Author of the article: Elena Petrenko Last modified: January 2021 29972
In some cases, plaintiffs are faced with an incorrect interpretation of legislative norms by the courts, which believe that the state duty for deprivation of parental rights by individuals must be paid, but is not paid when filing a claim by government organizations. Actually this is not true. To understand this issue, it is enough to study judicial practice and familiarize yourself with its review, approved by the Presidium of the RF Armed Forces on July 20, 2011.
Is it possible to deprive parental rights and paternity for non-payment of child support?
The conditions for deprivation of parental rights are regulated by Art. 69 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, in which clause 1. contains such a basis - evasion of parental responsibilities; the law also includes malicious evasion from paying child support. Thus, the law clearly defines the possibility of deprivation in case of non-payment of alimony.
However, not in all cases, failure to pay alimony can lead to such consequences.
Note: If, in addition to non-payment of alimony, the parent’s actions contain other grounds for depriving him of his rights to children, they can also be reflected in the claim and proven in court.
State duty when dividing jointly acquired property
- up to 20,000 rubles - 4 percent of the claim price, but not less than 400 rubles;
- from 20,001 rubles to 100,000 rubles - 800 rubles plus 3 percent of the amount exceeding 20,000 rubles;
- from 100,001 rubles to 200,000 rubles - 3,200 rubles plus 2 percent of the amount exceeding 100,000 rubles;
- from 200,001 rubles to 1,000,000 rubles - 5,200 rubles plus 1 percent of the amount exceeding 200,000 rubles;
- over 1,000,000 rubles - 13,200 rubles plus 0.5 percent of the amount exceeding 1,000,000 rubles, but not more than 60,000 rubles.
Rationale:
The requirement to divide the joint property of the spouses is property, is subject to assessment and is subject to state duty in accordance with clause 1 of part 1 of Art. 333.19 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Grounds and reasons for depriving a father of parental rights
To deprive a parent of parental rights who evades payment of child support, it is necessary to prove not only the fact of non-payment, but also that it is intentional. In law enforcement practice, intentional evasion is understood to mean the following circumstances:
- Concealing a place of work or other source of income;
- Absence from the place of registration;
- Long-term evasion of employment;
- Prosecution for evasion of alimony payments;
- Other actions indicating the parent’s reluctance to take part in raising the child.
It is especially worth paying attention to evasion of participation in upbringing, for example, if the child’s father does not pay child support, but regularly sees him and gives gifts, then there will be no grounds for deprivation of rights.
On the contrary, if child support has not been paid for several years, enforcement proceedings have been initiated, and the father is not interested in the child, then under such circumstances the second parent or government agency may demand deprivation of parental rights.
IMPORTANT: It is impossible to simply deprive a father of parental rights after a divorce, despite the clear desire of the ex-wives to do this. The Family Code provides an exhaustive list of grounds for deprivation of parental rights.
You are married
There are situations when a man and a woman are married, however, the woman is not satisfied with the participation of her partner in the lives of the children. For example, he pays absolutely no attention to them, does not show up at home for several days, does not feed the children, and does not bring money to the family. The above circumstances are good reasons to classify this as culpable behavior.
In order to prove the dysfunction of your spouse, you need appropriate documents confirming her words. For example, if he is in custody, the girl can provide the judge with a corresponding certificate. If he is an alcoholic or a chronic drug addict, then such data will also be documented. All you need to do is collect all the necessary papers and present them at the meeting.
Should the father or mother be held liable for child support before depriving parental rights?
Yes, because otherwise it will not be possible to confirm the fact of evasion of child support. In 2021, mandatory confirmation of the fact of malicious evasion of alimony payment is bringing to administrative responsibility.
As evidence, repeated decisions on bringing to administrative responsibility under Art. 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation or a sentence in a criminal case of conviction under Art. 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The simple fact of non-payment of child support, not confirmed by measures taken to collect the debt, will not be enough to deprive the father or mother of parental rights.
