How to register a residential building in SNT
On December 8, 2021, the law on the extension of the dacha amnesty No. 404-FZ came into force.
This means that owners of garden plots, until March 1, 2026, can forget about receiving a notification for compliance with acceptable parameters and other inconvenient issues regarding the coordination of the location of the facility with local authorities. You purchase a plot of land in SNT, build a house on it, and then register it with Rosreestr - this is a simplified procedure, no permitting documentation is needed.
Link to document:
Step-by-step instructions for registering a residential building:
- Order a technical plan. The production of this document is carried out by cadastral engineers.
An engineer will come to your site to take internal measurements and determine the location of the building on the site. By the way, the lack of land surveying will not in any way affect the process of registering a house under the dacha amnesty.
- The technical plan is issued to the owner in electronic and paper form, the first version is for submission to the authorized authority, the second remains with the customer of the work.
- All that remains is to submit the application along with the technical plan to Rosreestr.
The easiest way to do this is by visiting any branch of the MFC. However, for the emergence of the right you still need to pay a state fee - it will be 350 rubles.
- In 12 days, an extract from the Unified State Register will be ready for your home - registration is completed.
Documents required for drawing up a technical plan:
- Declaration. Most garden houses are registered according to a declaration, which is an appendix to the technical plan. By law, it is filled out by the property owner. In practice, engineers themselves enter all the necessary data into the declaration, and the owner of the site checks and signs. The document indicates the characteristics of the house - year of construction, wall material, number of storeys, area, etc. It will not be needed if you have design documentation.
- Extract from the Unified State Register or land certificate.
There is a very important note for those planning construction in SNT. When constructing a garden house, it is necessary to comply with boundary distances and other urban planning requirements. After all, a building that violates the norms, even registered in Rosreestr, can still be declared a self-development. The administration has the right to demand the demolition of such a building in court.
Order an extract from the PZiZ, urban planning plan (MFC, State Services portal). Familiarize yourself with the setbacks, maximum dimensions, maximum building percentage and other important parameters that are allowed in the area where your site is located.
As for the demolition of a registered house by court decision, this is only possible in case of very serious violations - a threat to life and health, damage to the property of third parties. However, in order to protect yourself in the future from any claims from local governments or neighbors, we recommend using town planning regulations during construction.
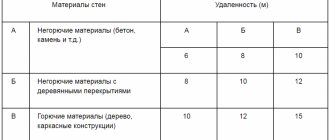
1. Residential buildings should be located on garden plots of land classified in accordance with the functional zoning of territories as a residential zone or an agricultural zone, not subject to landslide processes or annual flooding by flood waters.
2. The load-bearing and enclosing structures of a residential building must be in a working condition in which violations that arise during operation in terms of deformability (and in reinforced concrete structures - in terms of crack resistance) do not lead to disruption of the operability and load-bearing capacity of the structures, the reliability of the residential building and ensure safe stay of citizens and safety of engineering equipment. The foundation and supporting structures of a residential building must not have any destruction or damage leading to their deformation or the formation of cracks, reducing their load-bearing capacity and impairing the operational properties of the structures and the residential building as a whole. 3. A residential building must be arranged and equipped in such a way as to prevent the risk of injury to residents when entering and exiting a residential building, when moving in and around a residential building, as well as when using engineering equipment and to ensure the possibility of moving items of engineering equipment corresponding premises. At the same time, the slope and width of flights of stairs and ramps, the height of steps, the width of treads and landings, the height of passages along stairs, the basement, the attic in use, the dimensions of doorways should ensure the convenience and safety of movement and placement. 4. A residential building must be provided with engineering systems (electric lighting, drinking and hot water supply, drainage, heating and ventilation, and in gasified areas also gas supply). If there are no centralized engineering systems on the territory of gardening non-profit associations of citizens or it is impossible to connect to these systems in one- and two-story buildings, the absence of water supply and sewerage restrooms is allowed. 5. Engineering systems (ventilation, heating, water supply, drainage, etc.), equipment and mechanisms located in residential buildings must comply with sanitary and epidemiological safety requirements. It is not allowed to combine ventilation ducts of kitchens and sanitary facilities (auxiliary premises) with living rooms. The air exchange rate in all ventilated residential premises must comply with the standards established in the state standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 51617-2000 “Housing and communal services. General technical conditions". 