all of the above, we can draw the following conclusion: each case of dismissal of a pregnant woman from work should be considered individually. If forced dismissal occurs in situations not provided for by law, then, as a rule, it costs negligent employers, which is called “more expensive for themselves.” If the dismissal is legal and justified, then it must be carried out in full accordance with the strictly established procedure.
Extension of the contract term
Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges the manager to continue professional interaction with the future woman in labor for the entire period of her position, and in cases of an already presented break for its entire period.
However, for this, the interested party must fulfill a mandatory condition, which is expressed in the provision of two documents:
- personal written request;
- conclusion of a medical specialist.
Only with these papers will further interaction be possible.
The principle of job security applies to all working women giving birth. The nature of the work performed, as well as the peculiarities of interaction, with rare exceptions, do not play a role here.
The person must contact the manager with a request to continue interaction, documenting his position. According to current regulations, the boss can request such confirmation more than once, but no more than once every three months.
After submitting these documents, the manager is obliged to issue an order of the appropriate nature, on the basis of which an addition to the previously reached agreement will be drawn up and signed. A person is introduced to such papers with a personal signature.
The current norms have not determined the period during which a woman in labor must express her intention to continue the relationship. However, from the meaning of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it follows that interaction will continue only while in a situation.
Since it is quite problematic for a manager to inform a person who has temporarily interrupted his work and is outside the company, this can be done at the time of signing the agreement, warning about the period of the relationship and how to continue it.
Are there frequent cases when a manager does not continue mutual cooperation? referring to the fact that the person did not submit the relevant documents. However, judicial practice shows that a woman in labor can cancel such a decision.
Thus, the following is quite clear:
- even in the absence of documents, it is necessary to inform the person about his opportunity and request the necessary information from him or receive a written refusal;
- the continuation of the relationship is documented by an addition to the agreement;
- when a person is absent, the final day of work will be the day the break from work ends.
Possible problems
- An employee cannot apply for an extension of her employment relationship if she was initially hired for a temporarily vacant workplace. Immediately after the absent employee returns to work, the contract terminates.
- But in the case of a pregnant employee, the employer cannot simply part with her based on the above reasons. He must take care to provide another place for work that corresponds to the lost place to one degree or another.
- If he refuses to do this, the woman can safely contact the labor inspectorate or the courts, since Article 261 of the Labor Code (part three) has been violated.
- Exception of bankruptcy with subsequent liquidation of a legal entity. In this case, the employer is physically unable to provide a suitable vacancy for the pregnant employee.
- Another possible violation of an employee’s rights concerns the provision of a leave period to care for a child. There is no indication in the law that the employer is obliged to provide it. However, if such a request is reflected in the application, management does not have the right to ignore it.
What are the consequences for an employer of wrongful dismissal?
The law strictly protects the rights of current and future mothers , so illegal dismissal in such a case can have unpleasant consequences for the employer. In particular, he may be brought to criminal liability.
Such an employee can be dismissed only in specially specified cases and must be formalized by law. We must also remember that even if the application for termination of the contract was written by the employee herself, she may change her mind and demand reinstatement to her position - and this will be within the law.
Important! It is necessary to inform the employee of the decision to dismiss at least three days before the planned event (better, of course, earlier), and on the day of dismissal the employee should be fully paid and a work permit issued.
If, nevertheless, the rights of a pregnant employee were violated, she should seek help from the court. Groundless dismissal of a pregnant woman may result in a fine. Its size can be up to two hundred thousand rubles or will be equal to several months’ salary. In addition, the offender may be sent to compulsory labor.
Reinstatement at work
Cancellation of a dismissal order
Each significant action within the organization is documented in the appropriate document. The decision to cancel an existing dismissal document is also issued in the form of an order. The law does not provide for a strict form for this document, but it must contain the required information:
- Name;
- details of the document to be cancelled;
- information about the name of the enterprise and its registration data;
- grounds for cancellation;
- date.
The registration is completed by affixing the seal and signature of the manager. Next, the HR employee familiarizes the employee with the order, about which a corresponding note is made with the signature of the familiarized person.
