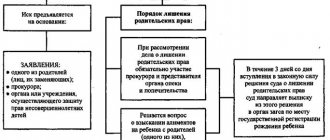
A parent, when committing the actions specified in the list below, may be deprived through the court of parental rights to his child under 18 years of age. The claim is filed by the guardianship authority, orphanage, orphanage, another parent, prosecutor, trustee or guardian in connection with the following actions of the parent:
- Abuse of your rights in relation to a minor. It is expressed in instilling in a young child an immoral worldview, stopping actions aimed at the moral and physical development of the minor, forcing him to engage in prostitution, begging, and inducing him to use alcohol and drugs.
- Leaving a newborn in a maternity hospital, leaving a child in a school, shelter, orphanage, hospital without good reason.
- The father or mother is recognized as suffering from drug addiction or chronic alcoholism.
- Committing a criminal offense whose purpose is to cause harm to the physical well-being or life of another parent, other family members, a minor child or spouse.
- Malicious failure to pay funds under a child support obligation, the recipient of which is a child. This means concealing earnings from which alimony can be paid; lack of information about where the alimony worker lives; putting a parent on the wanted list due to lack of child support payments; initiating a criminal case due to non-payment of alimony or issuing a resolution according to which the defaulter is brought to administrative responsibility.
- Cruel treatment of their child, for example, when a parent deprives children of food or water necessary for their life, forces them to satisfy their sexual needs, tortures or beats children, and exercises psychological terror against them.
The court, having decided to release a parent from having parental rights over his children, deprives him of the following powers:
- Inheritance after the death of a child.
- Receiving all kinds of benefits and benefits that minor children are entitled to from the state.
- The child is released from the obligation to pay alimony in favor of the disabled or needy mother or father who are deprived of their rights to him.
- Be a representative under the law.
- Raise him, participate in his education, solve medical issues.
- Meet with the child.
- Living with a minor in the same dwelling.
The powers of the father or mother were indicated above, which they will lose when the judge terminates their parental rights. What will happen to their responsibilities? Is it necessary to pay child support after the termination of parental rights, or is the irresponsible parent exempt from this obligation? This will be written about in the next chapter.
The relationship between termination of parental rights and child support payments
Russian legislation clearly establishes that parents are required to provide financial support for their young children who are not yet 18 years old. The relationship is documented using a birth register and is duplicated in the birth certificate. Those. the woman and man recorded in this certificate are officially recognized as parents and bear the burden of providing for a young child.
It does not matter whether the child’s parents are legally married or not. This fact cannot in any way affect the entry about parents in the birth book. Therefore, the question that if one of the spouses was deprived of parental rights, whether he should pay alimony, does not matter in this situation. A spouse, former spouse or cohabitant is required to pay alimony if he is registered as the parent of a minor.
The only condition that allows you to sever a family relationship with a minor is his adoption by another individual. After this, the burden of maintaining the child passes to the adoptive parent. Even refusal to exercise the rights of a parent does not in any way affect the obligation to provide for a young child.
Deadlines for filing and collection
The law does not indicate the exact time frame within which the procedure for collecting alimony can be initiated. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 107 of the RF IC, a person authorized to claim payments of this nature may declare his right at any time. It does not matter how many years have passed since the right to receive alimony arose.
Thus, the official representative of the child (the second parent, guardian or guardianship authorities) can file a claim for the recovery of alimony payments at any time, even if the child is already 18 years old.
However, alimony will be accrued only for the previous 3 years before the moment of going to court (Part 2, Clause 2, Article 107 of the RF IC). Moreover, one important condition must be met: the plaintiff must prove that measures were previously taken to obtain funds for the minor, but the defendant avoided his obligation in every possible way.
Measures in this case mean sending a written appeal to the second parent containing a request to pay alimony or enter into an agreement on its payment, filing an application with the magistrate’s court with a request to issue an order to assign such payments.
Procedure for calculating child support after deprivation of parental rights
During court proceedings, when it is necessary to decide whether to release a parent from his rights to a child or not, the issue of child support obligations is necessarily considered. Why is this being done?
- The court, according to Russian law, is obliged to promote the protection of children's interests, therefore, it must check that these interests are not violated.
- If the irresponsible parent has previously paid child support, the court must ensure that the amount of the child support payment is fair and reasonable and, if necessary, recalculate it. The alimony debt remains the same. If an irresponsible parent, for example, is in a formal marital relationship with the other parent, then by law he does not pay child support. However, as soon as he (she) is deprived of his rights, he is obliged to provide financially for the child with the help of alimony. Thus, in 100% of cases the court is obliged to study the alimony issue and make a correct and informed decision.
