What is an employment contract
This is the most important document that regulates your relationship with your employer.
It is the contract that you will refer to in case of disagreement and will go to court with it if something goes wrong. The text of the agreement must specify the responsibilities of the employer and employee. In particular, the contract guarantees you the payment of wages, vacation pay, sick leave in accordance with the law, and gives the company confidence that the required amount of work will be completed.
It is important to understand how this document is drawn up in order to ensure that your interests are respected.
Taxes
Let's consider all payments.
Personal income tax
By law, the employer performs the function of a tax agent. This means that income taxes will be withheld from your salary. Therefore, when you get a job, ask: will you receive the promised 30,000 in your hands or will you still have to subtract 13% tax from it to find out your real salary?
Insurance premiums
These expenses are no longer deducted from the salary, but fall on the shoulders of the employer, and wow!
- Insurance contributions to the pension fund. These contributions theoretically guarantee your pension in the future and support retirees now;
- Insurance contributions to the compulsory health insurance fund. These taxes support free healthcare;
- Insurance contributions to the social insurance fund. And thanks to these contributions, you can be sick at home for a couple of days and not lose your entire salary for the missed days. Thanks to the same fund, payments are provided to employees who have received a work injury, and maternity and child care leave.
The minimum that goes towards insurance premiums is 30% of your salary before personal income tax is withheld.
That is, you earned 30,000. You will receive 26,100 in your hands. Your personal income tax – 3,900 – will be sent to the tax office. And on top they will add at least 10,000 from themselves for insurance premiums. In total, 13,900 will go to the tax and various funds - almost half of what you earned!
Official employment: what is an employment contract, GPC and self-employment
What are the types of employment contracts?
Indefinite
An employment contract is concluded for an indefinite period until something changes for one of the parties. For example, until you decide to quit or the company ceases to exist.
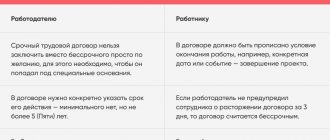
Urgent
An employment contract is concluded for a certain period, which cannot be established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 58. The term of an employment contract cannot exceed five years. At the same time, the employer must have grounds for drawing up just such an agreement, for example, replacing an employee during maternity leave. If there are no good reasons, the court may recognize the fixed-term contract as indefinite. This is done in order to protect the rights of workers.
Sometimes companies enter into fixed-term contracts without justification in order to freely fire an employee when the agreement ends. Often, this is done by companies with a precarious financial situation, which today can afford a certain number of employees, but tomorrow they can no longer afford it. With the help of fixed-term contracts, they try to save on compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties. But the law does not welcome such prudence.
Fixed-term and unlimited-term contracts
One of the difficult points that you need to pay attention to is fixed-term contracts. Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes cases when an employer has the right or obligation to conclude an employment contract with an employee for a certain period:
- for the duration of the duties of an absent employee whose job is retained;
- for the duration of temporary (up to two months) work;
- to perform seasonal work, when work can only be carried out during a certain time of the year;
- with persons who are sent to work abroad, etc.
Unreasonable conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract is prohibited. For violation of the requirements of labor legislation, Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for administrative liability in the form of a fine in the amount of:
- for officials - from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles,
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles,
- for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
If fixed-term employment contracts for a short period of time are concluded with an employee repeatedly (three or more times) to perform the same job function, the court can re-qualify such contracts as open-ended (clause 14 of the Resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 No. 2).
An employment contract for a certain period with a foreigner is drawn up on the same conditions as with citizens of the Russian Federation - in accordance with Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Employees of the company's personnel department should not be confused by the fact that a work permit, a patent, a temporary residence permit, and a residence permit have a certain validity period. The grounds for concluding a fixed-term employment contract with a foreigner do not change. This is indicated by Art. 327.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Who signs the employment contract?
The agreement is concluded between the employer and the employee. An employee is an individual. The employer can be an individual, an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity. In the first two cases, the employer himself signs the contract. This can be done on behalf of the legal entity by the director or the person to whom he has given such powers by order.
Make sure that the contract with the legal entity indicates on the basis of which document the specific person signed it. Information about this should be present at the very beginning of the agreement.
Conditions are optional, but useful
There may not be any additional terms of the contract at all. It depends on the needs of the employer and his openness. For example, if you hire a person to work in a separate unit located in another area, you should definitely clarify the work address. Optional items include information about the probationary period, access to commercial or official secrets.
It is also possible to include terms for payment for studies in this section if the applicant is already studying or there is a preliminary agreement with the employer that the studies will be paid for in full or in part. The employment contract must specify the conditions under which the employer agrees to train the employee. As a rule, the employer who paid for the training requires the employee to work for a certain time in the organization after completing the training course (three years, five years, another period) in order to justify the expenses incurred. If an employee breaks the agreement and quits on his own initiative before the end of the agreed period of work, he must reimburse the employer for training costs - usually in proportion to the time not worked.
Whatever points you include in the contract, remember one thing: the parties to the employment contract must come to an agreement, which means that the applicant can also make suggestions on the content of the document. By refusing to cooperate, an overly principled employer risks losing a valuable specialist whose search has already cost the company time and money.
What documents are needed
To conclude an agreement, you will need the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 65. Documents presented when concluding an employment contract:
- passport;
- SNILS;
- work book, if any (in the case of the first job, the company must create it independently);
- educational document - diploma or certificate;
- military registration documents.
