- Liability agreement: legislative framework
- Who can you make an agreement with?
- In what cases is financial responsibility specified in an employment contract?
- How to draw up a liability agreement
- Can an employee refuse to sign an agreement?
A liability agreement is a special type of obligation between an employer and an employee, thanks to which it is possible to preserve the valuable property of the enterprise. The document provides for measures to ensure safety and penalties in case of non-compliance by the employee with the established rules. Drawing up and signing a contract has many nuances. The Ministry of Labor provided clarification on the specifics of concluding an agreement in 2021. We have highlighted the main points for you. They will help you decide with whom you can conclude an agreement, and how to behave if an employee refuses to sign.
Liability agreement: legislative framework
The existence of an agreement implies that an employee who damages valuable property or wastes company funds is obliged to compensate for losses. To receive compensation for damage, it is important that the contract is drawn up in accordance with legal requirements.
According to Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in the absence of an agreement, the employer can only rely on recovery of damages in the amount of the average monthly salary of the offending employee. The only exceptions can be considered the situations provided for in Art. 243 TK.
Article 244 of the Labor Code regulates the rules for drawing up contracts with company employees. At the moment, there are two options for financial responsibility:
— complete with drawing up a contract;
— financial liability without concluding a separate agreement.
In the first case, a document is drawn up describing all the rules and actions for preserving valuables, as well as the degree of responsibility for their loss. Regulated by Article 244 of the Labor Code. The second option involves making a record of financial responsibility in the employment contract. The rules are described in Article 24 of the Labor Code.
Damage recovery algorithm
The sequence of actions of the company's top management to compensate for damage should be as follows:
- Determine the amount of damage caused.
- Analyze the reasons that led to it.
- Take written explanations from the employee responsible for the damage or record in front of witnesses the employee’s refusal to give such explanations.
- Establish the amount of financial responsibility of the employee.
- Issue an order for damages or apply to a judicial authority for a decision to withhold money from wages.
Who can you make an agreement with?
As before, it is impossible to oblige all employees to sign a financial liability agreement. The legislation does not provide for such a solution. But there are professions and positions in which signing a document is necessary. You can familiarize yourself with the list in Resolution No. 85 of the Ministry of Labor dated December 31, 2002. An agreement concluded with an employee whose profession is not included in this list will be considered invalid.
In general terms: execution of a separate document is necessary if the employee will directly interact with funds and valuable assets belonging to the employer. For example, such professions include cashiers, collectors, salespeople, and storekeepers.
If the profession is not included in the established list, but job responsibilities include the receipt, storage, transportation of funds, valuables and cargo, an agreement on financial liability can be concluded with the employee.
Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated November 17, 2020 No. 14–2/OOG-17024 regulates the list of positions in which an employee does not have the right to refuse to sign an agreement.
If a company creates a local regulation indicating that employees occupying positions not included in the list bear full financial responsibility, the agreements concluded with them will not have legal force.
When drawing up a liability agreement, you should adhere to three basic rules:
1) the employee must be an adult;
2) it must directly interact with funds or material assets;
3) the profession held by the employee must be included in the list of the Ministry of Labor Resolution No. 85 dated December 31, 2002.
Work of the judiciary
The judicial authorities consider the following cases of matrimonial liability:
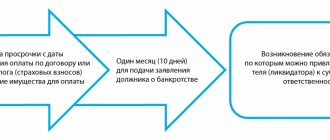
- A claim by the company's management for damages not exceeding the average monthly salary in the event that the money cannot be recovered by order. For example, management missed the deadline established by law for issuing an order; the employee terminated his employment contract with the company.
- A claim by the company administration for compensation for damages exceeding the average monthly salary of the employee.
- Claim by an employee who does not agree with the deduction made by management or with the amount of damages. A necessary condition for judicial proceedings must be the preliminary consideration of the employee’s claim in the prescribed manner.
To apply to a judicial authority, a company manager can use a sample statement of claim.
In what cases is financial responsibility specified in an employment contract?
