In the event of a delay in wages, the offended employee or the team as a whole has the right to file an individual/collective complaint with the State Labor Inspectorate. Although applying to the State Tax Inspectorate is not a mandatory procedure by law, for most employers decisive actions by staff can become a reason to pay off the monetary obligation as quickly as possible. However, employees have the right to file a claim for recovery of wages in the district court, bypassing the State Labor Inspectorate, or contact both authorities, as well as the prosecutor’s office.
Grounds for filing a claim
According to Part 6 of Art.
136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, salaries must be transferred to the employee at least every half month. During the payment of wages, the administration of the organization, in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, must notify the employee of the total amount of money to be paid, as well as the components of this amount. For reference: the salary includes not only the salary, but also bonuses, additional payments, vacation pay, compensation for delayed salaries (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For convenience of calculations, the employer usually approves the form of the pay slip, which is given to the employee in advance or at the time of payment of the salary.
In case of dismissal of an employee, settlement with him must be made on the last day of his work in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 84.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Upon dismissal, many employers draw up a special note-calculation (this can be either form T-61, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1, or any other form approved by the employer himself). The main objective of this document is to indicate in detail the amounts and grounds for accruing to the employee the amounts due for payment.
Accordingly, if an organization delays wages for any reason, two situations are possible:
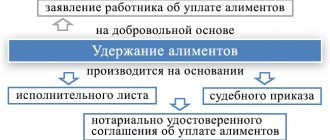
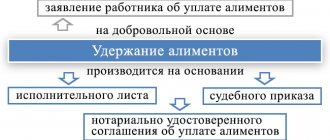
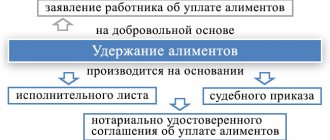
- The employee knows the exact amount of debt (pay slips or similar documents are available).
- The employee does not know the exact amount of the debt.
If the employee’s salary has been accrued (the amount of the debt is known and does not give rise to disputes), but has not been paid and the amount of the debt does not exceed 500 thousand rubles, based on the provisions of Art. 121 and 122 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, you should apply to the court for a court order. In other situations, the employee will need to prepare a statement of claim for recovery of wages and go to court in the general manner, that is, as part of the claim proceedings. Which one - read on.
Pre-trial procedure for collecting wages
The first and easiest procedure for collecting wages is pre-trial. In this case, this procedure provides two possibilities:
- Agreement of the parties. The parties to the labor relationship enter into a written agreement between themselves and implement it voluntarily. This procedure is good for those situations where the parties do not conflict and are ready to conduct negotiations aimed at results;
- Contacting the Prosecutor's Office and the Labor Inspectorate. The employer, so to speak, is forced to fulfill its obligations by supervisory authorities. This procedure is suitable in cases where the employee does not have any problems with documents. It will be enough to send an application to the Labor Inspectorate or the Prosecutor's Office (it is worth noting that the Prosecutor's Office often forwards applications to the same Labor Inspectorate only if there is no question of criminal liability for non-payment of wages, see the link for more details). There, under the threat of penalties, the inspector will explain to the employer all the grounds for repaying the debt in pre-trial order.
USEFUL: watch the VIDEO with advice from a lawyer on labor matters and find out how to win a dispute with your employer, write your question in the comments of the video and the lawyer will answer you today
Which court should I go to?
Before you begin preparing a claim for the collection of arrears of wages, you should clearly determine which court to file it with. There are two rules:
- Unlike other property disputes, debt collection in claims for non-payment of wages falls under the category of labor disputes. Therefore, only the district court should consider them.
- The territorial jurisdiction of a claim for the recovery of wages is determined by the Part. 1, 2 and 6.3 art. 29 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. That is, you can go to court at the location of the employer or the place of residence of the employee, or, if work is carried out in a branch of the company, at its location.
Documents for court
In accordance with Article 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the statement of claim will need to be accompanied by:
- labor or collective agreement;
- agreement on the procedure for paying salary;
- The order of acceptance to work;
- evidence of non-payment of funds (based on accounting statements, written testimony of witnesses, notifications, etc.);
- other documents provided for by the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
To obtain all the necessary documents for the court, you need to contact your employer with a written application. Copies of documents must be certified by an authorized representative of the defendant. The employer, by virtue of Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is obliged to provide documentation within 3 working days from the date of filing the application (registration, i.e. assigning it a number and date).