The grounds for canceling an order are:
- Voluntary withdrawal of resignation by an employee.
- Manager's decision. For example, when it is revealed that an employee has been unfoundedly accused of violations that served as the basis for termination of the employment contract. The employee's consent is required.
- A court decision to reinstate an employee at work.
In the first two cases, an order to cancel the decision is sufficient. They will differ only in terms of the grounds for cancellation.
A sample order is available.
If there is a court decision, the employer, in addition to the document discussed above, has the right to issue an order to reinstate the employee in the workplace.
Arbitrage practice
According to Art. 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the basis for terminating an agreement with a temporary worker is the actual departure of the absent employee. Absence due to maternity leave may be followed by absence due to childcare. Thus, the departure date of a permanent employee is delayed. The courts take the position that if the employee does not actually go to work, then the agreement with the temporary employee cannot be terminated in the absence of other significant circumstances.
There is an inaccuracy in concluded contracts with the wording “until the expiration of maternity leave”. Since the duration of the work for which a replacement person is hired is not determined solely by the duration of absence due to pregnancy and childbirth. The period is increased at the request of the woman in connection with caring for the child.
This fact does not depend on the company. Therefore, the nature of the contract is defined as concluded during the absence of a permanent performer. Despite the inaccuracies that are made when hiring, the duties of a substitute cannot be diminished. And the job must be reserved for him if the permanent performer does not actually return to work. When considering such cases, judges carefully examine this fact.
An example is one of the proceedings in the city of Belgorod. A woman hired for a temporary job to replace an employee on maternity leave was fired. The reason was the fact that the maternity leave was earlier than scheduled. She decided to take maternity leave later.
The dismissed employee felt that her rights were violated, and that the organization’s administration was obliged to change the terms of the contract with her or conclude a new one. She filed a claim for reinstatement at work. She was refused on the grounds that the plaintiff’s demands were unfounded. The judge concluded that the dismissal was legal and that the organization had no grounds to change the terms of the agreement.
If, at the time of drawing up the document on termination of the agreement with the replacement person in connection with the end of the main employee’s maternity leave, the employer had information about the further absence of the permanent employee due to child care, the dismissal is considered illegal. If a temporary performer is pregnant, this fact is not decisive, provided that she was hired for the replaced position.
The position of the judicial authorities is unanimous regarding the terms of performance of the duties of a substitute, which expire at the time the main employee actually returns from vacation. The release dates specified in the agreement do not matter, and the permanent contractor began his duties later or earlier than the prescribed deadlines. This rule is intended to protect the rights of the key employee.
Preliminary indication of specific start and end dates of employment is not prohibited. But at court hearings, the actual time of departure of the permanent contractor is established, based on which the legality of the dismissal is established.
Thus, there are no grounds for dismissing a temporary person if the main employee has not taken up his official duties. At the same time, if he starts them earlier than planned, the contract with the replacement person is legally terminated.
Important! Before terminating an agreement with a pregnant conscript, the organization is obliged to offer her available vacancies that correspond to her qualifications, including lower-level ones. The replacement employee should be explained her rights to fill another vacant position, as well as subsequent dismissal in the event of refusal. An act is drawn up, where a note is made about these clarifications, the fact of refusal is recorded against the signature of the conscript.
These actions must be taken in order to provide all the evidence in the event of litigation that the employer took into account the employee’s rights, which will indicate his reliability.
Dismissal when the replaced employee returns to work
This point is also regulated by Article 261. If, during the pregnancy of an employee, the specialist in whose place she was hired returns to work, dismissal is possible, but subject to certain conditions.
The expectant mother is obliged to return the position to the returning employee. The management provides the pregnant woman with information about all possible vacancies that correspond to her position and qualifications. If a woman has given her written consent, she can be transferred to a position with a different salary and qualifications. The location must be appropriate for the health condition.
Additionally
Part-time work and lower wages are acceptable.
Management may raise the issue of terminating the employment relationship if the following facts occur:
- Birth of a child;
- Termination of pregnancy for other reasons.
Attention
The company administration has the right to demand confirmation of her condition from the pregnant woman once per quarter.