If you believe adventure novels, receiving a large inheritance from an unknown or forgotten relative is extremely pleasant. However, for this to happen, someone must inform the heir about the inheritance and organize the process of receiving it. In novels, this is done by executors - people to whom the testator has entrusted the execution of the will.
Now they do not exist, and the functions of dividing the inheritance between heirs are carried out by notaries. Let's find out whether, according to the law, a notary must search for heirs. Cases regarding the division of inheritance can be complex. If you expect to inherit significant property, we recommend enlisting the help of a lawyer.
Fundamentals of Russian legislation on inheritance
Basic information about inheritance, heirs and inheritance is contained in Chapter. V Civil Code of Russia. There you can find out that inheritance is carried out either by will or by law.
Within 6 months after the opening of the inheritance, all heirs who are ready to accept it must inform the notary at the place of residence of the testator or at the location of the inherited property. The division of property occurs only between heirs who agree to accept it.
Absolutely any person, group of people, any organization or group of organizations can become heirs under a will. The distribution of shares among the heirs occurs according to the will of the testator, reflected in the will certified by a notary. In some cases, the function of certifying a will may be performed not by notaries, but by other officials.
The rights of the testator to distribute his property are limited by law. Disabled relatives who are heirs at law, regardless of the will, receive at least half of what they would have received if there had been no will. Notaries notify the heirs under the will about this and seek the allocation of the share of the disabled heirs.
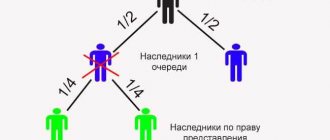
If there is no will, inheritance occurs according to law. Only relatives of the testator and local authorities can inherit in this way. If there are no heirs, the property becomes the property of local authorities.
Such property is called escheat. The testator's relatives are divided into succession lines. If there is at least one heir in the previous queue, applicants in subsequent queues do not receive anything. The legislation defines 7 lines of inheritance:
- Children, spouses and parents of the testator.
- Brothers and sisters, grandparents.
- Uncles and aunts.
- Great-grandparents.
- Children of nephews and nieces, brothers and sisters of grandparents.
- Cousins: grandchildren and granddaughters; nephews and nieces; uncles and aunts.
- Stepsons, stepdaughters, stepfather, stepmother.
The circle of heirs, depending on the circumstances, can be extremely wide. Some of them may indeed not know either about the inheritance or about the testator himself. Such heirs cannot contact a notary within the period established by law - 6 months after the opening of the inheritance.
The division of property is carried out without taking into account the interests of such people. But they do not lose the right to inheritance and can restore it through the court. If this happens, the division of property between the heirs will be carried out again, taking into account the rights of the new applicant.
If the property is sold, the new heir's share will have to be compensated with money. To prevent this from happening, oddly enough, the remaining claimants to the inheritance are most interested in finding an heir.
Is it possible to accept part of the inheritance and refuse part?
The law does not provide for the possibility of selective acceptance of property. Only the entire inheritance can be accepted (Article 1158 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Identified assets are divided equally among legal successors. At the same time, the debts of the testator are transferred to the heirs. Therefore, most heirs think about the possibility of accepting property and waiving debts.
Important! The law does not provide for the possibility of separating property from debts. Regardless of the basis for accepting the inheritance, each legal successor receives a share in the debt obligations of the deceased.
Applicants are given 6 months . The assignee will have to prepare a package of documents and submit a corresponding application. Upon expiration of the specified period, they lose their property rights.
The law provides for the possibility of accepting property on several grounds (by will, by law, the right to an obligatory share).
For example, if the testator made a will for the priority heir. However, it concerns only part of the property. Consequently, the successor can accept the inheritance by disposition and inherit the remainder of the property within the limits of the law.
Example. The family lived in a 2-room apartment. The housing belonged to the testator, as it was given to him under a gift agreement. The man also owned a car. One month before his death, the man made a will. He gave the apartment to his wife and daughter. There was no mention of a car being available. The eldest son lived separately from the family. He had his own home, so the testator did not indicate it in the will. The heirs, by order, submitted documents to the notary. Each got ½ of the apartment. In addition, the son, daughter and wife are entitled to 1/3 share of the car. However, the women refused the inheritance by law. The son received the vehicle.
Thus, a person can inherit partially. However, to do this, he must have the right to inherit on several grounds.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Evseev
Lawyer. Experience 12 years. Specialization: civil, family, inheritance law.
The law gives such a recipient the right to accept property on one or all grounds. Registration of an inheritance under a will is not a reason for abandonment of property by law and vice versa.
If necessary, the applicant can refuse property on one of the grounds. Here it is necessary to proceed from the actual circumstances of the case.