If necessary, the employer may require a certificate of no criminal record, as well as a certificate of administrative liability for drug use. And that’s all; you cannot ask the average citizen for additional documents.
Applicants for civil service positions will have to obtain a certificate of income when filling which employees are required to provide information on income, expenses, property and property-related liabilities and the Procedure for submitting this information.
TD or GPA?
Another difficult issue is the distinction between employment and civil law contracts. Letter of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated May 20, 1997 No. 051/160-97 “Recommendations on the distinction between an employment contract and related civil law contracts” contains a list of signs by which we can determine that we have before us an employment contract:
- the position is included in the staffing table or the employee is enrolled in the organization’s staff;
- the employee undertakes to perform any assigned work;
- the contract stipulates the labor function;
- the work is carried out over a certain period of time;
- the employee undertakes to perform a certain amount of work assigned during working hours, or he must complete a predetermined amount of work;
- the time worked is noted in the time sheet;
- the employee obeys the orders and instructions of the managers (supervisors) of the organization;
- the employee bears disciplinary liability under Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the employer has the right to reward the employee on the basis of Art. 191 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the employee is subject to internal labor regulations (charter, regulations on production discipline);
- the employee performs the work personally.
By inviting the applicant to sign a civil contract, the customer does not guarantee the contractor paid leave, temporary disability payments, does not reimburse travel expenses, etc.
The conclusion of a civil contract that actually regulates labor relations between an employee and an employer entails the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles; for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles; for legal entities - from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles (part 3 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
The employer will be forced, in addition to paying a fine, to include the employee in the workforce, provide all guarantees, compensation and benefits provided for by labor legislation, as well as pay additional social insurance contributions.
How is an employment contract concluded?
The agreement is concluded in writing and signed by both parties. You must be given a second copy. Keep it as the apple of your eye: it will come in handy in case of problems.
If the contract is not ready in writing, but you have actually begun to perform your duties with the knowledge of the employer, then the agreement is considered to be concluded by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 67. Form of the employment contract. The employer has three days to formalize everything properly.
The employment contract comes into force under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 61. The employment contract comes into force at the moment it is signed by both parties. It usually specifies the date on which the employee must begin activities within the scope of his position. If this is not specified, the first working day is considered to be the next after the conclusion of the contract.
Unified form No. TD-1 - when is it applied?
There is no single form of employment contract, because It is impossible to come up with the perfect sample for all occasions. Chief accountant, blacksmith, cook, system administrator - each position brings its own characteristics to the employment contract. For example, only in an employment contract can one provide for the working hours (for some professions with hazardous working conditions, a shortened working day is provided), the duration of vacation (for some categories, not only basic but also additional vacations are established), as well as various types of compensation and guarantees.
But you can make the registration process easier. For this purpose, there is a unified form of an employment contract (form TD-1) - it can serve as the basis for drawing up various employment contracts, since it contains general (standard) conditions provided for by law. the unified form TD-1 can be found by clicking on the picture below.
What should be specified in an employment contract
Labor function
The document specifies your position. This is especially important for those whose specialty requires special working conditions, additional vacation days, and early retirement.
Place of work
Enter the address of the office where you will be present. This line will protect you from a situation where the company decides to send you to another branch.
Start date and contract term
This has already been written above. Please be aware that if you do not show up for work on the specified day, your employer may cancel your employment contract.
Terms of payment
The document must specify the salary, additional payments, allowances, and bonus conditions. It is important. If bonuses are issued in circumvention of the employment contract, then they can very easily stop being paid. And you won’t even have anything to object to.
Work and rest schedule
The working week may be different from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 100. Working hours, but in the norm of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 91. The concept of working time. Normal working hours are no more than 40 hours. The contract should state whether you work five days a week from 9:00 to 18:00 with a lunch break, six days, or have a flexible schedule.
Guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and dangerous working conditions
For example, additional leave will be indicated here.
Conditions determining the nature of work
It's about whether you need to move around, such as visiting branches or customers. In this case, the traveling nature of the employment will be indicated.
Working conditions in the workplace
The workplace must be assessed by the Federal Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ, in order to correctly pay compensation if the conditions are harmful or dangerous.
Condition for compulsory social insurance of an employee
The employer is simply informing you of your rights.
Other conditions
The employer can make additions to the contract if they do not worsen the employee’s position. This includes information about the probationary period, non-disclosure of trade secrets, the obligation to work for a certain period after training at the expense of the company, and so on.
Parties details
The employee's last name, first name and patronymic, as well as details of his identity document are indicated. Employer information requirements depend on who is in that role. For an individual, it is enough to indicate your full name and passport details. The individual entrepreneur adds the TIN. The company indicates the TIN and details. All this is written down at the end of the document.
Taxes
Deductions differ depending on who the employer enters into an agreement with.
GPC with an individual
Deductions when concluding a GPC with an ordinary citizen are not particularly different from an employment contract, but are still more profitable for the employer.
He is also your tax agent, therefore he withholds and sends your income tax (NDFL) to the tax office. Usually he adds contributions to the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. That's it, contributions are not paid to the Social Insurance Fund with very rare exceptions.
GPC with IP
According to the GPC, individual entrepreneurs can also get a job (don’t forget that they also belong to individuals). And for the employer this is even more profitable, because individual entrepreneurs pay all taxes for themselves.
It looks like this: the entire amount for the work done comes to your bank account. You pay income tax on it depending on the chosen tax regime. Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs are fixed, and you also pay them yourself. An ideal situation for an employer!