It is necessary to deal with questions about whether the inheritance in jointly acquired property in a marriage is a divisible part in cases where family life has collapsed and it has come to divorce proceedings. The problem becomes finding out the due shares of the total amount of property assets (gifts, inheritance not acquired jointly). All household members use what they have acquired while they live together. Therefore, those who are faced with a similar problem need to study the judicial practice regarding the rules of inheritance of a spouse’s jointly acquired property if they have to get a divorce.
In what cases is an inheritance considered jointly acquired?
There are two legal acts regulating the rights to property. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation contains references to the fact that inheritances are not a jointly acquired share of property. In terms of use during the existence of families, this is clear. Commonly acquired property is considered to be items purchased with common money. Whether inheritances should be considered as such is stipulated in another law - the Family Code. There are also references to what is considered an undivided share of property in a divorce.
The dispute becomes the assertion that it is impossible to unambiguously answer whether the inheritance of one of the spouses is property jointly acquired by both. There is no clear distribution delineating the shares of property for each family member. The basis is the monetary equivalent of the acquired property, especially if it is not possible to divide it in kind. And family law makes things clear in the relevant articles (No. 34 is about what inherited property is subject to division).
This article indicates certain shares of property that fall under the category of common (acquired by joint efforts):
- Salaries, other official and unofficial income.
- Pensions, subsidies, social payments and subsidies.
- Purchased (acquired) things, apartments, houses, dachas, garages.
- Cars, motorcycles, any vehicle.
- Shares of enterprises, share payments, capital investments.
- Savings acquired in cash and lying in bank accounts.
- Obligation to repay loans, mandatory payments.
- Debt obligations to mortgage lenders.
- Business, if the spouse is a co-owner (owner) of the company.
Inherited property is subject to division if special conditions are met. What matters is the entry period, maintenance and repair costs, etc. A judge considers many facts and factors when making a decision and making a ruling. But all this makes sense only if people are officially married. Civil families do not have common values.
According to civil law, there are no agreements binding people who no longer want to live together. When dividing, it is taken into account how much each person paid for the disputed property. The calculations include the amount of wages, etc. And if the wife is not employed, but is a housewife or raising children, it is generally accepted that they have the same share and the claims are equal.
How to challenge a spousal share?
When the surviving spouse applies to a notary, by default ½ share in the joint property is allocated. But other heirs may not agree with such a division.
In order to increase the deceased’s share in the joint property of the spouses or to recognize the divided property as personal, it is necessary to go to court. The applicant in the process can only be an interested person (heir, creditor). The defendant is the surviving spouse.
In order for the court to satisfy the plaintiff's demands, it is necessary that he present irrefutable evidence that this property is the personal property of the deceased.
For example, it was purchased with donated money or personal funds of the deceased.
Regime of common property and its division
Initially, it is assumed that all family members have equal rights in terms of the use of property values (inheritance not acquired jointly) and the budget. If the marriage is unequal, the prenuptial agreement is always drawn up specifically for the purpose of determining the rules of division in case of divorce. According to general rules, the personal possession of the second spouse is individual items. It belongs:
- to clothes with shoes;
- to medications;
- to hygiene products;
- for educational supplies, etc.
This exception does not apply to jewelry and luxury items. Such objects are subject to division in accordance with the norms of current legislation. And during the period when the family lived together, it was impossible to dispose of the acquired property independently. Thus, during family life, an apartment cannot be sold, mortgaged, or given as a gift, unless the husband/wife has given written consent certified by a notary.
Using the conditions for classifying property as joint, it can be determined that the procedure involves the allocation of equal shares. However, there are a number of exceptions that establish a different procedure. There are two types of relationships between husband and wife. One is legal, on a general basis. The other is contractual, implying a preliminary agreement between them on the procedure for distributing values after the dissolution of marriage.
According to the law, the agreement cancels the legal method of division and the terms of the contract come into force. It is mandatory for the notary to certify that the document was signed without coercion, and that the parties were capable and sane. Otherwise, the document loses legal force and the trial is conducted legally. The decision is made based on the norms and requirements specified in the legislative acts of the Russian Federation.
