What does dismissal due to reduction mean?
Officially, dismissal due to reduction is called “termination of an employment contract due to a reduction in the number or staff of employees” (clause 2, part 1, article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Not only companies, but also entrepreneurs-employers can lay off employees. When staffing is reduced, one or more positions are completely eliminated, excluding them from the staffing table.
Create a staffing table using a ready-made template Try for free
For example, a company that no longer intends to sell retail closes a store and eliminates the positions of salesperson, cashier, and store manager from the staffing table. Accordingly, those who occupy these positions are either transferred to another job or laid off due to layoffs.
When staffing is reduced, the list of positions in the staffing table remains unchanged. However, the number of employees in one position or another is decreasing. For example, due to the liquidation of several retail outlets, instead of five sellers, there are only three. Those who are “extra” are transferred to other positions or made redundant.
IMPORTANT. There are no fundamental differences in the dismissal procedure depending on what exactly is being reduced - the number of positions or the number of employees. Moreover, these dismissals can be carried out simultaneously. In this case, some positions are completely removed from the staffing table, while for others the number of staff units is reduced.
Action plan for the employer
The procedure for dismissing employees due to staff reduction is established at the legislative level.
Violation of order will be a reason for the employee’s reinstatement in the workplace. At the same time, the employer will also be required to provide compensation for forced time off. To dismiss an employee due to redundancy in compliance with the procedure, you will need:
- Issue an order to change the staffing table. It indicates which option is to reduce the number or a specific position, or both.
- Find out which employees have preferential rights to retain their jobs.
- Create a list of employees or positions that will be eliminated.
- Transfer some employees to other positions.
- Notify the trade union and employment center about layoffs.
- Pay severance pay and all required compensation.
- Dismiss those employees who refused other positions offered.
It is also necessary to additionally agree with the trade union on the decision to reduce the number of participants in this organization.
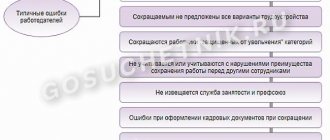
Who cannot be fired during a staff reduction?
It is prohibited to dismiss pregnant women, as well as women with children under the age of three, as well as single mothers raising children under the age of 14 (a disabled child under the age of 18). Also on the “prohibited” list are any employees who raise a child under 14 years of age (a disabled child under 18 years of age) without a mother, or are the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under 18 years of age. In addition, it is impossible to lay off an employee who has a child under three years of age if the family has three or more children under 14 years of age and the second parent (legal representative) does not work (Article 261 and Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
ATTENTION. When laying off employees with children, it is necessary to check not only the age of the child, but also the composition of the family.
In addition, there are categories of employees who cannot be dismissed due to redundancy within a certain period of time. For example, Part 6 of Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibits layoffs of those who are on sick leave or on vacation. It will be possible to dismiss an employee after the end of illness or vacation. Another example is employees who are members of an election commission with advisory voting rights. The reduction will have to wait until the end of the election campaign (Clause 19, Article 29 of the Federal Law of June 12, 2002 No. 67-FZ).
It is also impossible to lay off those who received the right to keep their jobs based on the results of an assessment conducted by the employer. Let us remind you that according to the rules of Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees with higher labor productivity and qualifications have a preferential right to remain at work. And with equal productivity and qualifications, the following persons can apply for protection from reduction:
- family workers with at least two dependents;
- the only breadwinners in the family;
- employees who received work-related injuries and occupational diseases during work;
- employees aimed at improving their skills without interruption from work;
- disabled people of the Second World War and combat operations to defend the Fatherland;
- Chernobyl workers who received or suffered “radiation” diseases;
- other employees who are granted such a right by the collective agreement.
Before deciding to downsize (especially when it comes to downsizing), the employer must evaluate employees based on these factors. Based on this assessment, a decision should be made as to whether or not they have a preferential right to retain their position.
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
Dismissal of a manager or chief accountant
It happens that managers or chief accountants quit. Payments will be accrued in the following cases:
- they were removed from office by the founders without any guilt;
- The new owner of the business decided to fire them.
There are several situations when a change of ownership of a company occurs:
- privatization of state and municipal property (sale or provision into private ownership);
- retransfer of property belonging to the organization in favor of the state;
- sale of the enterprise as a whole complex of property.