State duty on cases of increasing the amount of alimony
- up to 20,000 rubles - 4 percent of the claim price, but not less than 400 rubles;
- from 20,001 rubles to 100,000 rubles - 800 rubles plus 3 percent of the amount exceeding 20,000 rubles;
- from 100,001 rubles to 200,000 rubles - 3,200 rubles plus 2 percent of the amount exceeding 100,000 rubles;
- from 200,001 rubles to 1,000,000 rubles - 5,200 rubles plus 1 percent of the amount exceeding 200,000 rubles;
- over 1,000,000 rubles - 13,200 rubles plus 0.5 percent of the amount exceeding 1,000,000 rubles, but not more than 60,000 rubles.
Rationale:
This requirement is also property, since it is expressed in monetary terms, which is why it is subject to assessment and is subject to state duty in accordance with clause 1, part 1, art. 333.19 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
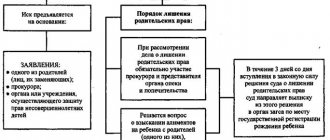
Order and procedure for deprivation of parental rights
An application for deprivation of parental rights is considered exclusively by the court. The applicant can be the second parent, or another citizen who is entrusted with parenting responsibilities, for example, a guardian.
Also, in the interests of a minor child, the guardianship and trusteeship authority or the prosecutor can apply if they receive reliable information about the obvious failure of the child’s parents to fulfill their duties.
Example: The mother of minor Ivan, citizen S., divorced her husband in 2011. Since then, he initially paid alimony irregularly, and for the last two years he stopped paying it altogether. Ivan’s grandmother, civil mother S., wrote a statement to the guardianship authorities with a request to deprive the parental rights of both her daughter’s ex-husband and the child’s mother. As arguments, she indicated that both parents do not take measures to support the child, and S.’s mother does not take measures to receive alimony from the child’s father. In this regard, the guardianship authorities filed a lawsuit in defense of the interests of the minor Ivan to deprive his parents of the rights.
Jurisdiction, where to take documents
This category of cases is heard in the district court at the defendant’s place of residence. If it is impossible to establish the place of residence, the statement of claim is filed with the court at the place of residence of the applicant.
Also, a claim for deprivation of parental rights can be filed at the plaintiff’s place of residence and if one of the claims is the simultaneous collection of child support.
Statement of claim for deprivation of parental rights for child support
A claim for deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of alimony is drawn up in accordance with the general requirements of Art. 131 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. The legislation does not provide for special requirements specifically for this statement of claim.
The claim will need to indicate:
- Name of the court, its address;
- Full name of the parties to the case: the plaintiff is indicated (full name, address), the defendant is the parent (or parents of the child);
- Name of third parties: guardianship authorities and prosecutor, indicating the address;
- The general circumstances of the case are described. Date of birth of the child, circumstances of birth (wedded, out of wedlock), description of family relationships and the relationship of the parent with the child;
- Evidence is provided of the child’s parent’s failure to fulfill his or her duties, as well as other grounds from the law that entail deprivation of rights;
- Links to laws, judicial practice;
- The demand for deprivation of parental rights is announced, and at the same time for the collection of alimony;
- The claim is signed personally by the plaintiff or his representative, a date is set and the attached documents are listed.
Nuances of drawing up and filing a claim
- It is advisable, but not at all necessary, to indicate the prosecutor and guardianship authorities. The court itself will involve them in participating in the case, but cannot return the documents to you due to their absence in the “header” of the application in the list of parties;
- The application itself is best prepared in printed form. The law does not prohibit writing it by hand, but given the nature of handwriting, we strongly recommend typing it on a computer;
- The claim is filed either in person at the court through the reception desk or sent by mail. In rare cases, when the plaintiff has his own digital signature, he can send documents via the Internet.
The judge has 5 days to accept the claim, after which the claim is either accepted or the plaintiff is sent a reasoned ruling with a list of shortcomings. If the deficiencies are eliminated, the claim is considered filed on the original date, but otherwise it is returned. You can correct everything and submit it again without errors.
Sample claim for deprivation of parental rights due to child support
Below is a sample that you can use to draw up your own statement of claim. But remember that the document reflects only a conditional situation, one of many possible ones, and to competently draw up a document in relation to your situation, it is better to enlist the support of a qualified lawyer.
