Not only objects of material property of the deceased testator can be transferred as inherited property by law and by will. You can also inherit intellectual property, which sometimes has a higher value than the property itself.
Inheritance of copyrights does not happen so often, because for its manifestation in real life it is required that the testator be creative during his lifetime: paint pictures, invent robots, create computer programs. All those objects of intellectual property, the possession of which gives rise to copyright, are specified in Art. 1259 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
How to properly and profitably dispose of this type of inheritance is a question of interest to many heirs. Let's try to give a detailed answer to it.
When does an exclusive right pass by inheritance?
An exclusive right is a legal basis for the use and disposal of an object of intellectual property. The person who owns it is called the copyright holder.
That is, not only its author can own an exclusive right. The author may transfer it to third parties.
For example, consider the situation with the popular sculpture Zhdun. The author of this work is the Dutch artist Margriet van Brevoort. However, the copyright for the sculpture belongs to C.D. Land Contact LLC. Please note that we are talking not only about the sculpture itself, but also about its images. Zhdun's photo and image cannot be used in advertising, on signs, or as a trademark. Any use for commercial purposes without the permission of the copyright holder (CD Land Contact LLC) violates copyright. That is, the rights to the sculpture and its image will be protected not by the author, but by their owner. In this situation, C.D. Land Contact LLC.
There is no need to confuse copyright and author's rights. The author's right cannot be transferred or alienated. The person who created the work remains its author forever. And copyright is the ability to use and dispose of a work. It can be transferred.
Let's summarize. Copyright and author's rights are exclusive rights. The first can be inherited, since it is transferable. And the second does not pass to the heirs. That is, not all exclusive rights are inherited.
Features of inheritance
In order for copyright to become an object of inheritance, the author must promptly think about its proper registration.
In most cases, this will greatly simplify the task of the heirs. During his lifetime, the author must:
- Collect documents that indicate its authorship.
- Register authorship with the Russian Authors' Society.
- Obtain documents (patent, certificate).
When copyright is inherited by several successors, its use is possible only with the consent of all heirs. It must be taken into account that the heirs are not subject to the general rule for co-authors, which implies a prohibition on preventing the use of copyright. Therefore, co-authors and all heirs can use it only with mutual consent. To confirm consent, it is necessary to conclude a separate agreement with each of the heirs.
The validity period of copyright after inheritance is 70 years (Article 1281 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). After which the work becomes part of the public domain.
Inheritance by law - order and sequence
Inheritance by will - procedure and timing of inheritance
Types of intellectual property and nature of inheritance
The types are shown in the table below.
| Name | Properties | Features of inheritance |
| Property rights | The author and rights owner can perform the following actions:
| By law or will. In the absence of heirs, they are transferred to the state |
| Moral rights | Authorship | Not transmitted. Rights to authorship remain with the creator of the work or scientific work |
| Following rights | Part of the profit from the use of the work, work, or their replication, as a percentage, is transferred to the copyright holder | It is not transferred by will. Heirs can use it during the copyright period |
| Right to public representation, amendments | Moral rights | Transferred by will. In this case, the testator stipulates his will in writing regarding actions with his work. This is recommended to be done to prevent controversial situations, since the law does not contain regulations in this part. |
Read also: Statement of claim to establish the fact of acceptance of inheritance
Allocation of spousal share
Copyright does not apply to joint property. Therefore, the spouse cannot demand the allocation of the marital share during inheritance.
The following situations are exceptions:
- The spouses provided for the inclusion of copyright in the common joint property in the marriage contract.
- The spouses were co-authors (this fact must be officially confirmed). Co-authorship must be registered with the Russian Society of Authors. If only one of the spouses is officially the author of the work, then the copyright will be included in the estate in full.
The surviving spouse will not be considered a co-author if he provided consulting assistance in the creation of the work, material assistance, technical or organizational support, and also if he controlled the result of the work to create the work. The author is considered to be a person who made a personal creative contribution to the creation of a work.
If the surviving spouse can prove that he personally participated in the creation of an object of intellectual property, then he can go to court to recognize it as a co-author even after the death of the spouse.
Heirs of intellectual property
The legal framework of our country provides for two ways of inheriting intellectual property: by will and by law. The testator can formalize his will in writing, where he will dispose of the property according to his preferences. He has the right to bequeath his property to relatives or citizens not related to him, as well as to various organizations (museums, foundations, etc.).
