Revision dated 06/04/2021
Limited Liability Company "Rhythm of Life", hereinafter referred to as the "Agent", places this offer to conclude an agency agreement on the conditions specified below (hereinafter referred to as the "Agreement"), which constitutes a public offer within the meaning of Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in relation to legal individuals, individual entrepreneurs, as well as individuals who are payers of professional income tax, users of the Company’s website (https://taxi-ritm.ru), hereinafter referred to as the “Principal” if the conditions set out below are accepted. For the purposes of this Agreement, the Agent and the Principal are hereinafter collectively referred to as the “Parties”.
Submission by the User (Principal) of an application on the Company’s website (https://taxi-ritm.ru), filling out by the Principal other documents containing all the necessary and reliable data that allows it to be verified, is an acceptance and means that the user (Principal) has read the terms and conditions of this Agreement, the Privacy Policy, and other legal documents posted on the Company’s website and undertakes to comply with them.
Terms and Definitions
Unless otherwise specified, the terms and definitions used in this Agreement have the following meanings:
- “Offer” – this document, which represents a public offer of the Agent, which is valid from the moment it is posted by the Agent until its withdrawal.
- “Acceptance” – the actions of the Principal, indicating the Principal’s full and unconditional acceptance of the terms of this Agreement, by filling out the application form on the Company’s website (https://taxi-ritm.ru), and sending the necessary information to the Agent.
- “Agreement” - this Agreement concluded by the Parties on the basis of paragraph 3 of Article 438 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the “Civil Code of the Russian Federation”) by fulfilling by the Principal the terms of the Agreement (Acceptance) specified in the Offer without signing a separate written document.
- “Principal” is a person using the website (https://taxi-ritm.ru) in any form in accordance with this Agreement.
- “Privacy Policy” is a document drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data”, which defines the procedure for processing personal data of users by the site (https://taxi-ritm.ru), and measures for ensuring their confidentiality on the part of the Agent.
- References to a word or term in the plural include references to that word or term in the singular, unless otherwise provided in the text of this Agreement.
Rent amount
The amount of rent is determined by agreement between the landlords and the tenant:
- by agreement of the parties - arbitrarily in accordance with Articles 421 and 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- based on market conditions for similar types of leases;
- according to the cost calculation for renting a vehicle, which includes all the owner’s expenses.
If a car rental agreement without a crew is concluded, the tenant can take into account the costs of fuels and lubricants, repairs, technical inspection and insurance.
Based on Articles 644 and 646 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clauses must be included in the contract stating that the costs of repairs, maintenance, and insurance “fall” on the tenant.
Subject of the Agreement
2.1. Under this Agreement, the Principal instructs, and the Agent undertakes, for a fee, on behalf and at the expense of the Principal, to perform the following actions:
2.1.1. find and transmit to the Principal customer orders for the transportation of passengers and luggage by passenger taxis, delivery and provision of other similar services through the software (including mobile applications) of Taxi Aggregators installed on the Principal’s electronic device; The agent acts as a provider of information services only.
2.1.2. organize the Principal’s connection to the selected Taxi Aggregators, completing all the necessary technical and other actions for this;
2.1.3. accept into your account from Taxi Aggregators funds received from the Principal's clients, taxi Aggregator bonuses intended for the Principal, and transfer them to the Principal or by direct transfer using the details provided by the Principal from the Agent's current account, minus his remuneration and expenses incurred related to the execution obligations under this Agreement, or otherwise in accordance with current legislation. The choice of option is made by the Agent.
2.1.4. Acceptance of this Agreement by the Principal is carried out by providing documents after approval of his application by the Agent, and is possible subject to simultaneous compliance with the following conditions:
2.1.4.1. familiarization of the Principal with the terms of this Agreement and the Privacy Policy;
2.1.4.2. the Principal's consent to comply with all the terms of this Agreement and the Privacy Policy.
2.1.4.3. Acceptance of this Agreement under conditions or with reservations is not permitted.
2.2. By concluding this Agreement, the Principal acknowledges and agrees that:
2.2.1. The Principal independently provides services to clients and is responsible for the quality and timeliness of their provision. The Agent does not participate in the provision of services to the Principal’s clients;
2.2.2. legal relations arising under this Agreement are not labor relations. The principal independently determines the schedule for providing services to his clients and their quantity and has the right to refuse to fulfill clients’ orders at any time.