Our specialists are ready to provide advice on any issues related to drawing up a statement of claim for deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of child support. The consultation is free, you can contact them right now!
Ask a Question
IMPORTANT: When drawing up a claim, the most important section is evidence. It is not enough to refer to non-payment of alimony or other facts; they need to be confirmed by the maximum number of facts that are confirmed by the attached documents.
What documents are needed to deprive parental rights: list, list
In addition to the statement of claim for deprivation of parental rights, you must provide the court with a package of documents substantiating the stated claim:
- A copy of the child's birth certificate;
- Divorce certificate – if available;
- A copy of the court decision on the collection of alimony;
- Certificate of arrears of alimony - if enforcement proceedings have been initiated;
- Characteristics of deprivation of parental rights of mother and father;
- A copy of the decisions on involvement under Art. 5.35.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- Information about the criminal case initiated or completed, including a copy of the verdict;
- Other documents indicating the existence of grounds for depriving a parent of rights in relation to a child.
Characteristics for deprivation of parental rights of mother, father (sample)
A certificate for depriving the parental rights of the father or mother of a child is issued by the guardianship and trusteeship authority, as well as other institutions:
- At the place of work;
- According to the place of education of the child.
An approximate example of it can be found on the Internet, but the guardianship authorities draw up the document independently, based on the actual circumstances of the case.
State duty
The state fee when filing an application for deprivation of parental rights is 300 rubles. It can be paid at any bank, payment details can be obtained directly from the court, or you can prepare a receipt for payment on the official website of the judicial authority in the “State Duty Calculator” section.
The payment document is attached to the claim.
IMPORTANT: According to the law, persons who go to court to protect the rights and interests of minors are subject to exemption from paying fees. In some courts, when filing a claim for deprivation of parental rights on the part of the child’s relatives, and not his parents, they still require payment of a fee. This is wrong, but it does happen.
How does the process of deprivation of parental rights for child support work?
In addition to the claim and documents, witness testimony will be required to successfully pursue the case.
The following may be brought in as witnesses:
- Employees from the educational institution attended by the child;
- Medical facility workers;
- Neighbors, relatives, acquaintances.
The testimony they give must confirm the arguments that the parent does not take part in upbringing, or refute them.
In addition, the court will necessarily hear the opinion of the guardianship and trusteeship authorities, so employees of this department can make a preliminary conclusion on the living conditions and upbringing of the minor. A conclusion will also be required during the court hearing.
In some cases, it makes sense to use as evidence the conclusion of a psychological and pedagogical expert commission, which must be done in advance, or to file a petition for its conduct directly in the trial. Experts will determine the child’s attachment and will be able to determine whether his testimony is valid or whether the child is “twisted” by the other parent.
IMPORTANT: If the child’s mother and father live in different regions or cities, the court instructs the guardianship and trusteeship authorities at each place of residence to conduct an examination of the child’s living conditions.
In addition to the listed actions, the court additionally requests, on its own initiative or at the request of the parties:
- Information about the condition of the parents registered in a drug treatment or psychoneurological dispensary (or with a local psychiatrist);
- Characteristics and certificates from the place of work, residence, as well as information from the district police officer about prosecution;
- Information from the territorial commission for minors about whether the parent was held accountable under Art. 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation on grounds other than alimony.
- Other information, if required, to be documented.
Example: At the court hearing, the following testified in defense of the mother’s demands to deprive the parental rights of an unscrupulous father:
- Kindergarten teacher N., who confirmed that the father of minor Ivan repeatedly failed to show up at the kindergarten to pick up the child;
- District pediatrician S., who confirmed that minor Ivan had fresh scratches and traces of blows on his body;
- The mother of the defendant Z., who confirmed that her son does not work anywhere and does not intend to, only helps her grandson with small amounts every month.
The court took into account these testimonies and referred to them when depriving the parental rights of an unscrupulous parent. Since the facts of leaving a child in an educational institution and causing him bodily harm were not documented, the testimony of witnesses was accepted only as indirect evidence. The main reason for the deprivation of parental rights was the extensive arrears of child support.
