A fixed-term employment contract is convenient if an entrepreneur needs to replace an employee who has gone on maternity leave, hire employees for a temporary project, or carry out atypical temporary work, such as reconstruction.
After the fixed-term contract is terminated, the parties are released from their obligations. Only if they didn't make mistakes. We have collected and analyzed the nuances associated with fixed-term employment contracts so that you do not have any problems with this.
If you don’t have time to read the entire article, check out “The Essentials in 30 Seconds” at the end.
In what cases is a fixed-term employment contract needed?
An employment contract is needed to replace an employee who is absent from work but retains his position, for example, after going on maternity leave or military service. Under a fixed-term contract, workers are hired for temporary or seasonal work.
There are several other grounds on which a fixed-term employment contract can be concluded by agreement of the parties; they can be found in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How to draw up a sample of an open-ended supply agreement
Despite the fact that each agreement is an individually executed transaction, it is possible to identify mandatory conditions that must certainly be present in the document. This:
1. Preamble. The introductory part of the contract, in which the supplier and buyer are identified through their installation data:
- Name;
- location (address);
- information about the managers or other officials who entered into the transaction, and details of the documentation on the basis of which such powers were delegated to them.
2. Subject of the agreement. The main section of the document, which determines the name and quantity of commercial products intended for delivery. Here the range, completeness and packaging of the goods can be agreed upon, although these conditions are not mandatory.
3. Rights and obligations of the parties. A section that specifies the powers of counterparties.
4. Price, conditions and stages of delivery. Important terms of the contract that require approval. When determining the procedure for payment for goods, it is advisable to indicate specific dates for payments or the date of final payment.
5. Duration of the contract. In relation to a long-term transaction, you will need to decide on one of the options for the duration of the transaction discussed above.
6. Addresses, details and signatures of the parties.
Contract term
A fixed-term employment contract is concluded with an employee for a certain period, and if necessary, it can be extended.
The minimum term of such an agreement is not established by law, the maximum is five years. Such agreements can be concluded by employers from small and medium-sized businesses if the number of their employees does not exceed 35 people, or 20 people for retail trade and consumer services.
Kirill Chudinov, executive director of UGMK ASK LLC:
As a rule, the employer enters into fixed-term employment contracts in order not to burden himself with the problems of terminating the relationship with the employee. When concluding such an agreement, the employer, in the case when he does not need the employee, is not forced to fulfill all the formalities of dismissal - a two-month notice of layoffs, offers of another job within the organization, and others. The employment relationship terminates automatically upon maturity.
Unlimited supply contract: legislation
The basic rules regarding the supply contract are established in § 3 of Chapter. 30 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which defines:
- concept of contract;
- procedure for resolving controversial issues when concluding such a transaction;
- provisions on delivery periods of a commercial product;
- procedure for delivery of goods;
- delivery terms;
- provisions for reimbursement of undelivered marketable products;
- rules for acceptance of goods by the buyer;
- the fate of goods not accepted by the buyer;
- payment procedure for goods;
- consequences of delivery of low-quality or incomplete goods;
- issues of contract termination.
In addition, the general rules regarding the following apply to the supply contract:
- transactions;
- obligations;
- contracts
In accordance with the above provisions, a supply agreement is defined as a transaction under which the supplier-entrepreneur undertakes to supply commercial products agreed upon by the parties to the buyer on the terms and conditions specified in the agreement. The above provisions also apply to long-term supply contracts.
Based on the general provisions of the contract, as a rule, the document determines the duration of its validity. Meanwhile, the planned relationship may involve long-term cooperation. Therefore, in some cases, it is advisable to conclude a supply contract for a long period or indefinitely.
What nuances to pay attention to
A fixed-term contract must include several points:
- information about the employee and employer,
- duties of the parties,
- duration of the contract and start date of work,
- grounds for concluding an agreement,
- salary,
- social insurance,
- work and rest schedule,
- guarantees for the employee.
Oksana Vasilyeva, expert on legal issues in business, General Director of Mariox Center LLC:
The following additional conditions may also be included in the content of a fixed-term employment contract: as a rule, these are the duration and conditions of the probationary period when hiring, as well as a condition on non-disclosure of trade secrets.
There are three more points that are important to remember in order to avoid problems.
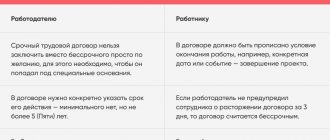
1) Three days before the end of the contract, the employee must be notified in writing of dismissal, otherwise the contract will automatically become unlimited.
