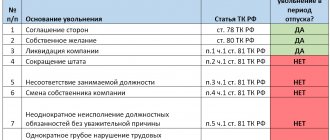
Examples of illegal dismissal
Illegal termination of an employment contract is the dismissal of employees without legal grounds or dismissal made in violation of the procedure itself. The reasons for termination of employment relations and the procedure for formalizing termination of the contract are prescribed in Art. 77–84.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, there are also additional grounds for termination of an employment contract:
- with the director of Art. 278 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- part-time workers (Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- workers hired by individuals (Article 307 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- remote workers (Article 312.8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- foreigners (Article 327.6 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- teaching staff of various categories (Articles 332, 332.1, 336 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- scientific workers of various categories (Articles 336.1, 336.2, 336.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- employees in Russian representative offices abroad (Article 341 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- employees of a religious organization (Article 347 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- with athletes, coaches (Article 348.11, 348.11-1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- assistants and employees of notaries (Article 351.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The presence of other or fictitious circumstances makes the dismissal illegal.
In order for the termination of an employment relationship not to be considered illegal, the following conditions must be met:
- The procedure for dismissing an employee at his own request requires the availability of a corresponding application. The absence of this document makes termination of the contract illegal.
- If a decision is made to reduce staff, then it is necessary that the positions held are actually eliminated and not restored after the employee leaves. In addition, it is the employer’s responsibility to warn employees in advance about the upcoming layoff.
- Dismissal due to violation of labor discipline must be supported by documents: witness testimony, conclusions of medical commissions.
For information on drawing up documents in case of violation of labor discipline, see the material “How to draw up an act of refusal to write an explanatory note.”
- If the contract is terminated due to low qualifications of the employee that do not correspond to the position held, certification is required.
- Dismissal may be considered illegal if, upon termination of the contract, the employee was not given all the documents (work book, certificates upon request), and the amounts due were not paid in full.
There is also a separate category of persons whose dismissal is impossible under normal circumstances. Thus, pregnant women, single mothers with children under 14 years of age (or disabled children under 18 years of age), women with children under three years of age, or single parents are not subject to reduction. If an employee is on leave (including to care for a child), his dismissal at the initiative of the employer is not allowed, except in cases of liquidation of the enterprise.
For more information on terminating contracts during the liquidation of institutions, see the material “The procedure for dismissal in connection with the liquidation of an organization.”
The legal consequences of illegal dismissal for employers may be as follows:
- compensation of average earnings to an employee for forced absences and his reinstatement at work (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- compensation for moral damage received by an employee when an illegally dismissed citizen appealed to the judicial authorities;
- inspection of the employer’s activities by the prosecutor’s office and labor inspection (Article 357 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, the illegally dismissed employee must be reinstated in his previous position.
Sign up for a free trial access to ConsultantPlus and read the article “Correct dismissal: checking with judicial practice and recommendations of Rostrud,” based on the latest clarifications of the legislation.
Welcome back!
Many controversial issues are also associated with the withdrawal of the “dismissal” application. Let us remind you that before the expiration of the notice period for dismissal, the employee has the right to withdraw his application in any form and at any time (paragraph 4 of article 80 of the Labor Code). It is the wording “in any form”, i.e. the uncertainty in which it is necessary to declare one’s desire to continue working in this company, that is the stumbling block.
The employee refers to...
...that he sent the application for revocation by registered mail without an inventory. The disputant can present a correctly and neatly executed application for revocation (and hint that he is ready to show this document in court) with a receipt for “registered” shipping and notification that a company representative received this letter. In fact, the situation resembles a “cheap scam”: he could not have sent any feedback, but put anything in the envelope (a postcard, an advertisement, etc.); but he will nevertheless have the shipping documents.
How an employer can avoid violating the Labor Code . If the situation arose before going to court, most likely it will not threaten you with anything. For your own peace of mind, you can ask the employee (secretary), who received and opened the “letter with nothing,” to write an explanatory note about this (ideally dated the date the letter was received). And make inquiries to see if the post office that serves the company has surveillance cameras.
If a violation is committed. Your main trump card in court is that the letter was sent without an inventory of the contents. After all, confirmation of sending does not mean that it was the withdrawal of the resignation letter that was sent, and not a printout of jokes about a stupid boss. And even if the opponent presents a copy (as he will probably claim, the second one) of the review, then again, the employee will not be able to prove that it was sent. If he suddenly brings two witnesses who allegedly saw him insert and seal the statement, then note to the court that this is at least strange. To do this, people who came to the post office on business had to clearly examine the paper being sent, closely observe the actions of the employee, and then leave him their coordinates. If the witnesses are acquaintances of your opponent, then it is quite possible to raise the question that they could well have entered into a conspiracy with your opponent.