Despite the fact that the testator can indicate who and in what order will receive exclusive rights in the future, the legal requirement to allocate a mandatory share in the inheritance for his disabled close relatives and dependents must be observed.
Intellectual property can be inherited by one or more persons. If the testator in his will did not show a desire to divide the rights, then they are inherited as a single whole. The presence of several heirs is not an obstacle to fulfilling such a requirement. They all equally claim copyright, which is indivisible. It is unacceptable to divide copyrights, that is, it is prohibited to bequeath them in parts to different people if it concerns the same object of intellectual work. Exclusive rights to creative heritage are bequeathed only in aggregate.
When a work is created in collaboration, the rights to use it and receive remuneration are partially transferred to heirs and/or other co-authors (by law or by will). As a rule, all copyright holders enter into an agreement among themselves on the principles of use of the work. The law does not regulate this area clearly enough. Rights to parts of a work that have independent value and significance are inherited in full.
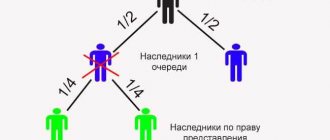
It happens that the author did not have time or did not express the desire to leave behind a will with precise instructions regarding his property. In this case, the inheritance is accepted by law. This means that the heirs of intellectual property will be close relatives (in order of priority), but not outsiders and organizations. If there are no relatives making up the first line (children, spouses, parents of the deceased), heirs of subsequent lines are allowed to inherit.
If the testator did not leave a will, all property passes to his relatives in order of priority.
Property acquired during marriage is usually considered marital property. After the death of one of the spouses, the second has the legal right to half of it. But this rule does not apply to intellectual property: only the one who is considered the author has the right to use the work, unless otherwise specified in the marriage contract. The only exception will be royalties. Thus, the copyright passes to the estate in full, and not in part.
When there are no heirs
It happens that a work becomes public knowledge. This occurs due to the fact that the author’s exclusive rights are terminated, and from then on his property is considered escheat. This is possible in the following cases:
- There are no heirs.
- None of the heirs has the right to inherit.
- All heirs are excluded from inheritance.
- The heirs did not express a desire to accept the inheritance and did not confirm their refusal in favor of another heir.
If it so happens that the work becomes public knowledge, then royalties are no longer paid. From now on, anyone can freely use the work without asking permission. At the same time, it remains inviolable (you cannot correct it and assign your own name to it).
Copyright inheritance order
The law allows copyright to be transferred both by law and by will.
But practice shows that it is advisable to transfer it to one heir. Therefore, if there are several legal heirs, it is recommended to draw up a will. However, the order of succession does not differ depending on the basis. Therefore, in any case, legal successors must adhere to the following algorithm:
- Collect documents.
- Contact a notary.
- To write an application.
- Pay state duty and other fees.
The inheritance must be registered within 6 months from the date of death of the copyright holder. If the successor misses this deadline without a valid reason, then the opportunity passes to the next recipients.
Stage 1. Collecting documents
Heirs need to prepare both general documents for inheritance and documents confirming copyright.
Common documents include:
- the applicant's civil passport;
- a will or document confirming family ties;
- a certificate from the last place of registration of the deceased;
- death certificate of the copyright holder;
- receipt of payment of state duty and other fees.
Information confirming the copyright of the deceased:
- patent;
- a certificate issued by the copyright society upon deposit and registration of the work;
- other documents, depending on the type of work.
Stage 2. Contact a notary
The heir must contact a notary who opens the inheritance case. But you cannot open an inheritance with any notary. The procedure is carried out in the notary office at the place of last registration of the copyright holder.
If at the time of death there is no registration address, then the heirs must contact the notary office at the location of the deceased’s real estate.
If the only object of inheritance is copyright, then the place of opening of the inheritance will have to be established through the court.
Stage 3. Write an application
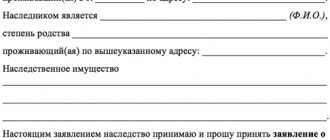
The heir must confirm the fact of acceptance of the inheritance with a statement. The document must include the following information:
- the name of the notary office at the place where the inheritance was opened;
- details of the heir (full name, registration address);
- Title of the document;
- information about the death of the copyright holder;
- information about the deceased's property, including copyright;
- grounds for inheritance;
- information about accepting an inheritance;
- date and signature.