A change in the composition of the company's participants (inclusion of new participants or withdrawal, exclusion of old ones, including a complete change in composition) does not constitute a change of owner.
The employer in accordance with Art. 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation pays the manager money in the amount established by the employment agreement, but not less than three times the average monthly salary.
But there are also nuances in the payment of benefits upon dismissal of managers, their deputies and the chief accountant - amounts of money are not paid if:
- there are illegal actions on their account;
- they made decisions that negatively affected the financial position of the organization.
What payments are due upon redundancy?
First of all, these are standard payments that are due to any resigning employee. Namely: wages for hours worked, bonuses, as well as compensation for unused vacation (the calculation of compensation in this case has its own peculiarities). Also, laid-off workers may qualify for additional amounts of money.
Vacation pay compensation
Employees who have worked more than five and a half months in the working year at the time of layoff can count on full compensation for unused vacation. This means that if the dismissed person did not take vacation days at all for the current working year, then he receives compensation for the full vacation (i.e. for all 28 calendar days). If part of the vacation has already been used, then compensation is paid for unused days of full vacation for this working year (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 28 of the Rules on regular and additional vacations, approved by the People's Commissar of the USSR on April 30, 1930 No. 169). For example, if an employee has worked for more than five and a half months, but has already taken 5 days off from his current vacation, then if he is laid off, he will receive compensation for the remaining 23 days.
ATTENTION. In some regions, the courts insist that the described algorithm must be applied to all laid-off employees, and not just those who have been working for the first year (see, for example, the Bulletin of judicial practice of the Moscow Regional Court for the fourth quarter of 2015, the appeal ruling of the Irkutsk Regional Court dated 11/12/14 in case No. 33-9318/2014). And although Rostrud gives explanations to the contrary (letters dated 03/04/13 No. 164-6-1 and dated 08/09/11 No. 2368-6-1), before paying “old” workers compensation according to the usual rules, you should weigh the pros and cons "against". In this case, you need to take into account the prospects for possible litigation and the practice that is developing in your region.
Severance pay
All employees have the right to receive it, with the exception of those with whom an agreement was concluded for a period of up to two months. The latter is entitled to severance pay only if it is provided for in a collective or labor agreement (Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of the benefit depends on the category of the dismissed employee. “Ordinary” employees are paid an amount equal to the average monthly earnings (Article 178 and Article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Seasonal workers receive smaller compensation - based on two-week average earnings (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculate your salary and benefits taking into account the increase in the minimum wage from 2021 Calculate for free
Two-month compensation
If a laid-off employee does not find a new job within a month after dismissal, then he retains his average earnings for the next month. It is paid by the former employer on regular salary payment days (clause 12 of the Regulations, approved by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated March 2, 1988 No. 113/6-64). This procedure applies only to “regular” employees. Seasonal and temporary workers do not have the right to additional payments for the period of employment (Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Average earnings for the second month after dismissal are paid based on the employee’s passport and work record book. If there is no record of hiring a new job at all, then the average salary is transferred to the redundant employee in full. If there is a record of employment, but it is not dated at the beginning of the month, then the average salary must be paid for the days preceding this date (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), appeal ruling of the Omsk Regional Court dated September 12, 2012 in case No. 33-5536 /2012).
The right to receive money for the third month after layoff is confirmed not by a work book, but by an official document from the employment service (Part 2 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer can appeal this document if he considers it unlawful (clause 2.2 of the ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of November 29, 2012 No. 2214-O, part 1 of article 218 of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation). Filing such a complaint does not exempt a former employee from paying money (this follows from Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). However, if the court finds the decision of the employment service illegal, the funds paid will be compensated to the employer from the budget.
IMPORTANT. Is it necessary to subject average earnings during the period of employment to personal income tax and insurance contributions? The answer to this question depends on the total amount of payments transferred in favor of the laid-off employee, taking into account severance pay. If the entire amount does not exceed three times the employee’s average monthly earnings, then there is no need to charge contributions and withhold personal income tax. Otherwise, contributions will have to be charged on the excess amounts and tax will be withheld from these amounts (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24 .98 No. 125-FZ).
