Consequences of bankruptcy of a legal entity for the company itself
Everything is simple here. There are only two consequences:
- debt write-off;
- liquidation of the company (exclusion of the company record from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities).
But these consequences of bankruptcy of an enterprise occur after the completion of bankruptcy proceedings—the last stage of bankruptcy. Moreover, some of them appear not at the moment of completion of this stage, but at the moment of its beginning (that is, when the arbitration court decides to open bankruptcy proceedings). These are the consequences:
- fines, penalties and penalties for the company’s debts cease to accrue;
- arrests imposed on the company’s property are lifted;
- a company can transfer its property only in the manner established by the Bankruptcy Law;
- no further collections from the company under enforcement documents can occur; bailiffs hand over writs of execution to the bankruptcy trustee;
- monetary claims against a company can only be made within the framework of bankruptcy;
- some other consequences.
Voluntary initiation of bankruptcy
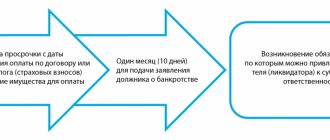
Any financially interested party in legal relations, including a tax authority or a creditor, can go to court and initiate bankruptcy of an LLC with debts. At the same time, the debtor is obliged to independently carry out such actions as soon as it is obvious that the available funds are not enough to make full payments on the accumulated obligations or if the liquidation of an unprofitable company has revealed financial insolvency. This often happens during audits and final reports. If this fact is ignored, the persons controlling the debtor may be held vicariously liable and accused of deliberately causing bankruptcy. A legal entity with debts has 30 days from the moment when these signs are identified to submit an application to the arbitration court. This is one of the legitimate attempts to return the company to profitable, normal activities or to get rid of debts in a civilized manner while preserving its business reputation.
Decision on financial insolvency
Bankruptcy of legal entities with debts begins with a decision made unanimously by the director or founders. Subsequently, it must be approved by the arbitration court. This is preceded by a deep legal and financial analysis with the involvement of specialists. Then:
- an order for liquidation of a legal entity is approved;
- a special liquidation commission is being formed;
- a full-scale accounting and inventory audit is carried out;
- a list of all available tangible and intangible assets is compiled;
- an evidence base is being collected to argue that assets are insufficient to cover debts;
- an application to the court is being prepared.
The arbitration court considers the validity of the application, and if a decision is made to accept the case, a multi-stage bankruptcy procedure for a legal entity with debts begins. The procedure includes several mandatory sequential stages - observation, financial recovery, external management, bankruptcy proceedings.
Observation stage
The arbitration court initially has no idea about the financial condition of the debtor, so the observation stage is applied. At this stage, a temporary manager is appointed who takes upon himself the responsibility of supervising the entire procedure. Initially, he is obliged to include information about bankruptcy in the EFRBS register and publish the information in the official publication. In addition, in accordance with the regulations, the manager analyzes the financial condition of the company and ensures the safety of property. He identifies the creditors of the legal entity, organizes a meeting of the founders and notifies each of them about the date and place of its holding. The bankruptcy of a company with debts suggests that the interim manager may file a petition to remove the company's management. This specialist is responsible for maintaining a register of legal claims made by creditors, submitting reports to the court and submitting minutes of the general meeting. The legal staff has qualified arbitration managers, so there is no need to attract additional specialists.
Limiting the actions of company management
Persons controlling the debtor are potentially subsidiary defendants. Therefore, the regulations and at the discretion of the financial manager partially limit their actions, namely, they are prohibited:
- placement of own shares and other securities on stock markets;
- payment of cash shares to the founders and dividends to shareholders from the profits received;
- creation of new representative offices and branches;
- lending to other persons and obtaining loans, transferring property into trust management without first obtaining the permission of the temporary manager;
- carrying out purchase and sale transactions and other acquisition of property without the knowledge of the financial manager, if the subject of the transaction exceeds 5% of the total value of the company’s property on the balance sheet;
- opening, self-liquidation or reorganization on behalf of a legal entity in respect of which bankruptcy has been initiated, new business entities;
- making decisions on joining other legal entities.