Consequences of deprivation of parental rights
In the event of a positive decision in the case of deprivation of parental rights, the parent in respect of whom it was made has no right to:
- Represent the interests of the child;
- Demand communication with him;
- Control the educational and educational process;
- Express disagreement with the actions of the other parent in relation to the child;
- Demand child support for your maintenance;
- Be a child's heir.
In fact, from the point of view of the law, the parent ceases to be such, and is deprived of all rights provided for by current legislation for parents.
A person deprived of parental rights may apply to the court for reinstatement, but he must provide sufficient evidence, including not having arrears in child support.
Deprivation of parental rights is the same as deprivation of paternity, but with the retention of responsibilities for financial support of the child. There is a deprivation of parental rights with maintenance of alimony until the child is adopted by a new parent. If adoption does not happen, the deprived parent will pay child support until their 18th birthday.
Arbitrage practice
Consideration of cases of deprivation of parental rights for evasion of child support is not that uncommon. In most cases, claims on this issue are satisfied, because The plaintiffs' arguments are well-founded, and the court always considers the interests of minors.
An analysis of judicial practice in this category of cases allows us to identify two main scenarios in which the process of deprivation of parental rights occurs.
In the first case, a claim is filed directly for deprivation. The court considers it and makes a decision, if the evidence base was good, then in most cases it is positive. This option is optimal in cases where there are several irrefutable arguments about malicious evasion of obligations to support the child, as well as in cases where the father does not object to the deprivation of his rights to the child.
Note: independent renunciation of parental rights is not allowed; if a parent wants to waive the rights to a child, then the second must initiate legal proceedings for deprivation.
The second option involves a longer trial.
- First stage: It is necessary to contact the FSSP with a request to bring the parent to criminal liability for evading the payment of alimony. The bailiffs initiate a case and, upon completion of the investigation, transfer it to court.
- Second stage: After the verdict in this case, a statement of claim is filed for deprivation of parental rights. In all cases, such an application is satisfied because in the first case, evidence will be collected to justify the parent’s dishonest behavior, even if he is not found guilty because an act or omission may not be enough to constitute a crime, but this will be enough to deprive one of parental rights.
If there is a judicial verdict on criminal prosecution, the vast majority of claims for deprivation of parental rights are certainly satisfied.
Evidence base
Like any other court, the family rights court does not make any verdicts without an extensive evidence base. It is worth understanding that the judicial system of the Russian Federation does not care what will happen to the parents in the future.
Its main task is to protect the baby and provide him with every opportunity to achieve a decent future.
If you want to win the trial, then the only way to do this is to provide all the evidence of your spouse’s improper behavior towards a small citizen of the Russian Federation.
Does a father who has been deprived of parental rights pay child support?
Deprivation of parental rights for failure to pay child support terminates all rights in relation to the child, but does not relieve the child from the obligation to support him. A citizen deprived of paternity continues to pay alimony, including if he has a debt on it, he is obliged to repay it.
The amount of alimony remains the same amount or the amount established in the court decision on deprivation of parental rights. The procedure for their retention and transfer also remains the same.
For alimony payments that are delayed, a penalty is charged in the same way as in the case of an eligible parent.
State duty on cases of reducing the amount of alimony
- up to 20,000 rubles - 4 percent of the claim price, but not less than 400 rubles;
- from 20,001 rubles to 100,000 rubles - 800 rubles plus 3 percent of the amount exceeding 20,000 rubles;
- from 100,001 rubles to 200,000 rubles - 3,200 rubles plus 2 percent of the amount exceeding 100,000 rubles;
- from 200,001 rubles to 1,000,000 rubles - 5,200 rubles plus 1 percent of the amount exceeding 200,000 rubles;
- over 1,000,000 rubles - 13,200 rubles plus 0.5 percent of the amount exceeding 1,000,000 rubles, but not more than 60,000 rubles.
Rationale:
The requirement to reduce the amount of alimony is property, since it is expressed in monetary terms, which is why it is subject to assessment and is subject to state duty in accordance with clause 1 of part 1 of Art. 333.19 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.