There are positions in which the employee bears full financial responsibility without concluding a separate agreement. For accountants and deputy directors, an additional clause is provided for this in the employment contract. But this is provided that their work involves direct contact with money and valuables. Otherwise, this clause will not have legal force and the money will be returned only in the amount of the average monthly earnings of the culprit.
The general director of the enterprise is by default the financially responsible person. Even if he does not have a separate agreement concluded and the above-described point is not stated in the employment contract.
Rules for writing instructions
The upper right part of the document contains basic information about the company and its leader. Typically, the organization's letterhead is used for this. The name of the instruction is written below in the center. After the text of the instructions itself, the specialist’s signature and its transcript are placed. You can also add the signatures of the responsible persons with whom the appointment is agreed upon. They may be the head of the warehouse or the deputy director of logistics.
General section
This section describes the qualification requirements for a storekeeper. It also regulates the process of temporarily replacing a specialist and the nuances of the procedure for his appointment and dismissal.
The qualifications of a storekeeper are subject to standard requirements: specialized experience and completed education at the school or technical school level. In addition, a list of knowledge that a specialist must have to get a job is given.
The section also contains standards that the storekeeper must follow.
Responsibilities
The section serves to list the functions that a storekeeper must perform. This includes responsibilities related to the main areas of warehouse work:
- document flow in the warehouse;
- acceptance of valuables into the warehouse;
- issuance of valuables from the warehouse;
- storage of valuables in a warehouse;
- informing about problematic issues in warehousing.
All functions related to these aspects of the storekeeper’s work must be described comprehensively in order to prevent work conflicts and disagreements.
Rights
This section establishes the rights of the storekeeper. In addition to general rights, it is necessary to focus on the right to receive data from employees of the organization, which is very important for the warehouseman to fulfill his duties.
The rights defined in this section must be related to the storekeeper's job responsibilities. Too broad or narrow the scope of rights can lead to confusion in the work.
Responsibility
The section serves to indicate the main prerequisites for bringing the storekeeper to various measures of responsibility. The section does not prescribe specific measures or penalties - they are determined during internal legal proceedings.
Additional sections
Their inclusion in the instructions makes sense if the goal is to more fully describe individual aspects of the storekeeper’s activities. For example, you can specify working conditions or job relationships.
The completed agreed instructions are printed on letterhead. In this case, the principle is observed: one specialist - one instruction. The document contains basic information about the specialist (his full name and passport details). At the final stage, signatures are placed: the storekeeper himself, the director and the person with whom, according to the rules of the organization, this appointment must be agreed upon.
The presence of a seal in the instructions is not required.
How to draw up a liability agreement
For the document, you can use the forms proposed by the Ministry of Labor or develop your own template. The main thing is to adhere to the established rules when drawing up.
There have already been precedents when the court refused to recognize the legal force of a document due to the absence of certain points. To prevent this from happening, be sure to check the following conditions in the contract:
Carefully describe the conditions for the transfer, reception and storage of valuables. In particular, indicate the document regulating the process and the responsibilities of the parties. Also indicate what the employee must do to protect assets and what actions are prohibited.
Indicate how and when the safety of the valuables entrusted to the employee will be checked (audit, inventory).
Establish the level of responsibility of the employee. After all, not in every situation the employee is to blame for damage or loss of valuables. List the circumstances under which he is not financially liable for damage. For example, in the absence of proper storage conditions, during natural disasters.
Add a clause about the method of compensation for damages. The phrase “the procedure for determining and compensating for damage is determined by current legislation” is usually used.
The liability agreement is drawn up in two copies when the employee is hired. One remains in the custody of the personnel department, the second is transferred to the employee.
Collective MO
The most common type of DMO.
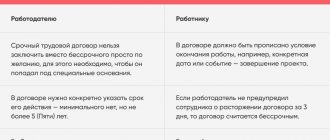
Its presence is regulated by Article 245 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which directly indicates its creation in the case when it is not possible to differentiate the responsibilities of storekeepers when performing work together. This type of DMO is also convenient because it practically does not require re-contracting in the event of the dismissal of one or more employees. It should be remembered that if the team changes by more than 50%, as well as if the head of the warehouse (or team) changes, the collective DMO must be re-concluded, as it loses legal force .
