From 2006 to March 1, 2021, a “dacha amnesty” was in force in Russia. It made it possible to legalize buildings on a summer cottage without permission to build a house in SNT, on the basis of a technical passport and property rights. The simplified registration procedure was in effect for almost 12 years and was extended twice.
But more than 35% of houses remain not included in the Unified State Register. In 2021, the rules for the construction and commissioning of a residential building on the territory of Garden Non-Profit Partnerships are changing.
How to obtain a building permit - step-by-step instructions
If before August 2021 it was necessary to obtain a construction permit, now the procedure has changed. According to Art. 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (https://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_51040/570afc6feff03328459242886307d6aebe1ccb6b/) before starting construction, the land owner is obliged to notify the authorities about this. The form of the document is slightly different, but in general it gives the same powers. Thus, this notification is permission to build a house in SNT. So what is the sequence of actions?
Checking the site category
Simply contacting the administration is not enough; before that, you need to check what category is assigned to the site, and also find out which municipality the land belongs to. If the site is located in a conservation area or in an area not intended for construction, permission will be denied.
Preparation of documents
Preparation of documents is an important stage; you should start with receiving an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
Then you need to fill out a notice of planned construction in the form approved by Order of the Ministry of Construction of the Russian Federation dated September 19, 2018 No. 591:
- passport details and full name of the person conducting the development;
- cadastral number, address and description of the location of the site;
- presence of other owners;
- information about the purpose of the site;
- layout of objects on the site, distance from borders and other objects;
- notification that in the future the premises will not be divided into several independent objects;
- contact details of the applicant and method of response.
Contacting the organization
The owner is obliged to contact the organization authorized to issue a building permit in a horticultural non-profit partnership (SNT). This could be the local administration, the department of land and property relations, or the town planning committee. Rosreestr, BTI, and the Cadastral Chamber do not deal with such issues.
You can submit documents in any way: by mail, in person, through the MFC, or the State Services portal. If a representative acts instead of the owner of the plot, his powers must be confirmed by a notarized power of attorney.
Read more about how to obtain permission to build a private house through State Services in our article.
Obtaining a building permit
A reasoned decision is made within 7 working days from the date of receipt of the application. If the structure does not exceed the maximum parameters provided for by law, permission will not be denied. If the project has critical deviations, it will be necessary to make adjustments and send the documents for re-approval.
IMPORTANT! The permit is issued free of charge and is valid for 10 years from the date of receipt.
For more information on how to obtain permission to build a house, read our article.
Documentation for registration
Before you begin planning the construction of a building on the site, you need to make sure that all the necessary documents are available. Otherwise, the owner of the land plot may have problems with the law. That is, it is necessary to have documents confirming ownership.
What documents confirm ownership:
- Agreement for the purchase/sale of land;
- A completed and notarized will;
- Deed of gift;
- Documentation on privatization of the dacha;
- Lease or permanent use agreement.
Also, in order to register a house and register in it, you must obtain permission from construction companies. To do this, you need to provide a project drawn up in accordance with all SNiP rules.
Registration of a house in SNT in 2021
If the owner of the plot built a house, this does not mean that he automatically became its owner. To prevent an object from being forced to demolish, it must be registered.
Now there is a simplified procedure, the so-called “dacha” amnesty, which can be used by:
- owner of the site;
- a person who has title documents to land;
- owners of plots in gardening partnerships.
Before registration, you need to collect a package of documents, the most important of which is the technical plan. As a rule, the plan is drawn up by BTI specialists who are qualified cadastral engineers. In the case when the owner does not have a boundary plan, i.e. the land plot is not registered, registration of the house will be refused. You will also need:
- permission to build a house;
- commissioning certificate;
- documents for land. This may be a gift agreement, purchase and sale agreement, or a corresponding court decision;
- receipt of payment of state duty;
- a completed declaration about the object (the form can be found on the Rosreestr website).
The package of documents is submitted to the MFC. After considering the application, the owner will be able to receive an extract that will confirm the registration of the residential premises. You can also register dachas collectively, through the chairman, who has the right to submit such applications on behalf of all SNT participants.
Can land be seized from the owner?
Yes . The Land Code contains a provision on the termination of the right to a land plot. If a land plot granted with the right of permanent (indefinite) use or lifelong inheritable possession is not used for 3 years, then it may be seized .
A plot can also be confiscated if the land is not used for its intended purpose. For example, a site is allocated for agriculture, and a store is built there, or an activity organized on the site is harmful to the environment (for example, a car wash operates).
Construction standards in SNT - requirements for facilities
SNiP 30-02-97, SP 53.13330.2011 regulate construction rules on gardening sites. According to the requirements of the documents, the owner of the site must comply with the following standards:
- the area of the plot should not be less than 0.06 hectares or 6 acres;
- a fence needs to be installed around the perimeter;
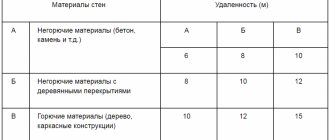
- Fire safety requires maintaining distances between objects in adjacent areas. This parameter is determined by the material from which the object is built: non-flammable - 6 m, with wooden floors - 8 m, made of wood - 10 m. In this case, the distance between residential and non-residential buildings on one site does not matter;
- sanitary and household requirements include several points:
- – the distance from the house to the border of the neighboring plot should not be less than 3 m;
- – distance from the house to the street – 5 m, to the driveway – 3 m;
- – if the building is used to keep livestock or poultry, then the distance increases to 12 meters from houses and 1 from other buildings, up to 4 m from trees and 2 m from bushes;
- – the distance between the well and the latrine should not be less than 6 m;
- – the house and the restroom (shower, bath) must be located at least 8 m from each other.