Oksana Vasilyeva, expert on legal issues in business, General Director of Mariox Center LLC:
A fixed-term employment contract automatically becomes indefinite if the employee does not receive notice of dismissal from the employer three days before the expiration of the fixed-term employment contract, or both parties have forgotten about the termination period and the employee continues to perform his job duties. If the rights of an employee under a fixed-term employment contract are violated, the court will reinstate him at work, force the employer to pay for forced absence, and possibly moral damages.
2) You cannot constantly renew a fixed-term employment contract with an employee who actually works as a permanent employee of the company. This strategy could result in a court summons.
Arthur Sinikhin, partner of the Legal Bridge Bar Association:
If the validity period of an employment contract exceeds five years, then if disputes arise, there is a high probability that such an agreement will be reclassified by the court as concluded for an indefinite period. Similar consequences may arise if it is established that the contract has been re-signed multiple times, including if the total term of its validity exceeds five years.
3) A fixed-term employment contract cannot be concluded as an alternative to an open-ended one, unless there are grounds for this. This is a violation of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, for which an official and an individual entrepreneur can be fined in the amount of 1 to 5 thousand rubles, and the company in the amount of 30 thousand rubles. up to 50 thousand rubles.
Article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Duration of the employment contract (current version)
1. Part 1 of the commented article, depending on the duration of the employment contract, provides for two types: an employment contract with an indefinite period and a fixed-term employment contract.
When concluding an employment contract for an indefinite period, the parties do not stipulate its duration at all. The agreement can only determine the date of its entry into force (see commentary to Article 61).
When concluding an employment contract for a certain period, the parties must provide for a specific period of its validity (one, two, four years, etc.). Employment contracts concluded for a specific period are called fixed-term employment contracts. Fixed-term employment contracts are usually concluded for a period not exceeding five years. An employment contract for a period of more than five years can be concluded only in cases expressly specified by the Code or other federal law.
2. Having secured the possibility of concluding fixed-term employment contracts, Art. 58, however, limits it to certain cases.
According to Part 2 of the commented article, a fixed-term employment contract is concluded in cases where the employment relationship cannot be established for an indefinite period, taking into account the nature of the work to be done or the conditions for its implementation. This general rule is specified in Part 1 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code, which determines which specific works, by their nature and conditions of execution, belong to the work for which a fixed-term employment contract is concluded (see commentary to Article 59). In other words, Part 2 of Art. 58, referring to Part 1 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code, actually reveals the content of such a legal category as “the nature of the work to be done or the conditions for its implementation.” In this regard, when concluding a fixed-term employment contract, it is necessary to indicate one of these circumstances (reasons) corresponding to the specific situation. Part 2 Art. 58 along with the circumstances listed in Part 1 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code, when a fixed-term employment contract is concluded taking into account the nature of the work and the conditions for its implementation, allows for the possibility of concluding a fixed-term employment contract by agreement of the parties in the absence of circumstances determining the nature and conditions of the work, in the cases provided for in Part 2 of Art. 59 (see commentary to it).
3. Part 3 of the commented article provides that if, when concluding an employment contract, the parties did not stipulate the duration of its validity, the contract is considered to be concluded for an indefinite period. Since this is a general rule, it should also apply to those cases where an employment contract is concluded in connection with the circumstances provided for in Part 1 of Art. 59 TK. Having concluded an employment contract with an employee for an indefinite period, the employer does not have the right to subsequently require him to conclude a fixed-term employment contract.
4. Part 4 of the commented article establishes the rule according to which, if neither party has demanded termination of a fixed-term employment contract due to the expiration of its term, and the employee continues to work after the expiration of the employment contract, the condition on the fixed-term nature of the employment contract is lost force and the employment contract is considered concluded for an indefinite period.
5. A fixed-term employment contract is considered a contract with an indefinite period even if it was initially concluded for a certain period without sufficient grounds, i.e. without taking into account the requirements established by the Code for concluding fixed-term employment contracts (see also commentary to Article 59), and this circumstance was established by the court (Part 5 of Article 58). For example, an employment contract concluded with an employee for a period of one year only on the basis that the employee is registered at his place of residence only temporarily must be recognized by the court as an agreement with an indefinite period. This rule is an important guarantee of protecting employees from the unreasonable conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract with them.
