Open map
The Labor Inspectorate of Russia is Rostrud and its territorial branches that monitor at the state level the implementation and compliance by employers with labor legislation on the territory of the Russian Federation. This article describes what the labor dispute inspectorate does in Moscow and the Moscow region, what powers it has, how to contact such a government agency and how long it may take to consider labor disputes.
About the company Rostrud
The service was created on March 9, 2004 and is subordinate to the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection. With its help, monitoring of compliance with labor law is carried out. Citizens can also contact Rostrud so that service employees can provide assistance in getting a job.
Rostrud regulates labor relations between employer and employee. The service conducts inspections of organizations and enterprises for compliance with labor laws. It also provides unemployment payments to citizens who are registered with the employment center.
What does the labor inspectorate do for employee rights in the Russian Federation?
Main functions and powers of the labor inspectorate:
- control over the employer's compliance with labor laws;
- guaranteeing the protection of labor rights and freedoms of citizens of the Russian Federation, as well as trade unions;
- providing workers and employers with important information about the most effective ways to comply with labor laws;
- informing the appropriate government agencies about possible violations and abuses that are not covered by labor laws;
- injury research, investigation and recording of emergency situations at enterprises;
- accepting complaints and statements from Russians about non-compliance with labor legislation in relation to them.
labor disputes considers issues simultaneously with other legislative bodies: executive, law enforcement, local government bodies and courts. It turns out that such an organization has the authority to request and promptly receive from these authorities the information required for the high-quality implementation of assigned tasks.
Other phones
Local Rostrud help service numbers:
| City | Contacts | Operating mode |
| Moscow | +7(495)-343-9190 | 09:00 – 17:00 |
| Saint Petersburg | +7(812)-746-5986 | 09:00 – 17:00 |
| Yaroslavl | +7(4852)-48-66-96 | 08:30 – 16:30 |
| Izhevsk | +7(3412)-63-63-08 | 08:30 – 17:00 |
| Ryazan | +7(4912)-76-25-71 | 08:30 – 17:30 |
| Kirov | +7(8332)-63-05-59 | 08:30 – 12:30 |
| Vologda | +7(8172)-72-10-73 | 08:00 – 17:00 |
| Kostroma | +7(4942)-62-42-30 | 08:00 – 17:00 |
| Permian | +7(342)-212-52-23 | 09:00 – 13:00 |
There is a hotline for citizens’ inquiries regarding labor legislation:
+7(495)-698-8206
The Rostrud hotline is only open on weekdays. Payment for calls is made according to the tariff of the mobile operator.
What to do if rights are violated
When an employee's official interests are violated, action must be taken. Legislation now provides workers with freedom to choose means and methods to obtain support.
You can resolve disagreements on your own, alone, or you can turn to certain bodies and committees for help to resolve your issue.
In this case, all options are good. The main thing is not to sit idly by, since inaction gives rise to impunity for the employer and gives him freedom to commit violations.
The main protection body is the State Labor Inspectorate . The inspectorate resolves disputes that arise between employees and management. In order to contact this organization, you need to submit a complaint in writing, outlining the essence of the problem in full.
In any case, the State Tax Inspectorate reviews absolutely all applications, provides answers, and if a violation is detected, sanctions are issued to the boss.
Other ways to contact Rostrud
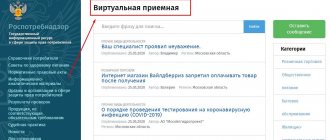
Citizens can send an appeal through the public reception on the official website or use email.
Website
The official website has a built-in “Public Reception” service, where users can report violations:
rostrud.gov.ru/
Social networks
Help center employees advise citizens via social networks on the following issues:
If you are unable to contact the help center by calling the hotline, you can send your request via email:
Personal Area
Through their personal account, users can subscribe to receive the latest notifications about changes in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You can also send an appeal through the public reception. Using your personal account, you can search for work in your region of residence. The “Information and Services” section presents documents that set out labor law standards.
rostrud.gov.ru/pers…
How to complain to the labor inspectorate about an employer
Every citizen of Russia, a group of citizens or a trade union committee of workers can contact this institution when there has been a violation of labor laws against them.
Reasons for complaint:
- wrongful dismissal;
- non-payment of bonus;
- non-payment of wages;
- delay of salary;
- violation or change of working conditions;
- denial of required leave, etc.
The deadline for filing an application when applying to this state organization is established by the Federal Law on State Labor Inspection and lasts 3 months from the time the employee learned that his labor rights were violated. It should be taken into account that if, due to unlawful dismissal, an employee needs to return to the workplace, then it is advisable to file a complaint as soon as possible.
Next, we will look in detail at how you can file a complaint with the labor inspectorate regarding employee rights, as well as possible deadlines for considering applications.
