Free legal consultation over the Internet 24 hoursLawyer on housing issues in St. Petersburg. Free legal consultation on labor disputes.
5/5 (5)
Warranty period by law
Is there a warranty period for clothes? The answer to this question is contained in Part 2 of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”. Based on the norms established in this part, the calculation of the warranty period, as well as the service life of the product, including clothing and shoes, begins from the day the product is transferred to the citizen, unless otherwise provided by the contract under which the product was purchased.
If it is not possible to establish the date of transfer of the goods, the calculation of the warranty period and service life of the goods begins from the day the goods were manufactured.
Please note! Based on the provisions enshrined in Part 1 of Article 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300- I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the consumer, having discovered a defect in the product, which the seller did not report at the time of purchasing the product, has the right to demand from the seller :
- replace a low-quality product with the same product of good quality, produced under the same brand;
- replace a low-quality product with an equivalent product of good quality with the necessary recalculation of cost;
- reduce the cost of goods purchased and found to be of poor quality in proportion to the detected deficiencies;
- immediately eliminate defects found in the product or reimburse the costs incurred by the citizen in eliminating the defects of the product, including costs for the services of persons involved in eliminating the defects;
- terminate the purchase and sale agreement under which a product was purchased that turned out to be of poor quality, and return the money paid for this product.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Claim consideration period
The period for consideration of the buyer's claim depends on the essence of the claims presented and is regulated by the provisions of Articles 20-22 of the Federal Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights.
So:
- to eliminate deficiencies in clothing - no more than 45 days;
- issuance of similar goods for the duration of repair – three days;
- replacement of the product with a similar model - within one week, counting from the day of its receipt. In its absence - one month;
- if it is necessary to conduct an examination at the initiative of the seller - 20 days;
- price reduction, refund of self-repair costs, money back – 10 days.
When resolving a dispute in court, the court, when rendering a verdict in favor of the buyer, has the right to apply penalties against the seller for refusing to resolve the issue peacefully.
The concept of a warranty period
Based on the norms enshrined in Part 6 of Article 5 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the warranty period is the period of time during which the consumer, having discovered that the quality of the purchased product does not meet the requirements , has the right to demand that this product be exchanged or repaired, the price of the product reduced in proportion to the defects found, or the product returned and received back the money paid for the product.
These requirements can be presented either directly to the manufacturer of the product, or to the seller or other person authorized by the manufacturer.
At the same time, the consumer should remember that it is possible to return a product in which defects were discovered during the warranty period only if the rules for using this product were followed, as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations for caring for the product.
Based on the norms enshrined in Article 476 of the Civil Code and in Part 6 of Article 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the seller, if he cannot prove that the defects discovered by the consumer in the product arose due to fault of the consumer himself, will be responsible for the quality of previously sold goods during the warranty period.
In this case, we are talking about cases when further safe operation of the product becomes impossible. However, if the clothing or shoes purchased by a citizen were found to have a seam rupture, a change in color, a damaged zipper, and so on, we can say that the quality of the product did not meet the requirements, or the product had a manufacturing defect.
Is it possible to return shoes to the store if I have already worn them?
In which court to file a claim for consumer protection, read here.
How to get a free online legal consultation, read the link:
How to make a complaint to the seller
Before proceeding to formal communication with the seller, it is recommended to resolve all issues peacefully. Often this behavior of the buyer contributes to the seller meeting halfway.
However, if verbal negotiations do not lead to the desired result, you should prepare to resolve the situation in court. To do this, it is necessary to draw up a legally competent written claim. If you have difficulties drawing up this document, you should seek help from a lawyer.
The current civil legislation does not impose requirements on the content of the claim, however, legal practice has developed its own approaches.
Remember! They are as follows:
- the claim must be drawn up in two copies. One is for the seller, the second remains with the buyer with a note from the seller about its receipt. If the seller does not agree to accept the document or make a note of its delivery, the claim is sent by mail;
- the document is drawn up in the name of the seller, indicating his full name, legal form of ownership, and legal address;
- indicate the full details of the buyer in the form of last name, first name, patronymic, residential address, means of communication;
- the essence of the problem that has arisen is stated: when, where and at what price the goods were purchased, the presence of a sales or cash receipt, a warranty sheet with a seller’s mark;
- an accurate and correct description of the product, its name, model, color, article number and other information by which the product can be identified;
- what is the defect of the product or the presence of other defects, how is this confirmed, the presence of a conclusion from a commodity expert or expert, which confirms that the defects in the product did not arise through the fault of the buyer;
- draw a conclusion that the identified shortcomings or defects do not allow the product to be used for its intended purpose;
- draw the seller’s attention that in case of disagreement with the stated requirements, he has the right to conduct an independent examination in the presence of the buyer;
- indicate the legal basis for filing a claim;
- set out the requirements that must comply with the provisions of the Consumer Protection Law;
- indicate the list of attached documents;
- enter the date, month and year of the claim, signature, surname and initials.
