The loss of a loved one is always a family grief, regardless of who goes to another world. The loss can be especially felt when people have lived side by side for many years.
But life does not stand still; we have to resolve all issues related to the re-registration of property rights.
How to properly register an inheritance after the death of a husband? What documents are needed and who to contact? We'll tell you in our article.
Husband's right to inheritance
Inheritance is the transfer of ownership from a deceased person to other persons. A person, both an elderly person and a minor child, has the right to inherit property.
There are two types of inheritance :
- by will;
- in law.
For your information
Inheritance under a will is formalized by the testator before his death. The initiator is a legally capable person who has reached the age of eighteen. The composition and content must be kept secret (Article 1123 of the Civil Code).
This document must be in writing, drawn up in two copies and executed in the presence of a notary. In it, the testator describes the property that he has, as well as the persons who will receive it in the event of his death.
This will is kept by the deceased, as well as in the notary’s office, where this document was executed. To find out whether there is a will, you should examine the personal belongings of the deceased. After this, within six months you should contact the notary who certified the document.
As for inheritance by law, it is valid in the event that there is no will. The law establishes certain lines of relatives who have the right to inherited property.
The wife is the person who is directly in the first line of heirs along with the children and parents of the deceased husband. If the testator does not have children or parents, all property will go to his wife (Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Example
The testator has relatives, namely: his wife, daughter, and parents. There is also real estate: an apartment, a summer cottage and a car. In accordance with Art. 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, they all have the right to claim this property in equal shares.
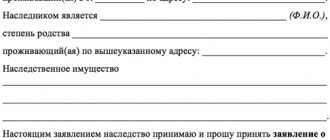
All of the above relatives who express a desire to inherit the property of the deceased submit an application and the necessary documents for acceptance of the inheritance to the notary's office. The application must be submitted within six months from the date of opening of the inheritance. The day of death of the testator is the day of opening of the inheritance.
Everyone has the right to refuse to accept an inheritance (Article 1157 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), for this it is necessary to submit a refusal in writing. If the heir does not submit any documents, refusals or statements within six months after the death of the testator, these inactions are regarded as a refusal of the inherited property.
Usually the testator's property is divided equally, but there are cases when the shares are not always equal .
Example
Ivanova, who survived her husband, has the right to 1/2 share in jointly acquired property, as well as a share of inheritance in the second half on an equal basis with other relatives. Consequently, the spouse's share increases.
After six months after death, the notary issues certificates of inheritance to relatives. If real estate is inherited, the transfer of ownership must be registered with the relevant government bodies (territorial division of Rosreestr).
Spouses' share in the distribution process
Despite all the ambiguity of family relationships and the variety of situations that arise, the inheritance of common and personal belongings of spouses is carried out in accordance with the following principles:
- The property of the spouses acquired by them during their marriage has the status of jointly acquired property and belongs to them in equal parts. After the death of the head of the family, only his property share is included in the inheritance mass, and the second half legally belongs to the wife.
- The husband’s personal belongings, acquired by him before the marriage relationship was formalized or received by way of inheritance during marriage, are fully included in the inherited estate.
- The husband’s personal property, in which the spouses’ common funds or the wife’s personal funds were invested, may receive the status of joint property.
- The equal ratio of shares in the common property of the spouses can be changed based on the actual contribution of each partner to the family property, or on the participation of each in the expenditure of common savings.
So, after the death of the husband, the hereditary mass includes:
- objects acquired by him before marriage or personally inherited during family relationships;
- 50% of the total property of a married couple.
The other half belongs to his wife and is not included in the estate.
How is property divided after the death of a husband?
The inherited property of the deceased husband includes movable and immovable things that belong to him at the time of opening of the inheritance, as well as other property, including rights and obligations. This could be a house, a car, cash, securities, as well as an obligation to pay a certain amount of debt that the spouse did not pay while alive.
Property belonging to a deceased spouse has the right to be inherited by his legal wife . She is included in the first place as heirs, along with her husband’s parents, as well as his children, regardless of whether they are married together or not. (Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The property of the deceased is divided in equal shares among all heirs according to the law of one priority. The wife, as well as other testators, have the right to refuse the inheritance; to do this, it is necessary to formalize the refusal with the notary in charge of the case. And in this case, the remaining heirs in line will inherit the property, also in equal shares.
Example
Ivanov’s wife renounced her inherited share of a three-room apartment. She has two children from her marriage to her late husband. The testator has no parents. Accordingly, the real estate will be inherited by two children, ½ share each.
The legal spouse receives the inheritance when the husband dies, in any case, but not always in full. If there is a will, the following categories of citizens from the first priority established by Art. 1142 Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- Wives, regardless of age, health status and length of marriage.)
- Minor children under 16 years of age, and in case of education – up to 18.)
- Disabled people of groups 1, 2 and 3, regardless of disability.)
- Citizens who have reached retirement age, as well as all disabled family members.)
- Dependents who have been in this condition with the testator for 1 year or more.)
According to the law, after the husband dies, the legal spouse enters into inheritance and has every right to claim half of the property. The other half is safely divided evenly among the remaining heirs.
The testator has the right, through a will, to change the order of things, then the persons not mentioned in the will, who are subject to compulsory inheritance, will receive only 50% of the share that could have been theirs . After the spouse has died, the will can be challenged, and if there is evidence that it was drawn up under duress, or when the person could no longer be aware of it, it is declared invalid (Article 179 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The practice of inheritance from its very beginning has had constant refusals of inheritance. The reason is that the inheritance is burdened with obligations. Thus, the most common example at all times is the inheritance of real estate in addition to a debt, which in its volume exceeds the price of the inherited property itself by several times.