How can the issue of alimony be resolved? The solution options are described in the table below.
| Agreement | The court's decision |
It is concluded before a notary in the presence of both parents. The approximate price of the service is 5,000 – 10,000 rubles. Spouses independently determine:
| If the parent has official employment and a “white salary”, alimony is calculated as a share of the salary. The calculation procedure is as follows:
The above share sizes may be changed if the judge finds the following circumstances:
Collection of alimony benefits in the form of a fixed (flat) amount is applied when the parent:
Child support is calculated based on the child's subsistence level established by law in the Russian region in which the child is registered. In the event that a child’s subsistence level has not been established in the region, then the all-Russian subsistence level for children is used for calculation (RUB 10,181 in 2018). When determining the amount of alimony, the judge must proceed from the following criteria:
|
When do persons deprived of parental rights fulfill their child support obligations?
In accordance with Art. 80 and paragraph 2 of Art. 71 of the RF IC, a mother or father deprived of parental rights is obliged to support minor children. When drawing up an agreement on the payment of alimony, the method and time period for payment of funds, the parties to the transaction have the right to determine independently (Article 99 of the RF IC). However, the agreements reached should not contradict the rules for collecting child support obligations and violate the interests of the child.
If payments for the maintenance of the offspring are ordered in court even before the issue of the parent’s loss of rights is resolved, financial assistance for the child is preserved and collected in accordance with the general procedure. Otherwise, the conditions for requesting payment of funds are determined in the same decision of the department by which the deprivation occurred.
Procedure for forced collection of alimony
It is carried out only in the district court and simultaneously with the resolution of the issue of deprivation of parental rights. In this case, the plaintiff has the right to choose the court where the case will be heard, namely:
- At your own place of residence.
- At the place of registration of the other party.
According to Russian legislation, the plaintiff may be:
- Another parent.
- Prosecutor.
- Guardian.
- Guardianship authority.
- Head of the orphanage.
- Trustee.
- Head of the Commission on Juvenile Affairs.
- Adoptive parent.
It should be noted that a representative of the state guardianship agency and a prosecutor will participate in court hearings. This is due to the fact that deprivation of parental rights is a fairly serious measure of responsibility for a parent, which occurs for him in case of absolute neglect of the interests of the child. Therefore, the prosecutor must check whether there are signs of a criminal offense in the actions of the mother or father, and the state guardianship agency must examine the home in which the defendant lives, and himself, in order to have an idea of what principles and values he (she) is guided in life.
Proceedings in court cannot be started without a statement of claim. When writing it, you can use a sample, which can be viewed at this link. There is no need to request details from the court for paying the fee, since it is not paid by the plaintiff.
The proceedings usually take about 2 months, since the state guardianship agency should visit the homes of the defendant and plaintiff and prepare a reasoned opinion on the subject of the claims. In addition, the prosecutor also needs time to study the case for violations of the Criminal Code.
If the circumstances alleged by the plaintiff are confirmed, then the court deprives the defendant of the rights of a parent. If the deprived parent does not challenge the decision, then after 30 days from the moment it was written in final form, it comes into force. Next, the secretary of the court session prepares an extract from it and sends it within 3 days to the state civil registry office where the child’s birth was recorded. Based on the extract, the registry office changes the entry in the birth book, indicating that the father or mother’s parental rights have been terminated from a certain day.
Methods for processing child support from persons deprived of parental rights
Chapter 16 of the RF IC defines the option of providing financial support to children from a father or mother who have lost the rights to their child, on a voluntary basis - in the form of an agreement. This method of receiving alimony is relevant if there are no disagreements between the parents and the minor regarding the terms of payment of assistance.
The second method of acquiring financial support for children from the father or mother of those who have lost the rights to the offspring is determined by Chapter 17 of the RF IC and implies the need to go to court. In practice, this option is implemented many times more often than drawing up an agreement to pay alimony. A lawsuit in court demanding the recovery of financial assistance from persons deprived of parental rights is used if it is impossible to reach a mutual agreement on the payment of funds to minor children.
List of documents for filing a claim
It includes:
- Child's birth certificate or certificate of paternity. The judge needs them to determine who is the mother and father of a young child.
- Marriage certificate or divorce certificate.
- Certificate describing the composition of the family.
- Characteristics of a kindergarten teacher and a class teacher at school about the role both parents play in raising a child.
- Testimony from neighbors and relatives.
- The bailiff's decision on the existence of alimony debt, if any.
- An alimony agreement or a court decision to award alimony.
- Information about the other party’s income or place of work.
Do I have to pay child support if I don’t have parental rights?
The court is not limited to “deprivation” alone; alimony is automatically awarded. The procedure for collecting and paying funds is directly regulated by the agreement and the provisions specified therein, as well as a court decision or order.
Maintenance funds can be expressed as a percentage of salary, a fixed amount paid one-time or systematically, or in kind (property).