By virtue of Art. 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and clauses 6.3, 9 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the claim is filed in the district court:
- at the place of the defendant - employer;
- at the employee's address;
- at the place where the employee’s work function is performed.
There is no state duty.
How to file a claim, what documents to attach, state fees
A statement of claim for non-payment of wages is drawn up according to the rules of Art. 131 and 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. A current sample statement of claim for recovery of wages, drawn up based on the listed requirements, is presented below.
The header of the application for the recovery of wages shall indicate:
- the name of the court where the plaintiff is applying;
- information about the applicant (initials and address);
- information about the defendant (if it is a company, then name and address, as well as identifiers - TIN and OGRN).
The main part of the statement of claim for recovery of wages must include:
- the essence of the violation of the employee’s rights;
- circumstances confirming the employee’s correctness;
- calculation of claims and, accordingly, the cost of the claim.
For the convenience of readers, the above points in relation to the indicated situation are described in detail in the sample claim for payment of wages presented above.
The document must be dated and signed by the employee.
For reference: in addition to the salary amount, an employee can also collect interest for the use of his funds according to the rules of Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in the amount of 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each day of delay, starting from the moment when a specific part of the salary should have been paid until the moment of actual payment.
Employee rights
Employees whose wages are delayed for more than 15 days can (there are certain restrictions under Part 2 of Article 142 of the Labor Code for specific categories of workers or during an emergency):
- suspend your work until the debt is repaid, having previously notified the company administration in writing;
- do not go to work place before salary enrollment.
For employees in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during downtime, the average earnings are maintained regardless of whether a person is present in the office or not. Average earnings are calculated according to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation using a special formula. If an employee receives a notification from his boss about his readiness to repay the salary debt, he is obliged to return to work after receiving the corresponding notification or to the next job. day.
Applications and state fees
To the claim in accordance with the requirements of Art. 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, you must attach a copy of it and copies of the annexes (for the defendant), a calculation of the claims (both the salary itself and interest, if the claim contains a demand for their recovery), as well as copies of other documents that confirm the plaintiff’s arguments. A specific list of documents for the convenience of readers is indicated in the sample statement of claim for delayed wages. Please note that it may differ depending on the actual situation.
Important! As for the state duty, due to the requirements of Art. 393 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is exempt from incurring legal costs; accordingly, they do not need to pay them.
If you work without an employment contract
Often citizens who work unofficially face the problem of non-payment of wages. If it is not possible to solve this problem peacefully, this category of working citizens can also turn to higher authorities for help.
A statement of claim to the court is filed in a standard manner. A significant difference when filing a claim is the fact that a citizen must provide documentary evidence that he actually worked for this employer.
Worker group lawsuit
In the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, in particular in Art. 40, does not contain such a term as “class action”. We are talking only about procedural complicity. At the same time, Part 3 of Art. 40 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation specifically emphasizes that each of the plaintiffs in such a situation acts in relation to the defendant-employer independently.
Accordingly, employees have the right to file a joint claim against the employer. In practice, this means combining several independent claims for payment of wages within the framework of one proceeding. In this case, each of the plaintiffs will need to either represent their interests independently or entrust this to one of the employees (or his representative). This will require a power of attorney. There are no special requirements for filing a joint claim. That is, it will be formalized according to the rules of Art. 131 and 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation with the difference that there will be several plaintiffs. Consequently, it will be more convenient to divide the claim into blocks for each employee (to describe the situation, calculate the amount of debt, etc. separately).
Procedure for drawing up a statement of claim
In accordance with the requirements of civil procedural legislation, there are general rules for drawing up statements of claim.
The structure of the document consists (conditionally) of 4 parts:
- Introductory.
- Descriptive.
- Motivational.
- Resolute.
The first indicates: name, details of the parties, cost of the claim. It is located in the upper right part of the form.
In the second, the name is written in the center. The essence of the claim and the circumstances are described briefly but completely.
The third contains legal norms that substantiate the legality of the applicant’s claim.
The fourth part consists of a generalization and presentation of requirements to the defendant. Start with the word “please.”
We fill out the application in writing or electronically on the court’s website (Article 131 of the Code of Civil Procedure).