Reasons for refusal vary:
- low cost of property share;
- alienation of an asset in favor of another person;
- presence of loan debts.
Responsibilities of a notary in searching for heirs
The notary learns about the death of the testator from one of the heirs. The law does not provide for any other communications for this purpose. If the notary knows the coordinates of other applicants for the inheritance, he is obliged to inform them about the inheritance.
The coordinates can be obtained by the notary from the will, from other claimants to the inheritance, or from other sources. So: the notary must inform the applicants for the inheritance, whose coordinates he has, but he is not obliged to search. Information about this is contained in Art. 61 “Fundamentals of legislation on notaries”.
In addition, the notary is not obliged to search for inherited property. He only has to check the estate at the address of the testator. Information about this is contained in Art. 71 of the above document.
The search for heirs of property falls on the remaining claimants to the inheritance, if they consider it necessary to do this. Without experience, it is extremely difficult to achieve results in such searches.
Applicants for inheritance should contact a search office or a notary. The notary is not obliged to search for inheritance and citizens who have the right to inherit, but he is not prohibited from doing so. The notary has access to the necessary databases and experience in such work. You can try to negotiate with him.
- To summarize, by law a notary is obliged to search for heirs if the notary: knows the place of residence of the heir;
- the place of work of the heir is known, which will allow him to be found.
Sources:
Order of succession by law
The notary's duty to notify the heirs
Checking the hereditary mass
Deadline for entering into inheritance according to law and will
After the death of a citizen, all his property passes to close relatives or persons specified in the will. If one of the heirs does not enter into rights, then the opportunity to take possession of the property of the deceased arises from another category of heirs, for example, distant relatives.
Attention! A citizen has the opportunity to inherit property in two cases:
- if he is a close relative of the deceased,
- if the deceased included it in the will.
You can enter into inheritance rights only after six months from the date of death. If the period for entering into inheritance has expired, the heir has the right to apply to the court for its restoration.
If the direct heir wishes to relinquish the property, the property passes to the secondary heir. In this case, the entry period is reduced by exactly half and is three months.
In what cases can absence reasons be valid?
A lawsuit for restoration of missed deadlines remains unsatisfied if the reason for the omission is unjustified. In addition, it must be proven documented.
Valid reasons for missing a deadline include:
- long-term illness
- long business trip,
- imprisonment,
- service by conscription, contract.
In any case, it is necessary to present a document proving the fact of a valid reason. If a person has been sick, an extract from the hospital or a medical card is provided.
Illiteracy is considered a valid reason. However, illiteracy is recognized as the inability to write and count, and not ignorance of the laws.
If a person missed the deadline due to circumstances beyond his control, due to fraudulent actions of third parties, then a certificate from the investigator or a court decision will serve as evidence of a good reason.
Important! Lack of knowledge about the death of the testator is considered a valid reason. For example, if the heirs of the second stage deliberately did not report the death of a relative.
Non-acceptance of inheritance as interpreted by law and its options
The heir could be inactive for various reasons. The most common are:
- ignorance of the heir about the death of the testator due to, for example, being on a business trip for a long time in a place inaccessible for communication;
- the impossibility of his filing a will with a notary to legitimize rights to inheritance due to extenuating circumstances. These include, for example, serving a sentence in prison, undergoing treatment in a hospital due to a serious illness, etc.
However, there is a situation where the heir was informed about the death of the testator, but deliberately did not take any action to accept his inheritance, despite complete freedom of action and the opportunity to do so. Then he may lose the right to the property left to him by will.
A lawyer will help you deal with the situation if the heir does not accept the inheritance
What to do if you know that one of your relatives deliberately does not accept the inheritance. A lawyer from the Pravosfera agency will help you deal with this issue. You can receive advice around the clock in any available way indicated on the website: online chat, hotline, email.
The agency’s specialists guarantee you a legal solution to the problem, which will be impossible to challenge. We can get involved in the case at any stage, even if it reaches a dead end, our employees will be able to correct the situation. Many years of experience in the field of jurisprudence and the narrow specialization of our specialists allow us to confidently say: “We can protect your interests!”
Out-of-court procedure for reinstatement
statements of consent to include among the heirs the heir who missed the deadline for accepting the inheritance free of charge in word format
It is possible to restore inheritance rights without a court hearing.
This is permitted subject to the following conditions:
- all heirs agree with the entry into law of a new successor,
- little time has passed since the death of the testator, most often less than five years,
- the citizen is a direct recipient, which can be documented.
To carry out an out-of-court procedure for restoring inheritance rights, it is worth collecting consent from each known owner. Then you need to contact a notary to extend the missed deadline. After receiving the certificate of inheritance, you can re-register the property.
