Reasons for voluntary dismissal of an employee
The provisions of the law (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) allow an employee to terminate an employment contract on his own initiative, having warned management in advance about his intentions and without explaining the reasons.
But in some cases, disclosing the reasons for dismissal can speed up the process. Thus, termination of the contract must be completed no later than the date specified in the application if the citizen retires or enters an educational institution.
Termination of the contract on any day appointed by the employee can also occur if management violates labor law standards. These include: delays in wages, violation of the terms of the contract, agreements, other internal acts, refusal to grant regular leave.
The reason for dismissal may also be the expiration of a fixed-term contract. If there is no desire on the part of the employer to terminate a fixed-term employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months, the employee should notify his superiors about his resignation, but no later than three days before the end of the contract.
General grounds for termination of an employment contract
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 77) defines the following reasons for termination of an employment agreement:
- joint decision of the parties;
- cancellation of the contract by decision of one of the parties;
- expiration of the valid contract period;
- the worker’s reluctance to work with another owner of the company if the owner of the organization has changed;
- employee refusal to work under the amended contract;
- termination of the production organization's activities;
- change of personnel's job responsibilities.
Which article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates dismissal at will?
Regulates the procedure for dismissal at one’s own request, Art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Its basis is clause 3, part 1, art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - this norm is reflected in the entry in the work book.
In Art. 80 shows possible options for terminating contractual obligations at the employee’s initiative. The main condition for dismissal can be considered filing an application. If it is impossible to submit an application in person, it is also possible to send it by mail - this is evidenced by the letter of Rostrud dated 09/05/2006 No. 1551-6.
ConsultantPlus experts provided step-by-step instructions for dismissing an employee at his own request. Get free access to K+ and go to the ready-made solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
Let's consider the procedure for voluntary dismissal under the labor code.
Procedure for termination of employment relations
If the reason for dismissal is legal and the procedure is not followed, then such dismissal can be overturned by the court. Then the company will have to reinstate the employee and fire him according to the rules, which means that he will have to pay for forced absences.
The correct thing to do is:
- issue an appropriate order;
- familiarize the employee with it;
- obtain a signature confirming familiarization with the document or draw up an act of refusal to familiarize yourself with it;
- make sure that the date of the last working day coincides with the day of dismissal;
- on the last working day, issue a work book to the subordinate with the appropriate mark;
- issue a settlement;
- if an employee refuses to pick up documents, then send a notice to the former employee about the need to pick them up.
Procedure for dismissing an employee at his own request (procedure, timing)
When dismissing at your own request, Article TC No. 80 regulates a certain procedure for this process.
The employee confirms his desire to terminate the employment contract by submitting a corresponding application to his superiors. At the same time, the timing of dismissal at one’s own request may vary, depending on the terms of the contract. If a fixed-term employment contract lasting up to two months is concluded, the employee’s working period lasts no more than three days from the date of submission of written notice of termination of the contract. The same rules apply to the procedure for dismissing an employee on a probationary period.
In other cases, unless otherwise provided by law, the employer has the right to terminate the contract two weeks after receiving the application. The counting period for this period begins from the next day. The contract may be terminated earlier at the discretion of management.
Within two weeks after submitting the document, the employee has the right to withdraw the application and continue working. The exception is cases when another person has already been invited to fill the vacant position, whose employment cannot be refused, for example, by way of transfer from another employer, according to Art. 64 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is possible to dismiss an employee on his own initiative even during the days he is absent from the workplace due to incapacity for work. However, if the employee is against it, then he should rewrite the application and change the expected date.
Termination of the contract is also allowed when the employee is on regular vacation. In this case, working the required period of two weeks may not be necessary. The day of dismissal is taken to be the last day of vacation.
More detailed information about this can be found in the material “How to properly arrange leave followed by dismissal.”
Upon dismissal, an employee must be given a work book and other documents upon request containing data on the amount of salary. The amounts due should be paid no later than the last day of work, and if this is impossible to do (for example, if the employee is absent from work) - at his request at any other time.
ATTENTION! The rules for maintaining work books in force from 09/01/2021 (approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 05/19/2021 No. 320n) do not provide for familiarization of the employee with the signature of the work records entered into the paper work book (previously, employees signed the dismissal record). Read more about the new rules for registering a work book, effective from September 2021, here.
