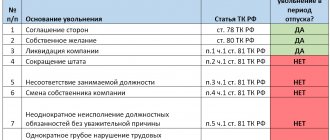
This labor function consists of exercising management of the organization (including performing the function of its sole executive body - Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) to perform actions on behalf of the organization to realize its rights and obligations arising from civil, labor, tax and other legal relations (to act without powers of attorney):
- in the scope of the owner’s powers to own, use and dispose of the organization’s property;
- in the field of rights of the copyright holder of exclusive rights to the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization equivalent to them;
- in the area of the rights and obligations of the employer in labor relations with other employees of the organization, etc. (Part 1 of Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
note
Employees who manage certain areas of the organization’s activities (for example, the artistic director of a theater, the scientific director of a scientific organization) or individual structural divisions of the organization without assigning them the functions of the sole executive body of the organization do not perform the labor function of the head of the organization (clause 2 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated June 2 2015 No. 21).
Basic rules for dismissing a director
Upon dismissal of the general director, an extraordinary meeting of company participants is convened with a summons to terminate the employment contract.
However, this issue can be raised among others at the scheduled regular or extraordinary meeting. You also need to issue an order to terminate the employment contract and familiarize the general director with it. The remaining technical stages in the process of dismissing a director are standard: making an entry in the work book and personal card, calculations, handing out the work book. There are several situations in which it is impossible to terminate an employment contract with the general director:
- if the manager is a pregnant woman, the exception is liquidation of the company (Part 1 of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the manager belongs to the category of persons named in Part 4 of Art. 261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- during a period of temporary disability or the director is on vacation, with the exception of liquidation of the organization (Part 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Dismissal of a director at the initiative of the owner
Since the general director is an employee of the company, his relations with the owners are regulated by labor law. Accordingly, when dismissing a director, it is important for owners to coordinate their actions with labor legislation.
In addition, the general director is a person with whom relations are regulated by corporate law. And this should also be taken into account.
An employment contract with the general director at the initiative of the owner can be terminated due to several circumstances:
- If there is a change in the owner of the company (clause 6 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The norm does not apply to cases where the composition of participants simply changes, as well as to reorganization in the form of affiliation.
- If a transformation of society has occurred, that is, the organizational and legal form has changed (division and separation). In this case, the owners may decide that it is necessary to terminate relations with the general director without indicating the reasons for dismissal.
- If by his actions the director caused damage to the interests of society (clause 9 of article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- If the director grossly violated his job duties one time (Clause 10, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Dismissal of a director due to a change in property ownership
The new owner of the property has the right, no later than three months from the date the right of ownership arises, to terminate the employment contract with management persons.
Having decided to terminate the employment contract with the general director, the owner must pay him compensation in the amount of no less than three times the average monthly salary (Article 75 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Dismissal due to damage caused by the actions of an official
In paragraph 9 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines a closed list of actions that can cause damage. According to the totality of labor law norms, in this case any actions that may be grounds for termination of an employment contract with an official are recognized. But such a procedure is quite complicated, since the fact will have to be proven. In particular, it will be necessary to conduct an internal investigation, demand explanations, etc.
Auditors, external consultants who conducted an analysis of economic and financial activities, as well as employees of the company can testify to the infliction of property damage by some decision of the general director. In this situation, it will be sufficient if the employee sees in the actions of the official a violation of the interests of society and informs the employer about this in writing. Based on the message, a decision is made to order an internal audit, an order is issued to create a commission, the issues that this commission will consider, as well as the facts and circumstances that it must establish, are determined.
Upon dismissal under Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to remember that all decisions that entail a violation of the safety of property or its unlawful use are methods of disciplinary action. Dismiss the director under clause 9, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible if two conditions are simultaneously met:
- If the decision was made by the director unreasonably or beyond his competence, without a proper analysis of the situation, based on incomplete data, on an emotional level.
- If the decision should entail negative consequences in the form of violation of the safety of property, its unlawful use or other damage to the organization’s property (clause 48 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2).
How can the owner find out that the general director has committed a violation regarding the safety of property? One of the employees can tell him. But often owners learn about this from consultants’ reports.