It should be noted that recognition of a fixed-term employment contract as an agreement with an indefinite period is possible only when the fact of concluding a fixed-term employment contract in violation of the requirements provided for by law is established by the court, and not by any other body.
6. Part 6 art. 58 provides additional guarantees to ensure the protection of employees from the unlawful conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract with them. In accordance with it, it is prohibited to conclude fixed-term employment contracts in order to evade the provision of rights and guarantees provided for employees who have entered into an employment contract for an indefinite period.
Thus, it will be considered unlawful to conclude an employment contract with an employee for a period of one and a half years on the grounds that after this period the organization plans to reduce the number or staff of employees. By concluding a fixed-term employment contract in this case, the employer clearly avoids providing the employee with guarantees and compensation related to dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees, because termination of an employment contract due to its expiration does not entail the obligation to pay any compensation.
It should be noted that established by Art. 58 restrictions on the possibility of concluding fixed-term employment contracts are fully consistent with ILO Recommendation No. 166 “On termination of employment at the initiative of the employer” (1982), which provides guarantees against the unlimited use of fixed-term employment contracts when hiring, placing workers in strict dependence on employer.
7. The expiration of the term of the employment contract, if the fixed-term employment contract was concluded lawfully, is the basis for its termination.
The initiative to terminate an employment contract due to the expiration of its term can come from both the employer and the employee himself. The employee does not have the right to insist on the continuation of the employment relationship if the employer has decided to terminate the employment contract due to the expiration of its term.
In the practice of concluding fixed-term employment contracts, the question arose whether the parties to an employment contract whose term has expired have the right to renew it for a new term or extend the term of this contract. The answer to this question should be negative, because... The Labor Code does not provide for a general rule on the re-conclusion or extension of a fixed-term employment contract.
In this regard, in cases where, after the expiration of the employment contract, the parties want to continue the employment relationship for a certain period, they will have to terminate the expired employment contract and enter into a new employment contract for the same or a different period.
It should be borne in mind that the conclusion of a new employment contract for a certain period is possible only in the presence of the circumstances provided for in Part 1 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code, or by agreement of the parties in cases provided for in Part 2 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code (see commentary to Article 59).
An exception to the general rule regarding the extension of the term of an employment contract, its renewal for a new term or changes are the cases provided for in Art. Art. 261, 332 and 338 TK.
In accordance with Art. 261 of the Labor Code, in the event of expiration of a fixed-term employment contract during a woman’s pregnancy, the employer is obliged, upon her written application and upon provision of a medical certificate confirming the state of pregnancy, to extend the term of the employment contract until the end of pregnancy (see commentary to Article 261).
According to Part 8, 9 Art. 332 of the Labor Code, when an employee is elected through a competition to fill the position of a scientific and pedagogical worker previously occupied by him under a fixed-term employment contract, a new employment contract may not be concluded. In this case, the validity of the fixed-term employment contract with the employee is extended by agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, for a certain period of not more than five years or for an indefinite period. When transferred to the position of a scientific and pedagogical worker as a result of election through competition to the corresponding position, the validity period of the employment contract with the employee may be changed by agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, for a certain period of not more than five years or for an indefinite period (see comment. to Article 332).
According to Part 2 of Art. 338 of the Labor Code, when sending an employee holding a position in the relevant federal executive body or state institution of the Russian Federation to work at a representative office of the Russian Federation abroad, changes and additions are made to the previously concluded employment contract with him regarding the term and conditions of his work abroad (see Commentary to Article 338).
Comment source:
Rep. ed. Yu.P. Orlovsky “COMMENTARY ON THE LABOR CODE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION”, 6th edition ACTUALIZATION
ORLOVSKY Y.P., CHIKANOVA L.A., NURTDINOVA A.F., KORSHUNOVA T.YU., SEREGINA L.V., GAVRILINA A.K., BOCHARNIKOVA M.A., VINOGRADOVA Z.D., 2014
How to terminate a contract without mistakes
If the employer warns the employee in writing about the termination of the fixed-term contract three days before the expiration of its term, the contract is terminated. Also, a temporary employee can resign early at his own request by notifying the employer two weeks in advance, or three days in advance if the term of his contract is less than two months. Or you can terminate the contract by agreement of the parties.
Oksana Vasilyeva, expert on legal issues in business, General Director of Mariox Center LLC:
According to labor law, a fixed-term employment contract can only be extended if the woman is pregnant. In other cases, either the term of the employment contract is changed, or the fixed-term employment contract is renegotiated. By agreement of the parties, three days before the expiration of the contract, a new fixed-term employment contract is concluded, or the employee is invited on an indefinite basis and an indefinite employment contract is drawn up in the same manner.
