Alexander Konchenko
Marketer, managing partner at the ACMEdigital agency, creator of the “Reverse Millionaire” Telegram channel.
One day a friend called me: “I lost the case to the bank. What will happen now? Will everything be taken away from me? But the truth is that nowhere are they taught how to communicate with bailiffs. This is the reason for writing this article.
You could default on the loan and take the matter to court. Avoiding alimony, not paying housing and communal services for a long time. There is only one principle - you must. There was a trial, you lost it. Collection - enforcement proceedings have begun. And then these guys appear.
Bailiffs are people like everyone else, with weaknesses. Having received a little power, they revel in it to their heart's content. But there are ways to ease your situation.
What will the bailiffs take away first?
They will start with money, because it is easier to take it out and return it to the lender. There are two easiest ways:
- Find out if the debtor has accounts. The bailiff has the right to request Federal Law No. 229-FZ of October 2, 2007 from banks for such information. If the accounts are found, the institution will be obliged to withdraw money from them and transfer it to the bailiffs. If funds are insufficient, debts will be collected from future earnings.
- Act through the employer. If the debtor receives a white salary, part of it, according to the court decision, will immediately be sent to the bailiffs. The amount usually does not exceed 50% Federal Law of October 2, 2007 N 229-FZ of earnings. But if we are talking about alimony debts, then you can lose up to 70%. All calculations occur after income tax is withheld from the salary.
What Federal Law No. 229-FZ of October 2, 2007 will definitely not take away from you are various types of benefits and compensation related to harm to health, death, and so on.
If it was not possible to pay off debts with money, the bailiffs move on to the next stage: they confiscate and sell the property.
How does debt repayment work according to law?
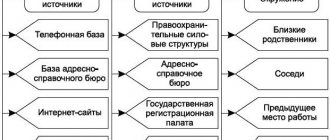
- — Bailiffs send requests to various structures to find out whether the debtor has vehicles or real estate.
- — If the debt exceeds 10 thousand rubles, the debtor is prohibited from leaving the country; this restriction can be applied several times.
- Bailiffs real estate and impose a ban on re-registration of the car, that is, the debtor can give it or sell it to anyone.
- — If bank deposits and plastic cards issued in the name of the debtor are discovered, all accounts on them are also frozen. All available funds are written off against debt.
If no money is found in the accounts, or the collected amount cannot cover the apartment is seized . It is first described , then seized, evaluated and sent to auction, which is held by special organizations. Of course, everything is sold at a low price. The proceeds will be sent to creditors or utility companies.
If in this case the funds are not enough to pay the debt in full, then 50% of all earnings, pensions and other income are confiscated from the debtor.
What property cannot be seized for debts
The list is quite long. It includes the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation Article 446:
- The only housing and the plot below it. An exception is if an apartment or house serves as collateral for a mortgage loan. Also, in rare cases, it is allowed to sell the only home when the amount of debt seriously exceeds the value of the property.
- Furniture, clothing, equipment necessary for life. That is, your bed, linen and stove will not be taken away from you. But you’ll have to say goodbye to the game console, mink coat and ruby ring.
- Property with which the debtor earns money. They won’t take away a sewing machine from a seamstress, a car from a taxi driver, or a laptop from a programmer. True, if an item costs more than 100 times the minimum wage (currently the minimum wage is 12,130 rubles), then they can still confiscate it.
- Farm animals, birds, rabbits and bees, food for them and buildings where they live. But only if they are kept for personal purposes. If animals and insects are used in business activities, they are subject to confiscation.
- Seeds for sowing.
- Products and money in the amount of the subsistence level, taking into account the debtor himself and his family members.
- Fuel for cooking and heating.
- Facilities necessary for a disabled person.
- Prizes and state awards.
Description of property by bailiffs
Good evening! FSSP application https://fssprus.ru/fssp_mobile
Deadline for execution of a writ of execution by bailiffs
What can bailiffs describe in an apartment?
In order not to waste time on bailiffs, there is an excellent way to pay off debts, namely: the debtor asks the debtor for bank details and transfers monthly (electronically or tops up the creditor’s card with cash), making sure to keep the receipts. THE IMPORTANT WHEN TRANSFERING OR DEPOSITING IS TO INDICATE THE NAME OF THE TRANSFER. FOR EXAMPLE, “PAYMENT BY DECISION/ORDER (name of the court) dated November 09, 2018. This option of settlement with the creditor will create the most comfortable conditions for repayment and settlement of debts. To transfer alimony, open a personal account/accounts for children in a bank and transfer alimony to them.
Find out about your debts https://fssprus.ru
The car is under arrest by the bailiffs, what to do?
Can bailiffs describe parents' property for children's debts?