Important! In the requirements put forward, the claim must contain references to the Federal Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, provisions of civil law that give the buyer the right:
- Article 18 of the Law and Article 503 of the Civil Code - return the purchased clothes and receive the money paid;
- Article 309 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation - the seller is obliged to fulfill his obligations, as required by law;
- Article 310 of the Civil Code, which does not allow unilateral refusal to fulfill the terms of the purchase and sale agreement for a product;
- paragraph 5 of Article 18 of the Law - the absence of a sales or cash receipt in the hands of the buyer is not a basis for refusal to accept a defective item;
- Article 7 of the Law - delivery of goods weighing 5 kilograms or more is carried out by the seller. If the goods were delivered by the buyer, he has the right to appropriate compensation for the costs incurred.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample claim for the return of a fur coat of proper quality:
Who establishes a product warranty?
Important! Based on the norms enshrined in Part 6 of Article 5 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300- I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the following have the right to establish a warranty period for a product:
- manufacturer of the goods;
- seller of the goods, if the warranty period was not established by the manufacturer.
Obviously, the company that manufactured the product has priority when establishing a warranty period for a product. If the manufacturer does not exercise the right to establish a warranty period, this right passes to the seller.
Based on the foregoing, it becomes obvious that the norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation do not provide for the possibility of establishing a double guarantee for a product from the manufacturer and the seller.
What happens if the service life for the CO is violated?
Sometimes employers accidentally or intentionally ignore established standards and “by eye” determine their own. Why? Extra expenses, because you need to purchase new kits every time, otherwise production decreases. Workers need special clothing. However, by violating the norms, enterprise management does not understand the consequences. After all, when studying the quality of the SS and its capabilities, the Ministry of Health and Social Development was primarily concerned about the protection of ordinary employees. Some professions require strict control over the quality and characteristics of the CRM. For example, a medical facility, a fire station or a scientific institute, a manufacturing plant, where people’s work is fraught with various dangers. Housing and communal services and agriculture also have their own specifics.
What consequences can await violators of the rules for storing and issuing CO:
For the employer and the enterprise - a fine, its amount will be determined by the scale of the violations. 30,000–50,000 rubles (enterprise), manager and other responsible persons 1,000–5,000 (if the violation is repeated, disqualification for 1–3 years).
Sanctions for missing deadlines or not issuing required certificates can be even more serious:
- officials - payments of 20,000–30,000 rubles;
- entrepreneurs (private companies) 20,000–30,000 rubles;
- legal entities already 130,000–150,000 rubles.
Important: the employer is responsible for the storage conditions and timely delivery of the required CO to the employee. He also monitors the timing and condition of workwear. However, the employee himself must maintain the serviceable appearance of the issued kit with careful attitude. Do not lose/break/tear the CO, and if something has deteriorated or stopped working, report it immediately.
From what date is the period calculated?
The rules for calculating warranty periods are set out in Part 2 of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”.
Please note! The warranty period begins:
- from the moment the goods are transferred to the consumer, unless other terms are specified in the contract under which the goods were purchased;
- if it is not possible to establish the date of transfer of the goods to the buyer - from the date of manufacture of the goods;
- If the product belongs to the category of seasonal goods and was purchased before the start of the corresponding season, then the warranty period will begin to be calculated from the date of the start of the corresponding season. If this product is purchased during the season, the warranty period will be calculated from the day the product is transferred from the seller to the buyer;
- when ordering goods remotely (by mail, via the Internet, using a catalog or sample) - from the moment the goods are delivered to the buyer;
- if the purchased product must be delivered, installed and mounted, and the dates of purchase and delivery do not coincide, the warranty period will begin to be calculated from the day of delivery of the product or from the date of completion of installation;
- if it is not possible to establish the date of delivery, installation and installation of the goods - from the date of conclusion of the purchase and sale agreement for the goods.