Lease agreement with crew (Article 632 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
If a rental agreement with a crew is concluded with an employee, then only the lessor himself can drive such a vehicle.
Very often, this type of agreement is concluded either with the head of the company, who uses his personal car on business trips, or with employees whose work is traveling and who are forced to travel in their own vehicles. When renting a car with a crew, the costs of repairing the car, as well as the liability for insuring the vehicle, are borne by the lessor. However, expenses associated with the operation of the vehicle, for example the purchase of fuel and lubricants, are paid by the lessee, i.e. organization.
Personal income tax must be calculated from the rental amount, but this payment is not subject to insurance premiums on the basis of clause 4 of Art. 420 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. An organization may pay accident insurance premiums, but only if such an obligation is clearly stated in the terms of the lease agreement.
It would seem that everything is clear, but the regulatory authorities, referring to civil legislation, interpret this agreement as a mixed type of lease agreement without a crew and an agreement for the provision of services for the management and technical operation of a car, justifying this with the provisions of paragraph 2 of Art. 635 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, their logic is clear; the procedure for calculating insurance premiums from these payments changes. Namely: insurance premiums are not charged with rental payments, but insurance premiums are charged with services for driving and technical operation of the car. Please note that there is a risk that tax authorities will charge additional insurance premiums on the total amount of the contract if the contract specifies the total rental price. Therefore, in order to minimize risks, companies are often advised to enter into two different agreements in this case - a bareboat rental agreement and an agreement for the provision of services for the management and technical operation of a vehicle.
Rights and obligations of the parties
3.1. The agent has the right:
3.1.1. Conclude agency agreements similar to this Agreement with other principals.
3.1.2. Withhold from the funds paid by the Principal's clients and received to the Agent's account from Taxi Aggregators, his remuneration and the amount of expenses incurred related to the fulfillment of obligations under this Agreement.
3.2. The Agent undertakes:
3.2.1. Organize the connection of the Principal to the selected Taxi Aggregators, carrying out the necessary technical and other actions for this purpose.
3.2.2. Search for clients for the Principal and transmit information about their orders to the Principal using Taxi Aggregator software.
3.2.3. Timely transfer to the Principal funds and taxi aggregator bonuses intended for the Principal.
3.2.4. Provide a report on the execution of the Principal’s instructions in the manner and within the time limits provided for in Section 5 of this Agreement.
3.2.5. Comply with the Privacy Policy.
3.3. The principal has the right:
3.3.1. Receive from the Agent the necessary information about the progress of the execution of its instructions under this Agreement.
3.4. The principal undertakes:
3.4.1. Pay the Agent remuneration for services rendered and reimburse the Agent for expenses incurred related to the fulfillment of obligations under this Agreement in the manner and within the time limits provided for in Section 4 of this Agreement.
3.4.2. Be independently responsible to clients whose orders were received from the Agent.
3.4.3. In the process of providing services to clients, comply with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation, including rules for the transportation of passengers and baggage, traffic rules, sanitary norms and regulations, rules for the maintenance and repair of vehicles, rules for issuing waybills, legislation of the Russian Federation on the application of control and cash register equipment, and independently bear responsibility for their violation.
3.4.4. Independently calculate and pay tax on amounts transferred by the Agent under this Agreement in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees.
Accounting for expenses for tax purposes for a company
But as for accounting for expenses for tax purposes for a company that uses both a general and a simplified taxation system with the object “Income reduced by the amount of expenses,” then compensation can be taken into account in expenses only within the established standards.
This is indicated by specialists from the Ministry of Finance in a letter dated 08/02/2019 No. 03-11-11/58296. They refer to the norms of expenses of organizations for the payment of compensation for the use of personal cars for business trips, established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02/08/2002 No. 92 “On establishing norms of expenses of organizations for the payment of compensation for the use of personal cars and motorcycles for business trips, within which, when determining the tax base for corporate income tax, such expenses are included in other expenses associated with production and sales.” According to paragraph 1 of this Resolution, the norms for organizations' expenses for paying compensation for the use of personal cars and motorcycles for business trips for tax purposes are set at 1,200 rubles. for passenger cars with engine capacity up to 2000 cc. see inclusive and 1500 rub. for passenger cars with engine capacity over 2000 cc. cm.
