The concept of land allocation
Among the methods of forming land plots, allocation occupies a special place. This is a system of cadastral and land management work associated with the separation of a share or shares from the total land plot in the area. When selected, one or more new objects can be created. In this case, the original area from which the allocation is made continues to exist within the changed boundaries.
Allocation of a land plot is possible when the object being converted is in common shared ownership. This legal regime is regulated by Chapter 16 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
A distinctive feature of shared ownership is that the shares of co-owners are known in advance. In addition, they can be unequal, for example: ½ + ¼ + ¼. For comparison: the shares of joint owners are determined only at the time of division of property. As a general rule they are equal.
A plot can become the object of common shared ownership for various reasons: inheritance, transaction, foreclosure on the debtor’s property.
Co-owners often find it difficult to determine what rights they have to the plot. By default, the shared ownership regime is established (Article 224 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The right of joint ownership is typical for the common property of spouses (by default), for farm assets (by agreement).
The Russian Land Code does not limit the range of possible shareholders. The site being converted may simultaneously be owned by:
- citizens;
- foreigners;
- organizations;
- states;
- municipalities.
Preferential category
Citizens of preferential categories can be allocated a plot of land free of charge; the list is determined by land legislation.
The first group of the preferential category includes:
- Tenants of a land plot, the right to lease, who received it back in Soviet times, on which a residential building stands. These citizens only need to re-register the land as their property free of charge.
- Beneficiaries also include citizens who have the right to indefinite or lifelong ownership of land. They can once exercise the right to receive land free of charge from the state.
The second group includes citizens:
- Veterans of the Great Patriotic War or other military operations.
- Military personnel who have served a term of military service under a contract for more than 15 years. They may be allocated land to build a residential building or organize a farm.
- Retired internal affairs officers who have worked in the organization for more than 15 years.
- Orphans are given plots of land that their parents used.
- Heroes of Labor and full Knights of the Order of Glory or other orders have the right to a free plot of land.
Citizens of these categories are allocated land free of charge on the basis of Federal Laws.
Converted and allocated land plots
A land plot is a special object of property rights, which is a part of the earth’s surface with an established border. Its legal regime is determined simultaneously by civil and land legislation. Like other individually defined things, a plot can be divisible or indivisible. According to Art. 133 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, property that cannot be divided in kind without changing its intended purpose is recognized as indivisible.
The Land Code of Russia has clarified these requirements in relation to plots. The latter are recognized as divisible if they can be divided into parts, each of which forms a self-sufficient plot, the permitted use of which can be carried out without being transferred to land of a different category. This provision takes on special significance in relation to agricultural land. When selecting, we are talking about the following objects:
- the initial section from which one or more parts are extracted. As a result of the procedure, it does not cease to exist, but is only transformed. The area of such a site decreases, its boundaries change.
- a newly formed plot or plots that did not previously exist as independent objects of civil and land law. They appear in connection with the separation.
For clarity, let us compare the composition of the initial and resulting objects during separation (Article 11.5 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation) and division (Article 11.4 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). In the latter case, the original plot, which serves as the territorial basis for the placement of newly formed plots, ceases to exist as an independent object of law.
The period for which the allotment is transferred for use
The permissible lease periods in relation to state lands are regulated by clause 8 of Art. 39.8 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. The maximum period for registering land for use is 49 years, no minimum has been established. The law provides for different terms of lease agreements in relation to public lands for individual purposes and can be:
- 3-10 years in relation to land plots that are provided for the construction of real estate;
- up to 49 years for placement of linear objects;
- 20 years for an individual housing structure within the boundaries of a populated area;
- 3-5 years for the development of the territory and the construction of a dacha farm;
- up to 3 years to complete an unfinished construction project.
We also talked about what could result in the loss of the right to use a land plot, and how to properly file a claim to remove obstacles to the use of land.
