Who is entitled to additional leave for harmful activities?
Additional vacation days should be provided to those whose workplace is classified as dangerous or harmful working conditions of the 2nd, 3rd or 4th degree. The employer receives such information from experts based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions (SOUT), which is required to be carried out once every 5 years.
It happens that the working conditions of workers were recognized as harmful or dangerous even before 2014, when the rules for certification of workplaces were in effect. Even if SOUT has not yet been carried out, all old benefits for pest workers remain, including the right to additional leave.
Some industries, professions and positions give the right to additional leave without special assessment or certification. For example, if they are listed in the List approved by the Decree of the State Committee of Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions No. 298/P-22 dated October 25, 1974. The duration of the vacation is also stated in it. Thus, an electric manual welder is entitled to 12 additional days of vacation when working indoors. A painter working with a brush with nitro paints – 6 days. If the employer has not carried out certification or a special assessment, benefits for harmful workers should be provided based on the list.
Additional leave for harmful activities is usually added to the main annual leave.
What activities are considered dangerous?
A deviating environment is one where there are factors that have a negative impact on human health. Among them are:
- physical exercise;
- harmful effects on the senses and central nervous system;
- external reasons (temperature, speed, humidity, sounds or vibration);
- IR, UV or X-ray waves;
- radioactive contamination;
- magnetic or electric waves;
- light levels or increased concentrations of chemicals or microorganisms.
In total, there are 4 main groups according to the level of influence on the body:
- optimal;
- acceptable;
- harmful;
- dangerous.
If the accepted standard values are exceeded, the risk of occupational diseases increases. To identify the group of “harmfulness” for the profession in question, it is necessary to carry out certification. If a discrepancy is detected between the positions and the workplace, regarding the information from the qualification directory, the bonus, preferential length of service, vacation and other preferences will be lost.
Duration and terms of additional leave
The minimum duration of annual additional leave, which is established for a pest worker during a special assessment, is 7 calendar days per year.
The number of days may be greater if this is stipulated in the collective agreement or the employer is subject to an industry or inter-industry agreement. The exact duration of leave is indicated in employment contracts.
For example, for construction organizations, the industry agreement of the Ministry of Construction No. 17/20-23 dated December 1, 2021 is in force. It states that the annual additional leave for pests increases by at least 3 calendar days for each degree of harm above 2nd (class 3.2) , and for work with hazardous working conditions (class 4) its duration is at least 14 calendar days.
Employees go on additional vacation according to the vacation schedule drawn up by the employer. In this case, the number of days is calculated in proportion to the time actually worked in harmful conditions. Unlike the main annual leave, additional annual leave cannot be obtained in advance.
Degrees of harm
Working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger are divided into four classes - optimal, permissible, harmful and dangerous working conditions (Article 14 of the Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ).
Harmful working conditions (class 3) are working conditions under which the levels of exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors exceed the levels established by hygienic standards for working conditions. Harmful working conditions are divided into four subclasses:
- 1st degree (subclass 3.1) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, after exposure to which the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, after a longer period than before the start of the next working day (shift) , cessation of exposure to these factors, and the risk of health damage increases;
- 2nd degree (subclass 3.2) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or mild occupational diseases severity (without loss of professional ability) arising after prolonged exposure (fifteen years or more);
- 3rd degree (subclass 3.3) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during working life;
- 4th degree (subclass 3.4) - working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can lead to the emergence and development of severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general ability to work) during the period of work.
Hazardous working conditions (class 4) are working conditions in which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which during the entire working day (shift) or part of it can create a threat to the life of the employee, and the consequences of exposure to these factors cause a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease during work. Working in such conditions is generally prohibited except in emergency situations.
How to calculate the number of vacation days for pest workers
The length of service that entitles you to leave for hazardous work includes only time worked in hazardous conditions. Experience is counted from the date of commencement of work. In this case, every 30 calendar days are converted into full months, and every 12 months - into years.
Periods when the employee was not in harmful working conditions are excluded from the length of service:
- annual leave;
- temporary disability.
The rules for calculating length of service for hazard leave are given in clauses 8-12 of the Instructions, approved. By Decree of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions No. 273/P-20 dated November 21, 1975. It is applied to the extent that does not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, the instructions say that the length of service must include a period of temporary disability. From 01.02.2002 this clause was declared ineffective.
As of 04/01/2017, the paragraph stating that days worked in hazardous conditions for less than half a working day are not counted towards vacation experience. Now part-time days are taken into account even if the employment rate is less than 0.5.
Additional leave is provided for each working year, that is, 12 full months from the date of hire. If an employee works in harmful conditions for at least 11 months in a working year, he will receive full leave. If less - in proportion to the time worked.
This is how days of additional leave are calculated if an employee worked in hazardous work for less than 11 months.
- Determine the average monthly number of working days. Divide the number of working days in a year by 12 months.
- Calculate how many full months the employee worked in hazardous conditions. Divide the “harmful” days worked during the working year by the average monthly number of working days. Round the result to a whole number according to the rules of mathematics. If the number after the decimal point is less than 5, simply discard the extra digits; from 5, round up.
- Calculate the number of vacation days for harmful activities. Divide the days of full leave for hazardous conditions by 12 months and multiply by the full months worked in hazardous conditions.
If the number of vacation days is not a whole number, it is rounded in favor of the employee (recommendation from letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-2/B-1045 dated October 18, 2021). For example, a value of 4.3 is rounded up to 5 days. The work year may span different calendar years. Then the calculation is done for each year separately and the results are summed up.
