When the initiative for dismissal does not come from the employee, any reason will be unpleasant to him. However, among all other situations where an employee leaves the service at the suggestion of his superiors, dismissal due to redundancy is one of the most “benign”, since it does not involve the employee’s fault. But this type of reduction is the most costly for the employer.
In this article we will try to cover all the points that an employer needs to know in order to properly carry out a reduction. The fact is that employees are legally protected much more strongly, and the employer has many obligations that must be observed in order to avoid conflicts or even litigation. To do this, you must strictly follow the protocol prescribed in the Commercial Code of the Russian Federation.
When staffing is downsized
In business, various unforeseen situations often occur. If they are associated with additional difficulties, including financial ones, it is necessary to cut costs, reduce costs, and reduce the number of personnel. To do this, employers choose one of two ways or combine them:
- trying to make do with fewer employees – reducing the number of staff;
- removing certain positions or staffing units for them - staff reduction.
REFERENCE! If positions that are currently vacant are removed from the staffing table, this does not constitute a reduction.
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates in detail all the provisions for the dismissal of an employee from a position as a result of reduction.
Grounds for dismissal at the initiative of the employer
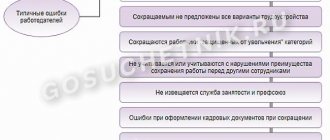
The management of the enterprise may hide the true reason for the layoff and termination of the employment agreement. This is done in order to save on payments. Therefore, any proposal or pressure from the director or boss is recommended to the employee to check for truth. This is not always easy to do.
The following reasons are used as grounds for dismissal at the initiative of the employer :
- The number of personnel is being reduced, the previously provided staff is being reduced;
- The employee does not meet the requirements for his position, and this is confirmed by certification;
- The persons controlling the enterprise have changed (director, chief accountant);
- Disciplinary sanctions repeatedly applied to an employee;
- A one-time, but gross violation of discipline on the part of the dismissed person.
Liquidation of an enterprise provides legal grounds for the dismissal of all personnel, including persons on sick leave or on parental leave, etc.
This is not an exhaustive list of reasons why an employer may voluntarily fire an employee. Separate reasons are provided for management personnel. For example, the management of an enterprise may resign due to making an unreasonable decision, which caused damage to the organization's property. In addition, if an employee who services banknotes committed a violation, due to which he lost confidence in himself on the part of management, this is grounds for his dismissal.
Legal rights of an employee: what you need to know?
In the case of a layoff at work, the employee has some temporary cushion that allows him to find a new job. Below is what you need to know and demand from management:
- Notice of dismissal due to reduction must be given 2 months in advance.
- At the time of dismissal, a full payment is made and a work book is issued.
- If an employee was unable to find a job within 3 months after dismissal, the company pays him the average salary for this period.
You can also find out who cannot be laid off when reducing staff by reading here.
Thus, if the legal rights of the person dismissed due to redundancy are respected, he has 5 months to find another job. Another thing is that the management of the enterprise is trying to save on the wage fund of such persons, therefore it can violate the dismissal procedure, force the employee to write a statement of his own free will, carry out his certification or part with him under the article. In such cases, it is the employee who is required to respond promptly and act competently.
Determining the working optimum
Before starting to select candidates for dismissal, the employer must answer the question of how many employees he intends to keep and in what positions. In other words, the staffing table should be revised. The employer makes a decision and, based on it, makes changes to the previously existing staffing table.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! In the new schedule, the reduction should actually be real. It is unacceptable, along with the reduction in the number of employees or the abolition of some positions, to introduce others in their place, to which other people will need to be appointed.
The head of the company, having drawn up a new staffing table, issues an order for its approval. This is not yet an order for staff reductions and layoffs, but a mandatory preliminary procedure. It does not matter much in what form this order will be drawn up; it is important that it contains the date from which the new staffing table will be considered valid. The employer will build on this date when planning the next stages of reduction, in particular, notifying employees.
If the employer refuses to sign the resignation letter
The manager does not have the right to prevent dismissal at his own request. You can decide to quit at any time, and you do not need to coordinate your resignation with your employer. The only limitation is that according to Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, you are required to notify your management about leaving in writing no later than two weeks in advance. A letter of resignation is just a form of warning, and it is important for you to have confirmation that the employer has received it. To do this, you can ask the person authorized to accept documents to sign for receipt of your application on a copy of this application (the copy remains with you). If for some reason they refuse to sign for you to receive the application, you can send the employer a telegram with acknowledgment of receipt - this will also be a notice of resignation in the proper form.