Reinstatement in case of illegal dismissal
In case of illegal dismissal from work, a former employee may claim protection of his rights, compensation for harm and moral damage, as well as reinstatement at work.
Disagreements in labor relations between employees and employers can be resolved in labor dispute resolution commissions and courts.
The deadline for filing a complaint with the labor dispute commission is 3 months from the date of violation of the employee’s rights (Article 386 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An appeal to the judicial authorities can take place within 10 days after the commission’s decision is made (Article 390 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An application to the court is given the opportunity to submit no later than a month from the date of dismissal (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Citizens may demand their reinstatement in their previous position at the workplace if the employer does not provide compelling reasons for the dismissal. In addition, the judicial authorities have the right to award payments in favor of the dismissed employee in the amount of his average earnings and demand compensation for moral damage from the employer.
Safety issues in labor disputes
Most workers know where to go if they are fired from work without reason - to the labor inspectorate. At the same time, it is worth trying to neutralize the conflict, as well as insure against possible provocations. This will at least give you time to prepare to leave and find a new place. The main thing is not to give in to emotions and not to aggravate the situation with rash actions.
Here are some ways to stay safe:
- Behave politely, restrainedly, correctly.
- Avoid violations.
- Take a vacation.
- Take sick leave. This reliably protects against dismissal.
- If it comes to applying sanctions, you should require that complaints be submitted in writing, with specific references to the norms that are allegedly violated.
- Accurately follow all work-related requirements and instructions. This applies even to those items that have not been used in practice for a long time, but have not been officially canceled. For example, cleaning the workplace or filling out the accounting journal in a timely manner.
- Study labor legislation and motivate your actions with its provisions. Point them out to your superiors.
- Contact your immediate superior or get a meeting with a senior manager and try to clarify the situation and look for a compromise solution.
- When threats or illegal demands are made, it is better to record them on a voice recorder and make a copy of the recording. In the future, if the relevant authorities and the court have to be involved in the situation, this may play a significant role.
- If there is a trade union at the enterprise, it is necessary to contact it with an official statement. It is possible that he will take the employee’s side.
- Officially declare your intention to contact the supervisory authorities.
By showing an exemplary attitude towards fulfilling his job duties, an employee can convince an employer who is about to part with him. The need to document violations that actually do not exist can reduce the number of complaints from management.
Following simple rules can defuse the situation. If dismissal cannot be avoided, the person will have time to prepare an official basis for appealing to supervisory and other authorities.
Results
The procedure for terminating employment contracts with employees and the reasons for its implementation must strictly comply with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Otherwise, illegal dismissal may give rise to legal proceedings between the parties concerned.
If the employer is found to be at fault, he may have to pay for the damage caused to the employee, as well as become the object of close attention from supervisory authorities. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
When the employer is not to blame
An employee cannot be fired without explanation. But before seeking justice, you should make sure that management really does not have arguments for dismissal. It is possible that the employee still has violations or that the termination of the relationship is due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties. This includes:
- Termination of the activities of an enterprise or organization, reduction of its staff. However, this does not eliminate the need for compensation and documenting every step of the employer.
- Inconsistency with the position. For example, an employee needs a certain certification result. It's not easy to dispute. In this case, the employee must be offered a different position, and if he does not agree to it, the employer has the right to dismiss the employee.
- Repeated failure to fulfill job duties - but only those specified in the contract.
- Absenteeism, going to work while drunk, and other violations for which the person was subject to disciplinary action. Absenteeism must be properly documented, and intoxication must be documented with a medical report.
- Violation of safety rules at work, which resulted or could lead to consequences in the form of an accident.
- Theft at work.
- Loss of trust in the employee (usually as a result of damage caused by the financially responsible person).
- Revealing the fact of providing false information when applying for a job.
- Loss of qualifications recognized administratively.
- Restrictions established by a medical commission that affect the mental or physical capabilities of a person and prevent the normal performance of a certain job.
In such cases, the option of dismissal at will is more beneficial for the employee. After all, this is definitely better than getting a compromising entry in the work book.
The employee was not informed about the refusal to give leave at his own expense
The employee wrote a statement requesting two days of leave without pay in connection with the funeral. The director gave verbal consent. The employee submitted an application to the document manager for registration, but the leave was never documented.
When the employee did not show up for work, he was fired for absenteeism.
The court's decision
The first and second instances drew attention to the fact that no agreement on the provision of leave was reached. Based on this, they considered the dismissal legal.
But the Supreme Court expressed a different opinion. He pointed out that the document specialist registered and filed the employee’s application in the incoming document folder. Moreover, when going on vacation, employees never waited for the order to be issued. According to established practice, it was enough to obtain the consent of the general director.
In addition, the employer must have notified the employee of the refusal to provide rest days. He had enough time for this, since the employee submitted an application in advance.