Generate payment slips for personal income tax and contributions with current details Try for free
Benefit amount and payment period
Severance pay is a lump sum payment upon dismissal and is issued or transferred to an employee of the company regardless of the payment of remaining earnings and compensation for unused vacation. The benefit is paid according to certain rules, administrative acts and dismissal orders with corresponding payments are drawn up on the basis of ordinary personnel forms and their unified forms. The following must be indicated:
- reasons and grounds for making a decision;
- amount of benefits and other compensation.
Also necessary in the document is the signature of the employee, confirming that he has read the document.
Compensation upon dismissal, as well as the grounds for its provision, are provided for in labor legislation and regulations or in a collective and labor agreement. The legislation provides for different amounts of monetary compensation - from two weeks' average earnings or more. It depends on the reason for stopping work.
You need to pay taxes and insurance premiums on your severance pay! Find out for free in ConsultantPlus how to do this correctly.
Payments for staff reduction in 2021: calculation procedure
To calculate the amount of severance pay, you must first determine the average daily earnings. It is calculated in a general manner based on the employee’s salary data for the previous 12 months. If the reduction occurs on the last day of the month, then this month is also included in the billing period (letter of Rostrud dated July 22, 2010 No. 2184-6-1). In other cases, the calculation is carried out according to the previous month (clause 4 of the Regulations on the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922; hereinafter referred to as the Regulations).
The specific amount of severance pay is determined by multiplying the average daily earnings by the number of working and non-working holidays in the first month after dismissal (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of November 13, 2019 No. 34-P). If we are talking about seasonal workers, then the average daily earnings must be multiplied by the number of working days and non-working holidays that fall in the two weeks following dismissal.
ATTENTION. Severance pay is paid for both working days and holidays.
There are nuances when calculating payments to employees for whom summarized working time recording is established. Here you need to calculate not the average daily earnings, but the average hourly earnings (clause 13 of the Regulations). The resulting value must be multiplied by the number of working hours according to the employee’s schedule in the first month (for seasonal workers - in the first two weeks) after dismissal. This means that for the purpose of calculating severance pay, it is necessary to draw up a schedule as if the dismissed employee continues to work.
Calculate all payments taking into account personal income tax for the dismissed employee
Who will be paid for 14 days
A dismissal payment in the amount of two weeks' average earnings is due in the following cases:
- Upon termination of an employment contract for medical reasons. If an employee is recognized as completely disabled or for any reason does not want to transfer to a new workplace, then he is entitled to severance pay upon dismissal for health reasons, two weeks’ pay and wages for the time actually worked. It is important to note that if an employee quits due to health reasons, but at his own request, then compensation is not paid.
- The legislator established severance pay upon dismissal from the army, which is compensation in the amount of two weeks' earnings and is paid upon conscription into the army or assignment to an alternative service replacing it.
- In case of dismissal upon reinstatement of the employee in service by a court decision.
- If an employee refuses to take a position when the company moves to another city or region.
- If you disagree with changes to the terms of the employment contract in the manner prescribed by Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What payments are not included in the calculation?
When calculating the average daily (hourly) earnings, on the basis of which the amount of severance pay is determined, it is not necessary to take into account social payments not related to wages. These, in particular, include financial assistance, compensation for the cost of food, travel, training, utilities, recreation, and others (clause 3 of the Regulations).
You must also remember that amounts accrued during the time when the employee did not work are excluded from the billing period. In particular, sick leave is not taken into account, including maternity benefits, remuneration for downtime, payment for additional days to care for disabled children and people with disabilities since childhood. In addition, when calculating, it is necessary to exclude accruals made during the time when the employee did not work (participated in military training, court hearings, investigative actions, etc.). This is stated in paragraph 5 of the Regulations.
Unemployment benefit
Unemployment benefit is a type of assistance from the state that is provided to a citizen who has lost his job while looking for a new one. In order to receive such a payment, you need to have an official job in the past, confirm the fact of dismissal and absence of work at the present time.
To receive assistance, you must submit a certificate of average earnings to the employment center. This benefit is limited in both its amount and time. In fact, the state will provide support for a maximum of 18 months from the date of job loss.
The amount of payment is determined by the state every year, and currently ranges from 850 to 4900 rubles. In addition, in the regions of the north, Siberia, and the Far East, coefficients can be established by which this amount is adjusted.