Can an employee refuse to sign an agreement?
Cases when a liability agreement is signed with an already working employee are quite rare. The legal value of a document concluded after hiring is difficult to prove. Often in such situations the problem has to be resolved through the courts.
Typically, a contract is signed upon hiring. In such a situation, the employee’s categorical refusal to sign the agreement can be considered as unwillingness to occupy the specified position.
If the profession involves financial responsibility, and the applicant refuses to sign, you have the right to refuse to hire him. This situation is interpreted as a lack of agreement on important labor issues.
If an existing employee refuses to sign a contract, this is regarded as a refusal to perform job duties and serves as a valid reason for dismissal.
By adhering to the above rules, you can protect your company from unwanted financial losses and protect against unnecessary litigation.
Specifics of the document
The instructions are useful in that they define the powers of the storekeeper, the scope of his responsibility and the scope of working relationships. All this, provided it is clearly formulated, contributes to the organization of a clear and harmonious work process.
For the warehouse manager, who is subordinate to the warehouseman, this instruction simplifies warehouse management.
In addition to these points, the instructions are used to prevent conflicts at work, as well as as a legally significant document in judicial and pre-trial proceedings. All of the above determines the importance of correct and thorough writing of the job description.
Results
Material losses of the company caused by the fault of its employees are subject to compensation.
To recover damages, the employer will have to work hard: take an inventory, create a commission, calculate damages, etc. All stages of this process, as well as general issues of interaction between the employer and employees regarding the safety of property are reflected in the provision on financial liability. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Briefly about the main responsibilities
The storekeeper in a warehouse is considered one of the key figures; he has enormous responsibility and, accordingly, responsibilities:
- Organize the work of the warehouse in such a way that all employees are involved and their working resources are sufficient for the normal functioning of the enterprise.
- Manage and directly participate in such warehouse operations as receiving goods, allocating space for them, moving goods around the warehouse, safety, ensuring proper temperature conditions and storage conditions for products.
- Assemble and package goods in accordance with consumable documentation and adhere to rotation (FIFO principle - first in, first out).
- Control of loading/unloading time of transport, organization of relevant work.
- Receiving and processing returns to and from the warehouse.
- Drawing up reports of substandard conditions, making write-offs within the limits of one’s capabilities.
- Maintaining incoming and outgoing documentation.
- Conducting inventories, reporting on recounts to the immediate supervisor and higher management.
- Monitoring the serviceability of inventory and other warehouse property.
- Compliance with labor regulations, safety regulations, and sanitary standards in person. Monitoring compliance by subordinates.
- Monitor the availability and serviceability of fire fighting equipment and the condition of the premises. Drawing up and timely submission of defective statements for faulty inventory, equipment, etc.
- Carry out other official assignments received from the manager.
Appendix No. 1 to the provisions on financial liability (as amended in 2021)
Guidelines for financially responsible persons of Ulyanovsk State University
1. General Provisions.
1.1 Financially responsible persons of USU are understood to be persons who have entered into an employment contract with the university and bear full financial responsibility for the shortage of property entrusted to them in accordance with the Regulations on financial liability and the legislation of the Russian Federation.
1.2 Financially responsible persons are appointed by the rector upon the recommendation of the head of the department and in agreement with the chief accountant of Ulyanovsk State University, with the further conclusion of an agreement on full financial responsibility.
1.3 The employee’s full financial liability consists of his obligation to compensate the direct actual damage caused to the university in full.
1.4 Financial liability in the full amount of damage caused is assigned to the employee in the following cases:
- lack of valuables entrusted to him,
— intentional infliction of damage;
— causing damage while under the influence of alcohol, drugs or other toxic substances;
— damage caused as a result of the employee’s criminal actions established by a court verdict;
— damage caused as a result of an administrative violation, if established by the relevant government body;
— damage caused by an employee’s failure to fulfill his job duties.