How much can bailiffs deduct from wages if there are children https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/skolko-mogut-vyichitat-iz-zarplatyi-sudebnyie-pristavyi.html
Do bailiffs have the right to withdraw money from pensions https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/imeyut-li-pravo-sudebnyie-pristavyi-snimat-dengi-s-pensii.html
Do bailiffs have the right to open an apartment without the owner? https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/mozhet-li-sudebnyij-pristav-vojti-v-kvartiru.html (Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 388. Conditions for the assignment of a claim, Part 2. It is not permitted to assign a claim under an obligation without the consent of the debtor, in which the identity of the creditor is essential for the debtor).
AntiCollector Russia https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.anticollector.rus&hl=ru (RF Criminal Code Article 163. Extortion)
Can bailiffs seize a card https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/mogut-li-sudebnyie-pristavyi-nalozhit-arest-na-kartu-sberbanka.html
Can bailiffs seize a credit account https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/mogut-li-sudebnyie-pristavyi-arestovat-kreditnyij-schet.html
Which accounts cannot be seized by bailiffs https://advokat-malov.ru/stati/kakie-scheta-ne-mogut-arestovyivat-sudebnyie-pristavyi.html
You must show documents confirming ownership of the property (checks, receipts). Show documents proving ownership by another person: sales receipts, contracts, deeds of gift, electronic receipts, bank statements, deeds of inheritance, draw up a simple purchase and sale agreement; in the absence of any documents, it is necessary to ask employees to send requests to organizations where they can confirm the ownership of a particular item of property. This procedure may take a long time, during which time the property will be seized; when it is impossible to determine ownership, there is a right to demand the exclusion of property, exemption from seizure and protection from sale. To do this, you need to send an application of the established form and wait for the start of the case in court. It is important to note that the person sending such a letter can be not only the owner of the thing, but also its pledgee or another person interested in it. The list of what will remain in the possession and use of the debtor in any case is approved by Federal Law No. 229 of 02/01/2008. The list is as follows: an apartment, house or other residential premises, which is considered the only place of residence (if it is not the subject of collateral); personal items for everyday use in the everyday sense; personal medals, orders and other awards; a means of transportation used to earn income or work; materials for heating and cooking; finances equal to the cost of living established in the region.
Any unlawful step of a representative of the FSSP can be appealed within 10 days by the party
against whom enforcement proceedings have been opened or by another person whose rights have been violated. The claim is written to the head of the service or directly in the form of a lawsuit in court. Each case is considered separately, and if abuse of authority is proven, the items will be returned to the applicant.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (as amended on October 11, 2018, as amended on December 19, 2018) Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 138. Limitation on the amount of deductions from wages. The total amount of all deductions for each payment of wages cannot exceed 20 percent, and in cases provided for by federal laws, 50 percent of wages due to the employee. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of salary withheld on account of the debt is calculated in the following proportions: according to the law - 20% of the salary; according to federal law or court decision - 50% of salary; exceptions to the rules (for example, alimony) – 70%. The most common rate is 50% withholding from wages towards credit debt. If the borrower has children, then the amount of withholding is reduced: The presence of 1-2 children - bailiffs do not have the right to withhold more than 30%; The presence of a child studying at a university not on a budgetary basis – 30%. Death of a spouse and presence of minor children – 25%. Death of a spouse and absence of minor children – 50%. According to the law, the court cannot withhold from the following types of profit: 1. Maternity capital and other payments for child support; 2. Compensation for work in hazardous industries or in difficult climatic conditions; 3. Compensation for damage to health received in connection with the work activity of the debtor (paid by insurance companies or employers); 4. Cash payments to the family of those killed at work; 5. Payments to a citizen caring for a group I disabled person; 6.Accruals during the period of dismissal of an employee. In accordance with the norms of clause 12, part 1, art. 101 of the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ for benefits to citizens with children, accrued from the federal or regional budget (including extra-budgetary state funds - FSS, Pension Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund) cannot to be levied under enforcement documents.
Article 446 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and Article 101 of the Law on Enforcement Proceedings contain information about what property is not subject to seizure: the only housing, if it is not purchased on credit and is not mortgaged (when it comes to a private house, then the land on which it it’s worth it, they also can’t arrest); basic necessities, personal belongings, household appliances as part of ensuring normal living conditions; things for performing professional duties, the cost of which does not exceed 100 times the minimum wage; domestic animals and poultry kept not for profit, as well as pastures, feed and buildings necessary for them; seed fund for future plantings; firewood, coal and other substances necessary for heating premises for one season; transport belonging to a disabled person and necessary for him to move; honorary badges, medals, orders, etc. belonging to the debtor. Knowing what property cannot be seized, it is worth remembering that there is a fairly extensive list of benefits, additional payments, payments protected from collection, including: compensation for health damage; payment for the loss of a breadwinner, for injury or death while performing a professional duty, for victims of disasters; subsidy for caring for a disabled person; federal surcharges for the purchase of medicines, travel expenses, etc.; alimony; travel and depreciation allowances; benefits for birth, death (funeral benefits) or on the occasion of marriage; social insurance payments (exceptions - pensions and sick leave); child benefits and maternity capital, state assistance to victims of a terrorist attack or the death of a close relative; financial assistance provided by philanthropists; compensation for a tourist package.