Refund period
The Consumer Protection Law allows 10 days for a refund to the buyer. The period is calculated from the date of receipt of the written claim.
Attention! Violation of the terms for the return of money or the seller’s refusal to do so entails the application of a penalty, which is accrued for each day of delay.
The law stipulates that refunds are made in the same form in which payment for the purchase was made. So, if the buyer paid with a bank card non-cash, then the money should be returned to the buyer’s card.
If the payment was made in cash, then they should be returned in the same way.
The refund period for cash payments is usually from three to ten days. However, modern banking technologies allow you to return money to your card on the same day.
Refunds to the card can be made within a longer period than 10 days. This may be affected by the state of the banking institution itself, and the features of the payment system that is used in a particular case. However, a violation is a violation. And the buyer has the right to demand payment of a penalty for each day of delay in returning the money.
How is the warranty period for clothing determined?
The current legislation of the Russian Federation obliges sellers to sell goods provided that the quality of this product meets the requirements. The sale of goods whose quality does not meet the requirements is possible only if the buyer has been warned in advance about the existing shortcomings of the goods.
The buyer must use the purchased product for its intended purpose and follow the recommendations for use and care from the manufacturer.
If it is determined that defects in the product arose as a result of improper use of the product or as a result of violations of recommendations for use and care, the buyer will be denied the right to warranty repair, return or exchange of the product.
Practice shows that most often the following defects are found in clothing items due to the fault of the manufacturer or seller:
- damaged or torn seams;
- traces left by foreign substances on the surface of the material from which the product is made;
- violation of the geometry of the fittings.
If the manufacturer or seller has doubts about the causes of the defect, an examination is carried out. If the buyer is not satisfied with the results of the examination carried out at the request of the manufacturer or seller, an additional independent examination can be carried out.
Remember! Establishing a warranty period is a right, not an obligation, of the manufacturer or seller. If neither the manufacturer nor the seller exercised this right, the warranty period for the goods will be established based on the norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation and will be two years from the date of sale of the goods.
If the date of sale cannot be determined, the warranty period will be calculated from the date of manufacture of the product.
For non-seasonal clothing, the warranty period begins to count from the date of purchase or, if the clothing was purchased remotely, from the day of delivery.
For seasonal clothing, the warranty period is calculated slightly differently. If this clothing was purchased outside of the season, then the warranty period begins to be calculated from the date of the onset of the season for which this clothing is intended.
If seasonal clothing was purchased directly during the season, the warranty period will be calculated from the date of purchase or delivery.
If the product being sold has obvious defects, and the seller warned the buyer about the presence of these defects before making the transaction, the product cannot be returned or exchanged.
In accordance with the norms of current legislation, a warranty period is established for clothing, both regular and seasonal, as well as for any product. The warranty period can be set by the manufacturer or the seller. If neither the manufacturer nor the seller has established a warranty period, the warranty for the clothing is established in accordance with the law.
However, the warranty for clothing will only be valid if the buyer follows the manufacturer's recommendations for use and care:
- strictly complied with the requirements set out on the tag or label;
- did not expose clothes to prolonged exposure to moisture, dried them in a timely manner;
- took care of clothes - regularly washed them in compliance with the temperature regime, and if washing was prohibited, used other cleaning methods.
It should be noted that a number of clothing items are not subject to exchange or return at all. These items include underwear and thermal underwear, hosiery, and so on.
We emphasize that if the buyer purchased a product with defects, the presence of which was notified by the seller, this does not mean that the warranty does not apply to this product in principle. This product comes with a limited warranty.
Attention! The warranty period for clothing does not apply in the following cases:
- pellets have formed on the fabric;
- as a result of prolonged exposure to sunlight, the fabric has faded or changed color;
- as a result of long-term use, signs of wear, tears or cuts have appeared on the fabric;
- violation of the geometry of the fittings, including complete failure;
- damage resulting from improper use of the product.
Most often, both manufacturers and sellers set a time period of 30 calendar days as a warranty period for clothing. In addition, clothes, like many other goods, can simply be returned or exchanged by the buyer within 14 calendar days from the date of purchase, even if the quality meets the requirements.
To do this, you will need to bring the product itself and packaging. It is also advisable to provide financial documentation confirming the fact of purchase of this product.
Watch the video. How to return clothes and shoes to a store - legal advice:
When does the period of use of the issued workwear begin?