Voluntary dismissal does not always go smoothly. Sign up for a free trial access to ConsultantPlus and familiarize yourself with the controversial situations of voluntary dismissal set out in judicial practice.
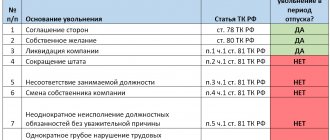
General grounds for dismissal
The grounds for the emergence, change and termination of labor relations are those points to which regulatory authorities pay increased attention, since the state seeks to protect the interests of workers. In this regard, the company’s management should responsibly approach the formalization of each of these stages of development of labor relations, so that in the future there will be no problems with the labor inspection.
When discussing the termination of a working relationship, it should be noted that the general grounds are listed in Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where the following options are indicated:
- at the initiative of the employee (Article 80);
- at the initiative of the employer (Article 71 and Article 81);
- by agreement of the parties. That is, the contract can be terminated at any time and on any conditions determined by the parties in a special agreement (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2);
- expiration of the contract (Article 79);
- dismissal due to transfer to another employer;
- refusal of an employee to work after a change of owner or jurisdiction of the organization (Article 75);
- employee’s refusal to work after changing the terms of the contract (Article 74);
- refusal of an employee to transfer to another position due to medical indicators that were identified during a periodic medical examination (Article 73);
- the employee’s disagreement to move with the employer (Article 72.1);
- circumstances beyond the control of the parties (for example, conscription into the army or a natural disaster, all listed in Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- concluding an agreement in violation of current legislation (Article 84);
- other grounds provided for by current legislation.
Let us dwell on the study of the most common grounds for dismissing an employee, which are often used by the parties when terminating an employment relationship.
Payments under the Labor Code upon dismissal at will
In case of voluntary dismissal, the Labor Code guarantees certain payments to employees:
- The employee has the right to expect repayment of the employer's wage arrears.
- In cases where the next vacation is not taken in full, management pays compensation for all unused vacation days. If the right to rest is exercised in advance, then from the salary of the dismissed person the organization has the right to withhold previously paid amounts for undue periods of leave. In this case, the total amount of deductions should not exceed 20% of payments (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
More information about deductions in such cases can be found in the article “Deduction for vacation used in advance upon dismissal.”
- Sometimes an employee can also count on severance pay. But this condition must initially be spelled out in internal local documents - labor and collective agreements.
Termination of an employment agreement at the initiative of the employer
- Reasons beyond the control of employees:
- termination of the enterprise's activities;
- reducing the number of employees as an anti-crisis measure.
- Reasons associated with low qualifications of employees:
- insufficient professional qualifications of the employee for the position held, identified during certification.
However, prior to the certification, management must notify employees in writing about the upcoming event so that employees have the opportunity to prepare for the exam. Certification should be carried out in relation to all employees, and not individual personnel. In addition, if several attempts at certification were unsuccessful for an employee, the employer is obliged to offer him other vacant positions (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Reasons associated with non-compliance with internal rules of the organization:
- the employee ignoring his obligations under the contract;
- gross violation by an employee of official duties or professional ethics;
- disclosure of state, commercial, industrial secrets;
- causing damage to the property of the enterprise (theft, damage to property, misuse of funds), established during an internal investigation and confirmed in court;
- violation by an employee of labor protection rules;
- loss of trust in the employee (if he works with material and monetary values);
- employee decisions that caused material damage to the company;
- falsification of documents - both those that were submitted upon hiring and those that were drawn up during the period of employment.
Results
In order to avoid further disputes between the employer and employees, it is necessary to follow the procedure for dismissal at will.
Ignoring by an employee of a mandatory period of work is often considered a violation of labor discipline, and then the contract can be terminated on completely different grounds. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties
These cases are specified in Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- conscription into the Armed Forces;
- reinstatement of the former worker by court decision;
- establishment of punishment by court verdict in the form of imprisonment;
- the employee’s inability to perform duties for medical reasons;
- expiration of the contract;
- force majeure;
- establishing a ban on work or holding a certain position;
- denial of access to state secrets if it is necessary for work;
- cancellation of the decision on reinstatement.