Example
The deceased person owns an apartment worth 3,000,000 rubles; in addition, a loan agreement was drawn up with him, and the amount of debt on it represents a large amount of money. In this case, the wife who inherited the real estate of the deceased spouse will be obliged to pay the debt that her husband did not pay at the time.
What points are considered controversial?
There are situations when the testator indicates in the will a stranger who is not related to him, and wants to give this person part of his property when he dies. In this situation, the issue of distribution of inheritance often has to be resolved in court. Although this decision is considered the will of the deceased, it cannot concern the share of property that belongs to the spouse by law, that is, half of it. There is a regime of community of property benefits, according to which the testator cannot dispose of half of the property jointly acquired during the marriage.
Example! Married couples can purchase housing while living together; if in the event of a divorce, the apartment or house was not divided and remained the property of the spouse, his ex-wife can receive half the value of the property after the death of the spouse.
If the spouses have drawn up a marriage contract, it will indicate a predetermined procedure according to which one of them can enter into inheritance rights after the death of the other. The ex-wife, from whom the deceased was divorced at the time of his death, is also able to claim 50% of the property acquired during the marriage. It is worth considering that if the deceased has a child, for example, a daughter or son, he will also be considered one of the primary heirs, who is entitled to his own share in accordance with current legislation.
Inheritance of a common-law husband
Our Russian legislation does not recognize civil marriage. Persons who live together and do not register their family relations with the registry office are called cohabitants .
At the everyday level, “civil marriage” refers to the cohabitation of a woman and a man, not formalized by a marriage certificate. They can run a joint household, have children, and live together in the same home, but their relationship is not documented anywhere, and accordingly they do not have any family legal relations.
It should be understood that such a “civil marriage” can lead to the fact that the joint funds accumulated by cohabitants, as well as the property they buy, can be inherited by complete strangers.
It is worth noting that it is more advisable for cohabitants to draw up a will in order to avoid the loss of this property and sell it to a specific person. But there is an exception in which the share of property after the death of the deceased husband will still belong to other persons - it will go to a disabled person who was dependent on the deceased and who lived together with him on the day of his death.
Disabled persons include minors, people of retirement age, disabled people, as well as persons recognized as incompetent. All of the above persons have the full right to receive a share in the property of the deceased, regardless of the type of inheritance (by law or by will).
If a spouse in a civil marriage dies, then the property belonging to him can go to his cohabitant only if he indicated her in the will . Otherwise, the common-law wife has no right to claim inherited property, except if she was disabled and dependent on him.
Example
Ivanova, Sidorov’s common-law wife, was his dependent for 3 years and lived with him. Sidorov died without leaving a will. In addition to his partner, he has two sons. In this case, his sons, as well as his common-law wife, who was a dependent, have the right to claim the inheritance.
The cohabitant still has a small chance of receiving an inheritance from her deceased husband. But for this it will be necessary to provide the court with undeniable evidence that they ran a common household and acquired property together.
How to register an inheritance after the death of a husband
The day of opening of the inheritance is considered the day of death. The place of opening of the inheritance is the place of residence of the testator, or the property of the highest value.
If the deceased person managed to draw up a will with a notary, then after his death, in order to find out about the presence of the document, you should look at his personal belongings , where this document may be located. The second copy is with the notary who executed the will.
If a document is found, you should also contact a notary to obtain a certificate of inheritance; his information will be written down in the found document. After receiving the appropriate certificate, the person has the right to dispose of the property. But it is worth remembering that real estate should be re-registered in your name , i.e. carry out the transfer of ownership. These actions are registered by the territorial bodies of Rosreestr at the location of such property.
Attention
If the will was not found, then within six months you should submit an application to the notary to accept the inheritance. After six months, the notary will issue a certificate of inheritance rights to certain property.
To register an inheritance, it is necessary to collect a certain list of relevant documents , namely:
- Passport of the spouse claiming the inheritance.
- Death certificate of the deceased husband.
- Documents that confirm the right to inheritance (this may be a will drawn up in the manner prescribed by law).
- Marriage certificate (to confirm the degree of relationship).
- Documents that confirm the last place of residence of the deceased spouse (for example, a certificate from the passport office).
This list of documents is not complete; depending on the specific situation, their list may change. In any case, when contacting a notary on issues of inheritance of property, he will definitely establish a list of documents necessary for this.
Amounts of state duties
Any heir is interested in the question of how much the procedure for registering escheat property that the deceased managed to acquire during his lifetime might cost. In addition to the general tax, the widow and other heirs will need to pay a state duty, the amount of which is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. One list of expenses should also include notary services and registration of the transfer of inheritance into shared ownership, the fee for which depends on the type of movable or immovable property. It must be remembered that 0.3% will be withheld from the total assessed value of the property received; this rate and price is intended for heirs of all categories.
Do the husband's children from his first marriage have the right to inheritance?
The husband's illegitimate children have the same right to inherit their father's property, along with his legal wife , his parents, and adopted children. All of them have the right to equal shares of the inheritance.
If the spouse has drawn up a will in which the object of inheritance after death will be transferred, for example, to his legal wife, then it is she who will formalize the inheritance for the property of the deceased husband. But there is an exception, if the spouse has minors or disabled children, regardless of the contents of the will, they will have the full right to inherit property . In this situation, the share of the property of the deceased will be transferred to the wife on the basis of the will drawn up by him, and to the children - as an obligatory share of the inheritance (Article 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Information
It is worth recalling that the legal wife is the first person in the list of heirs, along with the children and parents of the deceased. They all share the property in equal shares.