According to GOST, on each piece of workwear, the supplier institution puts the date of its manufacture. Storage, compliance with deadlines and issuance of kits is the task of the employer and other responsible persons. Therefore, it is important to understand how to correctly calculate expiration dates.
A single report (used most often in practice) begins at the moment the kit is actually issued to the employee.
If we talk about the suitability of wearing and storing insulated clothing (winter set), it is worth including the time, how long the new set lay before being released in the warehouse. After all, as you know, insulated items are issued later, in the fall and winter, when the temperature is lower.
"Until wear"
Some items are issued for a long time, and the employee wears them until they are completely worn out. For example, a work sleeve or glasses, protective gloves. This practice is typical for catering establishments or libraries, where the use of issued clothing items may take not a year, but much longer.
If “wear-out” periods are set for protective items, then a specialist must regularly check them, updating the quality certificate.
Important: management can set such a period if the specifics of the profession allow it. For example, if a cleaner or a cook can wear the gloves they are given “until they wear out,” then a firefighter’s helmet or a builder’s belt is unlikely to last that long.
Of course, the employer has the right to change the number of items in the set of workwear issued to employees and the suitability for use. If this does not harm the safety and performance of personnel. Some enterprises require employees to have an FSS certificate.
Can clothes be returned or exchanged?
Important! If a citizen discovers a significant flaw in previously purchased clothing, and the warranty period for this clothing has not yet expired, you should immediately contact the seller and verbally or in writing demand:
- replace goods of inadequate quality with goods of the same brand, the quality of which will meet the requirements;
- replace goods of inadequate quality with an equivalent product whose quality meets the requirements and recalculate;
- reduce the cost of the product in proportion to the detected defect;
- repair the product or compensate for the costs incurred by the citizen when carrying out repairs independently;
- return the money spent on the purchase of goods;
- compensate for the damage suffered by the citizen as a result of the fact that the quality of the product did not meet the requirements, including moral damage.
Please note that no matter how complex the repair is required for the product, no more than 45 calendar days should be spent on repairs. If the repair takes longer, the citizen has the right to demand payment of a penalty in the amount of 1% of the cost of the goods.
Consumer rights
According to the law, a low-quality product can be replaced with a similar one, and this will require recalculation of the cost. The buyer has the right to demand a discount, remove defects and pay money for repairs. You can return clothes and get your money back, regardless of the period of use and price changes. If the buyer suffers damage due to a product of poor quality, the seller must compensate for everything.
During a dispute, the question may arise as to why the defect arose, but this fact is established by an examination. It is carried out at the expense of the seller. The consumer can be present at this event and challenge the decision in case of disagreement.
If after 45 days the defect in the product has not been eliminated, then this is considered a violation of consumer rights. While the consumer is not using the clothing, it is repaired. This period is counted after the filing of the claim.
Warranty period for seasonal clothing: how is it determined?
A seasonal product is understood as a product that can only be used during a certain season. The warranty period for this product begins to be calculated not from the date of purchase, but from the beginning of the season to which the product corresponds. If the product was purchased during the season to which it corresponds, the warranty period will begin to count from the date of purchase of the product.
These rules apply regardless of whether the product was purchased in the usual way or was purchased remotely.
Generally speaking, the warranty period for seasonal goods begins to count:
- for a regular purchase - from the day of the onset of the season for which the product is intended;
- in the case of a regular purchase of goods during the season for which the goods are intended - from the date of purchase;
- when purchasing goods remotely - from the date of the onset of the corresponding season;
- when purchasing goods remotely during the season for which this product is intended - from the date of receipt of the goods by the buyer.
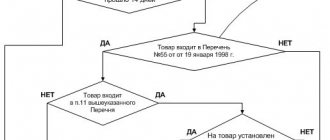
It should be noted that there is no list of seasonal goods approved by legal acts in Russia. However, in Part 2 of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” it is written: “For seasonal goods (clothing, shoes and others).”
Therefore, by seasonal goods, most people understand summer and winter clothes, forgetting about others. And the others can safely include, for example, snowboarding, since the use of a snowboard in most of the territory of our Motherland is possible only in a certain season.
When determining whether a product is seasonal, one should proceed from the information available about this product, take into account specific technical characteristics and recommendations for using the product.
Please note! Let us note that each subject of the Russian Federation independently determines the start dates of the seasons, based on local traditions and climatic conditions.
For example, on the territory of the federal city of St. Petersburg, the seasons begin:
- winter - December 5;
- spring - March 17;
- summer - June 2;
- autumn - September 12.
The basis for this is the Law of St. Petersburg dated June 6, 1997 No. 97-28 “On establishing the timing of the onset of seasons in St. Petersburg.”
Peculiarities
Overalls should be used only for their intended purpose. Kits are not considered the sole property of the employer. And after issuance, the employee should not use the CO outside the work area. If the employee himself deliberately damaged the kit, shortening its service life, the employer has the right to impose a fine on him, including the cost of the damaged CO.
You cannot work without CO or in a damaged suit. This is fraught with various consequences, sometimes even deadly (depending on the specifics of the production). If a loader or security guard can hurt himself or develop calluses without protective gloves, then a builder who goes out without a helmet can die.
Product without warranty
A citizen has the right to return a defective product only within the warranty period. But at the same time, the manufacturer or seller has the right, but not the obligation, to establish a warranty period. Cases when a purchased product does not have a warranty period are not that rare. But this does not mean that if the quality of this product turns out to be inadequate, it will be impossible to return it.
The consumer has the right to present the requirements set out in Article 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300- I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, even if the product does not have a warranty period, subject to the following conditions:
- the defect was discovered within a reasonable time, not exceeding 2 years from the moment the goods were handed over to the consumer;
- the consumer was able to prove that the defects found in the product, or the reasons that led to the occurrence of these defects, arose before the purchase of the product.
You should contact the manufacturer or seller of this product immediately after discovering any defects. In this case, the product should be taken out of service, not used or exposed. This is necessary to conduct an objective independent examination and establish the causes of deficiencies.
Based on the above, the consumer should report the detected defect immediately after discovery. If the case goes to court, then a reasonable period for identifying the deficiency will be set by the court, based on decisions already made by the courts in similar cases.
What is the quantity in question?
The Constitution of the Russian Federation is the fundamental law of our country. how to structure conversations with primary schoolchildren on the constitution of the Russian Federation. methodological development (grades 1, 2, 3, 4) on the topic
Every person has had situations when they had to buy a product of inadequate quality.
In this regard, Article 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” (hereinafter referred to as the Law) states that if during the purchase and sale procedure there is no problem of inadequate quality (the seller does not report the presence of possible defects), then the buyer is given the following options:
- free repairs or compensation for the cost of independent restoration work (in this case, you must provide a receipt for the elimination of defects as evidence);
- proportional reduction in cost, i.e. carrying out markdowns of goods in accordance with detected defects and defects;
- exchange for a product of the same model or similar with similar functions of another brand, taking into account the difference in price;
- termination of the purchase and sale agreement. Moreover, demand reimbursement of all expenses associated with the purchase of substandard items.
If the manufacturer has not indicated the warranty period, then the seller has the right to establish it. When the manufacturing company has determined this period, the seller has the right to increase it, but not shorten it. In this case, only the seller himself is responsible for the obligations assumed. Article 19 of the Law allows the buyer to contact both the manufacturer and the distributor regarding the occurrence of defects during the warranty period.
It is possible that the warranty period is less than 2 years, and defects were identified after its expiration, but within the two-year limit. In this case, contact the seller or directly the manufacturer. Take care to make a strong case for manufacturing defects. This rule is spelled out in Art. 18 of the Law.
Even if defects are discovered after the expiration of 2 years, the buyer has the right to make a claim, but provided that the defect turned out to be “significant”. The period for correcting a “significant” defect is limited to ten years, if the service life is not determined. In this case, the buyer will again have to prove that it is not his fault for the occurrence of malfunctions.
If the seller or manufacturer has not responded to it within 20 days from the date of filing a written claim, and the detected defect has not been eliminated, then submit the requirements established in paragraph 3 of Article 18 of the Law.
These include:
- free removal of product malfunctions or defects;
- compensation for losses resulting from the elimination of defects;
- exchange of goods of inadequate quality for an analogue;
- returning the purchase to the store with receipt of the entire amount of money paid.
Sometimes for advertising purposes sellers or. The law of the Russian Federation does not provide for abstract temporary positions and streamlined concepts that everyone can interpret at their own discretion. Therefore, all contractual obligations are based on specific deadlines and clear wording.
If the purchase and sale agreement is nevertheless concluded using the concept of a “lifetime guarantee,” then it often turns out that the company is not responsible for non-legal determinations of the seller, for example, in the form of oral promises. This leads to a free interpretation of rights and responsibilities.