Article on the topic Labor disputes. What does your employer owe you?
After the two-week warning period has expired, you will have the right not to go to work and demand registration of dismissal. By agreement with the employer, you can terminate the employment contract before the expiration of the two-week period.
What to consider when dismissing an employee
A manager, making a difficult decision about who will stay and who will be laid off, cannot be guided by his own desires or aversions. Retrenchment comes with a right of first refusal, meaning that some employees are less likely to be laid off than others. Let's consider the factors that influence the choice of a manager (Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Employee qualifications . Persons with higher qualifications have priority.
- Labor productivity . Those who perform better or exceed established standards, have fewer or have not been subject to administrative penalties, awards or other incentives, should be less afraid of layoffs than employees with less rosy reputations.
- Other priorities. If points 1 and 2 are approximately equal for different employees, the manager will choose to remain at work:
- having 2 or more offspring or other dependents;
- the sole breadwinner of the family;
- combat disabled person;
- an employee who was previously injured at the enterprise;
- employee sent to improve their skills.
- Preferential categories . All other things being equal, the preferential right will be on the side of employees who were “Chernobyl survivors” (clause 7, clause 1, article 14 of the Law “On Social Protection” of May 15, 1991), persons affected by the tests in Semipalatinsk (clause 10, art. 2 Federal Law No. 2 of January 10, 2002), as well as Heroes of the USSR and Russia and full Order Bearers of Glory (clause 1 of Article 8 of Law No. 4301-1 of January 15, 1993)
A comparative analysis of all these points should be reflected in the personal files of each candidate for dismissal.
Is it possible to contact the Employment Center with only registration in hand?
According to Article 31 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Employment of the Population in the Russian Federation”, the decision to assign unemployment benefits is made simultaneously with the decision to recognize a citizen as unemployed. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 3 of the Law on Employment, the decision to recognize a citizen registered for the purpose of searching for a suitable job as unemployed is made by the employment service authorities at the citizen’s place of residence.
We are talking specifically about the place of residence, and not about the place of registration (registration), therefore, if you receive a refusal, you have the right to demand that the refusal be formalized in writing and appeal it in court or to a higher authority (the employment department of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation).
Please note that registration at the place of stay and residence is only a method of registering citizens within the Russian Federation provided for by federal law, which is of a notification nature and reflects the fact that a citizen is at the place of stay or residence, which cannot serve as a basis for restriction or a condition for the exercise of the rights and freedoms of citizens .
See also: What to do if your boss quits his job →
Who should not be laid off?
Some categories of employees cannot be dismissed on this basis. Clause 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation cannot be applied to:
- those on sick leave (Part 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code);
- women in an “interesting” position (Article 261 of the Labor Code);
- mothers of children under 3 years old;
- single mothers, if their children are under 14, and disabled children are 18 years old;
- persons in whose care there is a child without a mother;
- members of the trade union organization (clauses 2, 3, 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code).
IMPORTANT! Workers from these categories who have been subject to unlawful layoffs are easily reinstated through the courts, causing the employer a lot of trouble.
In what cases are people fired due to reduction? Grounds according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
It has already been mentioned that the law does not specify cases of possible layoffs of workers. This, among other things, means that the employer has the right to make a decision on such a reduction on his own initiative and, having fulfilled all legal requirements, remain within the framework of the law.
This may not be the most pleasant news for employees, but in practice, enterprises rarely resort to staff reductions without special reasons, because procedurally, this operation is not so simple, and the costs of compensation will increase overall expenses, which is unlikely to be included in the business plans of the enterprise.
These provisions have been confirmed by judicial practice. First of all, we are talking about clause 10 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 of March 17, 2004 and the Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 413-О-О of July 15, 2008.
The main reasons for downsizing are:
- bankruptcy;
- crisis phenomena;
- moving;
- optimization, including increasing the level of mechanization / robotization;
- reorganization;
- liquidation.
In judicial practice, there are quite a few examples when laid-off employees filed a claim, claiming that the layoff was unjustified, i.e. assuring that their dismissal could have been avoided. In almost all such cases – directly or through cassation – the employers won. The court does not resolve questions about the expediency of the reduction - this, according to the law, is the right of the enterprise.
However, there are also examples when the court sided with dismissed workers, but these are due to the fact that the reduction was either carried out in violation of the rules or was fictitious. According to the latter, there is a striking example when an employer “cut down”, for example, salespeople, but instead sales floor managers or something similar appeared on the staffing table, i.e. in fact, the reduction tool was used to fire specific individuals and take others in their place.
When and who cannot be laid off?
Here we also need to dwell on the other side of the issue - who cannot be fired due to reduction. Let us say right away that the situation does not apply to cases of liquidation of an enterprise , as well as some options for reorganization (in which the actions are similar to liquidation).
In accordance with Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is impossible to reduce:
- Woman : pregnant woman working under an open-ended or fixed-term contract (which, if it expires during pregnancy, must be extended at the request of the employee), except in cases of a fixed-term replacement contract, which turned out to be fulfilled and the employer has no other offers.
- Single mother or father raising children without a mother : if there is at least one young child (under 14 years old) or a disabled child under 18 years old.
- Parent or guardian : raising a child under 3 years old if there are at least 3 young children (under 14 years old) in the family and the second parent/guardian is unemployed.
Here and further, it must be understood that we are talking about the norms of Federal legislation, however, there may be acts of a different level, including collective agreements, agreements with trade unions, etc., which, without contradicting the laws of the Russian Federation, introduce additional conditions, protection of workers and etc.
Alarming news delivered on time
The “lucky ones” whom the employer has decided to sacrifice to reduce staff should find out about this in advance. Within 2 months, employees will have written notice of their upcoming “freedom.” Soon-to-be-former employees must sign for this notice.
NOTE! Only handing over a notice against signature does not contradict the procedure. Oral announcements, negotiations, placing information on a stand, etc. the methods have no legal force: if the legality of the layoff is challenged, the employer will not be able to prove that he warned the employee on time.
The procedure for challenging management decisions
Any unlawful actions of superiors should be responded to with written complaints and statements. They can be submitted both to management and to regulatory authorities - the labor inspectorate and the prosecutor's office . The further procedure for challenging is drawing up and filing a claim in court. This must be done within a month after dismissal.
Special material has been prepared on the topic of where to file a complaint against an employer; we recommend reading it.
Layoff or other job
Before laying off an employee, the employer is obliged to offer him other positions according to his qualifications, if they exist and are vacant. They must be offered right up to dismissal. The list of proposals should be indicated in the notice given 2 months in advance. If the employee agrees, a transfer will follow instead of a layoff. If there are no suitable positions or the employee’s consent, the dismissal will continue as usual.
The union is aware
The trade union (if it operates in the organization) must be notified of the upcoming layoff within the same 2 months as the employees. If you plan to dismiss more than 15 people, the period will increase to 3 months. With such large-scale reductions, the Employment Service must also be warned.
What to do and how to behave if they want to fire you?
The first thing to do is understand the reasons for the dismissal. How to behave in the future depends on this. Next, it is necessary to clarify whether the employee is included in the list of those employees who cannot be laid off or whether they have a preferential right to remain. The first category includes persons on sick leave, on leave (including to care for children), as well as members of a trade union, company representatives, and pregnant women. If they want to fire these persons due to a reduction in work, then such actions are illegal and a complaint should be filed.
The second category includes people who:
- Two or more dependents or they are the only breadwinners in the family;
- Disability has been registered;
- Injured by an employer;
- Qualifications are increased as assigned by the management of the enterprise and at its expense.
Tips to avoid problems
If an employer intends to act in bad faith, employees should expect trouble. You can avoid problems if you follow some advice. First, before dismissal you will have to strictly adhere to the daily routine of the enterprise and other conditions specified in the contract.
Secondly, it is necessary to obtain a copy of the order to reduce staff as quickly as possible and demand notification of the impending dismissal. After the order was issued and the employee’s name was entered into the lists, he signed that he was subject to layoffs, the main thing was not to give a reason to dismiss him under another article.
Third, it is recommended to consult a lawyer regarding your rights. The specialist will describe the most effective algorithms for action in the event of unlawful actions by the employer. This step will help prevent wrongful dismissal.
Can they be laid off without registration?
There are two options here - the employee was not initially registered or he was officially hired, but they want to terminate his employment contract and lay him off without registration. In the first case, the employee is not officially protected; he can simply not be allowed into the enterprise and not be paid for the work done. Proving employment is difficult.
In the second case, as indicated above, the management of the enterprise resorts to tricks in order to save money. For example, instead of filing a dismissal due to layoffs at work, it is proposed to write a statement and stage the process as if the termination of the employment contract occurs by agreement of the parties. In this case, the actions of the company's management are illegal.
We decide whether it is more profitable by agreement of the parties
To understand how much more profitable or not it is to quit by agreement of the parties, you need to consider the following:
- The employee must be paid a salary for time worked and unused vacation.
- He is entitled to severance pay if provided for in the employment agreement or if there is a corresponding clause in the collective agreement.
The paid time to search for a job is reduced from at least 5 to 3 months, since the dismissal occurs immediately, and not after 2 (and in the case of a mass dismissal, 3) months. If nothing is specified in the contract about severance pay, the employee will not receive it. The decision is not in favor of the parties' agreement.
Compensating for job loss
This basis for dismissal provides the largest payments to exempt employees. Upon receiving an entry in the employment contract regarding the termination of an employment contract to reduce the organization's staff, clause 2, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee has the right to:
- severance pay (another salary calculated as the average amount per month);
- after dismissal, the average salary will be accrued for another 2 months if during this time the person fails to find a new job;
- another average monthly salary (for the third month after dismissal) can be accrued if the dismissed employee joined the labor exchange within two weeks and has not yet been employed during these months;
- regular dismissal payments - accruals for sick leave (if any), compensation for unfilled vacation days;
- additional compensation - if the employee leaves before 2 months after the news of the layoff (the amount will be proportional to the payment for the remaining time of work).
Legal grounds
The reduction procedure must take place in accordance with the rules established by law. It is regulated by the following documents:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation, articles 81, 82, 178, 179, 180, 261, 292, 296, 373;
- Law No. 1032-1 of April 19, 1991 “On employment of the population of the Russian Federation” (Articles 13, 25);
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 99 of February 5, 1993 “On the organization of work to promote employment in conditions of mass layoffs.”
In this case, it is necessary to take into account other regulatory documents that establish additional guarantees for those dismissed during layoffs.
It should be taken into account that the company has the right to provide additional measures to support employees upon dismissal. This is possible provided that the introduced rules do not worsen the situation of employees compared to the law. Such provisions can be fixed in the employment contracts of employees, the collective agreement of the enterprise, and in local regulations.
Step-by-step guide for employers
Let's summarize: we list all the procedures necessary for a manager to carry out when reducing numbers or staff.
- Order on approval of the amended staffing table.
- An extract from personal files of information confirming or refuting the candidates’ preferential right to dismissal.
- Notification of those being laid off against signature (2 months in advance).
- Offering dismissed employees other positions based on their qualifications.
- Informing the trade union body (60 days in advance or 90 days in case of mass layoffs).
- Issuance of orders for the dismissal of employees, familiarization with them against signature.
- Calculation of stipulated payments.
- Making a corresponding entry in the work book.
Downsizing – what is it?
Reducing the number or staff of employees is a method provided by law for terminating labor relations at the initiative of the employer (clause 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The reasons for such a reduction are not indicated, which means they can be anything, but the procedure itself is clearly regulated and its violation can lead to serious sanctions for the owners of the enterprise.
It is obvious that in the very wording, and in labor legislation, this very terminology is used - Reduction in the number or staff of employees, there is a difference between the terms “number” and “staff”. Is this an important parameter?
Reducing the number and staff - is there a difference?
There are no direct indications in the Labor Code of the difference between these terms. However, differences can be deduced from the letter and spirit of the law:
- A reduction in headcount is a reduction in the number of positions within the same type of staffing unit, despite the fact that the total number of such units remains greater than 0. For example, there were 10 cleaners working at the enterprise, and after the reduction in number there will be 5.
- Staff reduction is the complete elimination of staff for any position. For example, there were 10 cleaners, but after the reduction, there will be no cleaners at the enterprise at all.
In the context of the issue under consideration, the only difference in these concepts is the order (selection) of specific individuals for dismissal. When reducing staff, all units are fired without any advantages over each other, and the reduction in numbers implies a certain algorithm for selecting persons for dismissal. We will talk about this in more detail below.
Everything said below applies equally to any type of enterprise organization - individual entrepreneur, LLC, JSC, etc.
8(800)350-23-68
Dmitry Konstantinovich
Expert of the site "Legal Consultant"
Ask a Question
There is one more point that needs to be taken into account at the beginning of the proceedings. There is a process of dismissal due to liquidation of an enterprise that is largely similar, but still has fundamental differences. It requires a separate explanation, and will be touched upon superficially in this material.
Preferential right to work
When making a reduction, the manager must take into account some nuances. There are categories of citizens who cannot be fired. In addition, people whose qualifications and productivity are higher than other candidates are retained.
Preferential employment rights are given to married employees, provided that they:
- Raising two or more minor children;
- They are the only breadwinners in the family;
- Received a work injury in the organization or an occupational disease;
- Participated in hostilities and became disabled;
- Regularly undergo training and improve their skills.
Labor legislation protects the following categories of citizens from layoffs:
- Women raising children under three years of age;
- Single parents who are dependent on a disabled child;
- Single mothers, single fathers who are raising a young child (under 14 years old);
- Pregnant women;
- Employees undergoing treatment on sick leave;
- People on vacation.
There is no preferential right to work for people of retirement age. The commission considers their personal affairs in the same way as other employees.
If the organization employs an employee under 18 years of age, his reduction must be approved by the Labor Inspectorate for Minors.
Basic Concepts
The reduction procedure is carried out in strict accordance with the Labor legislation of the Russian Federation. According to regulations, there are two grounds for dismissing an employee:
- Reorganization of the company, due to which the number of jobs is reduced;
- Reduction of staff.
Job losses usually occur for economic reasons. However, the staffing table remains the same. For example, out of five people holding the position of sales manager, two are retained.
When staffing is reduced, the position is completely eliminated. For example, the responsibilities of a HR employee are transferred to an accountant.
Expert commentary
Kamensky Yuri
Lawyer
The reduction is due to adjustments to the staffing table. During the procedure, new amendments are made to the current document. The manager is obliged to familiarize employees with changes in the staffing table. In addition, the director issues an order explaining the reasons for the reduction.
Personnel reduction procedure
Use the step-by-step downsizing procedure with sample documents to help avoid costly mistakes.
Step 1. Prepare and issue an order. The order usually contains standard details and the following information:
- list of staff positions being reduced;
- optimization procedure, responsible persons, deadlines;
- composition of the commission to take into account the interests of employees, etc.
Step 2. Prepare a project and approve a new staffing table (with new positions or headcount by position).
IMPORTANT!
The new schedule should not take effect while the laid-off employees are working. If the procedure is not followed, there is a high probability that workers will be reinstated and the employer will be charged the average wage for forced absence. Judicial practice confirms that dismissal “due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees” is permitted only if there is an actual change, and not a planned one. The new staffing schedule should come into effect.
Step 3: Determine who has the advantage of remaining employed. If a staff position is being reduced (vacant), this step in the procedure is not needed. When maintaining a position and reducing the number of employees, another obligation of the employer when laying off workers is to provide advantages to those who have higher qualifications and productivity (Article 179 of the Labor Code). The decision to provide benefits during redundancy is made by the commission after a comparative assessment:
- qualification data;
- information about regular assessment or certification of personnel;
- bonus indicators and their implementation;
- labor discipline, etc.
If the indicators are the same, the commission notes this in the protocol and provides benefits to the following categories of employees (Part 2 of Article 179 of the Labor Code):
- family with two or more dependents;
- whose family has no other working members;
- received a work injury or occupational disease while working in the organization;
- disabled combatants and WWII;
- those who improve their qualifications without interruption from work in the direction of the employer;
- specifically specified in the collective agreement.
What else to pay attention to:
- Employees under 18 years of age are dismissed only with the consent of the labor inspectorate and the commission for minors (Article 269 of the Labor Code).
- Trade union members - in agreement with the primary organization (Part 2 of Article 82, 373 of the Labor Code).
- Do not dismiss an employee during the next vacation or during a period of temporary disability (Part 6, Article 81 of the Labor Code, paragraph “a”, paragraph 23 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 of March 17, 2004).
Step 4. A notice containing a warning about the dismissal of an employee should be received by:
- absolutely everyone is being laid off;
- within the period established by law.
Article 180 of the Labor Code defines the standard period - 2 months before the day of dismissal. In case of refusal to sign:
- read it out loud;
- draw up a document and have two witnesses sign it.
IMPORTANT!
A notified employee has the right to use the notice period of dismissal due to staff reduction to look for work - this is not a violation.
Features of notifications of some categories:
- Those hired under a fixed-term contract for up to two months are notified in writing at least three calendar days before dismissal (Part 2 of Article 292 of the Labor Code).
- Seasonal workers - seven calendar days in advance (Part 2 of Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Those on sick leave and on vacation are sent letters with a list of attachments - the date of notification coincides with the date of delivery.
The important question of how to determine the date of dismissal in case of staff reduction is resolved by Article 14 of the Labor Code. The two-month period begins to run from the day the employee receives the notice - they are fired the next day after its end (appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court in case No. 33-49512/2018 dated November 14, 2018).
Step 5. Don’t forget to analyze the available vacancies and offer them to those being laid off. Condition: they must be suitable in terms of qualifications and health (Article 81 of the Labor Code).
IMPORTANT!
Offers must be made as options arise - within two months, while the employee is finalizing the proposal.
Please note: the courts carefully check the compliance of the proposed vacancies with the staffing table and location (for example, the Appeal ruling of the Krasnoyarsk Regional Court in case No. 33-949/2015, A-9 dated 02/02/2015).
Step 6. Notify the union and the employment center. The trade union and the regional employment center are notified two months in advance (Article 82 of the Labor Code and paragraph 2 of Article 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation No. 1032 of April 19, 1991). Regions independently develop the forms of such notifications.
IMPORTANT!
In the event of a mass layoff of 20 or more people, the period for preliminary notification increases to three months. The specific level of mass participation is determined by regional and sectoral agreements between employers and trade unions (Part 1 of Article 82 of the Labor Code).
Carefully document the entire dismissal process (paragraph 2, part 1, article 84 of the Labor Code).
Step 7. On time, on the day of dismissal, prepare and sign the dismissal order. Use:
- forms No. T-8 or No. T-8a;
- form approved by the organization.
Familiarize the person being dismissed with it or draw up a notice of refusal.
Step 8. Complete all the necessary documents: a note for the calculation, an entry in your personal card and work book (or STD-R form), information about income and accrued and paid insurance premiums.
IMPORTANT!
If the employee did not show up for work or did not receive the STD-R, send a notice in accordance with Part 6 of Art. 84.1 TK. By decision of the employee, the STD-R form is sent to an email address (Article 66.1 of the Labor Code, clause 1.3 of the Filling Out Procedure, Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 23n dated January 20, 2020).
Step 9. Pay the employee in full, pay compensation for unused vacation (Article 121 of the Labor Code) and severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings.
IMPORTANT!
Severance pay is paid to everyone, including those who terminate their employment contract early.
Step 10. To receive benefits for the second month, the employee provides:
- identification;
- original work book without records of work after the date of layoff (if it is on hand).
It is more difficult to obtain benefits for the third month:
- within two weeks after dismissal, you must obtain unemployed status;
- be unemployed during the third month after dismissal;
- provide the employer with the decision of the employment service to make the payment.
Please note that in accordance with Art. 178 of the Labor Code, benefits for the third month are retained in “exceptional cases.” The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, in ruling No. 2214-O dated November 29, 2012, indicated what an employer must do if he does not agree with the decision of the employment service to maintain the average salary for an employee dismissed due to reduction - he has the right to appeal it in court. To assign the third payment, the presence of formal signs is not enough, and labor legislation does not specify the signs of exclusivity. In such cases, one should be guided by clause 15 of Review No. 2 (2017), approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on April 26, 2017, the rulings of the IC for civil cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 69-KG17-21 dated November 20, 2017, No. 69-KG17-12 dated 06/17/2017, No. 69-KG17-7 dated 06/19/2017. Employment authorities are recommended to take into account the following as circumstances making a case exceptional:
- social vulnerability of the dismissed person;
- lack of livelihood for him and his family members;
- serious illness;
- the presence of disabled dependents and the like.
There are features for the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas:
- a benefit is paid in the amount of average monthly earnings;
- the average monthly salary is maintained for the period of employment, but not more than three months from the date of dismissal (including severance pay) (Article 318 of the Labor Code).
In exceptional cases, earnings are retained for the fourth, fifth and sixth months, if the employee contacted the employment service within a month after dismissal and was not employed.
The legally sound algorithm of actions when reducing the number of employees is as follows.
In accordance with the law, the employer has the right to cancel the decision. The optimization procedure helps to understand how to reverse a job reduction at an enterprise - the steps are similar, but are used in a slightly different order:
- an order is issued canceling the previously issued one (if there was a decision of a collegial body, it will also be needed);
- Employees are notified against signature;
- information is sent to the employment service and trade union.