Change in material value
An improvement established in relation to an object is any increase in material value . This change must be caused by the actions of the second spouse, who is not the actual heir. Investing funds, carrying out repairs / reconstruction - indicate that the object has improved through human actions.
A standard example: a husband inherited a house in a village with a dilapidated roof and no communications. Through the efforts of the wife, internal and external repairs were made and communications were installed.
Accordingly, the market value will increase , which means that we can talk about an inseparable improvement. In case of divorce, the designated object will be divided either into equal parts , or the second spouse will receive a part commensurate with the costs incurred for improvement and maintenance.
What inheritance is joint property?
There are two mandatory requirements for jointly acquired property (not inheritance) to be divided. It is considered jointly acquired when, during a divorce, what appeared after the formalization of the marriage bond is divided between the spouses. The second condition is that the money for the purchase must be shared. Only if there are compelling reasons, the judge can make a different decision, but each argument of the plaintiff and defendant is supported by documents.
The property of the spouses (jointly acquired) is not considered to be that which was purchased or received into possession before the wedding. They also do not divide objects of disputes for the registration of which no money from the family budget was spent. Inheritance has a peculiarity - the right to decide to whom to transfer property belongs exclusively to the testator. And such property, by definition, is not considered jointly acquired (that is, purchased from common savings). But this is the case when upon entry you only had to pay state fees, taxes, mandatory fees (and nothing more).
In this case, on the basis of the absence of costs, the right to claim a share is completely excluded. However, if the family budget was used to pay for other significant expenses related to the object of the dispute, the situation changes. But the legislation has a mechanism to overcome this situation. So, if a spouse invested his own money in renovating an apartment, thereby increasing its value upward, he has the right to demand a portion. Monetary compensation resolves the conflict so that both parties are satisfied.
The money itself also belongs to jointly acquired property, if it is not an inheritance. In a safe deposit box or bank account, the amount is subject to division. If funds for the family budget are received by inheritance, the procedure is carried out according to the same principles as in other cases. The exception is that the inheritance does not require additional costs if it is a monetary amount in any equivalent. But in the case of real estate received by inheritance, a different rule applies. But the court can recognize the inheritance as jointly acquired.
It is taken into account when the inheritance came to the family. If this happened after the wedding, the apartment or house required serious repairs, the money was taken from the property acquired jointly during the marriage, then both spouses have the right to claim the acquired property after its dissolution. Also, when dividing, the size of wages and other income of each is taken into account in order to determine what part of the costs fell directly on the shoulders of the husband and wife. The judge will weigh the available facts and render a verdict.
In most cases, the inheritance remains indivisible and is assigned to the person who received it by will or by law. On the other hand, acquired (acquired) property may require large expenses, which the successor of the inheritance does not have. Then the second spouse spends his own money. This is also part of the jointly acquired property, but it makes sense to evaluate who earned it. And since money is jointly acquired property, the inheritance can be divided. At least the legislation allows this to be done.
What to do if your spouse refuses to recognize the inheritance as common
Often, heirs do not want to share even with legal spouses. There is only one way out - to act through the courts. Draw up a statement of claim, collect evidence. Strong arguments in favor of the plaintiff can be: a marriage contract, the indication of his name in the will as the second successor, and the fact that large-scale improvements have been made to the acquired property.
Procedure:
- Gather the necessary evidence to support the plaintiff’s claims. Written statements from neighbors, invoices, contract agreements, bank statements and other documents. If necessary, hire a specialist to conduct an independent assessment of the property.
- Submit a statement indicating all the circumstances of the case. Attach the following documents to the claim:
- plaintiff's passport;
- marriage/divorce registration certificate;
- title documents for the disputed object;
- evidence collected by the plaintiff;
- appraiser's report on the value of the property;
- receipt of paid state duty.
- Send all documents to the court. District courts deal with such cases. If the claim is accepted, a hearing date will be set. Inexperienced citizens are better off hiring a lawyer, he will help in drawing up the application and will be able to represent the client’s interests in the future.