The exact amount of the benefit depends on the average salary of the citizen at the previous place of work.
Depending on the period it is:
- The first 3 months - 75% of the average earnings for the last three months before the reduction, but not more than the maximum limit;
- The next 4 months - 60% of the average salary;
- The next 5 months - 45% of the average salary.
You might be interested in:
Deduction for unworked vacation days upon dismissal: in what case is it done and how?
After this period, for another 6 months, only the minimum benefit is paid, adjusted by the coefficient established in the region.
Attention! If, when the amount of the benefit is found, the received share of average earnings is below the minimum limit, then the minimum benefit is paid.
Features of payments for certain categories of workers
Pensioners
There is no special procedure for dismissal of pensioners. Therefore, parting with them on this basis occurs according to general rules. This means that pensioners have the right to receive the same payments as other “ordinary” laid-off workers (cassation ruling of the Yaroslavl Regional Court dated June 10, 2010 in case No. 33-2930).
REFERENCE. A pensioner dismissed due to layoff must be paid a salary and bonus for time worked, compensation for unused vacation and severance pay. He also has the right to receive average earnings for the second month after dismissal (in certain situations and for subsequent months), if he does not find a new job during this time (letter of Rostrud dated December 28, 2005 No. 2191-6-2, ruling of the Moscow City Court dated April 4. 16 No. 4g-2964/2016).
Workers on probation
There are no provisions for laying off workers who are on a probationary period. However, when calculating compensation for unused vacation, the following must be taken into account.
In general, the probationary period lasts no more than 3 months (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, an employee who is laid off during the probationary period will not be able to claim full compensation for unused vacation for the entire year. Compensation should be calculated in proportion to the time worked.
For certain categories of employees (managers and their deputies, chief accountants and their deputies, heads of separate divisions) it is allowed to establish a probationary period of six months. Therefore, a situation is possible when, on the date of layoff, such a “subject” worked in the current working year for more than five and a half months. In this case, he has the right to count on compensation for full vacation (provided that he has not previously used this vacation or part of it).
Residents of the Far North
When laying off employees of an organization located in the Far North or an equivalent area, additional guarantees are established. Thus, the average earnings for the period of employment can be maintained not only for the second and third months after dismissal, but also for the fourth to sixth months. In this case, special rules apply for the transfer of these amounts.
Calculate your salary taking into account all current local and regional coefficients and allowances
Thus, payments for the second and third months are made by the former employer on the basis of the employee’s work book and passport. Confirmation from the employment service is required only if the dismissed person wants to receive average earnings for the fourth to sixth months (Part 2 of Article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT. When transferring payments to persons dismissed from “northern” organizations, you need to remember tax preferences. The total amount of payments (including severance pay), not exceeding six times the average salary of a laid-off employee, is not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions. And only from the excess amount will it be necessary to withhold income tax and charge insurance premiums on this amount (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 20.2 of the Law No. 125-FZ).
The guarantees provided for workers dismissed from organizations located in the Far North or equivalent areas do not apply to part-time workers (Article 287 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that “northerners” - part-time workers cannot count on payment for the fourth to sixth month after dismissal. But are they entitled to payments for the second and third months? Let's figure it out.
Part-timers
As mentioned above, the average salary for the second month after a layoff is paid based on the work record book. And the work book of a part-time worker (if it is kept in paper form) must be kept by his main employer (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Part-time work means performing one more job, which is additional to the main one (Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that even after the layoff, the part-time worker remains employed (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated 08/03/18 No. 14-1/ОOG-6309).
Thus, in a normal situation, a part-time worker cannot claim to receive average earnings for the second, and especially for the third month after dismissal. However, in practice there may be exceptions.
Thus, labor legislation does not prohibit drawing up a contract for part-time work in the absence of a main job. Nor does it oblige you to stop part-time work or re-register it as your main job if the employee has already lost his main job during the part-time job.
Draw up and print an employment contract
In such situations, a part-time worker laid off due to layoffs becomes unemployed and can receive average earnings for the period of employment. To do this, he has a work book in his hands, in which there is no record of employment (cassation ruling of the Rostov Regional Court dated 10/17/11 in case No. 33-14084, ruling of the Moscow City Court dated 01/30/12 in case No. 33-2395).