1.5 The amount of damage caused to the university due to loss and damage to property is determined by actual losses, calculated on the basis of market prices prevailing in the area on the day the damage was caused, but not lower than the value of the property according to accounting data.
1.6 The financially responsible person is obliged:
— ensure complete safety of monetary or material assets taken into account
- carefully handle the material assets entrusted to him and monitor their use. In the event of a breakdown or damage to fixed assets, the financially responsible person must report this to the head of the unit and, if necessary, draw up a report indicating the reasons and those responsible.
— If the premises are discovered to be tampered with (the seal is damaged, the door, window is open, etc.), the financially responsible person is obliged to inform the UlSU security service and the head of the unit about this.
1.7 Heads of departments are obliged to:
- create conditions for employees necessary to ensure complete safety of the property entrusted to the employee;
- timely take measures to identify and eliminate the causes that impede the safety of entrusted property, identify specific persons responsible for causing damage;
-introduce employees to the current legislation on the financial liability of employees for damage caused to the university, as well as other regulatory legal acts (including local ones) on the procedure for storing and carrying out other operations with the property entrusted to them;
-consider reports from employees about circumstances that threaten the safety of the property entrusted to them and take measures to eliminate these circumstances.
1.8 Inventory of material assets, unfinished construction, and funds is carried out in accordance with the methodological instructions approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 49 dated June 13, 1995. and instructions for budget accounting, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance No. 174n dated December 16, 2010. Inventory surveys at the university are carried out according to the orders and instructions of the rector
Inventory is also a check of the work of the financially responsible person.
2. Accounting for material assets and control over their safety and operation.
2.1 All departments of the university are supplied through a central warehouse, except for computer software, when the contract manager is the head of the Department of Information Technology and Telecommunications.
Computer software, components and consumables are received from the supplier by the materially responsible person of the Department of Information Technologies and Telecommunications.
2.2 Accounting and storage of fixed assets.
The issuance of fixed assets from the warehouse into operation is carried out upon request - invoice f.0504204 , fixed assets worth up to 10 thousand rubles according to the statement of issue for the needs of the institution f.0504210 .
On the fixed asset, the financially responsible person must put down an inventory number, which is assigned by the accounting department of Ulyanovsk State University.
When releasing a fixed asset from the warehouse, the inventory number must be entered in the warehouse by the manager. warehouse
The number must be affixed with indelible paint or in another way that ensures the safety of the marking.
The number must be readable during inventory. If the object is complex, i.e. includes separate elements that form a single whole with it, then each such element must be marked with an inventory number.
The financially responsible person is required to maintain an inventory list of fixed assets.
For the transfer of fixed assets from one financially responsible person to another, issue an invoice for internal movement (f.0504102).
The financially responsible person transferring the object excludes this object from the inventory list, and the person receiving it includes this object in his inventory list.
In the classroom or room where fixed assets are located, the financially responsible person must draw up an inventory of fixed assets indicating the name, inventory numbers and their quantity.
When issuing material assets to a university employee for temporary use, the financially responsible person fills out an obligation card (for computer technology – workplace passport) with receipt of a receipt and indicating the date of return.
A fixed asset is deregistered in cases where it cannot be repaired or it is impractical to repair it.
2.3 When writing off fixed assets that have become unusable, fill in:
- defective statement (with a cost of over 100 thousand rubles - expert opinion )
— act of write-off of fixed assets f.0504104 (except for vehicles),
— minutes of the meeting of the commission on write-off of fixed assets.
The act of writing off fixed assets is signed by the commission and approved by the rector.
Fixed assets written off according to the act are confiscated from financially responsible persons and delivered to a warehouse for subsequent disposal; if necessary, they are dismantled (dismantling act).
Materials received from the liquidation of fixed assets and remaining at the disposal of the university must be capitalized.
Dismantling and dismantling of fixed assets before the approval of acts on their write-off is not allowed.
Fixed assets that have not reached their standard useful life and have a residual value are written off in a special manner.
2.4 Accounting, storage and write-off of inventories.
Material supplies are issued from the warehouse only to materially responsible persons upon request - invoice f.0504204.