Answer
In this case, the answer depends on many factors.
So, if the contract provides for payment after the end of the term for the provision of services, i.e. after 12/31/2020, the contract continues to be valid, since the party’s payment obligations have not been fulfilled, and the current contract can be terminated by agreement of the parties at any time.
If payment for services was made before 12/31/2020 and the services were provided within the period established in the contract, then the contract has expired and terminated on 12/30/2020. You cannot terminate a contract that has expired. Accordingly, the agreement to terminate the contract in this case can be concluded no later than December 30, 2020.
Flaws
When drawing up employment contracts, both fixed-term and open-ended, it is important to ensure their compliance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, otherwise the contracts are considered invalid. Prescribing additional conditions in the contract aimed at simplifying the dismissal of an employee by decision of the employer is illegal.
The disadvantages of an employment contract for an indefinite period include:
- the need to comply with the company’s internal regulations and rules,
- possible completion of a probationary period,
- When dismissing an employee who has signed an employment contract for an indefinite period, the employer will most likely require him to work for 2 weeks until he has time to find a worthy replacement for the resigning employee.
As a rule, the conclusion of an employment contract for an indefinite period is provided for in cases where a vacant position is included in the company’s staffing table and the employee’s constant performance of labor functions is required. Employment contracts should be concluded for an indefinite period, except for the cases described in Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The sample employment contract for an indefinite period does not contain a separate clause regarding the period of employment.
Employment contract with the director: features
Recently, more and more often, business owners hire outside directors. This is necessary if the founder simultaneously owns several corporations or when he realizes that he cannot manage the company. Not everyone has the necessary experience to successfully manage an organization and set up all processes to generate profits and optimize costs.
If the company's charter specifies the duration of the director's powers, then a fixed-term contract is required. In this case, the document may contain information about automatic renewal if neither party expresses an intention to change it or terminate it. However, an open-ended contract is allowed if the company’s charter does not specify the term of office of the manager.
It is worth noting that a director can only be dismissed if the provisions of the agreement are violated. This is done directly by the business owner. However, the law does not allow the company to recover losses that the company suffered due to the incompetent actions of the employee on its own. To do this, you need to go to court and prove your position. Then, on the basis of a court decision, collection will occur.
Hired director
Important! Today, some employers, when issuing calculations, remind employees, including directors, of all their mistakes. For this they deduct a certain amount themselves. This is not allowed. If an employee discovers such a violation of his rights, he can go to court or the prosecutor’s office to conduct an investigation and defend his rights.
What is retroactive force of a contract and when does it apply?
The retroactive force of a contract is the application of its terms to relations that arose before its conclusion. That is, if there is an actual relationship between you and the counterparty (for example, you rent out the premises, and he regularly pays) and then you enter into an agreement in which you stipulate that it applies to the rental relationship that existed between you previously.
If an actual relationship existed between you, but you did not agree on the retroactive effect of the agreement, it will not be possible to apply the terms of the agreement to these relationships. In particular, the landlord will not be able to collect rent from the tenant for this period in the amount specified in the agreement, but will only have the right to demand payment of unjust enrichment. Moreover, its size may turn out to be much lower than the rent (clause 1 of Article 1102, clause 2 of Article 1105 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note that it is impossible to apply the retroactive force of the contract if this is contrary to the law or otherwise follows from the essence of the relationship (clause 2 of Article 425 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). For example, it is impossible to give retroactive force to a license agreement for the period when the licensor did not have rights to the result of intellectual activity.
Relationship with the agent
How is the validity period of an agency agreement regulated in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation? The text of the law specifies the right of the parties to waive it if there is no agreement on the period of its validity. If the agent is declared incompetent in whole or in part, or is declared bankrupt, the agreement is terminated automatically.
At the same time, the agent and the principal are subject to the rules on services. The parties have the right to terminate the relationship at any time, subject to compensation for expenses or losses, depending on who initiated the termination of the relationship.
Often, the termination of the agreement is not associated with losses or expenses of the party and no mutual settlements are made.
Other conditions
Other conditions include the clause on registration of the transfer of rights under the agreement. This applies to other types of contracts. According to the law, they come into force from the moment of registration for third parties. For participants, obligations begin a little earlier: either from the moment of signing, or from the moment of transfer of property, or the commission of another action confirming the process of fulfilling the contract.