Possibility of canceling surcharges
If new high-tech equipment is purchased at a production facility that reduces or completely eliminates the negative impact on humans, then the employer is exempt from the need to pay for harmful effects. Also, measures to ensure normal working conditions include the supply of personal protective equipment.
If the influence of factors is not eliminated in full, then the percentage may be reduced according to the totality. Decisions on additional payments (establishment or removal) are made by management based on the examination of the SOUT. If the outcome does not suit the employees, then they may disagree with the commission and contact a higher supervisory body demanding a re-check of the results.
An example of calculating additional leave for harmful activities
The driver was hired on January 11, 2021. Based on the results of the special assessment, he was given additional annual leave of 7 calendar days. According to the schedule, the driver goes on vacation from August 30, 2021.
The driver worked in hazardous conditions for 129 days, and the total working days from the date of his appointment to the start of his vacation was 160.
The number of working days in 2021 according to the production calendar is 247.
Let's calculate how many vacation days a driver is entitled to for damages.
- Average monthly number of working days: 247 / 12 = 21.
- Number of full months due to harmful conditions: 129 / 21 = 6.1. Round up to 6.
- Number of vacation days for harmful activities: 7 / 12 * 6 = 3.5. Round up to 4.
What to do if additional leave is indicated in working days
Basic paid leave is calculated in calendar days. But the duration of additional leave for pests can be set among workers. This happens when the employer has not yet conducted a special assessment and is guided by a list of hazardous industries, workshops, professions and positions. In this case, working days must be converted into calendar days.
- Determine the start of the hazard leave. If additional leave is granted simultaneously with the main leave, then the start date will be the day following the last day of the main leave.
- From the received date, count the working days of additional leave according to the calendar, but according to the schedule of a six-day working week, that is, together with Saturday.
- Calculate how many calendar days there are from the beginning of the sick leave until the last day inclusive.
For example, from August 17, 2021, the pest worker begins an additional vacation of 7 working days. We need to convert them to calendar ones. According to the six-day workweek schedule, the last day of vacation is August 24, 2021. The number of calendar days of leave for harmful activities is 8.
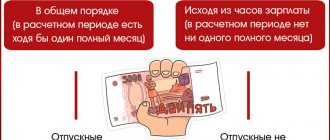
Is it possible to replace vacation for harmful activities with monetary compensation?
It is possible to replace unused additional leave for harmful activities with monetary compensation, but only to the extent exceeding 7 calendar days (Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 15-1/OOG-1710 dated June 18, 2020).
The procedure, size and conditions of such replacement must be specified in the industry (inter-industry) agreement and in the collective agreement. Written consent must be obtained from the employee and formalized as a separate agreement to the employment contract.
Compensation for unused vacation of a pest worker, which does not exceed 7 days, can be paid only upon dismissal.
Ratio of compensation payments for hazardous working conditions
The smallest amount for VUT is 4% of the base salary provided for workers who are not in potential danger at work. The fact of the increase is recorded in the pay slip as a component of the salary that is paid for the specified period.
The amount can be increased at the request of employees or a trade union organization, which is described when signing a collective agreement. An increased percentage of additional payment for harmfulness can be established for selected categories in the staffing table or PVTR. If there were no negative influences from surrounding factors during hiring and they appeared later, then an additional agreement is prepared.
Additionally, existing inter-industry agreements are taken into account, which involve setting an increased percentage.
If the enterprise is located in the northern zone, then a regional coefficient is added to compensate.
When calculating the amount of payment for VUT, a combination of factors that deviate from the norm are taken into account and are determined using a point system:
| Working conditions | Calculation by points | Surcharge amount (%) |
| Heavy, harmful | less than 2.0 | 4 |
| 2.1 — 4.0 | 8 | |
| 4.1 — 6.0 | 12 | |
| Particularly heavy, particularly harmful | 6.1 — 8.0 | 16 |
| 8.1 — 10.0 | 20 | |
| more than 10.0 | 24 |
Scheme
Additional payment to an employee employed at VUT is calculated according to the following algorithm:
- monthly output is multiplied by the piece price per unit;
- the resulting value is divided by the total operating time per month;
- the result is then multiplied by the number of hours in the danger zone, as well as by the percentage (4% or more).
Thanks to the modernization of accounting technology from Cleverence, the formula is calculated automatically based on the entered data.
Penalties for failure to provide leave
An employer who does not provide a harmful worker with additional annual paid leave violates Art. 114 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For this, the labor inspectorate punishes with fines under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- organizations - from 30 to 50 thousand rubles;
- officials and individual entrepreneurs - from 1 to 5 thousand rubles.
For repeated violations, fines increase (Part 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for organizations - from 50 to 70 thousand rubles;
- for officials - from 10 to 20 thousand rubles. or disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years;
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 10 to 20 thousand rubles.
There are relaxations only for representatives of small and medium-sized businesses. Their fines may be replaced with a warning if this is the first time they have violated labor laws.
Features of remuneration
The Labor Code regulates the relationship between workers and company management. So necessity is determined by Article 147, and Art. 219 guarantees compensation measures only for persons directly employed in an enterprise with negative factors. However, they are provided for positions and jobs that are assigned to employees according to the staffing table.
Refusal to assign additional payment to a person is recognized as a violation of the laws of the Russian Federation. Management in such situations is held legally accountable.