The bankruptcy procedure for an LLC with debts assumes that the maximum period of the observation stage is seven months, after which the materials are submitted for consideration to the court.
Financial recovery stage
The court, the meeting of creditors or any interested party may apply for financial restoration. This is the optimal scheme for counterparties if bankruptcy of a company with debts is initiated. A temporary manager is appointed. As a rule, this is the same temporary manager from the observation stage. It can only be replaced by an arbitration court at the request of the parties. The powers of this participant in the process are more expanded. Firstly, he can stop all illegal transactions through the courts. Secondly, if the payment schedule is violated, this entity demands payment of the debt from the guarantors at the expense of the declared security. The law allows a maximum of two years for this stage. As a result, the debtor is obliged to provide the arbitration manager with a report, and on its basis a conclusion is drawn up. Legal, realizing the importance of this entity, has experienced arbitration managers on its staff, which allows us to provide turnkey bankruptcy support services.
External control stage
If creditors convince the court of dishonesty and low organizational competence of the company's management, an external management procedure is launched. As a rule, it follows immediately after the observation stage, and its occurrence largely depends on the quality of the work of bankruptcy lawyers. The duration of this stage cannot exceed one and a half years. In exceptional cases, it is extended for another six months. An external manager is appointed, whose powers allow the manager to be removed from business or even fired. In this case, the documentation, materials and seal are transferred to the arbitration manager no later than within three days. The bankruptcy procedure of a legal entity with debts assumes that the external manager receives additional powers - to terminate unfavorable contracts in the first three months after their conclusion and, within the same period, refuse to fulfill obligations under unprofitable transactions. There is a moratorium on payments to creditors, which serves as the last chance to restore solvency without selling assets.
Bankruptcy stage
The company's failure to restore a certain level of profitability within a reasonable time prompts creditors to initiate bankruptcy proceedings. In fact, this is the sale of existing property to pay off debt. This stage is allotted a period of 6 months, which can be extended an unlimited number of times. At this stage, the court appoints a bankruptcy (arbitration) trustee. His competence: to remove management from conducting business, publish information and record the fact in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. A register of creditors' claims is formed, and everyone has a period of two months to submit relevant claims. The seizure of property is lifted, and the accrual of penalties and fines is suspended. In fact, this stage ends with the bankruptcy of legal entities with debts. The bankruptcy estate is drawn up, the value of the property is determined by the appraiser. Auctions are scheduled, and claims are settled in order of priority. This stage is associated with financial risks and the threat of undervaluation of property, so competent legal support will ensure a reliable legal position.
Consequences for the director and founders in case of bankruptcy of a legal entity
It is believed that the director is nothing more than an employee and there are no consequences for the director in case of bankruptcy of the company. Basically, this is true.
But in the Law “On Bankruptcy” there is Chapter III.2 “Responsibility of the debtor’s manager and other persons in bankruptcy.”
IMPORTANT: Chapter III.2 states that if a company cannot pay creditors due to the actions or inaction of a controlling person, then the court will recover money from this person at the expense of his personal property (apartments, cars, dachas, money, shares). This is called vicarious liability.
What are the actions or inactions that led to the company's bankruptcy? This is when the company's management deliberately ruined the company: they sold buildings at a very low price, entered into unfavorable contracts, and did not collect receivables.
Who are these controlling persons? This is the director or other leader. And also the founder. For the founder, by the way, there are no specific negative consequences of bankruptcy. After the liquidation of the company, he can open a new business.
The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation has 3 elements of crimes for which the head of a company can be charged (if there are serious grounds, of course):
- unlawful actions in bankruptcy (Article 195 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- deliberate bankruptcy (Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- fictitious bankruptcy (Article 197 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
When bankruptcy proceedings are opened, the director of the company is removed from work. After the liquidation of the company, he loses his post—this is another consequence for the director in the event of bankruptcy of a legal entity.
Features of the founder status
The subsidiary liability of a participant is established based on the status of this entity. In fact, it is temporary, since from the moment of registration of the LLC the share in the authorized capital is paid, and the founder becomes a participant in the company. However, in practice these two concepts are often identified. Claims are made directly to the founders if:
- the unfulfilled obligation is related to the establishment of the LLC and arose before its registration;
- joint and several subsidiary liability for the company's obligations is within the limits of the unpaid portion of the share;
- The LLC does not have enough property to fulfill its obligations, and there are legal grounds for holding the founder of the company liable.
In fact, in all other cases it is correct to talk about holding the LLC participant or the controlling debtor liable. Legal will help you understand these and many other subtleties of the process.
Consequences of bankruptcy of a legal entity. faces for workers
Once the bankruptcy process is completed, the company is liquidated. Therefore, the main consequence of the bankruptcy of a company for its employees is the loss of their jobs.
The Labor Code states that company management must warn employees about the upcoming dismissal 2 months before the dismissal or earlier. Next, the dismissal process proceeds as usual: after two months, dismissal orders are issued, and employees get acquainted with them and sign them. Next, a note is made in the work book.
The employee must be paid:
- salary for hours worked;
- severance pay (monthly salary);
- compensation for unused vacation.
Documents are issued to employees in the usual manner.
Criminal liability
In some cases, bankruptcy proceedings can lead to very sad consequences, namely, criminal liability for the founders and management of the company. But this is only possible when law enforcement agencies prove in court the fact of committing an economic crime and deliberate intent to do so.
The following interested parties can contact law enforcement officers with a statement of fictitious bankruptcy:
- bankruptcy trustees appointed by the arbitration court;
- creditors and lenders;
- external managers;
- observers;
- other persons and organizations having an interest in the case.
What are the negative consequences of bankruptcy of a legal entity?
- Bankruptcy is a forced, one might say, desperate measure. Companies don't go bankrupt because of a good life. Therefore, all participants in this process (except for the arbitration manager and the arbitration court) accept negative consequences.
- Creditors: in the vast majority of cases, the company's assets are not sufficient to pay all debts to creditors. Therefore, creditors suffer losses.
- Employees are losing their jobs.
- The head of the company also loses his job, but the risk of subsidiary liability still hangs over him.
- The budget is deprived of tax revenue: a bankrupt and closed company will never pay VAT, corporate income tax, or insurance premiums for employees.
Restrictions on the rights of founders after bankruptcy of an LLC
According to the law, if an enterprise is declared insolvent, this does not affect the rights of its founders in any way. In other words, the former owners of the company have every right to continue to engage in commercial activities, but within the framework of other organizations. They can also create new companies and register as individual entrepreneurs.
Important! If facts of major offenses are revealed, the management team of a bankrupt enterprise, that is, its chief accountant and director, may be deprived of the right to work in any area for up to several years through a judicial procedure.
Myths about bankruptcy: destroying stereotypes
In addition to the misconception that you cannot run a business during bankruptcy, in practice there are also other myths that need to be destroyed. The most common prejudices are:
- relatives will not be given loans, they will not even be able to get a mortgage. It is not true. The consequences of bankruptcy concern only the debtor - spouses, children and other close people are not limited in their rights in any way;
- your credit history will be forever damaged. In fact, everything is exactly the opposite. Initially, a debtor who is mired in debt has a very bad credit history. Bankruptcy, on the contrary, cancels a person’s past “financial biography”;
- no bank or microfinance organization will ever issue loans again and will stop servicing. It is a myth. Banks do not have the right to refuse customer service. At the same time, many credit institutions willingly issue loans to bankrupts - you just need to find the right organization;
- fired from work due to bankruptcy. This is also not true. Labor legislation does not contain a single norm that is related to financial insolvency. The bankrupt will still be able to continue to work in the same place and in the same position.
In other words, bankruptcy not only frees you from overwhelming debt - the procedure clears a person’s entire credit history. This guarantees the opportunity to start life with a clean slate and forget about past mistakes. Financial insolvency in this case really becomes a second chance, which every debtor can and should use.