Thus, in order to receive a plot of land from the state, it is necessary to meet the conditions set by law. To submit an application, contact the administration with the collected package of documents and an application. Within 30 days it will be reviewed and a decision will be made on the provision of land.
Formation of a land plot by allotment
An exclusive list of methods for creating land plots is stipulated by Art. 11.2 Land Code of the Russian Federation. Among them are:
- the only primary one is the allocation from undemarcated lands that are in municipal or state ownership;
- several secondary ones (section, allocation, merger, redistribution), involving the transformation of existing plots.
Thus, the concept of “allocation of land”, depending on the context, may have a different logical scope.
- Creation of a new object of civil law from virgin lands - previously unused spaces that are in public ownership. Municipal and state owned lands in Russia are still not demarcated. The plots of them have not been formed; they have not been registered with the state real estate cadastre and the Unified State Register of Real Estate. The development of such lands for various purposes (integrated development, laying pipelines, gardening) is inevitably accompanied by the allocation of plots, the definition and recording of their legal regime in the State Property Committee, the Unified State Register.
- Transformation of a land plot owned by two or more shareholders, according to the rules of Article 11.5 of the Land Code of Russia or in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 101 “On the Turnover of Agricultural Land”, the transformation of a land plot is carried out in the process of land management by determining the boundaries of the allocated plot, clarifying the boundaries of the original plots.
On March 1, 2015, a new procedure for the formation and provision of land from state and municipal property to individuals and legal entities came into force in Russia. The key points of the new order are reflected in the Federal Law of June 23, 2014 No. 171-FZ “On Amendments to the Land Code of the Russian Federation and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 171-FZ). These innovations are part of the large-scale land reform currently underway. In general, they are designed to make the process of acquiring land, both for rent and ownership, more understandable and transparent.
Law No. 171-FZ was developed and adopted with the aim of improving the procedure for providing land plots and urban planning regulation. Until this moment, the procedure for providing land plots was not properly regulated in legislation. For example, previously, only a land plot that had all the necessary characteristics could be at the disposal of an individual or legal entity: borders, cadastral number. In addition, this was possible only if the land plot had a right holder. Also, in practice, the transfer of unformed land plots, especially from state ownership, often caused great difficulties. Now these and many other points in the procedure for granting land have undergone changes. In addition, it should be noted that the legislator introduced the concept of “land plot” into the Land Code of the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 3 of Art. 6 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, a land plot as an object of ownership and other rights to land provided for by law is an immovable thing that represents a part of the earth’s surface and has characteristics that make it possible to define it as an individually defined thing. The conditions for the provision of land plots have changed. Innovations establish a new basic principle, in which the use of the territory is first planned, and then the land plot is provided in accordance with its defined function, and not vice versa, as was the case before the changes were made. Now the formation of land plots from lands or plots in state or municipal ownership is carried out in accordance with one of the following documents: a territory surveying project approved in accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, project documentation on the location, boundaries, area and other quantitative and qualitative characteristics of forest plots, an approved layout of a land plot or land plots on the cadastral plan of the territory. Thus, the old procedure for preliminary approval of the location of an object has been abolished. At the same time, the new procedure for determining the boundaries of a land plot is now in no way connected with the grounds for its provision. It is important that in the absence of an approved land surveying project, the formation of land plots from lands or plots in state or municipal ownership is permitted in accordance with the approved layout of the land plot or land plots on the cadastral plan of the territory. However, the law provides for cases when it is possible to form a land plot only if there is a land surveying project: from a land plot provided for the integrated development of the territory (that is, integrated development), from a land plot provided to a non-profit organization created by citizens for gardening, gardening, summer cottages economy or for the conduct of dacha farming by other legal entities, within the boundaries of the territory in respect of which, in accordance with the legislation on urban planning activities, an agreement on its development has been concluded (for example, if it is necessary to demolish a block of dilapidated housing and build a new one in its place), within the boundaries of an element of the planning structures built up with apartment buildings (that is, again within the boundaries of the block), for the placement of linear objects of federal, regional or local significance (pipelines, power lines, etc.). Thus, large-scale issues of land development require a land surveying project, but in other cases, you can get by with a land plot layout diagram. In addition to executive bodies of state power or local government bodies, citizens and legal entities can participate in the preparation of a land plot plan. The validity period of the decision to approve the scheme is two years. Moreover, if the boundaries of the land plot, which is formed in accordance with the site layout diagram, intersect with the boundaries of the site or plots formed in accordance with the territory surveying project, approved after the date of approval of the site layout diagram and before the expiration of the decision on its approval, formation land plot is carried out in accordance with the approved layout plan. The procedure for obtaining a plot through the procedure of preliminary approval of the location of the object has been abolished. Since March 1, 2015, a closed list of documents has been established - the grounds for transferring the right to a land plot owned by the state or municipality. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 39.1 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, the grounds for the emergence of rights to land plots provided from lands in state or municipal ownership are: § a decision of a state authority or local government body in the case of the provision of a land plot into ownership free of charge or for permanent (perpetual) use; § purchase and sale agreement in case of provision of ownership of a land plot for a fee; § lease agreement in case of provision of a land plot for rent; § agreement for free use in case of provision of a land plot for free use. At the same time, as a general rule, the sale of state or municipally owned land plots, the main type of permitted use of which is the construction of buildings and structures, is not permitted. Exceptions to this rule are provided in paragraph 2 of Art. 39.1 and paragraph 2 of Art. 39.3 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (in particular, exceptions include land plots formed as a result of the division of a site, provided by a non-profit organization created by citizens for the comprehensive development of the territory for the purpose of individual housing construction and related to public property of this non-profit organization). It should also be noted that the new rules do not provide for obtaining land without bidding through the procedure of preliminary approval of the location of the facility, and the main forms of providing public land for construction are rent and auction. Now, during an auction, it is prohibited to combine two or more land plots that are state or municipal property into one auction lot, unless otherwise provided by federal law. Also in accordance with paragraph 14 of Art. 39.8 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, a lease agreement for a land plot located in state or municipal ownership cannot establish requirements for the performance of any work or provision of services that entail additional costs for the tenant not related to the subject of this agreement, unless otherwise provided by federal law . This means a direct ban on the inclusion in the text of the agreement of any “social” or “investment” conditions that took place in previous practice. Methods for transferring rights to a state or municipal land plot The Land Code, as amended by Law No. 171-FZ, establishes various ways to transfer rights to a state or municipal land plot: 1) into ownership for a fee (Article 39.3 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The sale of land plots in state or municipal ownership is carried out only at auction. Without holding a tender, land plots are sold in a special manner for the integrated development of the territory, for individual housing construction, for gardening, gardening, dacha farming, for owners of buildings, structures or premises in them; 2) free of charge (Article 39.5 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The provision of state or municipal land to a citizen or organization free of charge is carried out on the basis of a decision of the authorized body. Including in the following cases: to a person with whom a territory development agreement has been concluded; a religious organization that owns buildings or structures for religious or charitable purposes; municipal employees in accordance with subparagraph. 7 paragraph 2 art. 39.10 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, large families in cases provided for by law; 3) for rent (paid temporary use). According to Art. 39.6. Land plots of the Russian Federation in state or municipal ownership are leased at auction and without auction. Without holding a tender, land plots can be provided to: § legal entities in accordance with the decree or order of the President of the Russian Federation; § legal entities in accordance with the order of the Government of the Russian Federation for the placement of social and cultural facilities, the implementation of large-scale investment projects; § legal entities in accordance with the order of the highest official of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation for the placement of socio-cultural and public utility facilities, the implementation of large-scale investment projects; § legal entities for the placement of facilities intended to provide electricity, heat, gas and water supply, sewerage, communications, oil pipelines, facilities of federal, regional or local significance; § formed from a land plot in state or municipal ownership, including one provided for the comprehensive development of the territory, to the person with whom the land lease agreement was concluded; § formed from a land plot provided to a non-profit organization created by citizens for the integrated development of the territory for the purpose of individual housing construction, with the exception of land plots classified as public property, to members of this non-profit organization or, if provided for by a decision of the general meeting of members of this non-profit organization , the non-profit organization itself; § to complete construction for owners of unfinished construction projects; § for running a peasant (farm) economy; § for the development of the territory for the purpose of constructing economy-class housing or for the integrated development of the territory for the purpose of constructing economic-class housing; § owners of buildings, structures, premises in them and (or) persons to whom these real estate objects are provided with the right of economic management or, in some cases, with the right of operational management; § formed within the boundaries of the built-up territory - to the person with whom the agreement on the development of the