Dismissal of a director due to a single gross violation of labor duties
It happens that the general director falls under the provisions of clause 10 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to the owners, a gross violation can be any violation of duties that are named in the employment contract. For example, the director must agree on the candidacy of an acting director during his absence. If he forgot to do this, it means he grossly violated the provisions of the employment contract.
A serious violation may be considered failure to submit required reports on time or failure to meet indicators that are named in the employment contract as responsibilities. It is worth noting that clause 10, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applies only to managers and deputy managers.
Since dismissal on the grounds specified in Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a disciplinary sanction, then in order to register this sanction in the work book as a basis for terminating an employment contract, the employer will have to prove the fact of a disciplinary violation. To do this, it is necessary to conduct an internal investigation.
Algorithm for conducting an internal investigation
- An official investigation can be initiated on the basis of a report, inventory results, etc.
- An order must be issued to create a commission to conduct an investigation (it indicates the names of the commission members, their positions, purpose, date of creation, validity period, powers).
- All members of the commission must familiarize themselves with the order.
- Acts and other documents are drawn up during the investigation, and a final act is prepared based on the results of the internal investigation.
- The manager must familiarize himself with the acts.
- A written explanation is taken from the manager.
- An order is issued to apply a disciplinary sanction, which the manager must familiarize himself with.
It is important to remember that two disciplinary sanctions cannot be applied for gross violations of an employment contract. You will have to decide what disciplinary action to take.
Beginning of the limitation period for criminal prosecution
The statute of limitations begins from the moment the crime was committed - this is the date of actual failure to pay the tax within the period established by law. These are different days for each tax and for insurance premiums.
It is important to remember that the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation “On the practice of courts in applying criminal legislation on liability for tax crimes” dated December 28, 2006 No. 64 explains that even if taxes were paid, but later than the established deadline, criminal liability may still arise ( item 3).
Income tax
The deadlines for paying income tax are established by Article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The tax period for income tax is a calendar year. The reporting periods are the first quarter, six months and nine months of the calendar year.
The last day for paying income tax, given that the tax period is one year, is March 28 of each year.
If March 28 falls on a weekend, the tax payment date is moved to the first working day. It is from March 28, if there are no transfers, that the statute of limitations for non-payment of income tax is calculated.
Value added tax
According to Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the VAT tax period is a quarter for all categories of payers.
The deadline for paying VAT in accordance with Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is set until the 25th day of the month following the end of the quarter.
If the tax payment date falls on a weekend, it is moved to the first working day. If there are no postponements due to weekends and holidays, these above-mentioned dates will be considered the final dates for paying the tax and the dates from which the limitation period is calculated. If the date is postponed, then the last date for tax payment will be considered the date to which the last day for tax payment was postponed. Accordingly, the statute of limitations will be calculated from the postponed date.
Insurance premiums
The procedure for paying insurance premiums is defined in Chapter 34 “Insurance Premiums”. What is a settlement and tax period is described in Article 423 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- reporting periods are the first quarter, half a year, nine months of the calendar year;
- The billing period is considered to be a calendar year.
Considering that January 15 is the last day for payment of insurance premiums for December (the last month of the billing period), the period for attraction should begin on January 16. However, there is not yet enough judicial practice, thanks to which one could confidently assert that this date is correct. In addition, we know that in practice tax authorities try to shift the deadlines for attraction not in favor of the taxpayer.
Personal income tax
The calculation of the personal income tax tax base and the tax amount are determined based on the results of the year. The tax period for personal income tax is established as a calendar year in accordance with Article 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Accordingly, the next day after the payment of wages for December (no later) personal income tax must be paid and the next day the period for criminal prosecution for non-payment of personal income tax, or more precisely for failure to fulfill the obligation to pay taxes as a tax agent, begins to run.
Dismissal of a manager on the basis of Art. 278 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. Situation No. 1: The company is introducing bankruptcy proceedings (clause 1 of Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The decision to remove the manager from office in this case is made by the arbitration court. The following may apply for the removal of the head of a debtor organization from office: a temporary manager, a meeting of creditors, an administrative manager, or persons who provided security.