Application Options
There are three options for submitting a claim to the labor inspectorate:
- personally come to the institution with a set of necessary documents and write an application locally;
- send a registered letter to the inspection with a notification, where you need to attach the originals of the necessary documents, but there is a risk that the documents may be lost during shipment;
- ask a question online to the labor inspectorate.
In the latter option, you will also need a number of documents that will need to be scanned, attached to the written application and sent to the institution. This can be done on the official page of the labor inspectorate. All you need to do is select your problem from the list of those proposed, then log in using your Unified Identification of Authorities account and follow the subsequent instructions. Applications to the labor inspectorate for an employer can be made on the official website of the labor inspectorate or on our website.
When contacting such an institution, you need to be aware that it is impossible to submit a complaint anonymously, since such applications are simply not accepted. Therefore, when filling out an application, both in the usual form and via the Internet, it is imperative to indicate correct personal data. In the application itself, if necessary, you can ask for non-disclosure of such information to the other party.
You can consult our free legal consultant on how to correctly fill out an application.
You can also get advice about such a service on the State Services website. However, such an appeal should not be confused with filing a claim with the labor inspectorate.
Individual and collective labor disputes
Compared to collective labor disputes, individual ones are resolved simply. The employee or employer have the right to agree among themselves to resolve the conflict, submit an application to the labor dispute commission or go to court. In accordance with Art. 382 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the bodies for considering individual labor disputes are only the labor dispute commission and the court.
More difficulties arise if the dispute is classified as collective. In this case, the first step is to resolve differences between the parties. To do this, a meeting or conference of employees is held, at which employee representatives are elected and demands are put forward. According to the law, a meeting will be considered valid if more than half of all employees of the enterprise were present; for a conference the minimum threshold is ⅔ of the number of employees. The employer has no right to obstruct the conduct of these events.
Requests drawn up in writing are submitted to the employer, he is obliged to accept them, consider them and provide a response within three days. If the employer satisfies the workers' demands, a labor dispute does not arise. Otherwise, employee representatives have the right to initiate conciliation procedures:
- consideration of all aspects of the conflict by the conciliation commission;
- involvement of an intermediary;
- consideration of the dispute by labor arbitration.
Neither employees nor the employer have the right to refuse to participate in conciliation activities that are carried out within the time limits regulated by law. At the reconciliation stage, workers have the right to defend and voice their demands through demonstrations, rallies, pickets, but only in compliance with current legislation.
Conciliation procedures for resolving collective labor disputes cannot be done without a conciliation commission. Essentially, this is a body created by the two parties within three days from the start of the dispute. The use of a conciliation commission is mandatory. The employer is obliged to provide all conditions for her work, and she herself is obliged to consider the conflict situation within 5 days. The countdown begins from the date of publication of the decree on its creation.
If the conciliation commission was unable to reach an agreement between the parties, by agreement, a mediator or labor arbitration is involved. The law gives three days for this, starting from the drawing up of a protocol by the conciliation commission. If during this time the parties are unable to agree on the choice of a mediator, the creation of labor arbitration begins. It is created with the participation of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment specifically to consider and resolve issues related to collective labor disputes. The next day (after the creation of arbitration) the parties to the labor conflict are required to hold a meeting, during which they decide to entrust the dispute to the created body. If they agree, the parties draw up a written agreement in which they indicate the mandatory execution of the decision of the authority. In case of violation of the agreement, the case is transferred further to the courts. At this stage, it is important to correctly determine the jurisdiction, competently draw up a statement of claim and collect a serious evidence base. Our labor lawyers will help you with this.
Procedure
The Russian Labor Code determines the procedure for protection. Initially, the deadlines for filing complaints must be respected. They are established by Article 392 of the Law. The total period is 3 months from the date of the violation.
If the issue is related to dismissal, then the complaint must be written a month in advance; time begins to tick from the moment you receive the work book.
If damage is caused to an employee by a supervisor, the recourse period is one year.
Do not forget that if an employee did not have time to defend his rights at the specified time due to valid reasons, illness, forced change of housing, business trip, etc., then he can apply later.
Most often, rights are first asserted at the local level - the employee makes verbal demands to his boss. He can send a written application, which must be examined within 30 days.
ATTENTION! If all of the listed methods at the local level did not bring the desired result, and violations could not be avoided, you should contact government agencies for help.
Contacting the prosecutor's office
The activities of the prosecutor's office are aimed at supervising the work of government organizations. Employees can file a complaint with the prosecutor on various issues, including:
- non-payment of wages;
- illegal dismissal, unjustified staff reduction;
- failure of the labor inspectorate to fulfill its duties, etc.