Step-by-step instructions for filing a labor claim
Step 1. Enter the name of the court to which the application was sent.
Step 2. Enter information about the plaintiff. For an individual this is full name, passport details, residential address, for an organization - name, location and legal address, information about the representative - name and address.
Step 3. Provide similar information about the defendant.
Step 4. Point out the non-compliance with labor laws that resulted in a violation of the plaintiff’s rights and formulate demands.
Step 5. You should describe the circumstances of the dispute - the grounds for filing an application. Give facts to prove them.
Step 6. Report the monetary value of the claim and the total amount to be recovered or disputed.
Step 7. In accordance with the law, provide information about the measures you have taken to resolve the dispute out of court.
Step 8: Make a complete list of applications.
Step 9. Enter the date of the application and sign the plaintiff (or his representative).
Include additional points in the application yourself:
- contact details of the plaintiff and his representative (telephone numbers, emails, etc.);
- other information for use in legal proceedings (for example, video and photographic documents, links to the media);
- The plaintiff's motions are submitted if available. These include requests to call witnesses and request evidence held by the defendant.
Mandatory applications are determined by law (Article 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation):
- copies of the claim are attached to the number of defendants and third parties;
- receipt of payment of state duty (for the organization);
- representative's power of attorney;
- documents confirming the circumstances and facts of violation of the applicant’s rights;
- pre-trial settlement documents;
- calculation of recovered wages, damages, disputed amounts of remuneration, etc.
Specifics of the claim after dismissal
Wage arrears can be owed either to a working employee or to one who has already been fired. If you file a claim for recovery of wages after dismissal, you should remember one important feature - the statute of limitations.
The specifics of this point are specially emphasized in paragraph 56 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation “On the application ...” of March 17, 2004 No. 2. Thus, if the employee continues his employment relationship with the company, then the statute of limitations is not applicable at all to disputes regarding the collection of wages, since the employer’s violation is considered lasting until the debt is repaid. This conclusion of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces, although not entirely compatible with the rules of Part 2 of Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but it is quite logical due to the need to ensure the protection of employee rights.
But if an employee is fired, then the statute of limitations, based on established judicial practice, will begin to be calculated from the moment of his dismissal.
For reference: in contrast to the general three-year limitation period for the collection of wages, a shortened period is provided, which is 1 year in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 392 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
An alternative conflict resolution option is a labor dispute commission
An alternative solution to non-payment of wages could be the creation of a labor dispute commission - a labor dispute commission. This is a method of pre-trial proceedings within the organization.
Features of KTS:
- Created on the initiative of employees. According to Articles 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses and 384 of the Labor Code, the employer does not have the right to refuse them this. According to the complaint for refusal to form a commission, he will be fined.
- Half of the members of the CCC are appointed by management, the other half are elected by employees.
- If an organization or individual entrepreneur violates any norms of the Labor Code, the worker has the right to appeal to the Labor Code.
- The meeting to discuss the issue is held for 10 days. The commission members decide what to do in this situation.
- For the proposed method to be approved, 50% of the votes + 1 vote are required.
- You are given another 10 days to appeal the decision.
If the commission comes to the conclusion that the employer is breaking the law, he is given 3 days to correct the situation. The committee also decides how exactly to correct it.
After this period, if no compliance measures have been taken, the applicant will be issued a CTS certificate for the collection of wages. In legal force, such a document is equivalent to a writ of execution. This rule is regulated by Articles 12 of the Federal Law No. 229 “On Enforcement Proceedings” and 389 of the Labor Code.
Also, with a CTS certificate, an employee has the right to contact the bank where the employer registered an individual entrepreneur or legal entity. By presenting this document, he can request the transfer of the debt to his account.
According to Article 70 of Federal Law No. 229, funds are required to be transferred on the day of application. The maximum delay in the transfer can be 7 days and is possible only if bank representatives have doubts about the authenticity of the CTS certificate.
Results
The procedural issues of filing claims to recover wages are spelled out in the legislation in sufficient detail and clearly.
In practice, employees often have difficulties proving the amount of debt, since the employer can pay some payments at its own discretion (for example, the amount of the bonus can be greater than the salary and paid depending on the results of work, the assessment of which, often subjectively, is given by the employer himself, etc. .d.). You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.