Additionally, the heir provides information about other potential heirs, if he has such information.
Sample application
Stage 4. Pay the state duty and other fees
Art. 333.38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains benefits for citizens who inherit copyright. Such successors do not pay state duty.
However, if the inheritance includes other property, state duty on it is paid in the manner prescribed by law.
Also, copyright heirs are not exempt from paying for legal and technical services of a notary. Depending on the region of inheritance, the citizen must pay a fee prescribed by the Regional Notary Chamber.
For a certificate of inheritance rights regarding copyright in Moscow in 2021, you will have to pay from 500 to 3,000 rubles. The cost of the service for other regions can be found on the FNP website.
Re-registration of copyright is not required. Proof of ownership in the order of inheritance is a certificate of inheritance.
KIMs in the Unified State Exam format for grade 10, on the topic “Civil Law”
Test: "Civil Law". Option 1.
1. Write down the word missing in the table.
| Type of responsibility | Peculiarity |
| Criminal | Imposed for the commission (as well as preparation and attempt) of a crime provided for by the norms of criminal law |
| …………………. | Based on the principle of compensation for damage caused by an offense; consists of the court imposing on the offender statutory obligations of a property nature |
2. Find a word that is generalizing for all other positions in the series below.
Legal entities, individuals, legal entities, cooperatives, institutions.
3. Below is a list of terms. All of them, with the exception of two, relate to personal non-property rights:
1) the name of the citizen; 2) inheritance; 3) authorship; 4) securities;
5) personal dignity; 6) business reputation
Find two terms that “fall out” from the general series and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table.
4. Indicate the sources of Civil Law.
1) Constitution of the Russian Federation; 2) Constitutions and laws of the republics that are subjects of the Russian Federation; 3) Civil Code of the Russian Federation; 4) Orders and instructions of the executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 5) Decrees of the governments of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 6) Federal laws
5. Establish a correspondence between the examples and consumer rights: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
| Main social institutions | Spheres of society |
| A) the citizen did not find information about the manufacturer of the product on the oil packaging | 1) the right to information about the product |
| B) a citizen purchased trousers, put them on once, and then discovered that several seams on the trousers had come undone | 2) the right to a quality product |
| B) the citizen began to use the hairdryer she had purchased, but the device burned out in her hands, causing burns | 3) the right to product safety |
| D) the citizen discovered that the product he purchased is not instant coffee, as written on the label, but a coffee drink |
Test: "Civil Law". Option 2.
1. Write down the word missing in the table.
| Process | Judicial cases |
| Criminal | Exposing criminals, bringing them to trial, imposing punishment |
| ……………………. | Claims for disputes arising from family legal relations |
2. Find a word that is generalizing for all other positions in the series below.
Possession; order; use; ownership; personal non-property rights.
3. Below is a list of terms. All of them, with the exception of two, characterize personal non-property rights.
1) the right to a name 2) the right to honor and dignity 3) the right to inheritance
4) right to life 5) right to private property 6) right to privacy
Find two terms that “fall out” from the general series and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table.
4. Select provisions related to civil law
relationships
1) Obtaining a loan from a bank; 2) Signing an act on industrial safety standards; 3) Conclusion of an agreement for the purchase and sale of an apartment; 4) Receiving part of the savings from parents as a loan; 5) Signing of a collective labor agreement.
5. Establish a correspondence between examples and types of civil rights: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
| Example | View |
| A) the right to lifelong inheritable ownership of a land plot | 1) property |
| B) copyright | 2) non-property |
| B) ownership | |
| D) the right to protection of honor and dignity | |
| D) right to business reputation |
Write down the numbers in your answer, arranging them in the order corresponding to the letters:
| A | B | IN | G | D |
6. 16-year-old Sergei applied to the court for emancipation. Find the items in the list below that correspond to the legal solution to this situation. Write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) plaintiff
2) victim
3) police
4) guardianship and trusteeship authority
5) civil proceedings
6) Criminal Procedure Code
7. Minor Ivan Savelyev submitted an application to the guardianship and trusteeship authorities with a request to declare him fully capable. Under what conditions can the guardianship and trusteeship authorities declare Savelyev fully capable? Enter the numbers in ascending order.