Additional information
You can contact the prosecutor's office in the following ways: 1) send an application by mail, telegraph, fax 2) come to a personal appointment. In addition, each prosecutor’s office must have a box “For appeals and applications,” which is placed in the reception area, and in lower prosecutor’s offices - in a place convenient for citizens.
An appeal to the prosecutor's office must be made in writing (application/complaint) or orally (during an official reception). Collective and individual complaints are considered within 15 calendar days. Additionally, the consideration period may be extended, but not more than by 15 days, if a detailed study of the current circumstances is required. The result of contacting the prosecutor's office is a written report on the work performed and the measures taken in relation to the unscrupulous employer.
The powers of prosecutors include:
- bringing the employer to administrative liability (if there is an administrative offense);
- filing a civil claim in court, acting as a defense on the plaintiff’s side;
- reporting to law enforcement agencies about the existence of an offense.
The listed powers are rights of employees, but not duties, therefore the applicant has no right to demand their execution.
The moment of violation of the rules of the Labor Code is considered the basis for bringing to legal responsibility the perpetrators, who can be both employees and employers. Let's get acquainted with the fines for violating the terms of payment of wages.
Basic methods of protecting employee rights
There are various forms of protecting people's business interests. There are several basic methods:
- Self-defense when the employee acts alone;
- Complaint to the union;
- Complaint to a higher authority;
- Contacting the official labor inspectorate;
- Complaint to the TC Commission;
- Contacting the prosecutor's office;
- Appeal to the courts.
State control involves the implementation of various inspections of the personnel activities of enterprises by the inspectorate for the purpose of calculating violations.
If we talk about presenting an appeal, then everything needs to be done in writing. When defending yourself, you can use an oral statement, the employee making demands on the employer.
ATTENTION! When sending documentation to different authorities, the complaint must be made in writing.
Labor Dispute Commission
A labor dispute commission is a special authority created at a specific enterprise or organization on the initiative of the employer or employees. The body deals with issues of labor disputes, therefore it must include representatives of each party. In turn, the parties to the conflict do not have the right to exert any pressure on the commission members.
To resolve labor disputes through a labor commission, you need to write an application in any form addressed to its chairman. If necessary, documents proving the rightness of the party are attached to the application. No later than 10 days after submitting the application, a meeting will take place, which can take place either in the presence of the applicant or without him. The progress of consideration of the application is recorded and then certified with a special seal or stamp of the organization.
The commission makes decisions through a secret vote of its members. A report on the result is drawn up in writing, which, in addition to the name of the organization and the details of its leader, displays information on the decision of the commission and the results of the secret vote. Copies of the document are transferred to each party to the labor dispute within three days. The commission's decision can be appealed within 10 days. If this does not happen, then after 3 days the decision must be executed.
Certificates issued by labor dispute commissions are equal in force to a writ of execution. However, it is not issued if one of the parties decides to continue the proceedings in court.
Concept and types of labor disputes
In Russian legislation, a labor dispute is understood as a conflict that has formed between an employer and his subordinate, which was submitted for consideration by a court or a special commission. Such disputes may be individual or collective. In the second case, the company may suffer serious losses as a result of the litigation.
Most often, a dispute is preceded by a violation by the employer of the rights of employees. This may be expressed in delayed wages, refusal to provide leave, or illegal layoffs. In addition, there are often conflict situations when the employer makes excessive demands, forces people to work on weekends without pay, and adds responsibilities not covered by the current employment contract.
Often a labor dispute arises when an employee quits and receives a paycheck. Unscrupulous workers try to pay settlements as little as possible and use various tricks to achieve this goal. This is especially true if the employee’s occupation involved material assets.
Causes of labor disputes
The prerequisites for the emergence of labor disputes may be different. Sometimes the culprit here is an incorrect interpretation of the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, both on the part of the employee and his employer. In some cases, the cause may be various technical errors, such as a software glitch.
Most often, the causes and circumstances of labor disputes will be as follows:
- unexpected change in working conditions under the contract for the employee;
- transfer of an employee to another unit or department;
- fines and other types of disciplinary action;
- refusal to provide vacation or days off due under the employment contract;
- non-compliance with the terms of the schedule (for example, instead of the promised 2/2 schedule, you have to work 6 days a week);
- delays in the payment of wages, incomplete payment;
- dismissal (downsizing) of an employee;
- causing property or other damage to an employer or employee;
- unreasonable, as well as violating the rights of a citizen, refusal to hire (for example, due to nationality).
Labor disputes may also arise due to the fault of the employee himself. Here we can name such reasons as showing up at work while intoxicated, systematic violations of work processes, being late, intentional or accidental damage to property, and violation of internal regulations. In these situations, the employer tries to apply disciplinary measures to the employee, up to and including dismissal, but the employee does not always agree with management’s decision. In controversial situations, it is often easier to hire a lawyer who will help defend the rights of the employee or employer without starting a dispute.