6. Engineering systems (devices, equipment) must be placed and installed in accordance with the safety requirements established in the Federal Law “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures”, instructions from manufacturers, as well as hygienic standards, including in relation to permissible level of noise and vibration created by these engineering systems (devices, equipment). 7. The external enclosing structures of a residential building must have thermal insulation that ensures in the cold season the relative humidity in living rooms is not more than 60 percent, the temperature of heated rooms is not less than +18 degrees Celsius, as well as insulation from the penetration of external cold air, vapor barrier from the diffusion of water steam from the premises, ensuring the absence of moisture condensation on the internal surfaces of non-transparent enclosing structures and preventing the accumulation of excess moisture in the structures of a residential building. 8. A residential building must be protected from the penetration of rain, melt and ground water and possible domestic leaks from engineering systems using structural means and technical devices. 9. The permissible height of an operated residential building must correspond to the class of structural fire hazard and the degree of fire resistance of the building established in the Federal Law “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements” and ensure the fire safety of the residential building. In accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements", fire distances must be observed between a residential building and other buildings and structures located on this and adjacent garden plots, depending on the degree of their fire resistance and fire hazard class, and also ensure the possibility fire equipment entrance. 10. In a reconstructed residential building, when the location of sanitary facilities changes, measures must be taken to provide hydro, noise and vibration insulation, provide them with ventilation systems, and, if necessary, the floors on which the equipment of the sanitary facilities are installed must be strengthened. 11. The space-planning solution of a residential building and the minimum area of rooms and premises for auxiliary use intended to satisfy citizens’ household and other needs related to their residence in a residential building (except for the hallway and corridor) must ensure the possibility of placing the necessary set of furniture and functional equipment taking into account ergonomic requirements. 12. The required insolation must be provided in at least one living room for a residential building with a number of living rooms from one to three, and for a residential building with a large number of living rooms - in at least two living rooms. The duration of insolation in the autumn-winter period of the year in a residential building must meet the requirements of sanitary rules and regulations “Hygienic requirements for insolation and sun protection of premises of residential and public buildings and territories. SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1076-01.” The natural light factor in living rooms and kitchens should be at least 0.5 percent in the middle. 13. The height (from floor to ceiling) of the rooms and kitchen (kitchen-dining room) must be at least 2.5 m. The height of corridors, halls, hallways, mezzanines must be at least 2.1 m. 14. Floor markings of rooms located on the first floor of a residential building, must be higher than the planning level of the ground. Placing living rooms in the basement and ground floors is not permitted. Exit from the living room directly to the outside (to the street) should be through utility rooms and (or) an equipped warm vestibule or extension. 15. Placing a restroom, bathroom (shower) and kitchen above living rooms is not allowed. 16. Living rooms and kitchens in a residential building must have direct natural light. Other auxiliary premises intended to satisfy citizens’ household and other needs may not have natural lighting. The ratio of the area of light openings to the floor area of living rooms and kitchens should be taken taking into account the lighting characteristics of windows and shading by opposing buildings, but not more than 1:5.5 and not less than 1:8, and for upper floors with light openings in the plane of inclined enclosing structures - no less than 1:10. 17. In living rooms, permissible sound pressure levels in octave frequency bands, equivalent and maximum levels of sound and penetrating noise must correspond to the values established in the sanitary standards “SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.562-96. 2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. 2.1.8. Physical factors of the natural environment. Noise in workplaces, in residential and public buildings and in residential areas. Sanitary standards” and not exceed the maximum permissible sound level in the daytime - 55 dBA, at night - 45 dBA. At the same time, the permissible noise levels created in residential buildings by ventilation systems and other engineering and technological equipment must be 5 dBA lower than the specified levels during the day and night. 18. In a residential building, permissible levels of vibration from internal and external sources during the day and night must correspond to the values established in the sanitary standards “SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.566-96. 2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. 2.1.8. Physical factors of the natural environment. Industrial vibration, vibration in residential and public buildings. Sanitary standards." 