1) Savelyev turned 16 years old.
2) Savelyev received general secondary education.
3) Savelyev works under an employment contract or is engaged in entrepreneurial activities.
4) Savelyev has not been brought to criminal or administrative liability over the past year.
5) Savelyev’s parents agree to declare him fully capable.
6) Savelyev underwent a medical and psychological examination.
8. Read the given text, insert the missing words.
One type of……(A) rights is property rights. The content of property rights consists of three powers - possession, …….(B) and disposal. In accordance with the legislation in the Russian Federation, the following forms of ownership are recognized and protected: private, municipal, ………(B). You can become an owner by collecting ………(G) things (fishing, picking berries), or by age of ownership. At the same time, property must be owned in good faith, openly, for ...... (D) property continuously for 15 years. In addition to contracts (purchase and sale, donation, etc.), derivative bases of property rights include…….(E) (transfer of rights and obligations from a deceased person to his heirs) and reorganization of a legal entity.
List of terms:
1) state 6) property
2) collective 7) inheritance
3) public ownerless
ownerless
4) real estate 9) property
5) use
Write down the number of the word you chose in the table under each letter.
| A | B | IN | G | D | E | |
| D) the mascara purchased by the citizen caused her a severe allergy; the examination found that the disease was associated with the manufacturer’s use of certain prohibited substances | ||||||
Write down the numbers in your answer, arranging them in the order corresponding to the letters:
| A | B | IN | G | D |
6. Stepan is 14 years old, Ivan is 12 years old. Which of the following actions does Stepan have the right to carry out independently, unlike Ivan? Write down the numbers they are listed under.
1) make deposits in credit institutions and manage these deposits
2) to be heard during the court proceedings to determine one’s place of residence in the event of a divorce of parents
3) make transactions to dispose of funds provided by parents for free disposal
4) exercise the rights of the author of a musical work
5) enter into an employment contract (courier work) with the consent of the parents
6) make small household transactions
7. Citizen Eremin, who has a wife and daughter, decided to leave all his property as an inheritance to his grandson. Under what conditions can a grandson become the sole heir of citizen Eremin? Write down the numbers under which the relevant conditions are indicated.
1) Availability of a notarized will of Eremin.
2) Eremin had not previously drawn up another will.
3) Eryomin’s wife and daughter are able-bodied.
4) Eremin is a legally capable person.
5) Eremin’s grandson is of age.
6) The grandson lives with Eremin and is dependent on him
8. Read the given text, insert the missing words.
“…… (A) is an industry whose norms regulate property and personal non-property relations. …. (B) civil law are individuals, ..... (C), the state. Property relations affect relations…….(D): relations regarding sale, exchange, donation, etc. The main……. (D) civil law are the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, others........ (E), for example, “On the protection of consumer rights.”
List of terms: 1) sources 2) laws 3) constitutional law 4) Labor Code of the Russian Federation 5) objects 6) legal entities 7) property civil law 9) subjects
civil law 9) subjects
Write down the number of the word you chose in the table under each letter.
| A | B | IN | G | D | E |
Key to the Civil Law test
| № | Option 1 | Option 2 | Points |
| 1 | Civil (civil law) | civil | 1 |
| 2 | subjects of law | ownership | 1 |
| 3 | 24 | 35 | 1 |
| 4 | 136 | 134 | 2 |
| 5 | 12313 | 12122 | 2 |
| 6 | 145 | 145 | 2 |
| 7 | 134 | 2 | |
| 8 | 896712 | 651347 | 2 |
Evaluation criteria:
“5” – 12-13 points
“4” – 9-11 points
“3” – 6-8 points
“2” – 5 points or less
When is it not inherited?
In accordance with paragraph 83 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 9, the exclusive right to an object of intellectual property can be inherited by legal successors, even in the absence of supporting documents.
But for some objects this rule does not work.
For example, copyright for inventions, utility models and industrial designs is recognized and protected only upon state registration in the manner prescribed by law (Article 1353 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, if the law establishes mandatory registration of an exclusive (including copyright) right, then inheritance is possible only if the right holder has completed the registration in a timely manner and in a proper manner.