built-up territory was concluded; § citizens for individual housing construction, running personal subsidiary plots within the boundaries of a populated area, gardening, dacha farming, citizens and peasant (farm) farms for the peasant (farm) farm to carry out its activities; § when withdrawing land plots leased by a citizen or organization for state or municipal needs; § in others listed in Art. 39.6 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation in cases; 4) for free (temporary) use (Article 39.10 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Land plots may be provided for free use to a limited number of persons. In particular, to state authorities and local governments, state and municipal institutions (budgetary, state-owned, autonomous), state-owned enterprises, centers of historical heritage of the presidents of the Russian Federation who ceased to exercise their powers, in the form of official allotments to employees of organizations, religious organizations for placement of buildings, structures for religious or charitable purposes for a period of up to ten years. Special attention is paid to the right of free use of land by a citizen. A citizen may be provided with a plot of land for temporary use for running a personal subsidiary plot or for a peasant (farmer) farm to carry out its activities in municipalities determined by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, for a period of no more than six years, for individual housing construction or running a personal subsidiary plot. in municipalities determined by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, to citizens who work in such municipalities in specialties established by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, for a period of no more than six years, if on the land plot there is service residential premises in the form of a residential building provided to this citizen, for the period of the right to use such residential premises. A detailed list is given in Art. 39.10 Land Code of the Russian Federation; 5) for permanent (indefinite) use (Article 39.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Land plots in state or municipal ownership are provided for permanent (indefinite) use exclusively to state authorities and local governments, state and municipal institutions (budgetary, state-owned, autonomous), state-owned enterprises, centers of historical heritage of the presidents of the Russian Federation who have ceased to serve their powers. Each method of acquiring a land plot has its own characteristics. The new edition of the Land Code of the Russian Federation has determined the features of acquiring a land plot at auction and without auction, as well as for a fee and for free. 1). Acquisition of land at auction (Articles 39.11-39.13 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The formation of a land plot for its sale or lease through an auction is carried out in the following order. The authorized body prepares and approves the layout of the land plot if the plot has not been formed by this time (this is yet to be done) and there is no approved land surveying project. If the formation of a site is provided for by a territory surveying project or a site layout plan, the authorized body ensures the implementation of cadastral work, as well as cadastral registration and registration of rights to the site (except for cases where the site is formed from lands for which state ownership is not demarcated). After this, the authorized body receives technical conditions for connecting (technological connection) of objects to engineering and technical support networks (exception - cases when, in accordance with the permitted use of the land plot, the possibility of constructing buildings, structures is not provided for, and cases of holding an auction for the right to conclude a land lease agreement plot for integrated development of the territory or running a dacha farm). After these procedures, the authorized body makes a decision to hold an auction. However, as a general rule, combining two or more land plots that are state or municipal property into one auction lot is prohibited. It is important that an auction, as well as the formation of a land plot for its sale or lease through an auction, can be carried out on the initiative of a citizen or company interested in providing the land. In this case, the listed preparatory actions are carried out by the interested person himself. 2). Providing land to citizens free of charge (Article 39.19 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). There is a procedure for one-time provision of a land plot to certain categories of citizens. These are citizens with three or more children, in the case and in the manner established by state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as other citizens and (or) non-profit organizations created by citizens, in cases provided for by federal laws, and certain categories of citizens in cases provided for by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (Heroes of Socialist Labor, Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation, etc.). 3). Provision of a land plot for buildings and structures (Article 39.20 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The exclusive right to acquire a plot of land as a property or lease belongs to citizens and legal entities that are the owners of buildings and structures located on such plots of land. Moreover, if the premises in a building or structure located on an undivided land plot belong to one person with the right of ownership, other persons with the right of economic management and (or) operational management, or if several buildings or structures belonging to the same persons are located on an undivided land plot persons with the right of ownership, and others with the right of economic management and (or) operational management, such a land plot can be provided to these persons for rent with a plurality of persons on the lessee’s side. The authorized body has the right to file a lawsuit to force the copyright holders of a building, structure or premises in them to enter into a lease agreement for the land plot on which such a building, structure is located, if none of the specified copyright holders has applied to acquire the right to the land plot.