Carefully read the documents in the enforcement proceedings. Take photographs of all documents in production. If you disagree with the materials of the proceedings, file a complaint against the bailiff online https://fssprus.ru/form or file a complaint through the office, the chief bailiff of your area against the bailiff who is obliged to execute the court decision. Print on two sheets of paper, one for the institution, the other for you with a mark (date, signature of the person who accepted the application) stamp of acceptance. If you do not receive a response within 10 days, complain to the FSSP Office in your region. If you do not receive a response within 10 days, contact the court at your place of registration with a statement to challenge the actions/inactions of the bailiff.
Applications to bailiffs https://fssprus.ru/search/?string=%E7%E0%FF%E2%EB%E5%ED%E8%E5&date_from=&date_to=&where=1
PROSECUTOR GENERAL'S OFFICE https://ipriem.genproc.gov.ru/contacts/ipriem/
If difficulties arise, I recommend contacting our office for a consultation with our specialists. The MIP legal group will draw up all documents, complaints and statements for you using the MIP promotional code 9. If you are in another city, you can send scans or photos of documents. The cost of services will be answered in a letter or call +7 (499) 938- 82-06 Moscow, Staropimenovsky lane 18 [email protected]
Attention! Promo code discounts are no longer valid
What property can be seized for debts?
It is allowed to seize what is not prohibited. There is no point in listing everything, but here are a few interesting options:
- Pets. By law, they are considered property of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 137. Animals, so they are subject to seizure and subsequent sale. For example, in the Stavropol Territory, the owner was arrested for debts. In the Stavropol Territory, a cat was arrested for debts. In 2015, a bill was introduced into the State Duma. The Duma proposed banning the arrest of pets, which would prohibit this, but it did not find support.
- Fence. In the Stavropol region, bailiffs arrested a fence in the Krasnodar region, a fence made of corrugated sheets. The fence was dismantled and sold at auction.
- Hay. Two hundred haystacks ended up “Instead of 200 thousand rubles - 200 haystacks”: bailiffs seized hay from an alimony defaulter and put it under arrest because its owner, a farmer, did not pay alimony.
- Door. The debtor made it himself and wanted to install it instead of the old one. But before the South Ural bailiffs had time to arrest the door.
In general, nothing is safe. Fortunately, you can Federal Law No. 229-FZ of October 2, 2007, choose for yourself what you need least and offer it for implementation. But only if the price of these things is sufficient to pay off the debt.
How should a bailiff act according to the law?
When meeting with the debtor, he is obliged to present his identification and resolution, and carry out enforcement actions within the framework of the law. Even if he is forced, he cannot raise his tone, threaten, or behave incompetently. After all, the debtor, for his part, can write a complaint against him or file a lawsuit in order to protect his honor and dignity. Such cases in court, as practice shows, are often resolved in favor of the debtor.
If necessary, consult a litigation lawyer.
Author of the article
What will they do with the property next?
He will be sold. How exactly depends on the price Federal Law dated October 2, 2007 N 229-FZ. Property with a total value of less than 30 thousand rubles can be sold by the debtor himself if both parties agree on its price. It is written down in the deed of seizure. If the property costs more than 500 thousand, then it will be sold at open auction in the form of an auction. Things that do not fall into both categories are sold by a specialized organization.
Part of the proceeds will be given to the creditor - in the amount of the debt specified in the writ of execution. Some will be collected by the bailiffs in the form of an enforcement fee Federal Law dated October 2, 2007 N 229-FZ. It is equal to 7% of the debt amount, but not less than 1 thousand rubles per person and 10 thousand per organization. The money will be transferred to the budget.
If the debtor voluntarily pays the debt within five days after receiving the order from the bailiffs, the enforcement debt need not be paid.
When should you think about the fate of your property?
After court decisions on debt collection come into force, bailiffs receive writs of execution. Now the bailiff can begin enforcement proceedings.
He goes in search of an apartment or other place of residence of the debtor. By mail, he sends the debtor a copy of the resolution on the commencement of enforcement proceedings. From this moment on, the debtor may lose part of his property.
The debtor may be given several days to repay the debt voluntarily. If he does not take advantage of this opportunity, then in five days a resolution will be issued to describe the property in apartment . And the amount of his debt will increase by another 7 percent.
The bailiff informs the debtor about his visit in writing, by phone or via SMS. The visit time for carrying out enforcement actions is set from 6 to 22 hours on weekdays. Visiting debtors at night and on weekends is prohibited, unless this is an exceptional case when the procedure cannot be postponed.
Law on seizure of property
Seizure of property is the deprivation of material assets of a suspected or accused person. The law also provides for the opportunity to dispose of property or use it for one’s own purposes. An arrest is imposed during a trial if representatives of the law have sufficient grounds.
This procedure applies to real estate or movable property, money, and securities. Seizure of the debtor's property is applied:
- in order to ensure the safety of property to be sold or directly transferred to the claimant;
- for the execution of a signed judicial act, which refers to the seizure of property belonging to the debtor and located with him or third parties.