The amount of money is determined by the court based on the financial situation of the payers. Withholding of funds can be made from compensation for food rations of a military personnel, from wages or additional remuneration from the main or auxiliary place of work. Withholding can also be made from profits brought by contracts that involve income, for example, purchase and sale, barter.
The collection procedure consists in the fact that the bailiff provides/sends a writ of execution to the administration of the organization in which the payer works. After receiving it, the administration of the company where the person providing financial support to the entitled party works is obliged to withhold alimony from wages or additional income (bonuses) every month, a percentage or a fixed amount and transfer it to the recipient in a timely manner (no later than 3 days from the date of payment of the salary/remuneration) .
Please note that child support cannot be more than half (50%) of the paying parent's salary or remuneration to the children.
Read: What is the penalty for failure to pay child support?
Arbitrage practice
The case was heard in the Novokuznetsk District Court of the Kemerovo Region in September 2021.
The application to the court was filed by the father of a minor child. He demanded that his mother be deprived of parental rights. The reasons for this, according to the father, were the following circumstances:
- The defendant often drank and for this reason did not raise the child.
- Several years ago she left the plaintiff and lives in a place unknown to him.
- During their cohabitation, the defendant often left home for several days, and when she returned, she demanded money for drinks, i.e. actually suffered from alcoholism.
- In addition, the child’s mother never worked, was never interested in her son’s affairs, academic success and health, did not buy him gifts, did not take part in parent-teacher meetings at school, etc.
All the time, counting from the moment of his son’s birth, the plaintiff took care of him: he took care of him, supported him, taught him, and monitored his development. His upbringing gave a positive result, which is confirmed by the excellent characteristics of the child from school.
Based on the examined case materials, the judge came to the conclusion that the defendant should be deprived of her parental rights for the following reasons:
- The state guardianship agency considers it necessary to terminate the defendant’s parental rights, since guardianship agency employees examined the house where the child’s mother lives and found it unkempt and abandoned. In addition, according to a survey of neighbors, the defendant is characterized negatively by them: according to them, she drank, did not go to work, did not take care of her son and left him to provide for her husband.
- The defendant, through her own fault, did not pay child support that was ordered by court order, and did not otherwise participate in meeting her son’s financial needs.
Agreement on payment of alimony by persons deprived of parental rights
The regulations for drawing up an agreement on material support for minors by a mother or father who have lost their rights to children are defined in Chapter 16 of the RF IC. Taking into account the provisions specified in the Family Code of the Russian Federation, in order for a document to be recognized as valid, the child and parents must ensure that three conditions are met:
- Voluntariness. An agreement can be concluded only in the absence of claims between mom or dad, who are deprived of parental rights, and the children, without coercion and with full mutual agreement on all positions.
- Certification by a notary (Article 100 of the RF IC).
- Respect for the interests of the child. So that the agreement is not declared invalid on the basis of Art. 102 of the RF IC, when drawing up a document, it is not allowed to indicate a smaller amount of payments than required by law.
Instructions for processing child support from deprived parental rights are expressed in the following actions:
- Initially, the parties need to reach an agreement on each position of the agreement, taking into account the interests of the child.
- The second step is to put the oral provisions in writing using a general template (you can also use the services of a notary or other specialist, such as a legal consultant on our website).
- The third stage is contacting a notary. Parents deprived of rights to children and the applicant must have all the necessary documents with them. An office employee checks the information received and verifies the applicants’ legal capacity.
- At the fourth stage, you need to pay the state fee for certification and for notary services at the established rate. The mandatory fee is 250 rubles. For the actions of a specialist, you will have to pay from 1 thousand - the amount may vary depending on the region.
After receiving the money, the employee of the notary office certifies the agreement on the payment of child support from persons deprived of parental rights and the provisions of the document acquire legal significance.
A sample of a classic alimony agreement is available.
Regulatory framework
| Laws | Articles |
| Family code | Article 69 contains several grounds for the forced termination of the rights of an irresponsible parent in relation to a child. Article 70 establishes the specifics of the judicial procedure for deprivation of parental rights. Article 71 describes the negative consequences for a mother or father who has been denied rights to a child. Article 81 establishes the rules for claiming alimony in the form of a share of earnings. Article 83 establishes the rules for claiming alimony in the form of a fixed amount. Article 103 establishes the minimum amount of alimony allowance collected by agreement between the father and mother. Article 104 establishes the methods and frequency of alimony payments by agreement. |
| Tax Code (Part 2) | Article 333.36 establishes a list of benefits for paying court fees. |
| Civil Procedure Code | Section 23 contains categories of cases that a magistrate may deal with. Article 29 contains categories of cases in which the right to choose a court belongs to the plaintiff. |
Why are parental rights deprived?