Please note! If the property was received by heirs of the second priority, then upon presentation of rights, the first-priority heir has the opportunity to take possession of all the property. If the applicant belongs to the same category, then part of the property is divided in proportional shares.
You cannot enter into an inheritance after, for example, a ten-year period. This is not prohibited by law, but it is impossible from a factual point of view. Surely the property was disposed of during this time and sold. Therefore, it becomes difficult to defend your rights, even with the involvement of judicial authorities.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample application for consent to include among the heirs an heir who missed the deadline for accepting the inheritance:
To go to court or not
Important! If the heir did not manage to assume his rights within the prescribed period, there are two ways to receive the property:
- through the court,
- by agreement with the heirs.
The second case is practically impossible. As a rule, no one wants to share an inheritance that they have already received. However, it is worth trying to come to an agreement with relatives. It is quite possible that they will agree to cede part of the inheritance.
The second method is a real chance to prove the right belonging to the heir by law.
It should be used in the following cases:
- if the heir of the second priority refuses to share the inheritance received,
- if the heir who missed the deadline was the only applicant to receive part of the deceased’s property,
- if the heirs of all orders missed the deadline for entering into inheritance rights.
As a rule, the first method is used more often. Although it is long, it is effective. Especially when the second-priority heir took possession of the property illegally, for example, deliberately did not warn the primary heirs about the possibility of obtaining the property.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Judicial procedure for restoration of rights
If it is not possible to resolve the issue of restoring the right to inheritance out of court, the involvement of judicial authorities is required. To do this, you need to prepare a complete package of documents.
In court you will have to explain the reason for missing the deadline. If she is not respectful, the court has the right to refuse to restore the terms.
Please note that the more competently the statement of claim is drawn up, the greater the chances of a positive outcome.
The application reflects all existing heirs. In addition, you will have to prove your right to receive part of the inheritance. If the relative is distant, then the court will legally make a negative decision.
Remember! The territorial division of the judicial body is selected at the request of the plaintiff:
- place of death of the testator,
- place of residence, registration of the testator,
- place of residence, registration of heir.
Important! If no one has entered into inheritance rights, then the local government body acts as the defendant, since the actual owner of the property is currently the state.
Required documents
Along with the statement of claim, the future heir must prepare a complete package of documents. The list directly depends on the situation.
Attention! Most often required:
- death certificate (the main document in the case, ensuring the legitimacy of the claims),
- a court ruling if the death is recognized as having occurred in connection with a court decision,
- documents establishing family ties,
- plaintiff's civil passport,
- an extract from the local administration on registration,
- papers that make it possible to claim the property of the deceased, for example, a will,
- the results of the examination, which revealed the total value of the inheritance,
- receipt of payment of state duty,
- refusal of the notary to restore the missed deadline,
- papers that can confirm a valid reason for missing the due date.
The statement of claim is drawn up in several copies. The number is determined by the number of participants.
A valid reason can be confirmed by the following documents:
- imprisonment: certificate of release, court verdict,
- long business trip: employment contract, travel certificate, written order of the chief director,
- treatment: patient card, discharge from a medical institution, doctor’s certificate, sick leave.
If the reason for missing the right to enter into inheritance is unjustified, the court has the right to refuse to restore the deadlines.
How to draw up a statement of claim to the court for recognition of the right to inheritance.
Claim to a judicial authority
To restore inheritance rights through the court, you will need to draw up a statement of claim. There is no single form, but territorial judicial bodies are developing their own models. The finished form can be downloaded from the website of the judicial authority.
lawsuit to restore the deadline for accepting an inheritance free of charge in word format
According to the general rules, the statement of claim must contain the following information:
- name, location of the judicial authority,
- if possible, the last name, first name, patronymic of the precinct judge,
- plaintiff’s details: last name, first name, patronymic, place of registration, residence, passport details, contact phone number,
- information about the defendant: last name, first name, patronymic or name of the organization, place of registration, residence, contact phone number if available,
- the name of the document itself, that is, a statement of claim to restore the terms of inheritance,
- the actual reason for going to court (the possibility of reinstating the missed deadline),
- demand (what the plaintiff wants to achieve in the event of a positive court decision),
- date of compilation, signature,
- list of documents attached to the claim.
Who has the right to inherit if there is a will?
It is mandatory to pay a state fee. If the heirs received the property illegally, the case is being developed by the investigative authorities. The applicant pays a state fee equal to 300 rubles.
The general procedure for calculating the amount of state duty is described in Article 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The basis is the value of the inheritance. The percentage and fixed rate depend on its size.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample claim to the court to restore the deadline for accepting an inheritance: