Reducing the number of employees is one of the effective ways to reduce costs or slow down the pace of production activities if the organization's product has ceased to generate sufficient profit. In this article we will tell you how to avoid mistakes when reducing staff.
If an employer decides to reduce the number of employees, he needs to take into account all the nuances of this complex process. Mistakes made do not reduce, but, on the contrary, significantly increase personnel costs.
For example, a court may reinstate an employee at work and oblige the employer to pay him the average salary for the entire period of forced absence (Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), as well as to compensate for moral damages (Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the employer is obliged to pay all legal costs (Article 88 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, if an employee applies for protection of his rights to the labor inspectorate, if the reduction is incorrectly executed, the employer faces administrative liability under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
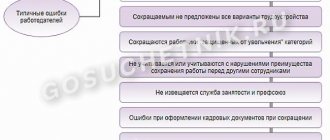
Let's look at the typical mistakes that employers make when filing staff reductions.
Common mistakes
If we talk about typical mistakes when abbreviating, these include:
- absence (non-delivery) of notice of reduction;
- dismissal of an employee before the two-month notice period;
- failure to notify employment authorities and the trade union (if any) within the established time limits;
- failure to offer vacancies when available.
When it comes to reducing the number of employees, a fairly common mistake is failure to conduct or incorrect assessment of the preemptive right (Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, employers often have no criteria for assessing labor productivity and qualifications at all, or these criteria are recognized by the courts as subjective.
THE PREFERENCE RIGHT TO REMAIN AT WORK DOES NOT TAKE CONSIDERATION
You may encounter such a problem during downsizing if there are several positions of the same name in the staffing table. For example, a department has three sales managers, but only one needs to be laid off. In this case, part one of Art. 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires that the employer, when laying off workers, retains workers with higher labor productivity and qualifications.
Qualifications can be verified using an education document and work record, but assessing labor productivity will require some effort from the employer.
- How to evaluate labor productivity? It is not difficult to assess the productivity of working personnel - it is enough to find out whether employees comply with labor standards (time and output). The situation with assessing the productivity of knowledge workers is much more complicated. Here are some tips:
1. If the organization conducts an annual personnel assessment, we recommend attaching its results. The results of the certification, if any, will also be useful.
2. If the organization has established bonus indicators, the productivity of employees can be assessed by the size and frequency of bonuses awarded to them. You can also take into account the regular performance of additional work (for example, part-time or by special order). We recommend assessing the employee’s work discipline. If discipline is low or there are comments or reprimands, then such an employee does not have a preemptive right.
- How to Document Performance Evaluations. The first step is to issue an order to create a commission to determine the preferential right to remain at work. The order must contain the following provisions:
The results of the assessment must be indicated in the minutes of the meeting of the special commission. In court, the protocol is evidence that the employer took into account the preferential rights of employees. The protocol should be accompanied by tables assessing the employees’ compliance with production or service standards, plans, instructions, etc. (see table).
If labor productivity and qualifications of workers in identical positions are approximately equal, you should go further and give preferential rights to the following categories (part two of Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
•family with two or more dependents;
•persons whose family does not have working family members;
•workers who, while working in the organization, received a work injury or occupational disease;
•disabled people of WWII and combat;
•workers who improve their skills without interruption from work in the direction of the employer;
•other categories of employees in accordance with the collective agreement.
Supporting documents should be requested from such employees. For example, an employee with two or more children must provide birth certificates, as well as a passport with registration confirming residence with children; combat disabled person - certificate.
Who can't be laid off?
Art. 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes categories of persons who are not subject to reduction. These include:
- pregnant woman;
- a woman with a child under 3 years of age;
- a single mother raising a disabled child under the age of 18;
- a single mother raising a child under 14 years of age;
- another person raising the above children without a mother;
- a parent (other legal representative of the child) who is the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under the age of 18 or the sole breadwinner of a child under 3 years of age in a family raising three or more young children, unless the other parent (other legal representative of the child) is in an employment relationship.
For more information about the categories of persons who cannot be laid off, read the article “6 situations when laying off an employee can result in a lawsuit.”
Responsibility for violation of payments
For violation by the employer of labor legislation and failure to pay statutory deductions on time, Part 6 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for the following fines:
- for officials - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
Order to reduce staff
Order to dismiss an employee
How and why to prove the fact of reduction
The burden of proving the fact of layoff lies with the employer. The launch of the reduction procedure begins with a decision by the authorized person of the company to carry out the reduction.
Such a decision must be made in writing. This could be, for example, an order from the general director or a protocol of the board of directors. Based on this decision, an order is issued to change the staffing table and the staffing table is directly changed. It is these documents that will serve as proof of the reduction.
In addition, since labor disputes most often arise after dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees, the court also examines whether a new employee was hired for the same position after the dismissal. In this case, the reduction may be considered illegal (“imaginary”). From this we can conclude that the fact of a reduction can be proven by the absence of a position in the staffing table in effect at the time of consideration of the dispute.
DO NOT OFFER ALL SUITABLE VACANCIES
If there are vacancies in the organization, they should be offered to the laid-off employee (if they suit him in terms of qualifications and health) as they appear within two months, while the notice period for dismissal due to layoff is valid (part three of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
Often, courts reinstate employees precisely because they were not offered all the vacancies. The courts carefully check whether the positions in the staffing table and in job offers coincide (see, for example, the Appeal ruling of the Krasnoyarsk Regional Court dated 02.02.2015 in case No. 33-949/2015, A-9).
It is necessary to offer not only positions that correspond to the employee’s qualifications, but also lower ones.
QUESTION ON THE TOPIC
Do I need to offer a vacant senior position?
If you know for sure that your qualifications are insufficient, you do not need to offer this vacancy (see the Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated March 30, 2015 in case No. 33-10408/2015).
But if it is not known for sure whether the employee can hold a higher position (perhaps he has undergone additional training or has experience that is not reflected in the work book), the risk of disputes increases. For this purpose, we propose to inform the employer about qualification documents unknown to the employer in the layoff notice (see Example 1).
Thus, you need to ensure that there are no extra vacancies left in the staffing table (just in case). All vacancies that are not currently being searched should be excluded.
The employer is obliged to offer vacancies only in a given area, unless otherwise provided by the labor or collective agreement (see the Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 24, 2012 in case No. 11-25754).
Let us note that the position in which a woman on maternity leave worked, in the opinion of most courts, is not considered vacant (see, for example, Determination of the Moscow City Court dated May 29, 2014 No. 4g/8-3516). This position is temporarily vacant - because the woman can return, and we don’t know when - in three months or three years.
Why is a redundancy commission needed?
Legislatively, the employer has no obligation to create a redundancy commission, but from a practical point of view, its necessity is beyond doubt.
First of all, it is needed to determine the categories of employees who are not subject to layoffs. In addition, the work of this commission is useful in assessing the preemptive right. The staff reduction commission reviews the information provided for each candidate for dismissal. The decision made regarding employees who are not subject to layoffs and have a preferential right to remain at work is documented in writing - a protocol, a decision, etc.
The commission is created by order of an authorized person. The commission, as a rule, includes personnel specialists, one or two employees who are members of a trade union (if the company has one), and lawyers.
Early dismissal: how to do it right
The dismissal procedure step by step is as follows:
- The decision on layoffs, execution of the corresponding order indicating the positions and names of employees.
- Written notification to employees who have been laid off: 2 months before dismissal, against signature. If an employee refuses to sign a document, a special commission draws up a report about this.
- Offer employees other similar vacancies, if any.
- Receiving an application (sending an offer) for early dismissal if one of the parties to the employment contract has such a desire.
- Signing of the document by both parties to the labor relationship.
- Issuance of an order for early dismissal due to reduction, if an agreement is reached between the employee and the employer. The details of the previous, general reduction order are indicated as grounds for the early dismissal of this employee. The document is also signed by both parties to the employment contract.
- Preparation of documents for dismissal and payment of all amounts due to the laid-off employee.
Since a redundant employee can be dismissed early only with his consent, you should take the application seriously.
An employee’s application for early dismissal due to staff reduction must, in addition to the full name of the manager and employee, the name of the document (application), contain the following information:
- reason for dismissal - staff reduction;
- grounds for early dismissal – Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- information that the employee has received a notice from the administration about staff reduction;
- request for payment of additional compensation in the amount of average earnings for the remaining days - with reference to Part 3 of Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
At the end there is a signature and date.
Similar information is usually contained in a document from the manager to the employee, formalized, accordingly, as a proposal from the administration, in the form of an agreement. The director signs it.
The signature of the second party to the employment contract on the documents makes them the basis for an order for early dismissal. The order is issued according to f. T-8 or in a non-unified form used in the organization. In personnel documents, the basis is indicated in clause 2, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is worth noting that if a citizen changes his mind about resigning earlier, he can try to revoke his consent. There is no legal ban on this. However, the manager has no obligation to agree with him - in other words, the employee can be fired on a previously agreed date. This position is supported by the judges (determined by the Moscow City Court on case No. 33-15827 of 05/26/11)
Let us also pay attention to this nuance: according to the text of Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the initiator of early dismissal during layoff is the employer, and the employee has the right to agree with him or not. Formally, the employee does not have the right to initiate early dismissal. At the same time, in case of refusal to accept the relevant application, the employer risks entering into a protracted legal dispute. With a high degree of probability, the dispute may be lost, since such a formal approach puts the dismissed employee in unequal conditions with the employer. The remaining possibility of early dismissal - at his own request - deprives him of the right to receive redundancy payments.
Seasonal workers and conscripts
The legislation provides for specifics in the procedure for laying off seasonal workers and workers who have entered into a fixed-term employment contract of up to 2 months. Please note that for other employees with whom a fixed-term employment contract has been concluded for other reasons, the reduction procedure is similar to that provided for employees with whom an employment contract has been concluded for an indefinite period.
The specifics of laying off seasonal workers and workers with whom a fixed-term employment contract of up to 2 months has been concluded relate to the timing of delivery of notice and payment of benefits.
Thus, an employee engaged in seasonal work must be notified of his upcoming dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of the organization’s employees at least 7 calendar days in advance.
Accounting and tax accounting, employee settlements, reporting to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat, currency accounting - all in one service.
To learn more
For employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to 2 months, the period is even shorter - they must be notified of the upcoming layoff at least 3 calendar days in advance.
As for the payment of severance pay to these categories of employees upon dismissal under clause 2, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then for seasonal workers the amount of benefits is equal to the amount of two-week average earnings. And employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to two months are not paid severance pay upon dismissal as a general rule, unless otherwise established by federal laws, a collective agreement or an employment contract.
What payments are due upon redundancy?
First of all, these are standard payments that are due to any resigning employee. Namely: wages for hours worked, bonuses, as well as compensation for unused vacation (the calculation of compensation in this case has its own peculiarities). Also, laid-off workers may qualify for additional amounts of money.
Vacation pay compensation
Employees who have worked more than five and a half months in the working year at the time of layoff can count on full compensation for unused vacation. This means that if the dismissed person did not take vacation days at all for the current working year, then he receives compensation for the full vacation (i.e. for all 28 calendar days). If part of the vacation has already been used, then compensation is paid for unused days of full vacation for this working year (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 28 of the Rules on regular and additional vacations, approved by the People's Commissar of the USSR on April 30, 1930 No. 169). For example, if an employee has worked for more than five and a half months, but has already taken 5 days off from his current vacation, then if he is laid off, he will receive compensation for the remaining 23 days.
ATTENTION. In some regions, the courts insist that the described algorithm must be applied to all laid-off employees, and not just those who have been working for the first year (see, for example, the Bulletin of judicial practice of the Moscow Regional Court for the fourth quarter of 2015, the appeal ruling of the Irkutsk Regional Court dated 11/12/14 in case No. 33-9318/2014). And although Rostrud gives explanations to the contrary (letters dated 03/04/13 No. 164-6-1 and dated 08/09/11 No. 2368-6-1), before paying “old” workers compensation according to the usual rules, you should weigh the pros and cons "against". In this case, you need to take into account the prospects for possible litigation and the practice that is developing in your region.
Severance pay
All employees have the right to receive it, with the exception of those with whom an agreement was concluded for a period of up to two months. The latter is entitled to severance pay only if it is provided for in a collective or labor agreement (Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of the benefit depends on the category of the dismissed employee. “Ordinary” employees are paid an amount equal to the average monthly earnings (Article 178 and Article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Seasonal workers receive smaller compensation - based on two-week average earnings (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculate your salary and benefits taking into account the increase in the minimum wage from 2021 Calculate for free
Two-month compensation
If a laid-off employee does not find a new job within a month after dismissal, then he retains his average earnings for the next month. It is paid by the former employer on regular salary payment days (clause 12 of the Regulations, approved by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated March 2, 1988 No. 113/6-64). This procedure applies only to “regular” employees. Seasonal and temporary workers do not have the right to additional payments for the period of employment (Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Average earnings for the second month after dismissal are paid based on the employee’s passport and work record book. If there is no record of hiring a new job at all, then the average salary is transferred to the redundant employee in full. If there is a record of employment, but it is not dated at the beginning of the month, then the average salary must be paid for the days preceding this date (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), appeal ruling of the Omsk Regional Court dated September 12, 2012 in case No. 33-5536 /2012).
The right to receive money for the third month after layoff is confirmed not by a work book, but by an official document from the employment service (Part 2 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer can appeal this document if he considers it unlawful (clause 2.2 of the ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of November 29, 2012 No. 2214-O, part 1 of article 218 of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation). Filing such a complaint does not exempt a former employee from paying money (this follows from Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). However, if the court finds the decision of the employment service illegal, the funds paid will be compensated to the employer from the budget.
IMPORTANT. Is it necessary to subject average earnings during the period of employment to personal income tax and insurance contributions? The answer to this question depends on the total amount of payments transferred in favor of the laid-off employee, taking into account severance pay. If the entire amount does not exceed three times the employee’s average monthly earnings, then there is no need to charge contributions and withhold personal income tax. Otherwise, contributions will have to be charged on the excess amounts and tax will be withheld from these amounts (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24 .98 No. 125-FZ).
Generate payment slips for personal income tax and contributions with current details Try for free
Dismissal of an employee upon change of ownership
First of all, it is worth noting that a change of owner does not automatically terminate the employment contract with existing employees.
The categories of employees with whom the employment contract can be terminated and the periods during which dismissal can be effected are limited. To employees with whom employment relations can be terminated on the basis provided for in clause 4, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (change of owner of the organization’s property), includes the head of the organization, his deputies and the chief accountant.
The period during which the new owner has the right to terminate the employment contract with the above-mentioned persons in connection with a change in the owner of the organization’s property must be no later than 3 months from the date his ownership rights arise.
A change in the owner of the organization’s property is not grounds for terminating employment contracts with other employees of the organization.
If the new owner decides to carry out a reduction, then starting this procedure is allowed only after state registration of the transfer of ownership.
When staffing is downsized
In business, various unforeseen situations often occur. If they are associated with additional difficulties, including financial ones, it is necessary to cut costs, reduce costs, and reduce the number of personnel. To do this, employers choose one of two ways or combine them:
- trying to make do with fewer employees – reducing the number of staff;
- removing certain positions or staffing units for them - staff reduction.
REFERENCE! If positions that are currently vacant are removed from the staffing table, this does not constitute a reduction.
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates in detail all the provisions for the dismissal of an employee from a position as a result of reduction.
Guarantees and compensation
When an employment contract is terminated due to a reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees, the dismissed employee is paid a severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings. He also retains his average monthly salary for the period of employment, but not more than 2 months from the date of dismissal (including severance pay).
In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary will be retained by the employee for the third month from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within two weeks after dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not employed by it.
It is worth noting that Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes minimum guarantees. Thus, an employment contract or collective agreement may establish an increased amount of severance pay, with the exception of cases expressly provided for by law.
One cannot fail to say something about the “northern” workers. They retain their average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than 3 months from the date of dismissal, including severance pay.
In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary is retained for the specified employees during the 4th, 5th and 6th months from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within a month after dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not they are employed.
The procedure for calculating average earnings is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 No. 922.
PERSONNEL DOCUMENTS ARE COMPLETED WITH ERRORS
Errors in the preparation of personnel documents can lead to fines and even reinstatement of the employee. To avoid them, you need to carefully formalize his dismissal on the last day of work (paragraph two of the first part of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 35 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
Below we list the actions of the employer on the last working day of the dismissed employee.
- We issue a dismissal order. The order is drawn up according to the unified form No. T-8 or No. T-8a [1] or according to the form approved by the organization (Example 7). If the order is drawn up later than the day of dismissal, in a controversial situation the court will declare it invalid.
The employee must be familiarized with the order against signature. If you refuse to familiarize yourself, you must draw up a corresponding act, which must be signed by two or three employees (Example 8).
- We draw up a note-calculation. The calculation note is a mandatory document for publication and is sent to the accounting department on the day the employee is dismissed. It is drawn up either according to the unified form No. T-61 or according to the form approved by the organization. In it, the personnel officer reflects the number of days of unused or advance-used vacation (Example 9).
- We make an entry in our personal card. An entry about the dismissal of an employee must be made in section XI of the personal card of Form No. T-2, which the employee must be familiarized with against signature (Example 10).
- We issue a work book. On the day of dismissal, the employee must be given a work book with a record of dismissal (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) against signature in the work record book (Example 11).
If an employee refuses to receive a work book, a statement about this must be drawn up signed by two or three employees (Example 12).
If the employee does not show up to pick up the work book, you must send him a notice before the end of the working day about the need to pick up the work book (Example 13) or give written consent in any form to send it by mail (part six of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is better to send the notice to all known addresses of the employee to increase the likelihood of receiving it.
- We issue certificates. Upon dismissal, the employer is also obliged to provide the employee with:
•a certificate of the amount of his earnings, on which insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund were calculated (Part 2 of Article 4.1 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On Compulsory Social Insurance in Case of Temporary Disability and in Connection with Maternity”[2 ]);
•a certificate with information on accrued and paid insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation (Article 11 of the Federal Law of April 1, 1996 No. 27-FZ “On individual (personalized) accounting in the compulsory pension insurance system” [3]).
Advantages and disadvantages
Of course, layoffs are not a pleasant thing for an employee, especially during a crisis in the labor market. But still, a reduction, in contrast to voluntary dismissal, has a plus - it is severance pay, paid in the amount of average monthly earnings and retained by the employee for at least two months.
For the employer, the advantages are obvious - his initiative, that is, the employee cannot refuse, further optimization of expenses and reduction of the fund for wages. However, such a procedure will only further reduce the fund, since the reduction procedure itself is expensive.
Example of an order
This order is drawn up according to the standard scheme for this type of document.
Document header
First, in the middle of the line, its full name is written (with a short indication of the essence). Then, just below, the locality in which the enterprise is registered and the date the order was drawn up are indicated.
Document body
The next part is the main one. First, the reason for the reduction in staff is recorded here, then the order itself is transmitted, which includes several points.
- The first contains the date and full name of the company, as well as those positions that are subject to abolition and the number of employees employed in them.
- Then instructions are given to the head of the personnel department or another authorized person - here it is necessary to enter his position and full name - to bring information about the staff reduction to those employees who are directly affected by it (remember that this must be done two months before the event itself).
- Then a clause is written about the requirement to prepare all the necessary documents and carry out the procedure in a legal manner. Also here you need to include an instruction on the preparation of a new staffing table, in which there will no longer be any positions being eliminated. All this must be done before the actual reduction of employees takes place.
- At the end, you need to give a link to the document (i.e. name it and indicate the date of preparation and number) on the basis of which this order was issued.
- Then the order should be approved by the signature of the head of the company, indicating his position (director, general director or other person acting on the basis of a power of attorney, etc.), last name, first name and patronymic, and signature with a transcript.
- Lastly, the order is brought to the attention of the employees subject to reduction, who must also put their signatures on it.
Mass layoff
In order for an employer to understand whether he has a mass layoff, he should refer to industry and (or) territorial agreements. Part 1 of Art. speaks about this. 82 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
So, for example, in Moscow, according to the Moscow tripartite agreement for 2016-2018 between the Moscow Government, Moscow trade union associations and Moscow employers' associations, the criteria for mass dismissal are considered to be the indicators of the number of dismissed employees of organizations registered in the city of Moscow, with a workforce of 15 or more people for a certain period of time:
- dismissal within 30 calendar days of more than 25% of the total number of employees;
- dismissal of employees in connection with the liquidation of an organization of any organizational and legal form;
- reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees in the amount of:
- 0 or more people within 30 calendar days;
- 200 or more people within 60 calendar days;
- 500 or more people within 90 calendar days.
THEY DO NOT NOTIFY THE EMPLOYMENT SERVICE AND THE TRADE UNION
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation dated April 19, 1991 No. 1032 - 1 “On employment in the Russian Federation” (as amended on July 29, 2017, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 1032-1) on reducing the number or staff, even if only one position or one employee, you must notify the employment service no later than two months in advance. If the reduction is massive, three months before the start of the reduction. Each region has its own notification form. It should be clarified on the websites of regional employment services. Let's give an example of a notification in Moscow (Example 5).
The mass scale criterion is determined by sectoral, territorial or regional agreements between trade unions and employers (part one of Article 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If these agreements are not applicable to a specific employer, you must be guided by clause 1 of the Regulations on the organization of work to promote employment in conditions of mass layoffs (approved by Government Decree No. 99 dated 02/05/1993).
According to part one of Art. 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if the organization has a trade union, it must be notified within the same time frame (Example 6).