Companies using the simplified tax system also need to pay attention to the fact that only compensation for the use of cars and motorcycles for business purposes can be taken into account in expenses that reduce the taxable base (clause 12, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Compensation for the use of an employee’s personal truck is not included in the closed list of expenses under the simplified tax system and therefore does not reduce the taxable base under the simplified tax system. If an employee’s freight transport is used for business purposes, it is best for companies using the simplified tax system to enter into a vehicle lease agreement with the employee, in which case rental payments can reduce the tax base of the tenant organization.
If a company applies a simplified taxation system with the taxation object “Income,” then compensation payments cannot be taken into account for tax purposes.
To receive compensation, an employee must submit an application indicating the frequency of use of personal transport for business purposes, attaching to the application a copy of the vehicle registration certificate and documents (receipts, cash receipts, etc.) confirming the expenses incurred by the employee for fuel and lubricants.
Accounting entries when calculating compensation to an employee are similar to accruals under lease agreements:
Debit 20, 26, 44 ... Credit 73 - compensation has been accrued for the use of the employee’s car.
Financial relationships
4.1. Agent's remuneration:
4.1.1. 3a execution of an order under this Agreement, the Principal pays the Agent a remuneration, which represents a certain percentage of the amount of each order. The exact amount of the Agent's remuneration is determined in accordance with the tariffs and is indicated on the website (https://taxi-ritm.ru).
4.1.2. The provision by the Principal of services for at least 1 (one) client order received from the Agent indicates the Principal’s agreement with the specified amount of the Agent’s remuneration. If the Principal disagrees with the amount of the Agent's remuneration, the Principal is obliged to refuse the Agent's services, including the execution of client orders received from the Agent.
4.1.3. The volumes of services provided are determined according to the data contained in the Agent’s Partner web interface provided by the Order Service service. The Agent's remuneration is determined from the amount of proceeds received by the Principal to the Agent's account from the Order Service, reduced by the amount of proceeds transferred to the Principal's personal bank accounts. The amount to be transferred to the Principal’s benefit is determined by the availability of funds in the Principal’s virtual account in the Order Service application, which contains the balance of funds, taking into account the Agent’s already automatically withheld remuneration for services rendered under the agency agreement.
4.1.4. In addition to the Agent's remuneration specified in clauses. 4.1.1., 4.1.2. of this Agreement, the Agent has the right to demand payment of additional remuneration for certain actions. The availability and exact amount of the Agent’s additional remuneration is determined by individual agreement between the Agent and the Principal. The provision by the Principal of services for at least 1 (one) client order received from the Agent indicates the Principal’s agreement with the specified amount of the Agent’s additional remuneration. If the Principal disagrees with the amount of the Agent’s additional remuneration, the Principal is obliged to refuse the Agent’s services, including the execution of client orders received from the Agent.
4.1.5. The Agent's remuneration is paid by deducting the amount of remuneration from the funds received by the Agent into his account for orders from the Principal's clients.
4.1.6. The amount of the Agent's remuneration from orders of the Principal's clients paid in cash is withheld from other amounts received by the Agent to his account from Taxi Aggregators and due to the Principal.
4.1.7. In case of insufficient funds in the Agent's account to withhold the remuneration. The Principal undertakes to pay the Agent's remuneration by depositing funds into the Agent's account within 5 (five) calendar days from the moment the debt arose.
4.1.8. Value added tax (hereinafter referred to as “VAT”) on the amount of the Agent’s remuneration is paid in the manner prescribed by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the “Tax Code of the Russian Federation”). The amounts of remuneration indicated in accordance with paragraphs. 4.1.1. – 4.1.3. of this Agreement in mobile applications of Taxi Aggregators do not include the corresponding VAT.
4.2. Payment of funds to the Principal:
4.2.1. Based on agreements between Taxi Aggregators and the Agent, the Principal’s revenue is transferred to the Agent’s bank account. Subsequently, the Agent transfers the proceeds to settlement accounts specified by the Principal in any bank of the Russian Federation or to any bank settlement accounts of third parties specified by the Principal, including to the bank accounts of the car lessor or employer with whom the Principal, as the executor of orders for the transportation of passengers, has and luggage on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there is an employment contract or a vehicle rental agreement, or offsets counterclaims, minus the Agent’s remuneration and expenses incurred related to the fulfillment of obligations under this Agreement (including expenses for paying for the services of Taxi Aggregators). If In this case, in accordance with subparagraph 9 of paragraph 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, funds transferred to the Principal by the Agent are not the Agent’s income and are not taken into account when determining its tax base.