Another way to conclude an agreement is to send a proposal in the form of a draft document, where you only need to put signatures and seals. The transaction is considered concluded from the moment the consent is received by the person who made the offer.
What is the duration of the contract
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (in particular, Article 425) uses the concept of the duration of the contract, but does not define it. Based on the provisions of Art. 425 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the contract begins to operate from the moment of conclusion or
earlier, if the parties extended its effect to previously established relations.
The termination of the contract is determined by the parties independently, if there are no instructions in the law regarding a specific transaction. As a rule, the parties themselves set the deadline.
The duration of the contract can be limited in different ways:
- specific date. For example, “the agreement is valid from November 30, 2020 to November 30, 2021”,
- some time period. For example, “1 year from the date of conclusion (signing) of the agreement”,
- a fact (event) upon the occurrence of which the contract ends,
- the fulfillment by the parties of all their obligations under the transaction, that is, the achievement of the goals for which it was concluded.
It is IMPORTANT to check not only how correctly the duration of the contract is indicated, but also how correctly the clause on termination of the obligation is formulated. If it is not specified that the end of the contract means the end of the obligations, they will remain, and the contract will be valid until the moment designated as the end of their fulfillment (clause 3 of Article 425 of the Civil Code).
Probation
According to Art. 70 of the Labor Code, as a general rule, a probationary period may be established for an employee. According to Part 5 of Art. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the probationary period cannot exceed three months, and for heads of organizations and their deputies, chief accountants and their deputies, heads of branches, representative offices or other separate structural divisions of organizations - six months, unless otherwise not established by federal law.
A six-month probationary period when hiring can be established only for the above categories of workers (Letter of Rostrud dated November 20, 2015 No. 2630-6-1).
A probationary period is established even if a fixed-term employment contract is concluded. When concluding a fixed-term contract for a period of up to two months, a probationary period is not established (Article 289 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). When concluding an employment contract for a period of two to six months, the trial cannot exceed two weeks (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The probationary period is established according to the following algorithm:
1 step. It is necessary to determine the possibility of establishing a probationary period.
This possibility depends on two main factors:
– the term of the most urgent contract;
– categories of employees for whom a probationary period is prohibited.
These categories include:
| Grounds for concluding a fixed-term employment contract | Example |
| Performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee | An employee who is hired to take the place of a maternity leaver during her maternity and child care leave |
| Performing temporary (up to two months) work | Distributors of advertising products (promoters), who are hired for the duration of the advertising campaign |
| Seasonal work (Article 293 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | Bus drivers on routes operating only in summer |
| Performing work outside the normal scope of the employer's activities | Builders hired for the period of reconstruction of the warehouse of a trading organization |
| Performing a specific job if its completion cannot be determined by a specific date | Commissioning and testing engineer, who is hired for the duration of installation, commissioning and testing of new equipment |
2 step. Determine the categories with which a fixed-term contract can be concluded.
A fixed-term employment contract is not concluded with all employees, but only in exceptional cases established by law. 3 . Establish what maximum trial period can be included in the contract.
The table shows that the test period depends on:
– categories of workers;
– the term of a fixed-term employment contract.
| Test period | Category of workers | Norm |
| Up to two weeks | Employees with whom an employment contract is concluded for a period of two to six months | Part 6 art. 70 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Up to three months | Employees for whom the law does not provide for other terms | Part 5 art. 70 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Up to six months | Heads of organizations and their deputies Chief accountants and their deputies Heads of branches, representative offices, and other separate structural divisions of the organization | Part 5 art. 70 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| From one month to one year | Citizens entering the civil service for the first time Citizens or civil servants entering the civil service, appointment to or dismissal from which is carried out by the President of the Russian Federation or the Government of the Russian Federation | Part 1, clause 1, part 2, art. 27Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ |
| From one to six months | Citizens appointed to civil service positions who previously served in the civil service of the Russian Federation Civil servants appointed to civil service positions by transfer from another government agency | P. 2, 3 parts 2 tbsp. 27Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ |
Step 4 Obtaining employee consent.
The employer often forgets that the terms of the employment contract are established by agreement between the employee and the employer.
Step 5 Establishing a probationary period in an employment contract.
The employee’s written consent to the probationary period is expressed in the employment contract concluded with the employee.
In the future, it is important to calculate the probationary period, that is, the time that the employee actually worked.