Legal consequences of land allocation
The legal consequences of the allocation of a land plot may be as follows:
- The original (transformed) site changes its area and boundaries, otherwise its legal regime remains the same.
- The newly created (allocated) plot is taken into account as an independent property. By default, it acquires the legal regime of the original object: it belongs to the same category and territorial zone, and the same types of uses are allowed in relation to it.
- After the allocation, easements and encumbrances continue to operate within the same legal scope and territorial boundaries.
- The shareholder, upon whose application the plot is allocated, becomes its sole owner. He loses the right of shared ownership of the reduced original plot.
- The remaining shareholders retain their rights to the transformed plot, and their shares increase proportionally. Considering that the area of the common property has decreased, objectively the scope of the rights of the co-owners remains the same, that is, in the event of a division, they will be able to claim the same area as before.
Terms of service
To receive a free plot of land, several conditions must be met: the land must fall under the type of permitted use, that is, for individual construction.
There are several other conditions for receiving a free allotment:
- If a citizen does not, and has never had, his own plot of land for individual housing construction or running a personal household.
- There must be permanent registration in the Russian Federation for at least 5 years.
- If he lives in a private house, but not its owner.
- If you live in dormitories with your family, or the standard living space in an apartment is less than that required for 1 family member, then this is a condition for receiving a free land plot.
- If citizens fall under the category of “young family”, or there is only one parent in the family who does not own land.
- Young professionals who graduated from higher educational institutions and came to live and work in rural areas upon concluding an open-ended employment contract with the local administration of the settlement.
- Those young specialists who will work in budgetary local organizations, for example, in the educational or medical field.
It is worth noting that land for individual construction is first formalized as a land lease agreement for a period of up to 3 years. After the house is completed and put into operation, the land can be registered free of charge.
The procedure for allocating a land plot to shared ownership
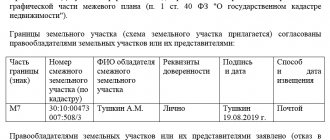
Art. 252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation guarantees the shareholder the opportunity to demand the allocation of his share from the common property. The procedure is carried out on the initiative of one or more co-owners of the site, which is in shared ownership.
To carry out the allocation, the consent of all interested parties is required, including tenants, mortgagees and pledgees (Article 11.2 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The opinion of the persons in whose favor the easement is established is not sought.
The allocation of a share of a land plot in kind can be the result of:
- the decision of the shareholders adopted at the general meeting on the application; interested person;
- court verdict.
The decision of the general meeting of shareholders approves:
- land surveying project;
- a list of owners of the created plots, if there are several of them;
- recalculation of shares for the original plot.
If a plot is formed on the basis of a decision of a meeting of shareholders in accordance with the land surveying project approved by this meeting, then additional approval of the location of the boundaries of the new plot is not required. Otherwise, the owner of the allocated share turns to the cadastral engineer. The latter, on a contractual basis, prepares a land surveying project for allocation against the land share.