4.3. By concluding this Agreement, the Principal acknowledges and agrees that:
4.3.1. in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 11 and paragraph 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the Agent is not the source of payment of the Principal’s income and does not act as his tax agent, therefore, on the basis of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the Principal is obliged to independently keep records, calculate and pay taxes on income earned by him in the manner established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation;
4.3.2. The Principal's revenue passing through the Agent's current account in connection with the fulfillment of obligations under the agency agreement, with the exception of intermediary remuneration and minus the expenses incurred in connection with the fulfillment of his obligations under this Agreement, is not the Agent's income and is not taken into account by him for calculating the tax base.
4.3.3. The obligation to pay taxes on the proceeds transferred by the Agent to the Principal, to the personal accounts of individuals, bonuses from taxi aggregators, insurance premiums, as well as from the proceeds received by the Principal from the Charterers in cash for services for transporting passengers by passenger taxis, by virtue of the terms of this agreement, lies on the Principal, as the beneficiary and payer of taxes and fees, as a person carrying out commercial activities for the transportation of passengers and luggage by passenger taxis.
4.3.4. The Principal is independently responsible for the correctness of the specified details for the Agent’s transfer of funds. The Agent is not responsible for the consequences of the Principal entering erroneous details.
Lease agreement without crew (Article 642 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
If an employee enters into a rental agreement for a vehicle without a crew, then in this case both the owner of the car and any employee of the organization can drive the car.
When renting a car without a crew, the costs of maintaining the car are borne by the renting organization.
Personal income tax must be calculated from the rental amount; these payments are not subject to insurance premiums.
For any form of agreement concluded, it is necessary to indicate in the agreement the data from the vehicle registration certificate, namely: the make of the car, the year of its manufacture, color, body number, engine number, state registration number. car number, number and series of vehicle registration certificate. The agreement must also establish the lease term, amount and procedure for payment of rent.
The accounting department of the tenant organization will have to reflect the receipt of a car for rent on the basis of an act of acceptance and transfer of the vehicle, reflecting this operation on off-balance sheet accounts.
Debit 001 - a car received under a lease agreement has been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting.
When calculating rental amounts for the use of a car for an employee, the following entries must be made in accounting:
Debit 20, 26, 44 ... Credit 73 - a fee has been charged for renting a vehicle from an employee.
Debit 20, 26, 44 ... Credit 69 - insurance premiums have been charged for services for the management and technical operation of vehicles.Debit 73 Credit 68 - personal income tax withheld.
When concluding any of the above types of agreement, accounting for the costs of paying lease payments and the costs of maintaining vehicles in the lessee company is the same:
- Operations for the provision of personal transport for rent are not subject to VAT due to the provisions of Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- If the lessee company applies a general taxation system, then when calculating income tax, expenses associated with rent can be taken into account as expenses in the amount of actual costs.
- If the tenant company applies a simplified taxation system with the object of taxation “Income reduced by the amount of expenses”, then take it into account as expenses that reduce the taxable base in accordance with the provisions of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation can be the amount of rent, costs of fuel and lubricants and other expenses related to the maintenance of transport.
- If the lessee company uses a simplified taxation system with the taxation object “Income,” then the company will not be able to take into account the costs of rental and other payments related to the maintenance and operation of vehicles for tax purposes.
However, it must be borne in mind that under any taxation system, actual expenses in accordance with current legislation must be justified and documented, and under the simplified tax system also paid. Specialists from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation once again pointed out the obligation of documentary evidence of expenses in their letter dated March 25, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/20067.
Agent's report on the execution of the Principal's instructions
5.1. A report on the execution by the Agent of the Principal’s order, which represents the history of the Principal’s operations for the purpose of executing the order under this Agreement, is automatically generated in the Principal’s personal account on the Agent’s website (https://taxi-ritm.ru) or sent by the Agent to the Principal by email.