Dismissal due to liquidation of the organization or staff reduction
The fact that they want to dismiss an employee due to the liquidation of the company or staff reduction must be notified in advance no later than two months before the expected date. The notice must be handed in against signature. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer the employee another job. It is up to the employee to agree or refuse. If a company plans to reduce staff, jobs are primarily saved for:
- those who are in a family and have two or more dependents;
- a person who is the only worker in the family;
- a person who received a work injury or illness in connection with work at the enterprise;
- disabled people of the Second World War and disabled people fighting to defend the Fatherland;
- an employee who improved his qualifications in the direction of the employer without interrupting his work activities.
If an employer wants to dismiss employees under eighteen years of age, then he will need to obtain the consent of the State Labor Inspectorate and the Commission on the Affairs of Minors and the Protection of Their Rights. Compensations that are due to an employee dismissed due to liquidation or staff reduction:
- severance pay, which is equal to the average monthly salary;
- maintaining the average salary for the period when the citizen is looking for work, but no more than 2 months from the date of dismissal;
- preservation of the average salary for the period of employment on an exceptional basis and during the third month from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service authority (there is a caveat: the employee must contact the employment service within 2 weeks);
- compensation related to unused vacations;
- additional compensation if the employee agrees to quit before the notice period expires (2 months). The amount is calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of this period.
Employees who are dismissed due to the liquidation of the company during pregnancy or who are on maternity leave should receive additional payments.
Benefits and risks for the employee
The benefits of terminating a contract on this basis for an employee:
- the citizen himself has the right to initiate the procedure;
- It is not necessary to indicate a specific reason for the desire to terminate the employment relationship;
- there are no time limits for filing a resignation letter;
- it is possible to reach an agreement with the employer at any time during employment, even during periods when dismissal is prohibited by law (for example, on vacation, if the parties have agreed on this);
- you can agree on the terms of termination of the contract and propose your own;
- this reason for termination of the relationship does not in any way affect the employee’s reputation;
- if an employee is dismissed by agreement of the parties, this often means that the employee was expelled due to his fault.
Employee risks:
- the decision cannot be revoked;
- the trade union in this case does not exercise control over the actions of the employer;
- The law does not indicate the obligatory payment of severance pay; this is done only under a separate additional agreement or if such a condition is in the collective agreement.
Why do you need a work book and what information does it contain?
Before starting a more detailed conversation about records for reasons for dismissal, let’s consider why a work book is needed in the first place. As the law explains, a work book is an important document that allows you to calculate your total work experience, for example, for calculating a pension; contains information about education, and also informs employers about the merits of the new employee in previous places of work and the reasons for dismissal from there. The following must also be included in the work book:
- dates and reasons for the employee’s transfer from one position to another;
- information about hiring and dismissal;
- information about obtaining additional professions;
- messages about completed advanced training and retraining courses;
- part-time data;
- information about awards and achievements, etc.
If an employee has changed his last name or his name has changed while working for the company, this must also be noted in the work book.
At the same time, experts do not recommend making entries in the work book with details of penalties. Rare exceptions are those situations where a gross violation of some rules served as the basis for dismissal from office.
Now let’s take a closer look at the most common reasons for dismissals and the rules for entering information about this into the work book.
Drawing up an agreement
There is currently no unified, standard form of agreement on termination of an employment contract, so company employees can create this document in free form, or, if the organization has a developed and approved sample, using its template. The main requirement that must be met is that the composition of the agreement meets certain rules of office work, and in relation to the text it contains a number of certain information.
The structure of the document can be divided into three parts: the header, the main section and the conclusion.
The name of the employer company, place, and date of conclusion of the agreement are entered in the “header”.
The main part of the agreement includes information about the employee:
- his position;
- FULL NAME;
- reference to the employment contract, on the issue of termination of which the parties have reached an understanding (number, date of conclusion);
- the fact of reaching an agreement is recorded;
- the date on which the employee leaves.
If there are any additional terms of the agreement, they must be included in the document.
It is necessary that the document be endorsed by the head of the organization (or a person authorized to act on his behalf) and the resigning employee.
If the regulatory legal acts of the enterprise stipulate a requirement to certify papers using seals, the form must be stamped.
Cons of the agreement
To be fair, it should be said that terminating an employment relationship by agreement also has its downsides. In particular:
- in most cases, the employee does not have the right to withdraw his application unilaterally;
- The company's management can fire him even during a period of temporary incapacity.
Sometimes employers refuse to reach an agreement with an employee, especially if the latter has previously committed a serious offense.