The size of the allocated plot is determined on the basis of documents certifying the right to a land share. Taking into account the specific configuration of the land plot and the properties of the soil, the final area of the allocated plot may differ from that indicated in the title documents, up or down. Persons whose rights have been violated may request monetary compensation.
What you need to do to get land for free
- If the location of the plot has been agreed upon with the administration, then it is necessary to write a statement about the decision made on the location of the plot.
- Order a cadastral plan of the land.
- The authorities notify neighboring owners about the provision of land for the construction of individual houses.
- Write an application to check the communications passing through the site, obtain permission to carry out construction work from the architectural department of the district. After the work is completed, the absence or presence of infrastructure facilities is noted on the plan.
- They draw up an act with the local administration on the transfer of the selected site for construction work.
- Then again a cadastral specialist is needed; according to his information, the plot can be registered with the cadastral register.
Let's talk separately about permission to build a residential building. Without this document, all work performed will be considered illegal, and the constructed house will be demolished.
To do this, topographic documents for the site are submitted to the settlement administration, where all communications passing through the site are marked. The authorities will independently regulate the issue with the real estate department. After 30 days, you can obtain a building permit.
Allocation of land through the court
If the shareholders were unable to reach an agreement on the method and conditions for dividing the common plot, the interested party has the right to allocate the land plot through the court on the basis of Art. 252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Based on the results of the consideration of the case, the court has the right to refuse the plaintiff-shareholder if the allocation is impossible without disproportionate damage to the common property associated with the impossibility or inconvenience of its use for its intended purpose (clauses 35, 36 of the joint Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court and the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 01.07.96 No. 6/8 ).
In case of refusal, the interested party is faced with a choice: to remain a co-owner of the property or to demand monetary compensation from the remaining shareholders. As a general rule, replacing the allocation of a land plot in kind with such compensation requires the initiative of the right holder.
However, the court has the right to make such a decision on its own initiative without the consent of the shareholder if:
- its share is insignificant;
- it cannot be isolated in nature for technical reasons;
- the shareholder is obviously not interested in using the common plot.
If the allocation is carried out through a court, the latter’s verdict is recognized as a document of title and a full replacement for the decision of the general meeting of shareholders for the purposes of state registration.
What types of memory transfer exist?
According to the law, there are 4 options for providing land from the state to individuals and legal entities:
- sale (bidding may take place or the right of first refusal may be exercised without it);
- rent (also through tenders or without them, if there are intentions to extend the contract);
- permanent unlimited use (with or without timely payment for the use of the site);
- gratuitous temporary use (provided if the applicant has the opportunity to use such a right on a preferential basis).
When receiving a free plot of land, a purchase and sale agreement is drawn up, but the recipient does not make any payments. This happens for the reason that when preparing the necessary documentation and paperwork, a person will spend a certain amount of money.
In the case of provision of a land plot in the form of gratuitous fixed-term use, a loan agreement is drawn up, where the applicant for the land is the borrower, and the state is the lender.
Certain categories of citizens have the right to receive land from the state:
- citizens with three or more children and young families who have not yet enjoyed the right to land from the state;
- Veterans of Labor of the Russian Federation and the Soviet Union;
- Heroes of the Russian Federation and the Soviet Union;
- young specialists (doctors, teachers).
For these categories of citizens, there is a special procedure for receiving land from the state on a preferential basis and special programs.
Details about the different types of land use can be found here.
Registration of land allocation
A shareholder interested in the allocation will receive significant relief when registering with the State Property Committee. To form a site you only need:
- application for registration of a newly formed facility;
- documents necessary for its cadastral registration.
The state does not oblige the shareholder who is allocating a land plot to submit an application for registration of changes in the boundaries and area of the converted object (Article 24 No. 221-FZ “On the State Real Estate Cadastre”). Their registration is carried out automatically within three days from the date of state registration of the right to the allocated plot.