5.2. The Principal is obliged to familiarize himself with the Agent’s report within 5 (five) calendar days from the moment of its formation in his personal account and, in case of disagreement with a particular operation listed in the report, submit reasoned objections to it.
5.3. If during the period specified in clause 5.2. of this Agreement, the Principal will not submit reasoned objections, the report is considered agreed upon and accepted by the Principal in full.
Agreement on compensation (Article 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
Another option for registering the use of personal transport is the conclusion of an additional agreement to the employment contract on compensation for the use of personal vehicles for business purposes.
In this case, as in rental with crew, only the owner of the vehicle will be able to use the car. The amount of compensation for the use of a personal car for business purposes is not provided for by labor legislation; accordingly, the organization establishes the methodology for calculating compensation independently, either by setting a fixed fixed monthly payment price, or by monthly calculating compensation depending on the intensity of use of the car.
The basis for payment of compensation when using personal vehicles is an order from the head of the company to pay compensation, which stipulates the amount of such compensation.
Please note that compensation is not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions in the full amount that was agreed upon between the employer and employee, based on the provisions of clause 3 of Art. 217, para. 10 pp. 2 p. 1 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility of the Parties
6.1. For failure to fulfill obligations under the Agreement, the Parties are liable in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.2. If the Principal's representations and warranties provided for in Section 7 of this Agreement are unreliable, the Agent has the right to unilaterally refuse to fulfill this Agreement, as well as demand compensation from the Principal for losses caused by unreliability.
6.3. The agent is not responsible:
6.3.1. to the Principal's clients for the quality and timeliness of services provided to them;
6.3.2. to passengers or other third parties in the event of damage to them or their property as a result of a traffic accident when the Principal provides services to its clients;
6.3.3. in case of violation by the Principal to comply with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation in the process of providing services to clients.
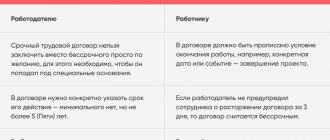
How to rent a car from your employee: rental agreement or employment contract
According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, there are two types of car rental agreements:
- rental of a vehicle with crew;
- rental of a vehicle without a crew.
In the first case, the lessor provides the lessee with a vehicle for a fee for temporary use and provides services for driving the vehicle and its technical operation. The procedure for such a lease is described in Articles 632-641 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
In the second case, the lessor provides the lessee with a car for a fee for temporary use without providing management services and its technical operation. The procedure for this type of lease is described in Articles 642-649 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An organization has the right to rent a car from both legal entities and individuals, including its employees.
Disadvantage of the lease agreement:
The driver, under the contract with the car, is required to undergo pre-trip control
Do I need to issue waybills when renting an employee’s car?
According to Article 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if an employee uses his personal property with the consent of the employer and in the interests of the organization, the employee is paid compensation for the use, wear and tear (depreciation) of transport, equipment and other technical means and materials, as well as expenses associated with their use. The amount of reimbursement of expenses is determined by agreement of the parties to the employment contract, expressed in writing.
Therefore, the use of a personal car by an employee to travel on company business can be included in the employment contract and the amount of reimbursement of expenses can also be specified there. You can sign a separate additional agreement.
The agreement must be drawn up in writing, and it must establish the amount and procedure for compensation for the use of personal property, as well as the amount of the employee’s expenses for the purchase of fuel and lubricants.
Representations and Warranties
7.1. By concluding this Agreement, the Principal, in accordance with Article 431.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, assures and guarantees that:
7.1.1. The principal carries out its activities in accordance with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation, including having all the necessary permits obtained in the prescribed manner. In relation to orders for the transportation of passengers and luggage by passenger taxi, the Agent cooperates only with the Principal who has permission to carry out the relevant activity, and therefore, in the event of the absence or cancellation of the said permission from the Principal, the Agent terminates such cooperation.
7.1.2. The Principal accepts the rules and requirements of the Taxi Aggregators to which he connects and undertakes to comply with them.
7.1.3. In case of failure to comply with the obligations specified in this paragraph, the Taxi Aggregator may apply liability measures to the Principal provided for by the relevant rules and requirements, including disconnection from the Taxi Aggregator.
Waybill
One more thing remains to determine whether it is necessary to issue a waybill:
- If rented cars transport passengers or cargo, then the use of a waybill is mandatory.