Separate standards relate to the height of the room; the construction of a house in SNT in 2021 must be carried out taking into account all safety requirements. Thus, the distance from floor to ceiling cannot be less than 2.2 m, outbuildings, basements - 2 m, and cellars - 1.6 m, the number of floors - no more than three.
Otherwise, there are no restrictions, the layout, the presence of stairs depends entirely on the wishes of the owner of the site.
But organizing water flow to neighboring areas is strictly prohibited.
A separate requirement concerns water and electricity - access to these communications must be required. The lack of sewerage, gas pipelines, and heating is not considered grounds for refusal to issue a building permit.
Advantages and disadvantages
When deciding to start building your garden plot, it is important to understand all its pros and cons, and not act under the influence of a trend for your own country houses.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons, especially if you have no previous experience of living in a private home and caring for it.
What benefits does the owner receive when building a house on garden land:
- The plot is already owned or is much cheaper than for individual housing construction.
- Low payments for the use of utility infrastructure.
- No noisy neighbors or freeways outside your windows.
- Your own home is built in accordance with personal concepts of beauty, including exterior and interior decoration. Compliance with building codes is mandatory.
- The progress and speed of construction depends on your desire and financial capabilities.
- Favorable environmental conditions: clean air, water, land, natural sounds of wildlife around.
What are the main disadvantages of living on a garden plot:
- Building a house that meets all requirements and standards is expensive.
- SNT members pay considerable annual fees, which go towards maintaining infrastructure facilities.
- Low transport accessibility. Public transport outside the city runs on schedule, with large intervals. This leads to the need for each family member to have their own car.
- The infrastructure is poorly developed. Troubleshooting (broken wires, broken water tower) takes a lot of time.
- The peculiarities of the winter climate with heavy snow drifts impose restrictions on physical activity.
- Maintaining your home during the cold winter months requires significant effort.
- Registration in a garden house is possible only through the court.
- The arrangement of social and transport infrastructure, even for garden villages located within the boundaries of a populated area, is carried out at the expense of the owner-gardeners. The new law No. 217-FZ provides for co-financing programs for such expenses, but it is not yet known whether there will be funds for them in the regional budgets.
In some cases, the owner may initiate changes to the VRI of his plot. More details about the procedure can be found in a special article.
Read more about the main differences between garden land and individual housing construction in a separate article.
New law on SNT in 2021
Since June 2021, Federal Law No. 162 “On amendments to the Federal Law “On gardening and horticulture by citizens for their own needs and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” has come into force. Now permission to build a country house can only be obtained on lands that are part of territorial zones (TZZ), for which town planning regulations have been approved and limits on permitted development have been developed.
For more information on whether it is possible to build a house on a summer cottage, read our article.
An important change concerns the procedure for legalizing buildings for commercial and residential purposes. If they are built on a plot of less than 6 acres, it has become easier to legalize such real estate and obtain registration. The procedure for transferring a non-permanent structure to a capital one and back has also been simplified; now, this does not require organizing a commission visit; it is enough to obtain a positive opinion from a specialist.
Intelligence
SNT can be divided into gardening and horticultural plots. On the first types of plots, the construction of large houses is completely prohibited. It is possible to build a residential building on horticultural lands, but with some restrictions:
- The land must be within a populated area.
- There are town planning regulations according to which it is allowed to build garden/residential buildings.
If the site is located outside the town, then any construction is prohibited. On a site in SNT, you can build residential and garden houses, and the latter can only be lived in in the summer, while residential ones are suitable for year-round use, and they require permanent registration. The legislation establishes the types of land where construction is prohibited - this is water, forest, industrial or defense land, as well as specially protected areas.
Responsibility for unauthorized constructions
Liability for buildings in a gardening non-profit partnership without obtaining permission is provided for in Art. 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The violator will not be able to obtain documents confirming ownership, and he will be banned from using and living. It is also impossible to sell, donate or bequeath such a building.
According to Art. 25 Federal Law No. 169 “On architectural activities in the Russian Federation”, as well as Art. 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a citizen may be required to demolish an unauthorized structure, as well as return the site to its original appearance.
Only a court can recognize a building as illegally erected by issuing an appropriate decision, which must enter into legal force.
District commissions and local administrations do not have the right to demolish a house on their own or force the owner to do so. But their powers include issuing orders that may become the basis for the imposition of administrative fines. In addition, they have the right to apply to the court to declare the building illegal, including in relation to buildings for which the ownership rights were registered with violations.
Article 24 of Federal Law No. 169 provides for the imposition of administrative sanctions. In particular, they may be required not only to eliminate the violations committed, but also to hold them accountable in accordance with Art. 9.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, namely:
- for violation of technical regulations and requirements for the construction of buildings, impose a fine on an individual in the amount of 1,000 to 2,000 rubles;
- for deviations from the design values of building parameters, which may pose a risk of being fined 2,000 - 4,000 rubles;
- Repeated violation will result in a fine of up to 5,000 rubles.