- The result of legal proceedings is a court decision. Then the parties must act according to the instructions in the document. Or challenge the decision by filing an appeal within the specified period.
The court does not dispute the fact of receipt of the inheritance and the ownership of it. The main task of the process is to determine whether the other party can lay claim to the property. Whether large-scale improvements have been made to the property or there are other circumstances that make it possible to consider the property as part of joint ownership.
Is it possible to change the current state of affairs?
The right to dispose of property acquired jointly over the years of life is inalienable. And it does not matter whether the property was improved using jointly acquired funds. In the event of a conflict between the parties, it is necessary to prove that the money is from this source. The question will also be asked how many there are and what exactly they were spent on. Documentary evidence - receipts, checks, invoices, acts. But you can do without them.
Marriage agreement and acquired property
A marriage contract is an agreement in which you can specify the conditions for the division of jointly acquired property, including inheritance. If the latter is received before marriage and after marriage, it becomes marital property. But now the shares are determined by the parties themselves. In other proportions, no one has the right to claim it (inheritance).
Agreement on division of acquired property
Jointly acquired property and even inheritance can be divided without scandals and legal disputes. It is enough to sit down at the negotiating table and discuss how much is owed to whom: what part of the maintenance will be one payment, what part will be regular (if, for example, we are talking not only about a wife, but also about a child). The document is drawn up in free form. The main thing is to carefully describe the jointly acquired property and the shares of the applicants. Notarization is not necessary, even if we are talking about inheritance.
Improvement or prenuptial agreement?
It was previously said that inherited property, in addition to the above options, can also be divided through a marriage agreement . Not a single legislative norm prohibits the heir-spouse from independently disposing of the inheritance received (Article 41 of the RF IC).
However, some requirements must be met.
Main requirements: it must be concluded only in the proper notarial form , and only property rights must be reflected in it. In addition, the terms of the described agreement should not significantly infringe on the preferences of either party. Concluding a contract under pressure or through blackmail is not allowed .
If the improvement still has to be proven in court, then if there is a contract, the division is made in an imperative (mandatory) manner. It will be extremely difficult to challenge a previously concluded agreement if all requirements are met during the drafting process.
Recognition of the individual acquired property of one of the spouses as community property in court
By law, the owner's certificate is the only document identifying the owner. Property may be recognized as jointly acquired property by the court if special conditions are met. For example, these are joint expenses for the maintenance and improvement of inherited property.
A statement of claim is filed and the state fee is paid. A hearing date is set. Property (inheritance) that must be recognized as jointly acquired is assessed. If it is not possible to divide the inheritance in kind, monetary compensation is assigned, which is paid by one of the spouses.
Refusal of spousal share
The owner has the right to refuse property that belonged to him by right of common joint ownership (Article 236 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). To renounce the marital share, you must submit a waiver application to a notary. In this case, the share will pass into the estate and will be divided along with the other property of the deceased.
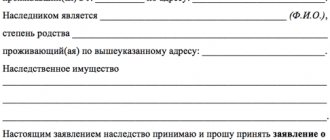
Sample application
First heirs upon death of wife
Now let's look at who the first heir is after the death of his wife. Her immediate family will also claim her property:
- official spouse;
- children (natural and adopted);
- mother and father.
Heirs of the first priority
The grandchildren of the testator can also be considered heirs of the first priority, but only by right of representation. This means that grandchildren will receive the right to inheritance if their parent (child of the testator) died before entering into the inheritance.
In Art. 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that these persons are in the first line of inheritance and have priority over other relatives of the deceased.
Biological children of the deceased who were adopted by other people have limited rights to inheritance due to the loss of legal ties with their natural mother. An exception is if the child continued to communicate with her while living in a foster family. In such cases, the courts rule that children have the right to receive shares in the inheritance of their natural parents and adoptive parents.
Along with the primary heirs, dependents whom she supported during her lifetime for 1 year or longer can receive a share in the inheritance of the deceased.
In order for a dependent to have the right to inheritance, it is necessary to establish the fact of being a dependent and prove it. How to do this, see the next video