Playing and using film clips
Recently, there are more and more articles on the Internet that use stills from films as illustrations. How legitimate is this?
A picture (screenshot) of a film is part of a creative work, and is subject to the exclusive rights of the copyright holder of the film.
However, Article 1274 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation allows the free use of a work for informational, scientific, educational or cultural purposes without the consent of the author and the copyright holder, but with the obligatory indication of the author’s name.
If a part of a movie or its frame is used in an article or on a website, the following must be indicated:
— author or copyright holder;
— source of borrowing;
— the materials serve educational purposes;
— a form for submitting possible complaints.
By taking these precautions, you can avoid complaints from copyright holders.
How is a work inherited?
When inheriting, it is necessary to distinguish between copyright and ownership of a work. They can be transferred either to one heir or to different ones (according to a will).
For example, the author created a painting. If the right to it is properly registered, the author can separately bequeath the painting and the copyright to it. The painting can be transferred to one heir and kept by him. And the copyright goes to another heir. And in the case of using the image of a painting on posters, to decorate candy boxes or for other purposes, it is the copyright owner who will apply for the protection of their rights.
But what about reproductions of paintings whose authors have long since died?
Not everything is so simple here, because there is
According to Article 36 of the said law, the rights to publish museum exhibits and collections are assigned to the museum in which they are located. In addition, the production of any products with images of museum objects can only be carried out with the permission of the museum itself.
For example, in 2011, the State Hermitage Museum sued fashion designer Iya Viktorovna Yots. The head of the fashion house Iya Yots used Thomas Gainsborough's Lady in Blue in her store and at the fashion show of the collection as a backdrop for the catwalk.
Several court hearings took place: the fact of violation of the Hermitage’s rights to the painting was established. The fashion designer was banned from using the painting and ordered to pay legal costs.
Another example: the well-known painting by I. Shishkin “Morning in a Pine Forest” is successfully reproduced on a candy wrapper with the permission of the Tretyakov Gallery.
Arbitrage practice
Heirs have the right to inherit copyright in fact, like any other property. But they will be able to confirm this officially only in court.
To prove actual entry into inheritance, citizens will have to prove that they actually accepted other property of the deceased.
For example, they began to live in an apartment belonging to the deceased, received debts for him, provided security for his car, moved it to the garage, carried out repairs at the dacha, and so on.
The fact that the heirs actually accepted the property within 6 months from the date of death of the copyright holder must be proven.
If the deadline was missed, it is necessary to prove that it was missed for a good reason.
Otherwise, the exclusive right is considered an object of the public domain. And any individuals and legal entities can use the work, including for commercial purposes.
What papers will be required?
In order for a legal entity (notary office) to confirm the transfer of property, the heir will have to confirm the copyright ownership of the deceased person. A patent for a discovery or any certificate indicating the creation of an intellectual creation by the testator can be used as confirmation. A certificate from the Authors' Society of Russia or any creative union will be legitimate.
Important!
Scientific inventions do not require confirmation.
Entry into inheritance requires provision of:
- a certificate confirming the death of the testator;
- heir's passports;
- documents that make it possible to inherit the property of the deceased (papers confirming blood ties);
- will;
- marriage certificate (marriage agreement, court verdict, etc.);
- papers with state registration of intellectual property rights of the testator;
- payment document for payment of state duty.
Lawyer's answers to frequently asked questions
Grandfather wrote prose. After his death, I want to register his copyright and formalize it as an inheritance. How to do it?
Literature is not subject to mandatory state registration of rights. Therefore, the author is considered to be the person indicated on the first edition of the work. You need to contact the Russian Copyright Society to find out whether the copyright has been registered and whether someone has been entrusted with its protection. After which you can receive a certificate in the name of your grandfather. This certificate must be presented to a notary to obtain a certificate of inheritance rights. The inheritance of copyright is not subject to state duty.
2. Aunt made translations of foreign books. Copyright for translations is registered. I am the heir under the will. Where can I get a document confirming copyright?
Contact the Russian Copyright Society.
3. My father bequeathed to me the copyright to his books. But his wife reached 55 years of age. Can she claim a share of the inheritance?
She has the right to an obligatory share in the inheritance. The notary will give her a ¼ share in the copyright. But only if there is no other property at the expense of which her right can be satisfied.