Key points for this situation:
- The basis for issuing the order is the ruling of the arbitration court on the removal of the head of the organization from office.
- The last day of work is the day when the owner of the organization’s property became aware of the entry into force of the court’s ruling.
- The director is not paid severance pay (with the exception of cases where such payment is provided for in an employment contract or other local regulatory act of the organization).
2. Situation No. 2: The authorized body of the legal entity decided to terminate the contract (clause 2 of Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
An employment contract with a director may be terminated by a general meeting of shareholders or the board of directors. Dismissal of the head of the organization on the basis established in clause 2, part 1, art. 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can happen at any time and without specifying motives.
How to leave a manager if he is the only founder
Let's consider a special case of how to dismiss the director of an LLC at his own request, if the first person is simultaneously the sole organizer of the company and its owner.
The first person of the company has the right to write a letter of resignation at any time and make a decision about his dismissal. There is no need to notify anyone of your upcoming dismissal. The maintenance procedure is significantly reduced. Simultaneously with the decision to dismiss, the sole founder appoints a new general director of the company.
Dismissal at the initiative of the General Director
The manager has the right to terminate the employment contract early, but he must notify all owners of his intention to resign, in writing and no later than one month in advance (Article 280 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Letters are sent to all founders, owners, shareholders according to the register, with notification of delivery. In the letters, the director asks to convene an extraordinary meeting with a summons to terminate the employment contract. The procedure for transferring affairs and property is determined in advance so that the owner does not initiate arbitration processes.
If a manager resigns at his own request, he is not paid monetary compensation in an amount not less than three times his average monthly salary.
Dismissal of the director due to the expiration of the employment contract
Since the executive body is appointed for three or five years, the powers of the director may be terminated due to the expiration of the contract. In this situation, dismissal is carried out in the general manner - the same as in the case of ordinary employees. However, the director must be warned by the employer (company owner) no later than three days before the expiration of the employment contract.
The employer sends the employee a corresponding notice, which is signed by him or an authorized person (for example, the head of the human resources department).
Next, a dismissal order is issued, a corresponding entry is made in the work book (Part 4 of Article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and a calculation is made.
Making changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities
Since the Unified State Register of Legal Entities contains information about a person who has the right to represent the interests of the Company without a power of attorney, it is fundamentally important to remove information about the former manager from there. However, only a new director can do this by sending a corresponding application to the Federal Tax Service within three days after his appointment. Five days after registering the application for changes, the tax authorities remove the former manager from the register.
The retired manager cannot influence this process, however, it is necessary to monitor the introduction of changes, because otherwise:
- he may not be accepted for a leadership position in another organization;
- he may be held vicariously liable for the debts of the LLC in the event of bankruptcy.
If the changes were never registered, the former general director may apply to the court to request that his name be removed from the register.
What guarantees can a director count on upon dismissal?
First of all, compensation is provided in the form of three times the average monthly earnings (Article 279 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, as noted above, there are cases when this compensation is not paid - upon dismissal as a result of bankruptcy of a legal entity, upon expiration of the contract and at the request of the employee.
Compensation must be paid if the owner of the organization’s property changes (Article 181 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, simply a change of company participants does not constitute a change of property owners.
Act of acceptance and transfer of documents from the former director to the new one: document structure
Such an act may contain the following elements:
1. Information block, which reflects:
- date, place of drawing up the act;
- Full name of the resigning director;
- Full name of the new director (deputy).
2. Block, which reflects the actions certified by the act: transfer by the resigning director and acceptance by the new one of documents related to the financial and economic activities of the organization.
3. Block with a list of documents to be transferred (by categories, which are reflected in the Regulations).
This block is optimally presented in the form of a table, the columns of which reflect:
- serial number of the position;
- name of the transferred documents (inventory numbers for groups of transferred documents);
- number of sheets of transferred documents (number of documents in inventories);
- necessary notes.
4. Block with signatures:
- the person transferring powers and documents;
- person accepting powers and documents.
In some cases, this block may be supplemented with signatures of the chief accountant and other competent persons. In addition, there is a possibility that the deed will need to be certified by a notary. Let's consider what factors this may be due to.