19. In a residential building, the permissible level of infrasound must correspond to the values established in the sanitary standards “SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.583-96. 2.2.4. Physical factors of the production environment. 2.1.8. Physical factors of the natural environment. Infrasound in workplaces, residential and public buildings and residential areas. Sanitary standards." 20. In a residential building, the intensity of electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency range from stationary transmitting radio engineering objects (30 kHz - 300 GHz) should not exceed the permissible values established in the sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises." 21. In a residential building at a distance of 0.2 m from walls and windows and at a height of 0.5 - 1.8 m from the floor, the electric field strength of an industrial frequency of 50 Hz and the magnetic field induction of an industrial frequency of 50 Hz should not exceed 0.5, respectively kV/m and 10 µT. 22. Inside a residential building, the equivalent radiation dose rate should not exceed the dose rate permissible for an open area by more than 0.3 μSv/h, and the average annual equivalent equilibrium volumetric activity of radon in the air of operated premises should not exceed 200 Bq/cubic meter. m. 23. The concentration of harmful substances in the air of a residential building should not exceed the maximum permissible concentrations for the atmospheric air of populated areas established in the hygienic standards “GN 2.1.6.1338-03. Maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) of pollutants in the atmospheric air of populated areas. Hygienic standards." At the same time, the assessment of the compliance of a residential building with the specified requirements is carried out based on the maximum permissible concentrations of the most hygienically significant substances that pollute the indoor air, such as nitrogen oxide, ammonia, acetaldehyde, benzene, butyl acetate, distylamine, 1, 2-dichloroethane, xylene, mercury, lead and its inorganic compounds, hydrogen sulfide, styrene, toluene, carbon monoxide, phenol, formaldehyde, dimethyl phthalate, ethyl acetate and ethylbenzene.
Reconstruction
Reconstruction of a residential building in SNT can also be carried out without the approval of changes by the authorities.
Registration procedure for reconstruction of a residential building on a garden plot:
- Preparation of a technical plan.
To do this, you need to have a legal document for the plot and the house to be converted, provide design documentation (if any) and a technical passport (if any).
- Submitting an application to the registration authority to make changes regarding the location of the building and its area. The application itself is prepared by an MFC employee, and a technical plan in the form of an electronic document is attached to the case. When making changes, the state fee is not paid, since the right has already been registered.
- Receiving an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate with updated graphic and text parts completes the process of legalizing the reconstruction.
What is the best way to register a country house?
Having your own home on a garden plot is always a pleasure. All that remains is to figure out what status to assign to the building? We found out that a country house can be residential or non-residential.
- If registration is required
You can only register in a residential country house. If the building is suitable for permanent residence, no problems will arise. Non-residential garden buildings do not serve as a place for registration of citizens.
- If you need to save money
It is better to choose the option with non-residential premises. A dacha or garden house is a summer real estate option. In winter you will not have to pay for electricity, water and gas supply. But the owner of residential property pays receipts all year round.
Expert opinion
Dmitry Nosikov
Lawyer. Specialization: family and housing law.
The garden house tax has not changed in 2021. It is still calculated according to the rules of Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But there is a difference in terms of the cost of objects - a non-residential building is cheaper than a residential cottage. This means you can pay less tax on your dacha. Sometimes the Federal Tax Service (IFNS) does not charge property tax at all (only for the plot). For example, if the dacha is registered until 2021, but the ownership is not registered. In fact, the object is not listed in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, which means that the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate does not know about it either.
- If you plan to sell your house
Residential property is a plus to the cost of land. When planning to sell a garden plot, you can combine it with a house. The price will be higher, and there will be more buyers (see “How to sell a share in a house with land”)
- If you are on the housing register
Designate the dacha as a non-residential building. By indicating that the property is non-residential, you will save your place in the queue of those in need of improved housing conditions (Article 52 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). Conversely, by reporting the presence of a residential building, you risk being removed from the housing register as provided with housing.
A garden house in SNT is always a non-residential premises. Innovations in 2019 confirmed this fact. However, it is possible to convert a garden house into a living space. A simplified procedure is in effect as part of the second “dacha amnesty”. A residential building must comply with the requirements of SNIP - namely, be convenient for year-round living, capital and safe. Not all dachas fall under these criteria.