- if the transportation of goods or passengers is not carried out, then, as indicated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated July 09, 2019 No. 16-15 / [email protected], the waybill is only one of the primary documents confirming the expenses incurred for the purchase of fuel - lubricants.
Department specialists pointed out that if taxpayers do not belong to road transport organizations that are required to follow Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated September 18, 2008 No. 152 “On approval of mandatory details and the procedure for filling out waybills,” then they can use waybills only as one of the documents confirming the costs of purchasing fuels and lubricants, securing the specified procedure in the accounting policy for profit tax purposes.
Accordingly, to confirm travel routes and the validity of gasoline expenses, it is possible to use other documents confirming the expenses incurred. However, in any case, the formal procedure for processing documents can only be recognized as an attempt to evade taxes and contributions.
To summarize, we can say that choosing how to formalize the use of an employee’s personal transport for business purposes is not such a dilemma; you just need to legally correctly document contracts or agreements so that the inspection authorities do not have the desire to argue with the taxpayer.
Unlock access to the private part of Clerk with a Premium subscription. Get hundreds of webinars and online courses, unlimited consultations and other proprietary content for accountants.
Hurry up to subscribe with a 20% discount until October 15, 2021. Read more about “Premium” here.
Force majeure circumstances
8.1. Neither Party shall be liable to the other Party for failure to fulfill obligations under this Agreement due to force majeure circumstances that do not depend on the will of the Parties, arose after the conclusion of this Agreement and which could not have been reasonably expected, avoided or overcome at the conclusion of this Agreement. Such circumstances include, but are not limited to: natural disasters (earthquake, flood, hurricane), fire, mass diseases (epidemics), strikes, military operations, terrorist acts, sabotage, prohibitive measures of states, bans on trade operations and other similar circumstances.
8.2. A Party that fails to fulfill its obligations due to force majeure circumstances must notify the other Party of such circumstances and their impact on the fulfillment of obligations under this Agreement within 10 (ten) calendar days from the moment they occur.
8.3. Failure to fulfill the obligation to notify of the occurrence of circumstances deprives the Party of the right to refer to such circumstances that resulted in failure to fulfill obligations under this Agreement.
Electronic document management
9.1. The parties agreed on the possibility of using electronic document management within the framework of this Agreement, which has legal force equal to the legal force of written document management.
9.2. The Parties recognize the legal validity of actions carried out in the Principal’s personal account on the Agent’s website, as well as documents sent by a Party to the other Party by email. Legally significant actions in the Principal’s personal account on the Agent’s website and documents sent by the Parties to each other by email are recognized by the Parties as documents in simple written form, signed by an analogue of a handwritten signature (email address and telephone number).
9.3. Documents sent by email are considered received by the Party on the day of their actual receipt, confirmed by receipt by the other Party of a reading notification.
9.4. The parties undertake to exchange information about email addresses used under this Agreement within 5 (five) calendar days from the date of conclusion of this Agreement.
Dispute Resolution
10.1. All disputes and disagreements arising from this Agreement shall be resolved by the Parties through negotiations in compliance with the mandatory claims procedure in accordance with this section of the Agreement.
10.2. Claims may be sent by the Parties to each other by email. The period for consideration of claims made by the Parties under this Agreement is 15 (fifteen) calendar days from the date of receipt of the claim.
10.3. All disputes arising from this Agreement and not resolved during the claim procedure are referred to the courts at the location of the Agent in accordance with the procedural legislation of the Russian Federation.
Duration of the Agreement, procedure for its termination
11.1. This Agreement comes into force from the moment of its acceptance by the Principal.
11.2. This Agreement is considered concluded for an indefinite period and is valid until its termination.
11.3. This Agreement may be changed unilaterally by the Agent at any time. The Principal is obliged to independently monitor all changes on the Agent’s website.
11.4. Each Party has the right to terminate this Agreement unilaterally by sending the other Party a notice of termination of the Agreement 2 (two) calendar days before the expected date of termination.
Final provisions
12.1. In all other respects that are not provided for in this Agreement, the Parties are guided by the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
12.2. Each Party is obliged to promptly notify the other Party of changes in its details within 5 (five) calendar days from the date of such changes. A Party that fails to notify the other Party of a change in details within the appropriate period bears the risk of negative consequences associated with the lack of appropriate notification.