5
Deprivation of parental rights is a long process, involving several authorities, requiring study and knowledge of legal acts. Therefore, in this case it is difficult to do without legal assistance, and in practice, much more stringent requirements are imposed on depriving a mother of parental rights. According to the law, after a divorce, parents have equal rights to their children, but some willingly fulfill their obligations, while others avoid them in every possible way. Unfortunately, sometimes a mother can also be an unscrupulous parent.
Grounds for deprivation of parental rights of a mother
The Family Code of the Russian Federation lists the reasons why guardianship authorities and judicial authorities are obliged to deprive the mother of parental rights.
| No. | Reasons |
| 1 | Persistent reluctance to raise and support children: pay child support, care for the child, take an interest in his education, health |
| 2 | Refusal to abandon a child in the maternity ward of a hospital, as well as refusal to pick him up from an educational, medical or social institution |
| 3 | Abuse of the rights of family members - use of child benefits, alimony for one’s needs |
| 4 | Alcoholism and drug addiction of the mother, established by relevant documents in a medical institution |
| 5 | Committing a criminal offense against the life and health of close relatives or a child |
These reasons are exhaustive. The court has no right to use other arguments to deprive the mother of parental rights.
Example . Often fathers scare the child's mother that they will deprive her of her rights and take the child for themselves. In most cases, these are empty threats, because the child is always left with the mother, even if she does not work. Only in the exceptional cases listed above, the child can be handed over to the father, and the mother can be deprived of all rights to her child.
It is extremely difficult to deprive a mother of parental rights. Most often, such measures of influence are awarded to generally dysfunctional families, when both parents are deprived of their rights at once. There are much fewer cases when a mother is deprived of her rights to a child, and the latter remains with the father.
Required documents
When there are grounds for depriving the mother of her legal rights to the child, the plaintiff prepares an application and a package of documents to submit to the court. The evidence base must be complete and reliable, otherwise there is a chance of losing the meeting.
The following package of documents must be attached to the statement of claim:
- second copy of the claim;
- child's birth certificate;
- document on marriage and divorce (if any) of the minor’s parents;
- an extract from the house register stating that the child lives with his parents;
- characteristics of parents (from neighbors, supervisor, colleagues);
- characteristics of a minor (from an educational institution);
- a psychologist’s opinion on the child’s mental health (can be obtained through the guardianship authorities);
- an act recording the living conditions of a minor (drawn up by the guardianship authorities);
- certificate of the presence or absence of alimony debt (issued by the bailiff service);
- court verdict (if the woman was previously convicted of any crime, especially related to children);
- certificate confirming that the police were called;
- a doctor’s report on the child’s general condition and the presence of injuries;
- certificates attesting to the mental and physical health of the parents;
- title documents for the premises where the minor will live if he is left with the second parent;
- income certificates of both parents.
The court has the right to request other documentation that will help confirm the grounds for the claims being made.
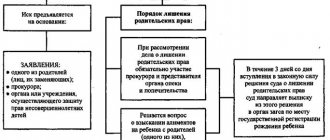
Procedure and order
The procedure for depriving the mother of rights is similar to the mechanism of influence on the father. The issue of depriving a mother of her rights to her child is considered in court.
You can file a claim:
- father of the child;
- legal guardian or trustee;
- guardianship authorities or prosecutor in the interests of the minor.
Who deprives a mother of her rights to her child?
The only body that has the right, on the basis of law, to deprive children of rights is the court. Guardianship authorities, contrary to the opinion of the majority, do not have such a prerogative. Their responsibility is to submit an application to the court and participate in court proceedings, collect evidence, and help the second parent protect their rights.
Guardianship authorities always protect the family, so when they see a difficult situation that threatens the life and health of a child, they do not stand aside. They prepare a conclusion about the unacceptable living conditions of the children and act on the initiative of the second parent or the court.
However, there are situations when government agencies try to interfere in the lives of wealthy families. In such cases, a lawyer will be able to help defend their interests for the child.
Example . Former husband Sergei N. filed a lawsuit against the mother of their common child, Alina N., demanding deprivation of her parental rights. In the lawsuit, the man stated that the woman does not work, has no source of livelihood, often leaves the child with her grandmother, and does not participate in raising her.
The guardianship authorities, having gone to the place where the mother and child lived, found that the child had everything necessary for development: clothes, food, his own room, toys. The mother works unofficially, sometimes on night shifts, so she is forced to involve the child’s grandmother in looking after the baby.
The child's father's claim was completely denied.