Household and consumable materials, in accordance with the approved standards of the University, are issued to materially responsible persons according to the statement of issue for the needs of the institution f. 0504210 with simultaneous debiting from the balance sheet.
Alcohol is also issued from the warehouse upon request - invoice f.0504204.
The movement of material assets between financially responsible persons is carried out upon request - invoice f.0504204 .
Soft inventory items should be marked in the warehouse with a stamp without damaging the appearance of the item, indicating the name of the Ulyanovsk State University, with indelible paint, and when put into operation, additional marking should be done indicating the year and month.
Accounting for material reserves shall be kept by financially responsible persons in the inventory book by name and quantity.
The financially responsible person should keep records of alcohol in a journal, which must be numbered and laced.
Accounting is carried out in physical terms.
Keep records of precursors in a journal for registering transactions related to the circulation of precursors, narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, which must be numbered and laced. Accounting is carried out in physical terms.
Keep records of broken dishes in the broken dishes registration book f.0504044 (for canteens).
2.5 Write-off of spent inventories is carried out in the following form:
— Act on write-off of inventories (0504230),
- Statement of issuance of material assets for the needs of the institution (0504210),
-Act on write-off of soft and household equipment (0504143)
The write-off of construction materials should be carried out in accordance with the estimate and on the basis of the work completion certificate approved by the chief engineer of Ulyanovsk State University.
Alcohol is written off on the basis of standards approved by the 1st Vice-Rector for Academic Affairs.
The subsequent issuance of alcohol from the warehouse is carried out after using the previously received one, on the basis of write-off acts and the alcohol logbook.
The act of writing off alcohol is approved by the 1st Vice-Rector for Academic Affairs.
The write-off of consumables for educational purposes should be carried out in accordance with the schedule of educational and laboratory classes, in accordance with approved standards.
The write-off of soft equipment should be carried out when it is no longer possible to use it due to dilapidation and wear. If necessary, bring rags when writing off.
Write-off of precursors is carried out monthly according to the act for write-off of chemical reagents based on the log of transactions related to the circulation of precursors, narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
Strict reporting forms (diplomas, academic transcripts, certificates, certificates) are written off according to act f.0504816 with a report on the movement of the BSO attached.
The report on the movement of diploma forms, applications, academic certificates is approved by the head of personnel management.
Report on the movement of certificates, certificates, certificates - heads of structural divisions.
The write-off of consumables for office equipment and computer equipment when put into operation is carried out according to the list of materials issued f.0504210 , in accordance with the established consumption standards.
The write-off of fuel and lubricants is carried out in accordance with waybills and according to the standards approved by order of the rector.
The write-off of medications in the Chaika health center and other departments of the university is carried out according to act f.0504230 on the basis of a report approved by the head of the department.
3. Absence of a financially responsible person.
3.1 During the absence of a financially responsible person (illness, vacation, etc.), if necessary, material assets are transferred to another financially responsible person by order of the head of the department on the basis of a matching sheet f.0504087 .
3.2 The temporarily appointed materially responsible person is obliged to hand over, within three days, according to the act, all material assets received to the main materially responsible person, after the latter returns to work.
4. The procedure for dismissing a financially responsible person.
4.1 Upon dismissal of a financially responsible person, an order is issued from the rector on the recommendation of the head of the department where the financially responsible person works, indicating the composition of the commission for the transfer of valuables, the timing of the inventory and the transfer of material assets to the newly appointed person on the basis of a matching sheet f. 0504087.
The inventory must be carried out before the employee is dismissed.
The transfer of inventory items from one financially responsible person to another is carried out based on the results of the inventory, on the day of acceptance and transfer of cases.
When changing financially responsible persons, two signatures of the MOL must be present in the inventory lists: the person who accepted the property must sign for receipt; surrenderer - in the delivery of this property.
The participation of the financially responsible person in the inventory is mandatory.
4.2 Upon dismissal, financially responsible persons submit to the Personnel Department a bypass sheet with a note from the Accounting and Control Department about the absence of debt on material assets.
Chief Accountant E.G. Kurchangina