Other payments (salaries, bonuses, compensation for unused vacation, severance pay) are transferred to part-time workers on a general basis.
When they will only pay if agreed upon with the employer
Upon resignation of one's own free will
If the contract is terminated at the request of the employee, then no incentive or compensation payments are provided for by law, that is, severance pay is not provided for voluntary dismissal. But if management wants to reward an employee for long and fruitful work, they will award a bonus on their own initiative; such cases are known.
By agreement of the parties
Typically, dismissal by agreement occurs on an individual basis. The amount of the fee is not established, so payment is made by mutual agreement of the parties. The problem of the amount of payment, how to calculate severance pay upon dismissal by agreement of the parties, is solved within the framework of individual agreements.
But the salary, which was not paid to the employee for the period worked, is issued without fail on the last day of work.
Upon retirement
Labor legislation does not provide for severance pay upon retirement, but in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, similar bonuses are allowed to be prescribed in the employment contract or they may be provided for by internal regulations of the organization itself. Such payments are provided at the request of the employer and are not regulated by law. The organization has the right to establish any number of financial assistance measures without restrictions. This type of help is, rather, gratitude for the work.
Early layoff
The employee must be notified at least 2 months in advance of an upcoming dismissal due to a reduction in numbers or staff. If the employee and employer agree, dismissal can be formalized before the end of this period. In this case, the employee is entitled to additional compensation (Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT. Receiving compensation for early dismissal does not deprive the employee of the right to severance pay, as well as to payment of average earnings for the period of employment.
Additional compensation is calculated as follows. First, you need to determine the average daily (if working time is calculated hourly) earnings of the laid-off employee based on data for the previous 12 months. The resulting value should be multiplied by the number of working days (with cumulative accounting - hours) that fall after the day of “early” dismissal and before the day of “planned” layoff (Part 3 of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Additional compensation, like other amounts due upon dismissal, is paid on the last day of work upon final payment (part 4 of article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part 1 of article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This compensation in full is not subject to personal income tax or insurance contributions (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 03.08.17 No. 03-04-06/49795 and dated 31.07.17 No. 03-04-07/48592, Federal Tax Service dated 21.08.17 No. BS- 4-11/ [email protected] ).
It happens that after receiving a notice of dismissal due to reduction, an employee decides to terminate the employment contract on his own initiative. In this case, it is enough for him to submit a letter of resignation of his own free will. However, he will not receive any additional payments, including severance pay and average earnings for the months after dismissal. Therefore, in order to avoid conflict situations, we recommend that you notify the resigning employee of such consequences against signature.
Consequences of late payments
If the employer does not pay in full or is late in issuing all payments due to the dismissed citizen, he will be fined:
- For individual entrepreneurs, the fine ranges from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles.
- For companies - from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
In addition to the fine, the employer is obliged to pay the employee interest for the delay in compensation. The amount for each overdue day is added to 1/150 of the key rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. This rate will begin to be calculated from the day following the established payment date until the day the money is actually issued.
about the author
Klavdiya Treskova - higher education with qualification “Economist”, with specializations “Economics and Management” and “Computer Technologies” at PSU. She worked in a bank in positions from operator to acting. Head of the Department for servicing private and corporate clients. Every year she successfully passed certifications, education and training in banking services. Total work experience in the bank is more than 15 years. [email protected]
Is this article useful? Not really
Help us find out how much this article helped you. If something is missing or the information is not accurate, please report it below in the comments or write to us by email
What to do if the employer does not pay severance pay
If an employee is not paid benefits after being dismissed due to staff reduction, he can send a complaint:
- To the labor inspectorate;
- To the prosecutor's office;
- To the court.
Initially, the employee can submit an application to the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office. They will order an inspection of the employer, and when a violation is confirmed, they will impose an administrative fine and an order to pay the debt. If this does not help, and the payment is never made, then you can collect documents for the court.
A claim against an organization must be filed at its location. The exact address can be found in the extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. The court will not consider the application if it is completed incorrectly and does not contain all the necessary documents.
Attention! The employee is not charged for legal expenses in disputes in the field of labor law.