Filling out an application for deprivation of parental rights of a mother
A document that contains a demand for deprivation of parental rights is called a statement of claim for deprivation of a mother's parental rights to a minor. It is drawn up within the framework of the Civil Procedure Code (Articles 131-132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation) and is considered only by the court.
The statement of claim must include the following information:
- name of the court, parties, their exact addresses;
- circumstances of the case: information about the marriage, relationship between the child and the parent who is being deprived of rights;
- information about the place of residence of the child and the “problem” mother;
- conditions for depriving a mother of her rights to a child;
- specific actions of the mother that contradict current family legislation and entail loss of rights;
- evidence and references to regulations;
- claim to court;
- date of preparation of the document, personal signature of the plaintiff and list of attachments.
Only a competent specialist will be able to correctly and based on the law draw up a statement in which he will competently and concisely outline the circumstances that worsen the child’s life. You can first consult with our lawyers completely free of charge!
When drafting it yourself, you can use the general sample claim for deprivation of the mother’s parental rights. But be careful - preparing documents yourself often leads to mistakes and may lead to denial of the claim.
Evidence base
At the legislative level, a complete ban is established on interference in the family life of citizens by anyone. Government agencies are no exception. However, there are cases where their intervention is permitted. These are cases of parents failing to fulfill their responsibilities in raising children.
In fact, the procedure for proving failure to fulfill one’s duties is a long and labor-intensive process.
An important role is played by:
- certificates from the place of work, previous, present.
- neighbors' testimony, certificates from clinics about the presence of addiction.
- conclusion of the guardianship authorities;
- information from the police;
- information about the mental health of parents.
This is only a small part of the evidence. Professional lawyers will be able to collect all the necessary documents in the shortest possible time and protect children from unfair treatment by the mother.
Duty
Plaintiffs are exempt from paying fees for claims to protect the rights and interests of minors.
A fee of 300 rubles will be collected from the defendant if the mother is successfully deprived of parental rights.
What to do if they want to deprive you of parental rights?
In order to defend your right to be the legal representative of a child, you need to prepare a powerful evidence base. First of all, you need to collect documents that:
- confirm the proper fulfillment of responsibilities for the maintenance of the baby;
- absence of alcohol and drug addiction;
- characterize you in a positive way.
You should also attract witnesses who can confirm that you treat your child well, that he loves you and is not afraid. Photographs, call printouts, etc. may be used as evidence.
After you receive official notification that a claim has been filed against you, you should file a response (objection) or send a counterclaim. This document must require regulation of the procedure for communicating with the child.
Is it possible to take a child away from its mother without going to court?
The law provides that if there is a threat to both the health and life of a minor in general, he can be taken away without waiting for a court decision. This can be done by the guardianship authorities, who determine the whereabouts of the child and then apply to the court for deprivation of rights.
Most often, the child is handed over to either the second parent or a close relative, who will subsequently be appointed as a guardian. If there are no parents or relatives, then the child ends up in an orphanage.
A family deprivation lawyer will advise you on what cases are considered urgent, how you can prevent this, and also protect yourself from illegal actions of government bodies.
Who can become a guardian?
If the minor has a father, the deprivation is in favor of the father. If the father is already deprived of his rights or the mother is the only parent, then the minor is transferred to the care of the guardianship department.
Specialists must select a family for the child’s future residence. First of all, specialists notify relatives on the father’s and mother’s sides about the current situation:
- grandparents;
- brothers and sisters;
- uncle and aunt.
In order to adopt a child, they must collect documents in the general manner. however, if there are several candidates for accepting a child into the family, priority is given to blood relatives.
If, for health reasons, a blood relative cannot obtain an opinion on the possibility of adopting a child, but he wants to raise him, then his spouse can obtain guardianship.
Placement of foreign citizens of the Russian Federation into a family for upbringing is possible only if there are refusals from all adult blood relatives. If the child has not been placed in a family within 12 months after the court decision, he may be placed in foster care with a family of foreign citizens.
Sample statement of claim for deprivation of maternity by father
Limiting contact with children
Of course, there are situations when failure to fulfill the responsibility to raise and support children is the result of the illness of the parents. These include mental illnesses, due to which parents are not aware of what is happening.
Sometimes the reason for a mother’s inappropriate behavior is a difficult life situation. Regulatory legal acts give the court the opportunity in such cases to limit the child’s communication, removing him from the insane parent.
This is not yet a complete deprivation of rights, but it is already the first stage - the child can be sent to a guardian, and the mother will have the opportunity to prove her parental qualities over the next period of time.