The procedure for state registration of land plots by allotment is established by Art. 22.2 of Federal Law No. 122 “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it.” The legal basis may be:
- agreement on the allocation of land plots;
- decision of shareholders to approve the layout of the allocated plot on the cadastral plan of the territory;
- decision on preliminary approval of the provision of a land plot in public ownership;
- decision to seize a site for municipal and state needs;
- court verdict as a self-sufficient legal document.
State registration of the creation of a site is carried out on the basis of an application from an interested person, to which are attached:
- title documentation for the original plot (not provided if the converted object is registered in the Unified State Register);
- notarized consent of copyright holders (tenants, mortgagees and pledgees) for the allocation.
The legal basis for state registration of ownership of a plot formed during the allocation on account of a land share is recognized as documents confirming the ownership of such a share. Attached to them is a photocopy of the minutes of the general meeting of shareholders - co-owners of agricultural land, certified by an authorized official of the municipality, which approved:
- land surveying project;
- list of owners of newly created objects;
- their shares in the common area.
Simultaneously with the registration of ownership of newly formed plots, state registration of existing restrictions and encumbrances is carried out. If the rights to the original (transformed) plot are not registered in the Unified State Register, then they are registered simultaneously with the allotment. It is noteworthy that an entry is made in the register about both new (changed) and old (existing before the allocation) boundaries.
Registration of the allocation of a new object from a land plot that has already been registered in the Unified State Register has the following consequences: the registrar, on his own initiative (without the application of shareholders), enters into the register information about changes in area and shares. In this case, the size of the shares is expressed in simple fractions.
Cost and process of division in 2021
The price for the services in question is quite high. The following factors influence it:
- the price of land plots in the total mass;
- the status of the company carrying out geodetic work;
- the amount of cost for the work in question for the subject;
- the area of the land;
- status that a locality has.
As an example, agricultural lands are valued lower than those intended for individual housing construction. Also, work carried out in the near and far Moscow region differs in cost by up to 10 times.
Sample application for division of land
In addition to the fact that the applicant is required to pay for geodetic and cartographic work, some localities establish as an additional payment the cost of transportation for surveyors regarding arrival at the site. You are allowed to bring them to the place yourself.
The division process begins after the necessary documentation has been prepared and geodetic work has been paid for. Before land surveying begins in real life, specialists develop a diagram that serves as the basis for the work being carried out. After preparing a preliminary project, surveyors visit the plot and carry out demarcations according to what the customer indicated.
When the procedure is carried out between two or more owners, several nuances must initially be taken into account:
- all plots have separate access to the road;
- sections are formed in such a way as to have an even shape relative to the geometry, that is, there should be no wedges or anything else;
- There should be no overlap of allotments, as well as crossing and displacement of boundaries (OPrav _ 171,).
When the listed requirements are not met, land surveying cannot be carried out. The result of land surveying is that engineers carry out a geodetic survey, verify whether the plot corresponds to the established dimensions, and then begin dividing it into shares.
Company employees set boundaries that will divide independent plots. Within the boundaries, the right of a particular person applies. The owner can use it at his own discretion.
Stages of land surveying
During the work, employees of geodetic companies install boundary signs; they are contained in marks that are established by standards. At the initial stage, they appear in the form of temporary pegs; after the marking is completed, a permanent location is determined for them. Major formatting of the main points is also being carried out.
Those signs that are installed are prohibited from being changed arbitrarily until a new survey is carried out. Marks are entered on the allotment map and indicated in accounting records.
The boundaries established during boundary work have legal force and are confirmed in the relevant records. After part of the share has been allocated and boundaries have been drawn, the owner remains to go through the procedure of registering rights to the allotment. To do this, you need to contact the cadastre and cartography department.
In this case, you will need to provide documentary evidence of land surveying:
- boundary project;
- an act confirming the achievement of agreement with neighbors;
- permission to perform this procedure by the remaining owners;
- the act according to which boundary signs were installed.