The grounds and conditions for deprivation of the parental rights of a mother or father are comprehensively described in Art. 69 RF IC. The list given in the law is exhaustive, which means that neither the second parent nor the competent authorities have the right to demand deprivation of rights on other grounds not included in this list.
Most often, deprivation of parental rights is initiated for:
- Evasion of a mother or father from fulfilling the duties assigned to them by law in raising a child;
- Malicious evasion of payment of alimony;
- Violence against children (this includes both physical and mental violence, humiliating treatment of offspring);
- Refusal of a parent to pick up a child from a maternity hospital or other social, educational or medical institution (kindergarten, school, hospital);
- Abuse of your rights for personal purposes and to the detriment of the interests of the child;
- The presence of a chronic disease of alcoholism or drug addiction;
- Committing a criminal act against your child, as well as against the life and health of other family members.
If any of the grounds is present, the parent may be deprived of parental rights.
IMPORTANT: The law does not provide additional explanations for each of the grounds. The court will determine the circumstances. Examples of avoidance of parental responsibilities include neglect of children, leaving them at home unattended for the sake of leisure, children wandering and general antisocial behavior. The court will examine all the evidence presented and, based on the identified violations of the rules of raising children, will make a decision.
Legal consequences
A father or mother who has been deprived of parental rights loses all privileges towards the child. After the court decision comes into force, the negligent parent is deprived of the rights to:
- Communication.
- Upbringing.
- Inheritance of a child's property in the event of his death.
- Receiving alimony from a son or daughter after they reach the age of majority.
- Benefits, allowances.
Important: due to the fact that children belong to the most vulnerable category, their rights based on the fact of relationship with their parents are preserved.
What privileges does a parent who abandons a child lose?
In accordance with the RF IC, parents who are no longer considered as such by a court decision lose their rights based on the existence of family relations. These include rights to:
- participation in raising children;
- communication with them;
- protection of their interests and rights;
- demanding them from other persons;
- approval of transactions made by a child aged 14–18 years;
- filing a petition to deprive (limit) his ability to spend his own funds at the above age;
- an agreement to emancipate until he turns 16;
- receiving maintenance from the child in the future;
- acquisition of benefits and payment of benefits from the state to which citizens with children are entitled;
- pension provision for the loss of a breadwinner after the death of a child;
- the right to be heirs by law.
The law does not prohibit a parent deprived of rights to a child from being his heir under a will. However, the possibility of challenging such a will by other heirs is quite high.
In addition to the deprivation of these rights, additional disadvantages for the “former” parent arise from the rights that the mother acquires. These include:
- Travel abroad by a mother and child without the consent of the biological father.
- Changing the name of a minor without his permission.
- A ban on meeting the child and participating in his upbringing and education.
- The possibility of allowing adoption upon marriage to a new spouse without taking into account the opinion of the ex-husband.
All of these consequences occur until the moment when the rights to the child are restored in court. According to Art. 72 of the RF IC, this can be done in cases where the parent has radically changed his negative behavior towards his son or daughter and revised his attitude towards raising the child.
Drug and alcohol addiction
The use of drugs and alcohol not only prevents a father from fulfilling his financial obligations to his children, but also contributes to their psychological trauma.
You can prove dependence using:
- Certificates from the drug dispensary stating that the father is registered.
- Videos that show parents using alcohol or drugs in the presence of a minor.
- Protocol for the arrest of a father or mother who was under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- A court verdict passed against one of the parents, according to which the guilty person was held accountable for possession or distribution of drugs.
If the applicant does not have the above evidence, it is worth turning to witnesses for help. Persons who have seen the parent's inappropriate behavior can confirm the plaintiff's words in court.
Evidence base
Deprivation of parental rights is one of the most difficult procedural procedures. It is quite difficult to prove evasion of duties. Therefore, the parent who is the plaintiff in the case must prepare the necessary documents in advance.
What documentary evidence will influence the outcome of the trial:
- If the father or mother was previously prosecuted - a court verdict.
- If a parent has been avoiding paying child support for a long time - the corresponding writ of execution, as well as restrictive orders issued by the bailiff.
- If one parent abuses alcohol or drugs - a detention report. Due to the fact that medical examination notes are classified as medical secrets, they are not handed over to strangers. In this situation, the plaintiff may request that the court make a request to the relevant medical institution.
- If communication with the father is harmful to the psychological health of the child - the conclusion of a teacher or psychologist. During the court hearing, the court may initiate an independent psychological and pedagogical examination.
- If cases of violent acts have been recorded against a minor, a report from the attending physician indicating a list of injuries.
In addition, it is worth attaching a reference from the place of work or place of residence, audio and video recordings, which are evidence of the immoral behavior of the parent.