Terms of deprivation and restoration of parental rights
A woman is deprived of her rights indefinitely, but has the opportunity to regain parental rights. She will have to change her lifestyle, correct her behavior, and then file a corresponding application with the court and guardianship authorities.
If at the time of filing the application the child is not adopted, then government authorities will meet the mother halfway. If within six months a woman makes attempts to restore parental rights, the child may be adopted and in the future it will be impossible to restore her rights. The exception is the cancellation of adoption. You cannot demand restoration of rights if the child is already 18 years old.
The court acts solely in the interests of the child, so the mother is given a chance to reform. By changing her lifestyle and proving her correction and intention to raise her child again, a woman can get a chance to exercise maternal rights.
A representative of the guardianship authorities and a prosecutor are involved in the court hearing on the restoration of rights to the child. The woman should invite witnesses who can confirm the change in the plaintiff’s lifestyle and her sincere desire to live with the child again and participate in upbringing. A child who has reached the age of 10 has the right to express an opinion regarding the restoration of the mother’s rights.
Restoring parental rights
Russian laws are humane, therefore, subject to certain conditions, restoration of deprived rights is still possible.
The Family Code includes:
- changing the lifestyle of parents;
- recovery;
- change in attitude towards the child;
Important! All of the above can only be applied if the child has not been adopted. Adoption is possible after 6 months from the date the court decision enters into force. In the future, it will be almost impossible to cancel the adoption without the help of an experienced family lawyer
A family lawyer is necessary in such a situation, since it will not be easy to prove to the court that the parent’s life has really changed. Only a competent specialist with extensive practical experience can do this.
In what cases can a mother not be deprived of her rights?
Deprivation of maternity is applied in exceptional cases, therefore, in the absence of proper evidence, the following can be applied:
- Limitation of motherhood. If the woman is not to blame for the current situation (for example, she does not fulfill her duties due to illness). The law gives a period of 6 months for correction. If the mother does not correct the situation, then she may be deprived of motherhood.
- Warning. If the fact of non-fulfillment of duties is not confirmed in court, a decision on a warning may be issued. In case of repeated application, this fact will be taken into account by the court.
A woman who does not fulfill her duties due to illness cannot be deprived of motherhood. The only option is a lifetime restriction on parental rights. Since the woman is not to blame for the current situation. Lifetime restrictions apply in the case of mental illness and tuberculosis.
If the mother does not work, this is not grounds for deprivation of rights. A woman may have other income (pension, rental housing, alimony from her ex-husband).
A minor mother cannot be deprived of her rights. In such a situation, a guardian must be appointed for the child until the mother reaches 18 years of age.
How to deprive a mother of legal parental rights if she drinks?
Chronic alcoholism is a disease. In order to deprive an irresponsible alcoholic mother of parental rights, she must be registered with a narcologist or undergo a medical examination. A woman is unlikely to agree to do this voluntarily. But if she commits an administrative or criminal crime, she may be forced to undergo an examination.
How can you deprive an alcoholic mother of legal parental rights if there are no medical reports on hand? It's practically impossible. Even numerous witness statements will not help here. If a woman comes to the court hearing sober, she may well refute them, explaining this as a hostile relationship.
If you were unable to obtain a medical report, and you do not know how to deprive an irresponsible alcoholic mother of parental rights, do it in a roundabout way. Surely a drinking woman does not take care of her children properly. Most likely, he often demonstrates cruelty to them. Gather relevant evidence and go to court on these grounds.
Who can become a guardian?
Only fully capable adult citizens. The court will take into account their personality characteristics, moral qualities and financial support. Guardianship is formalized six months after the deprivation of rights.
Consequences for the mother
When deprived of rights to a child, a woman loses absolutely all rights in relation to a minor. The child's father takes the child's accommodation for further upbringing. If the father is absent, or he has also lost his rights, the guardianship authorities assign the child to an orphanage or to the guardianship of the closest relatives.
Consequences of deprivation of rights for the mother:
- The obligation to provide for the child by paying alimony, but at the same time the loss of the right to receive alimony payments from the child in the future.
- Deprivation of the rights to communicate, educate and protect the interests of a minor.
- Cancellation of all existing benefits and benefits that were previously paid to the minor.
- Deprivation of the status of a mother of many children, as well as the right to maternity capital, provided that the child was associated with obtaining such status.
- Evictions from an apartment if it was provided under a social tenancy agreement.
- Impossibility of entering into the inheritance rights of a child, unless otherwise expressly stated in the will.
The child retains the living quarters in which he lived before the mother was deprived of her rights. Based on a court decision and if there are compelling reasons, the mother can be evicted. Based on a court decision and if there are compelling reasons, the mother can be evicted.