Determining whether a garden house or a residential one is not so easy. Often there are third-party factors in a case: category of land, technical nuances, entry in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, rights of neighbors, remoteness of a settlement, discrepancies in legislation. Not all dachas can be converted into residential buildings. There are nuances that you need to be aware of. When understanding the intricacies, do not forget about the help of lawyers. Our experts are ready to provide you with any legal assistance with your dacha building and land. Ask questions and get answers – for free!
More details about residential and non-residential buildings, the difference and the possibility of construction are described in the video:
Attention!
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
- via the form (below), or via online chat
- Call the hotline:
- Moscow and the Region
- St. Petersburg and region
- FREE for a lawyer!
By submitting data you agree to the Consent to PD Processing, PD Processing Policy and User Agreement.
Anonymously
Information about you will not be disclosed
Fast
Fill out the form and a lawyer will contact you within 5 minutes
Tell your friends
Rate ( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Author of the article
Maxim Privalov
Lawyer. 2 years of experience. I specialize in civil disputes in the field of housing and family law.
Author's rating
Articles written
610
What is a country house according to the new law?
All DNT are SNT, and country houses are garden houses, according to Federal Law No. 217-FZ of July 29, 2017. The concept of country houses and permitted use as summer houses has been abolished.
Country property is equivalent to garden property. On the former DNT, as well as on the SNT, it is possible to build capital construction projects and register them according to the technical plan; these will be full-fledged residential buildings with the right to register residence.
Another current form of the ONT partnership is plots for vegetable gardening. But on these lands it is not allowed to build houses, even for seasonal residence, only buildings for storing equipment.
Link to document:
Read: Dacha amnesty extended until 2026: how to register a house and land
Registration agreement without right of residence
The current legislation does not provide for a special form for this type of agreement. In accordance with Federal Law No. 36, adopted in 2013, the registration of citizens must correspond to their actual place of residence. According to this regulation, if a fictitious registration is discovered, it is canceled. In practice, there are cases when the owners of residential real estate register citizens in it and enter into an agreement limiting the right to live in this living space, but this is not correct from the point of view of legislation.
A mortgage with state support, what it is and what conditions you need to know about this type of lending, see the link.
How to find out the cadastral value of your property?
Do you know that before buying an apartment you must check it? Read our material on how to do this correctly.
Suspension of accounting
Reasons why the registration of a residential building may be suspended:
- The building extends beyond the cadastral boundary of the site. This is usually detected immediately after the engineer’s measurements. To resolve the issue, it matters on whose lands the building is partially located - neighboring or public lands, as well as the size of the protruding part of the house.
If the house falls on a neighboring land use, it is possible to redistribute this piece with the neighbor. When occupying gardening lands, if they are not registered within the boundaries, you can try to change the cadastral boundary of the plot on which the house is located.
- In place of the erected object, another object is listed in the Unified State Register of Real Estate (garden house, summer kitchen, etc.). Most likely, you have already demolished the old building, but you have not legally registered its demolition. In this case, it is necessary to prepare an inspection report for the destroyed building, submit it to the MFC in order to remove information about the liquidated object from registration, and then resume registration of the residential building.
- The presence of an encumbrance on the site - for example, a ban on capital construction due to the location of the site on the site of the railway right-of-way. Or any other restriction related to special use zones. The urban planning plan of the site or an extract from the Unified State Register of Land Registers contains information of this kind.
- A minor error in the documents submitted for registration, which is corrected by resubmitting the electronic form of the technical plan.
Is it necessary to register a house on a garden plot?
Why do you need to register a house in SNT:
- to dispose of real estate at your own discretion - sale, pledge or gift, registration of inheritance, etc.;
- for the absence of an illegally erected structure and, as a consequence, a trial and associated costs;
- for connecting communications - gas supply, water supply, electricity, etc. Without a legal document for a house, it is impossible to conclude agreements with the relevant organizations;
- to obtain registration;
- to assign an address.
While registration of auxiliary and outbuildings can be delayed, registration of a residential building is a mandatory procedure that cannot be avoided if you plan to permanently live in such a house.
Read: Registration of a bathhouse on a land plot in 2021