Act of approval of the location of the land plot limits
With the listed papers, you need to visit the cadastre department and register the plot of land. After receiving the cadastral passport, you will have to collect a new package of documents:
- acts that have legal significance for the allotment;
- cadastral documents;
- evidence of the establishment of boundary signs.
Such documents will be required to register the owner's rights. It is worth considering that after the allotment procedure is implemented, the applicant will only have the deed of title to the old allotment in his hands. Regarding a new site, such a document will be a land surveying act.
Attention! The file cannot be used as a document. It is for informational purposes only.
Allocation of land from agricultural land
There are many reasons why commercial agriculture involves the use of large areas of land. For example, crop production requires sowing changes, the use of special equipment, and land reclamation work. The specifics of agricultural land are taken into account by the legislator when regulating the procedure for the formation of plots.
The allocation of a land plot from such lands is regulated by Federal Law No. 101 “On the turnover of agricultural lands.” The requirements of the Land Code of the Russian Federation and the relevant law are correlated as general and special. In case of conflict, the law must be applied.
Art. 13 of Federal Law No. 74 “On Peasant (Farm) Farming” guarantees the shareholder the opportunity to demand the allocation of a plot on account of his share that arose during the privatization of agricultural land before the entry into force of Federal Law No. 101 for the creation or expansion of a farm. The specifics of allocating agricultural land must be observed in this case as well.
Many legally significant actions with the land share of agricultural land can be carried out without allocation in kind. Among them:
- transfer to trust management;
- contribution to the authorized capital of an agricultural enterprise using a common plot;
- relinquishment of ownership rights;
- will;
- sale/donation to another shareholder, agricultural enterprise or farm member who uses a common plot.
In order to exercise other powers to dispose of land, the share must be allocated in kind. The procedure is regulated by Art. 13 of Federal Law No. 101. It is established that shareholders have the right to allocate agricultural land as shares if this does not contradict the requirements for the formation of agricultural land stipulated by the relevant Law No. 101.
The key feature of the procedure is the need to take into account the condition of the soil (the rules are approved by the constituent entity of the Russian Federation). To achieve these goals, it is allowed to allocate a plot of larger or smaller area than is assumed by the title documentation. In this case, interested parties have the right to claim additional payment.
The allocation of shares from agricultural lands that are in municipal ownership occurs in accordance with the rules in force for private lands.
According to the Land Code of Russia, unused lands of poorer quality are allocated first.
In relation to agricultural land, there is a specific rule on state registration of rights through Rossreestr or MFC. If the original plot is owned by five or more citizens, the procedure can be carried out at the request of a person authorized by the shareholders.
His rights are confirmed by an extract from the minutes of the general meeting, certified by a municipal official (clause 2.1, article 22.2 of Federal Law No. 122).
Author of the article
Features for allocating land for agricultural purposes
The procedure under consideration has its own characteristics in relation to lands allocated for agriculture. This is due to the fact that plots belonging to this category are located in one massif, among which there are fields, meadows, and pastures.
The procedure for privatizing a small plot can cause difficulties for an entity that carries out economic activities. In this regard, the allocation process is implemented by local authorities quite reluctantly. The municipality preferably concludes lease agreements.
Registration of a plot of agricultural land
In most cases, the municipality makes a decision on allocation, after purging and weighing all the nuances. It will be easier to obtain the right to allotment if you initially draw up a lease agreement for the site. This means that individual entrepreneurs at a certain point may initiate a procedure for allotment of such lands. After this, the land is registered as the property of the individual entrepreneur.
In such a situation, the allocation is made according to the discussed algorithm, which is established for cooperatives of summer residents, but you will need to obtain permission from the municipal administration. A ban has been established regarding the allocation of plots from lands related to:
- to areas under special protection;
- protected areas;
- forest and water resources;
- fertile soils.
The remaining plots are allocated at the discretion of the administration.