The fact is that oral advertising statements sometimes relate to specific information about the company, and the guarantor will have to answer for false or unreliable information in accordance with Art. 12 of the Law. Ultimately, all terms of the contract that do not comply with the provisions of the Law and limit the rights of citizens are considered invalid.
When considering such a dispute in court, the law enforcement agency will not even accept this agreement from the seller. Therefore, study legislative documents and use them in your life.
How to return clothes to a store
Remember! Regardless of whether the clothing purchased by a citizen was ordinary or seasonal, if at the time of purchase there were no shortcomings in this clothing, and the seller did not declare any shortcomings, but during use the shortcomings appeared, the citizen should act as follows:
- contact the store where the clothes were purchased and, during negotiations with an authorized person, offer to make a return or exchange;
- if negotiations do not lead to success, prepare and send a pre-trial claim to the seller. The claim is drawn up in two copies, each of which is sealed with the citizen’s handwritten signature with a transcript and the date of signing. One copy is handed over to the authorized person of the seller against signature or sent by registered mail with a list of attachments and notification of delivery;
- if the seller refused to satisfy the citizen’s demands or simply ignored the claim, the citizen will have to defend the legal rights and interests during legal proceedings.
Let us note that at any of the above stages, a citizen has the right to seek help in protecting legal rights and interests from highly professional lawyers.
Legal experts will help assess the prospects of the case, prepare all the necessary materials, and, if necessary, represent the interests of the citizen in various authorities.
Attention! Based on the norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation, clothing can be returned or exchanged in the following cases:
- the quality of the clothing meets the requirements;
- The clothing contains defects that were caused by the fault of the manufacturer or seller.
In the first case, the exchange of goods will be carried out on the basis of Article 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”. In accordance with the standards set forth in this article, a citizen has the right to exchange unsuitable goods within 14 calendar days from the date of purchase.
If the seller cannot provide the citizen with an equivalent product as a replacement, the purchase and sale transaction will be terminated. The money is returned to the buyer, and the goods are returned to the seller.
A citizen’s demands for the return or exchange of goods of proper quality must be satisfied within 3 days from the date of the citizen’s request.
To return a product whose quality meets the requirements, within 14 days from the date of purchase, a citizen will need:
- bring the clothes and the packaging intact to the store where the clothes were purchased and ask for an exchange or refund. It is recommended to bring financial documentation confirming the fact of purchase, but this is not required;
- if an exchange or return is refused, the citizen will need to draw up and send to the store a pre-trial claim demanding a return or exchange of the goods;
- If the seller ignores the claim or refuses, the citizen must file a claim in court.
If a defect is found in the purchased product, the situation may develop as follows:
- if the warranty period was not initially established or has expired, the consumer, in accordance with the provisions of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992. No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, it is necessary to prove that the defect, or the reasons leading to the defect, arose before the citizen received the goods from the seller;
- if the product warranty is still valid, the consumer has the right to demand, based on the norms enshrined in Articles 18 and 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-I “On the Protection of Consumer Rights,” return, exchange, repair of the product or payment of compensation.
In these cases, communication with the seller should be structured according to the scheme described above.
It should be noted that a citizen has the right to conduct an independent examination of the product. If the examination establishes that the defects of the goods appeared due to the fault of the manufacturer or seller, then the seller is obliged to reimburse the citizen for the costs of the services of an independent expert.
Additional things you need to know about the warranty
Any item purchased by the buyer may be returned to the seller without stating a reason within 14 days, starting from the next day from the date of purchase. However, all documentation, sales and cash receipts, labels, packaging must be kept in their original form.
Violation of this requirement does not entail the seller’s right to refuse to accept the goods, but it complicates the process of returning the goods.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample application for the restoration of a lost check:
You will have to formally submit a written complaint. In court, provide evidence that the item was purchased from a specific seller.
Where is warranty information found?
Information about the warranty period is always reflected in the clothing coupon. Also, relevant information may be included in the text of the agreement on the sale of the item. Most often, a contract is drawn up for expensive goods, for example, for a product made of natural fur or leather.
Each buyer has the right to require the seller to issue a warranty card. This approach will subsequently allow you to quickly resolve possible problems related to product quality or customer dissatisfaction.
Wardrobe:
5. Slippers.
How long do you think slippers can “live”? You won't believe it, only half a year ! Then, according to scientists, a whole breeding ground for microbes and bacteria, in general fungus, is formed in them (I think this applies specifically to slippers made of fabric or fur).
6. Bra.
Here the expiration date already depends on how often you wear it (in the sense of the same). With each wash, it will change shape, stretch and thereby cease to perform its main function - to support the breasts. And most importantly, due to close contact with the skin, dirt and dead skin cells accumulate in the cups of the bra, which is also not very good. Therefore, the maximum service life of a bra is considered to be 1.5-2 years .
How to report on the use of work clothes
Typically, the responsibility for keeping track of work clothes is assigned to a responsible employee, for example, a warehouse manager. But, according to the law, the main responsible person, who during the inspection will answer to the commission, is the immediate supervisor of production.
Reporting can be carried out both in written and electronic form, and can be presented either in a journal or in a card index.
PPE accounting scheme
Establishment of the period: “until wear”
As already mentioned, some personal protective equipment is issued to the employee “until worn out.” This list includes a signal vest, the service life of which is unlimited, safety glasses, noise-cancelling headphones, knee and elbow pads, some types of support belts, etc. The issuance of new PPE is provided only in the event of loss, theft, breakage, obsolescence and beyond the operational time frame , installed by the manufacturer.
Sample order for standards for issuing workwear
Thus, for example, if for supporting belts GOST provides for maximum use for a period of up to 25 years, then if during this time it has not become unusable, it is in any case subject to write-off.
In addition, the employer must conduct regular inspections of personal protective equipment. The enterprise must have a log in which each inspection will be recorded.
Additional Information! Typically, for long-life PPE, inspections are carried out every six months or a year.
How to determine for accounting purposes the wear period of workwear if the issuance rate is set “until worn out”
Any wear time can be set for items of equipment, the main thing is that it does not exceed the standards for maximum use of the product by GOST or the manufacturer of the product.
For example, the useful service life of safety glasses can range from a couple of months to 20 years. Therefore, for accounting purposes, it is possible to establish a systematic write-off every year, referring to the conditions of the work performed.
Overalls for line personnel
Depending on the type of production, line personnel include different groups of workers, not only those who work in production. This also includes catering workers, medical organizations, cashiers, salespeople, etc.
Their standards for compliance with workwear are approximately the same. Usually this is a cotton robe or a suit of jacket and trousers.
Additional Information! In winter, line workers who perform job duties outside are required to be given felt boots, a winter jacket or a quilted jacket.
The average service life of overalls for line personnel is limited to 24 months. In some cases this period may be 18 months. If the manufacturer does not indicate an expiration date, the clothing is disposed of after 24 months.
Deduction of cost upon dismissal
It is important to understand that work clothes purchased for workers become the personal property of the enterprise, not the worker. Simply put, it is put on balance. Upon dismissal, the employee is obliged to return to the employer the protective clothing on the balance sheet.
Additional Information! If the dismissed employee does not do this, the employer has the right to withhold the market value of the purchased clothing from the calculated salary. But according to the labor code, the employer does not have the right to withhold more than 20% of the employee’s salary.
How standards for wearing workwear depend on the type of production
Standards for issuing workwear by profession
The legislative framework provides for the issuance of protective clothing and personal protective equipment to 195 types of professions. In general, the service life of workwear, the standards of which are prescribed in Resolution of the Ministry of Labor No. 997n, depends on three factors - climatic conditions, type of production and work responsibilities of the subordinate. So, for an employee of one workshop where metal is melted, the wearing standards will be different from the norms for an employee of the next workshop where the same metal is processed.
Additional factors:
- type of pollution;
- there is a danger of electric shock;
- temperature indicators;
- presence of toxic substances;
- work associated with increased risk.
How it looks like in an example. Let's say we have a fleet driver and a battery technician. For them, the terms of use of workwear at the enterprise, the table of which is in the above-mentioned resolution, is:
- The driver, who additionally carries out car repairs in the company’s garage, is entitled to the usual cotton overalls, which are issued for up to two years, and gloves, one pair of which is required for 2 months of use;
- For a battery operator, the standards provide for the issuance of a suit with protection from acid burning for 1.5 years and 6 pairs of rubber gloves for 1 year, rubberized boots and an apron with a bib for up to 2 years, gloves made of dielectric material, glasses and galoshes “until worn out.”
An example of standards for the use of personal protective equipment by a repairman
Additional Information! The duration of wearing overalls is additionally established by a special commission during production certification.